Patents
Literature
131results about "Wound field motor control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
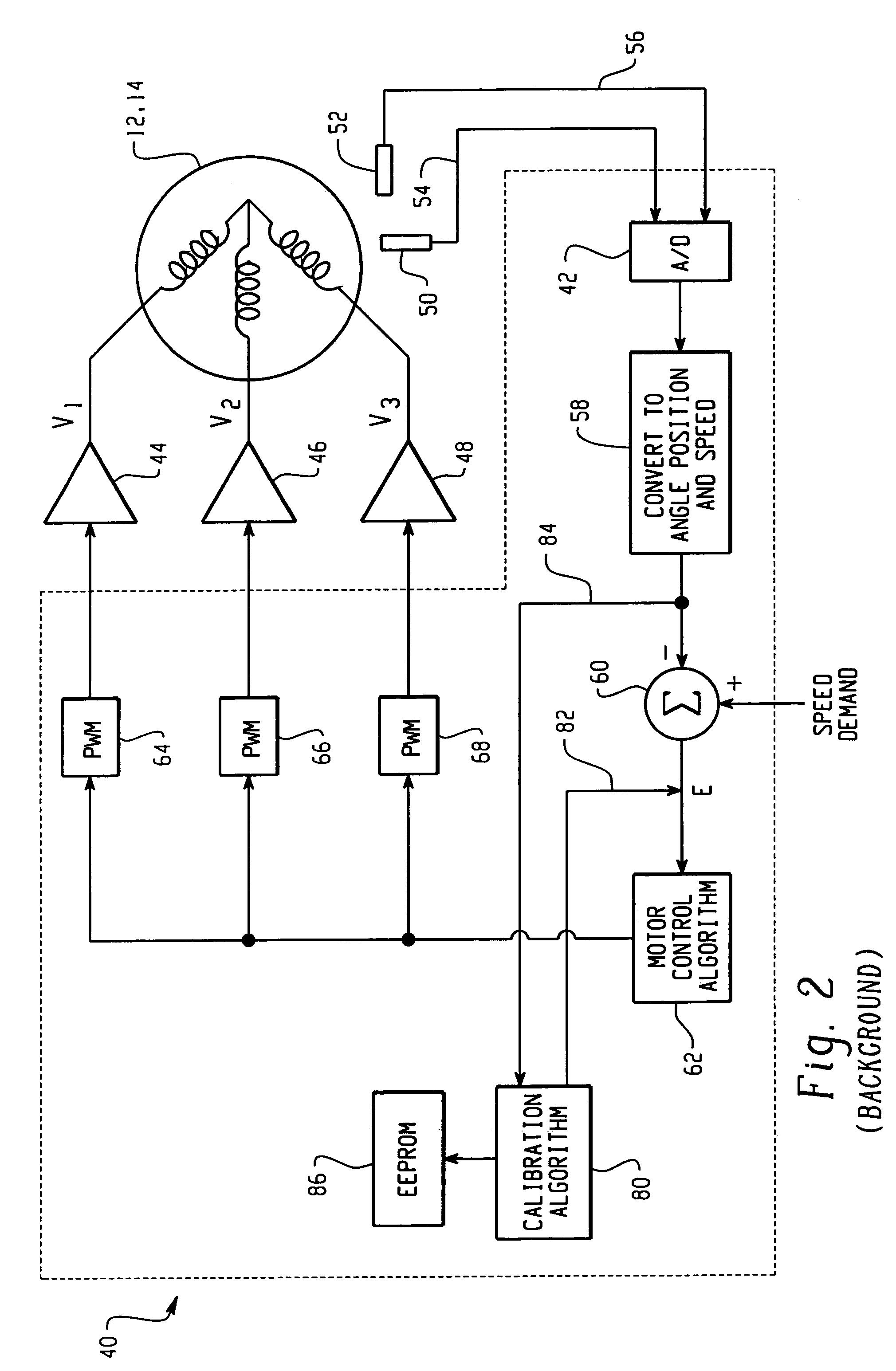
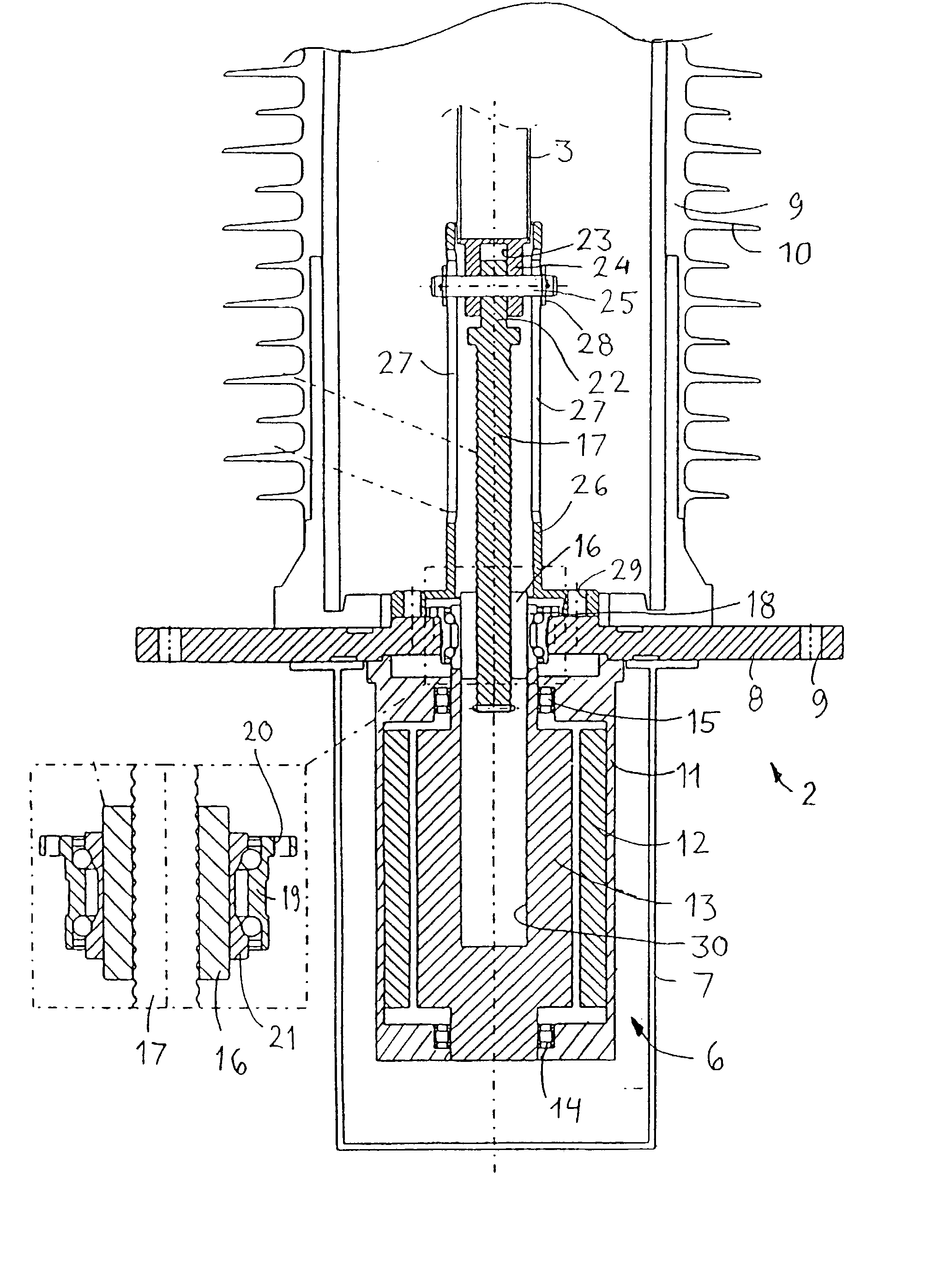
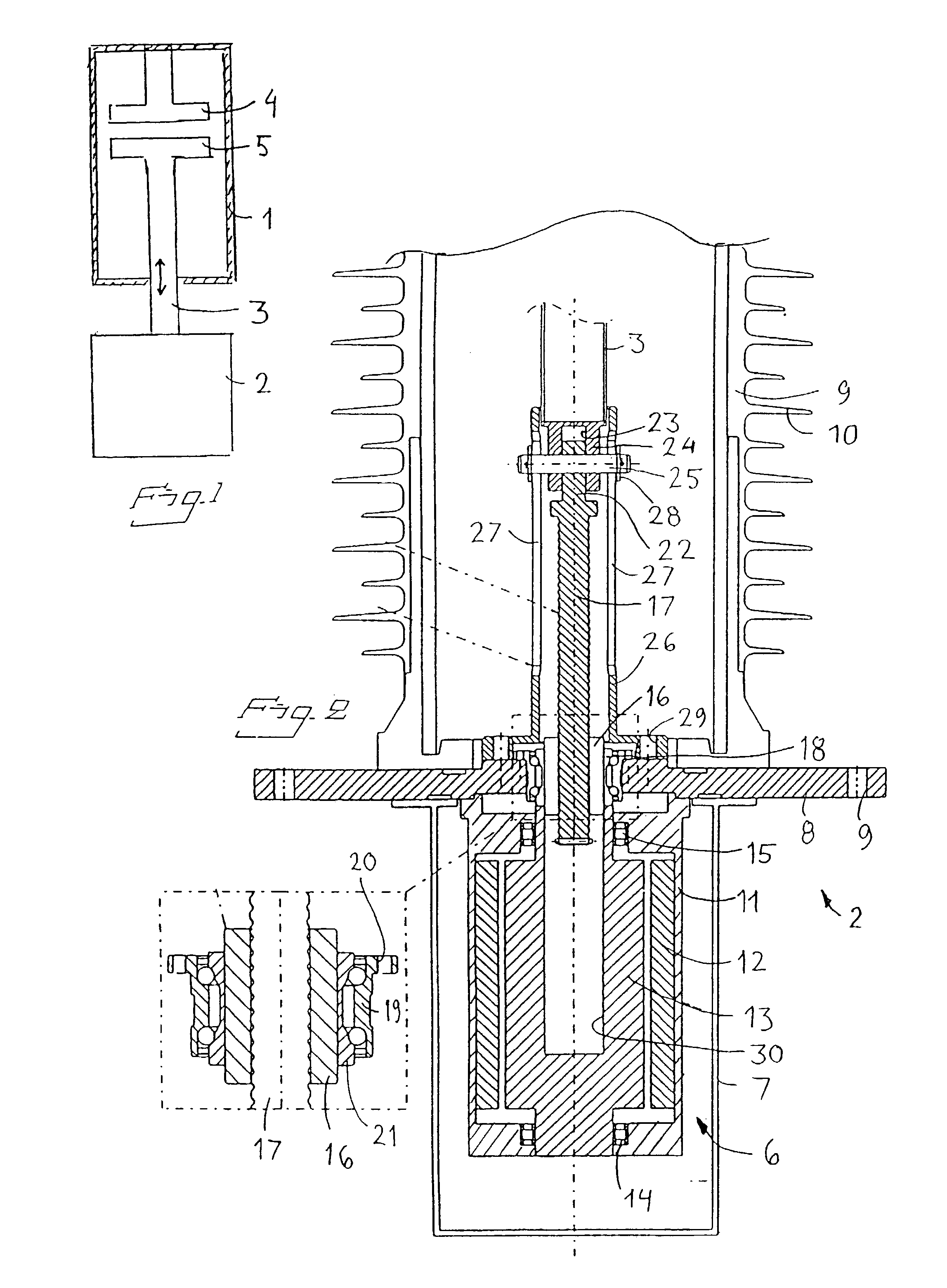
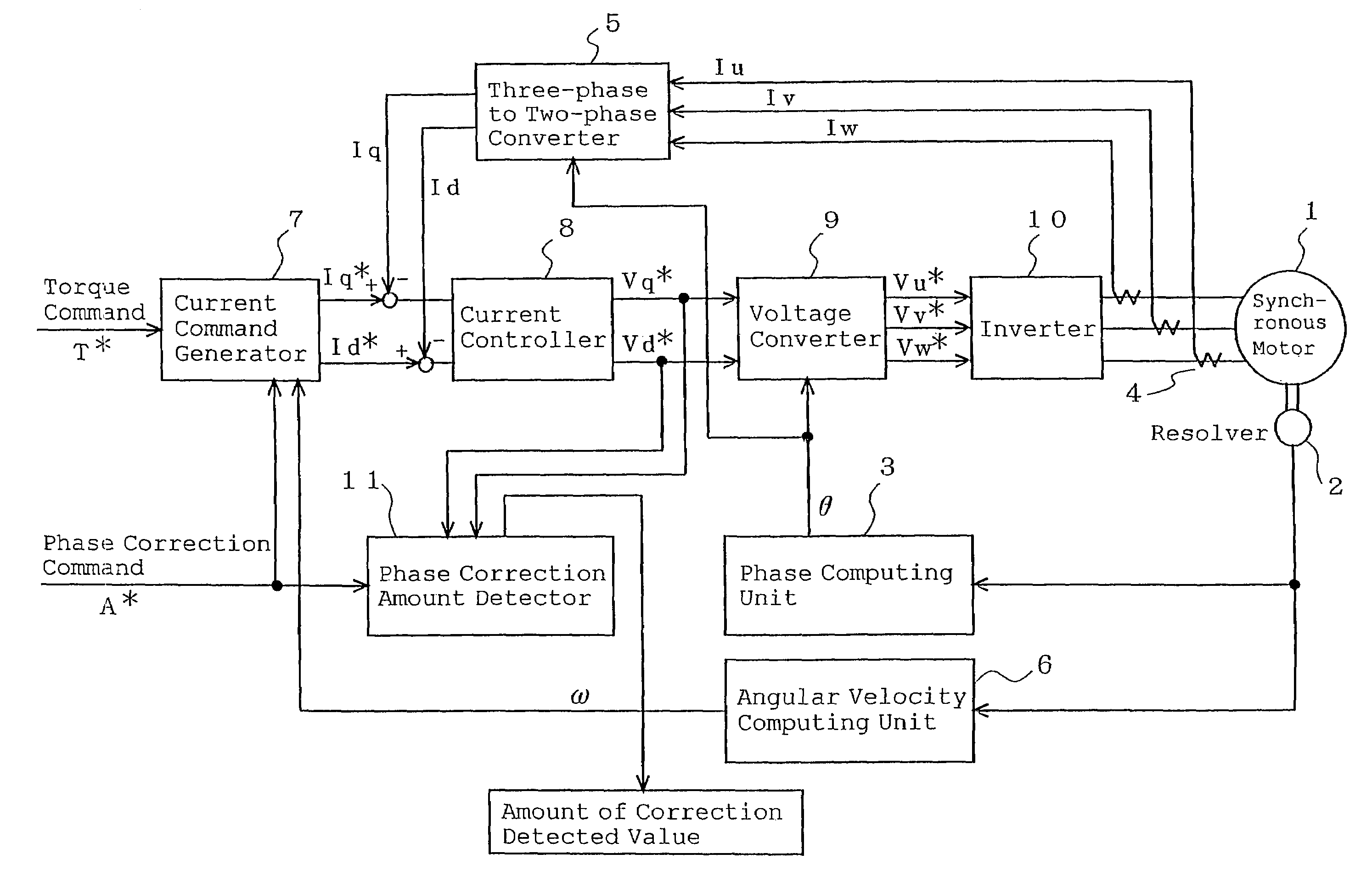
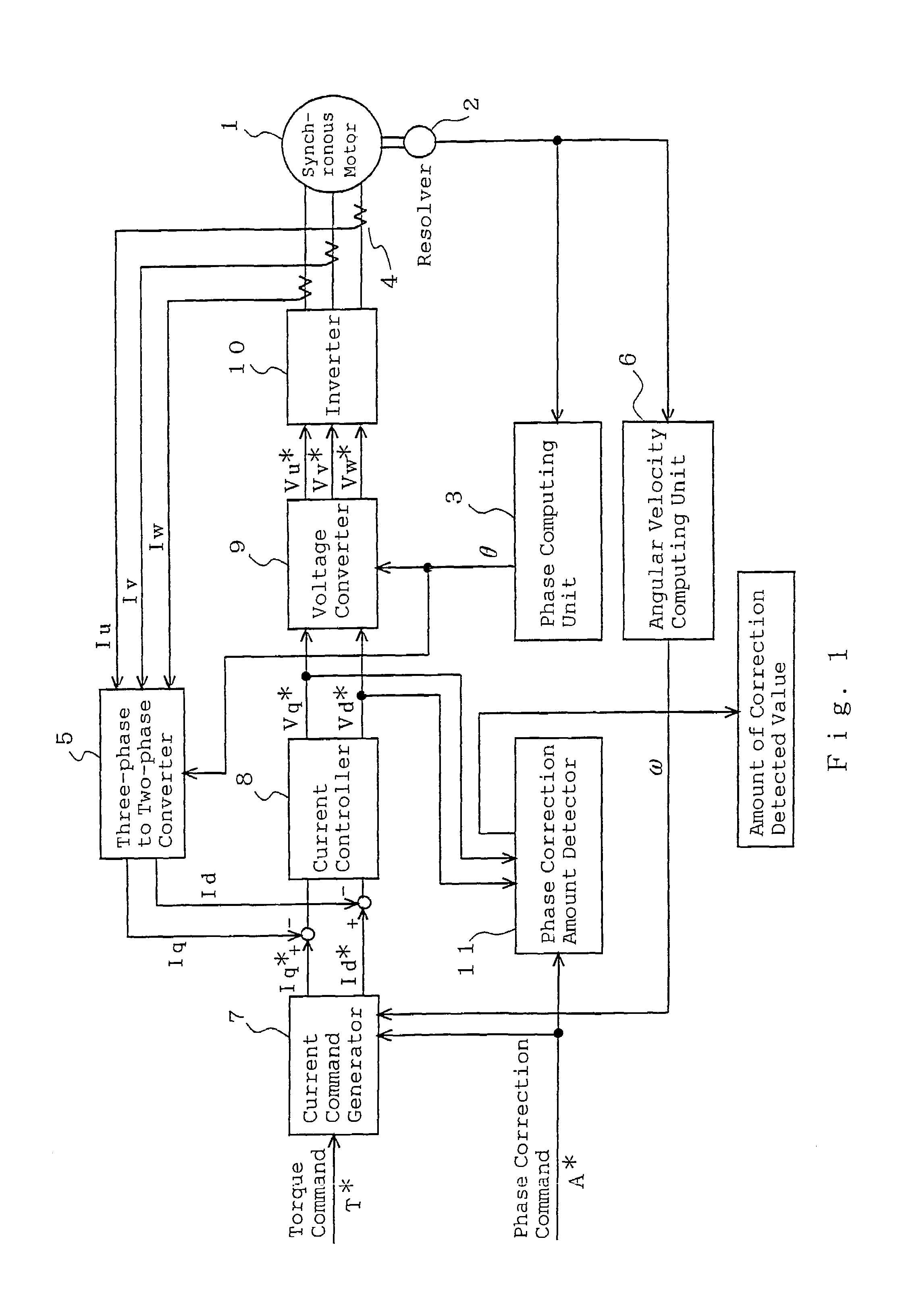
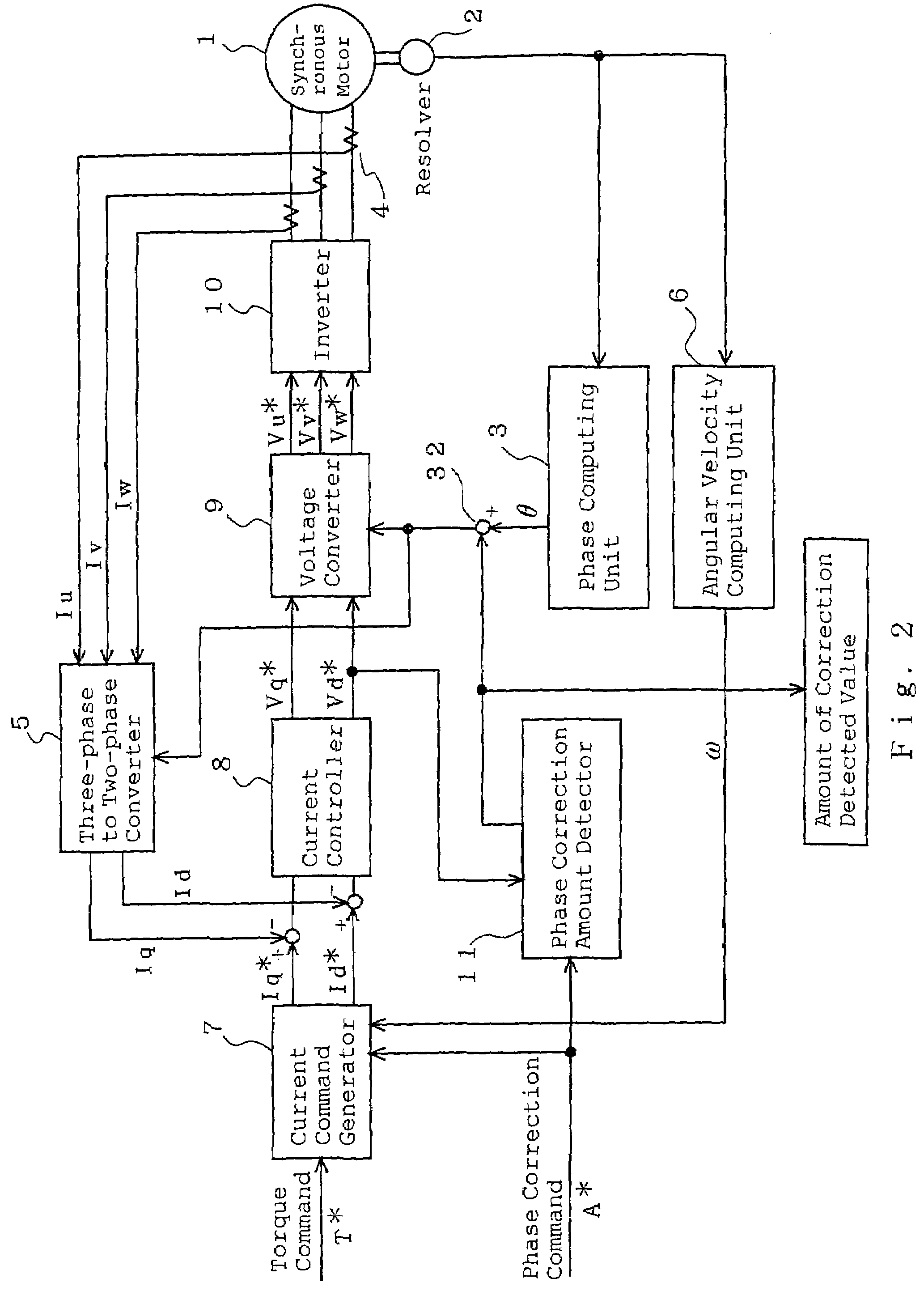
Synchronous motor and electric driving system
InactiveUS20060202582A1Reduce vibrationImprove installabilityMagnetic circuitSingle motor speed/torque controlElectricitySynchronous motor
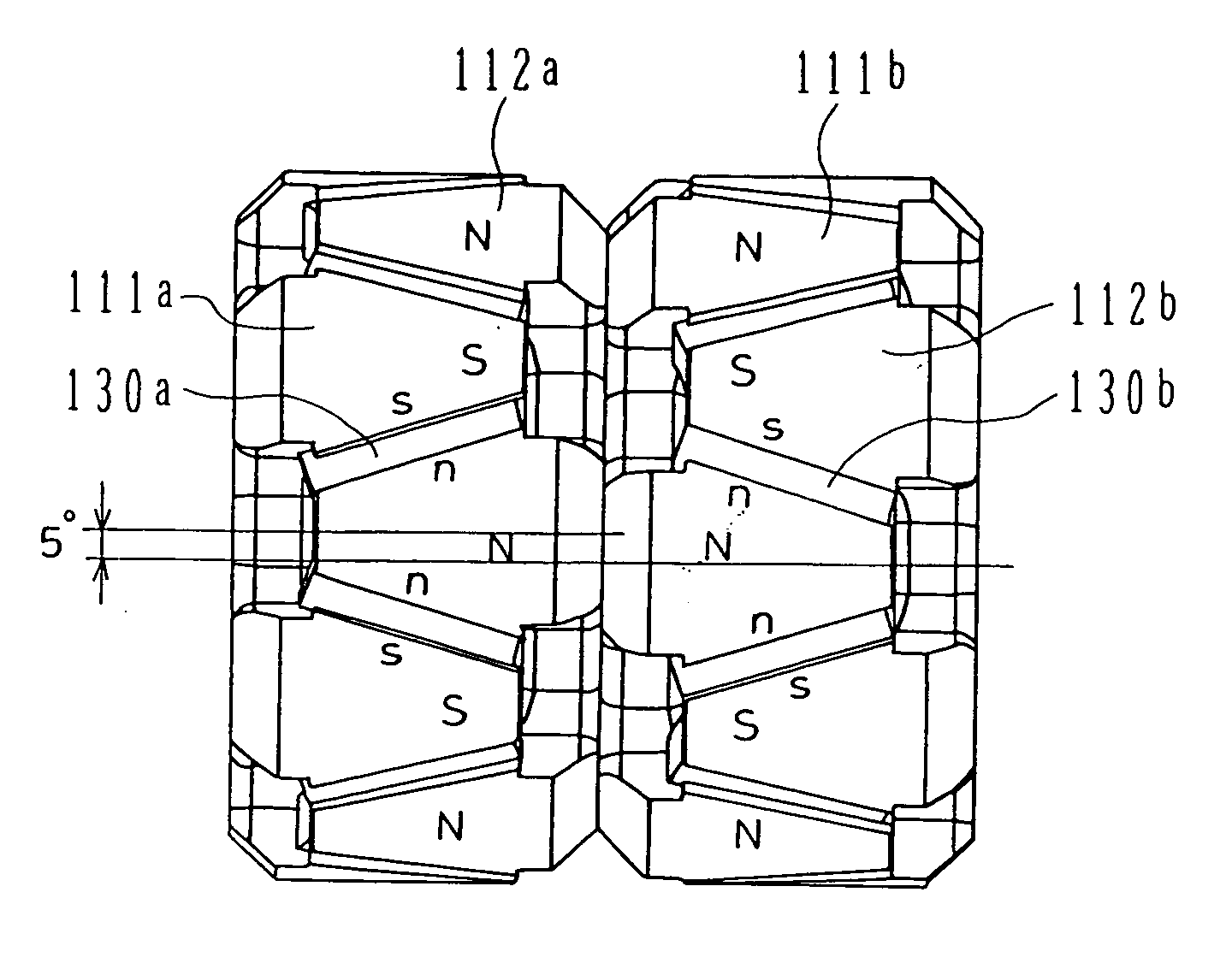
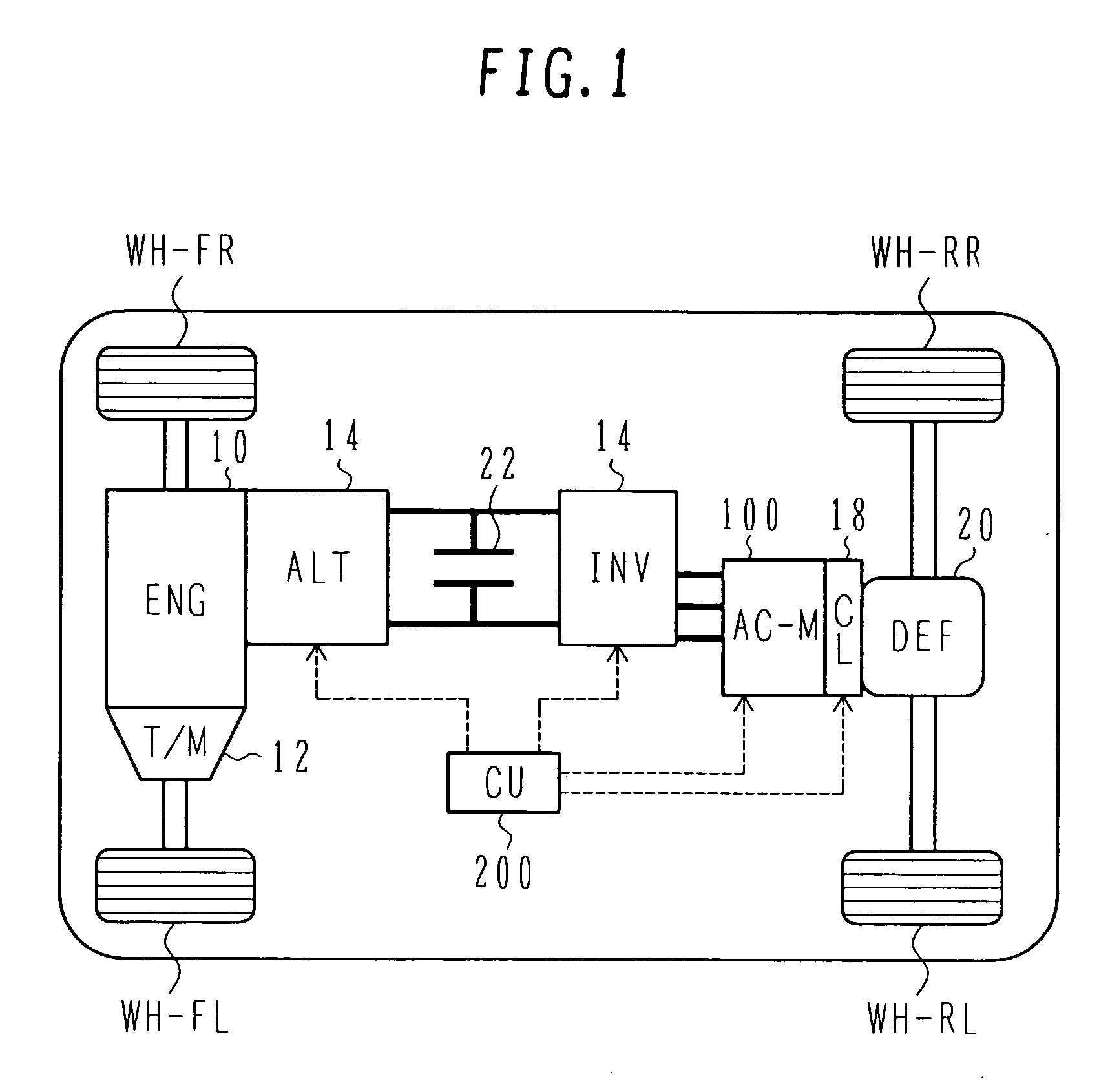
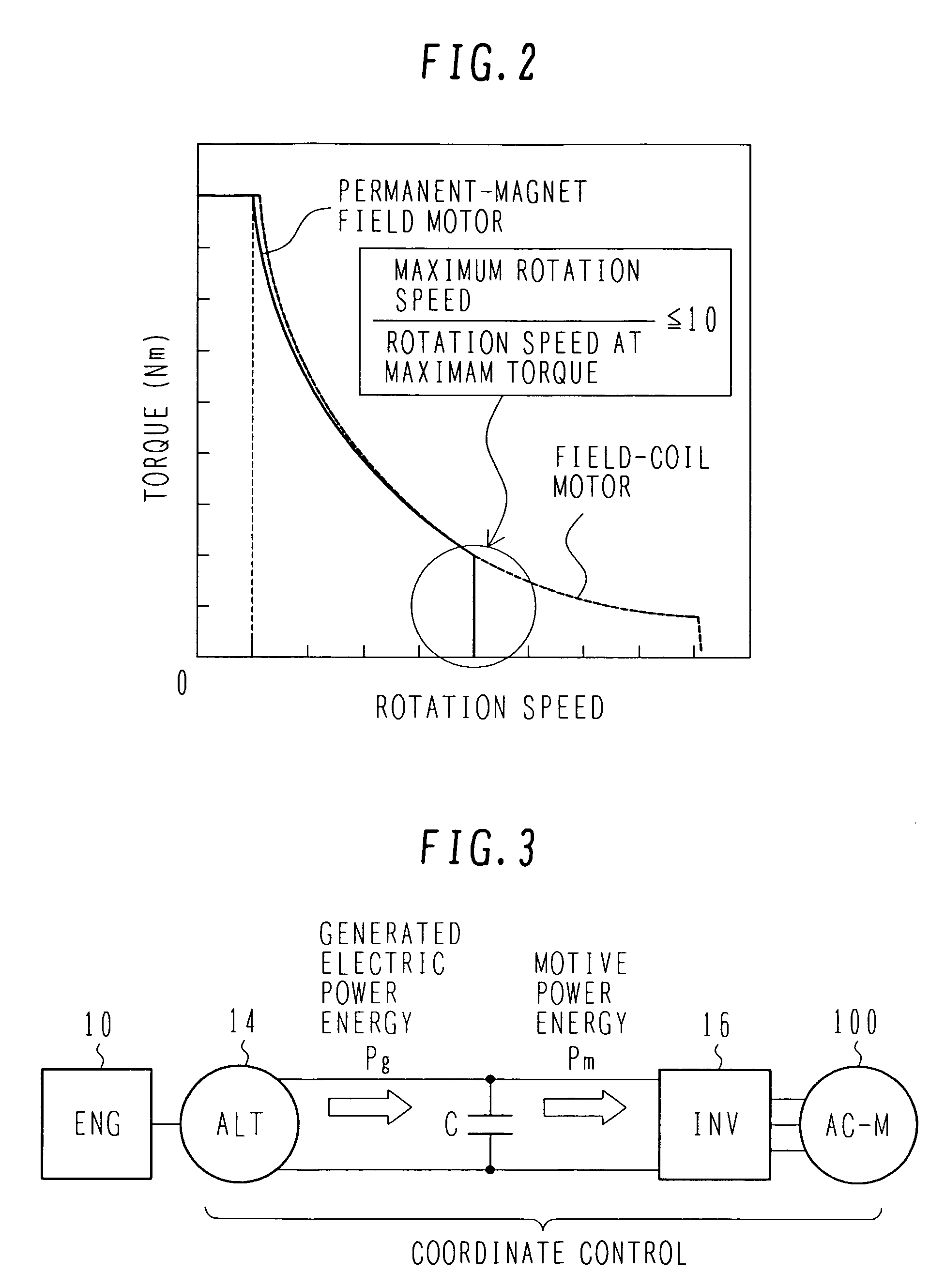
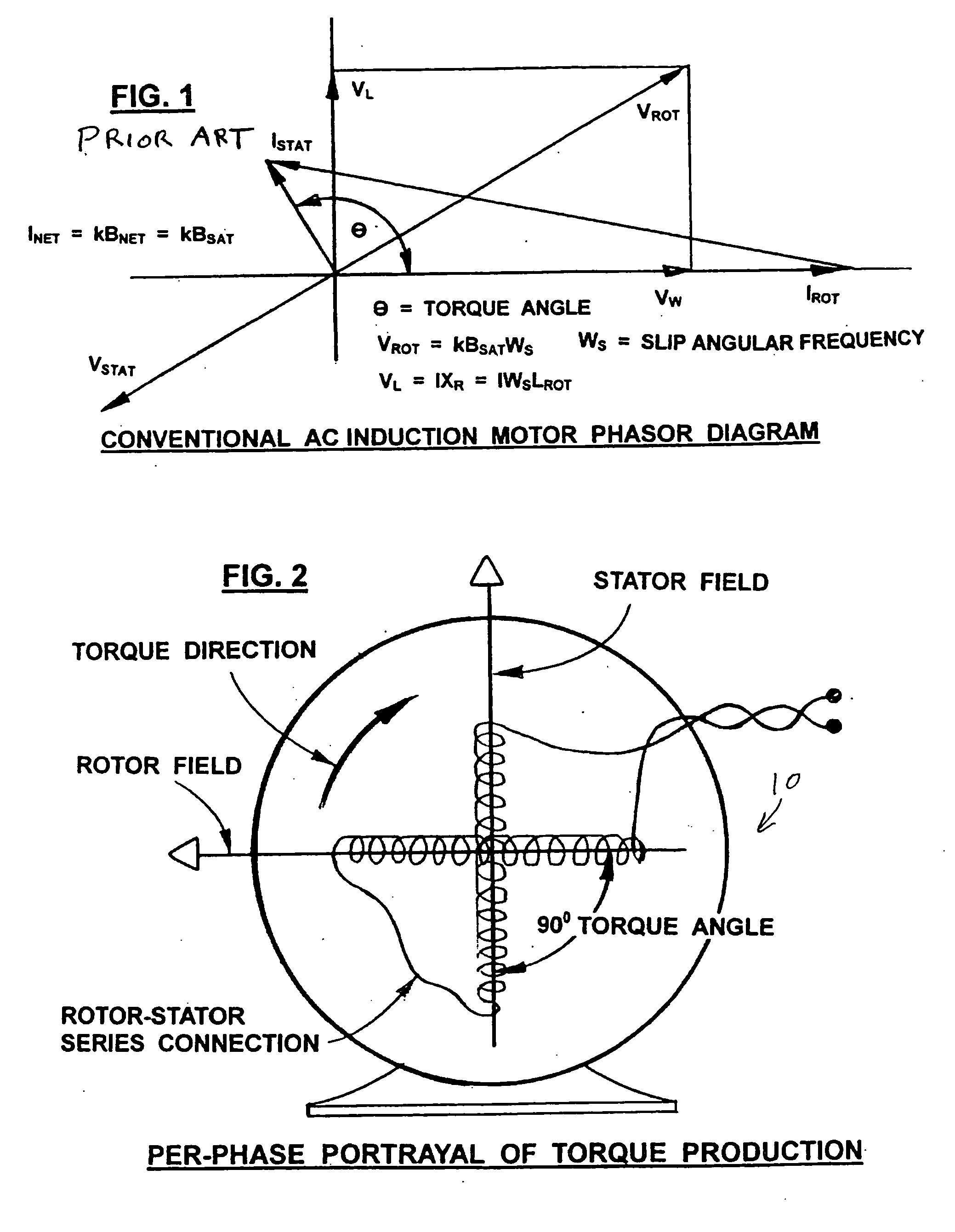
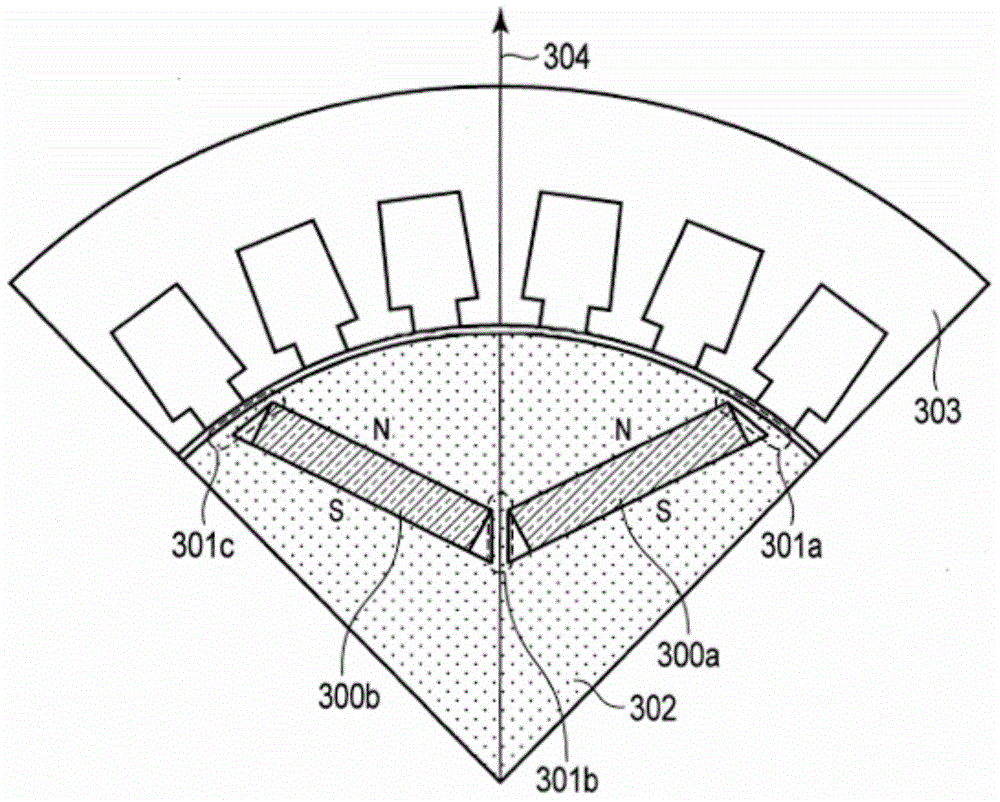
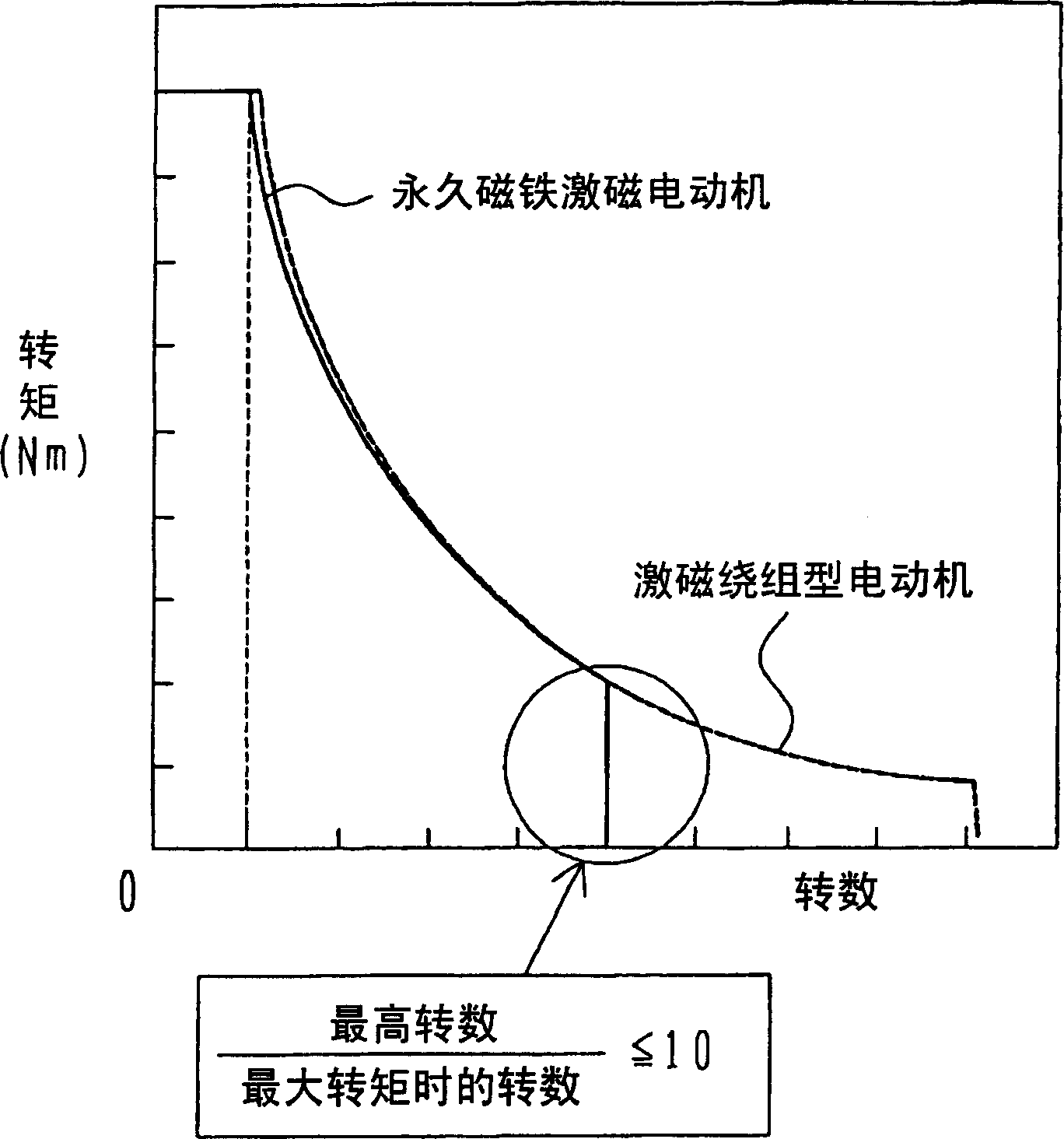
A synchronous motor with low vibrations and an electric driving system using the motor. A field-coil synchronous motor comprises a stator and a rotor rotatably supported at the inner peripheral side of the stator with a gap left relative to the stator. The stator has a stator coil supplied with electric power while being controlled such that driving torque is reduced as a rotation speed of the rotor increases, and the rotor has a field coil supplied with a field current while being controlled such that the field current is reduced as the rotation speed of the rotor increases. The rotor is a tandem claw-pole rotor comprising plural pairs of N- and S-claw poles disposed side by side in an axial direction, and the plural pairs of claw poles of said tandem claw-pole rotor are relatively shifted from each other in a circumferential direction.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for detecting/adjusting synchronous motor rotor position
ActiveUS20060113949A1Improve performanceIncrease production capacitySynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlProduction rateSynchronous motor
To obtain an adjustment method of rotor position detection of a synchronous motor with excellent productivity. An adjustment method of rotor position detection of a synchronous motor, wherein a synchronous motor having a stator wound around a stator coil and a rotor provided with magnetic poles, and a rotational position detector having a sensor rotor fixed to the rotor and a sensor stator disposed opposite to the sensor rotor for detecting a rotational position of the rotor are provided, and wherein an amount of deviation between the rotational position of the synchronous motor determined from an output of the rotational position detector and an actual rotational position of the synchronous motor is adjusted, the method comprising: a step of detecting the amount of deviation during rotation of the synchronous motor; and a step of mechanically adjusting a relative position between the rotational position detector and the synchronous motor based on a detected value of the amount of deviation, is provided.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
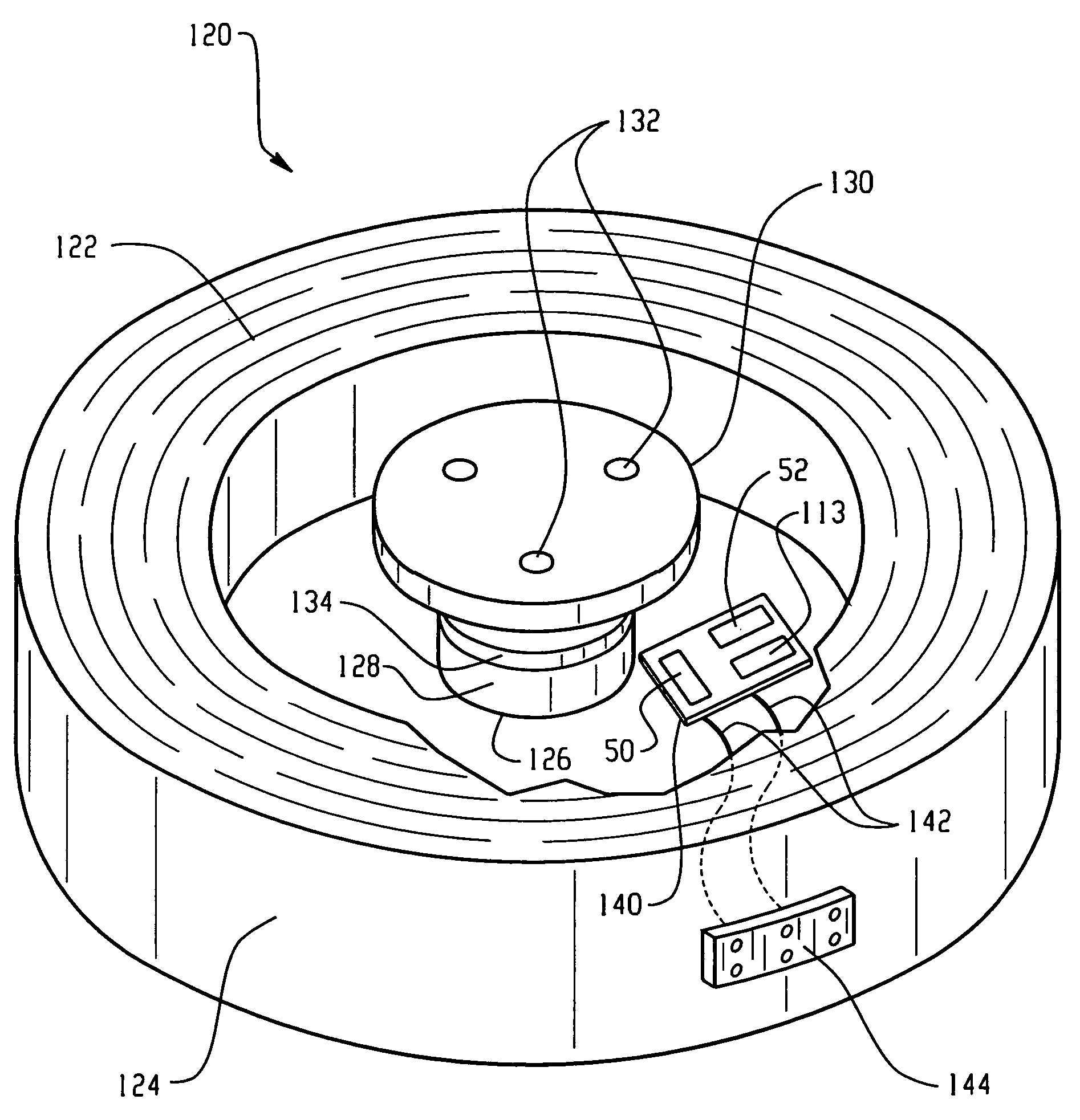
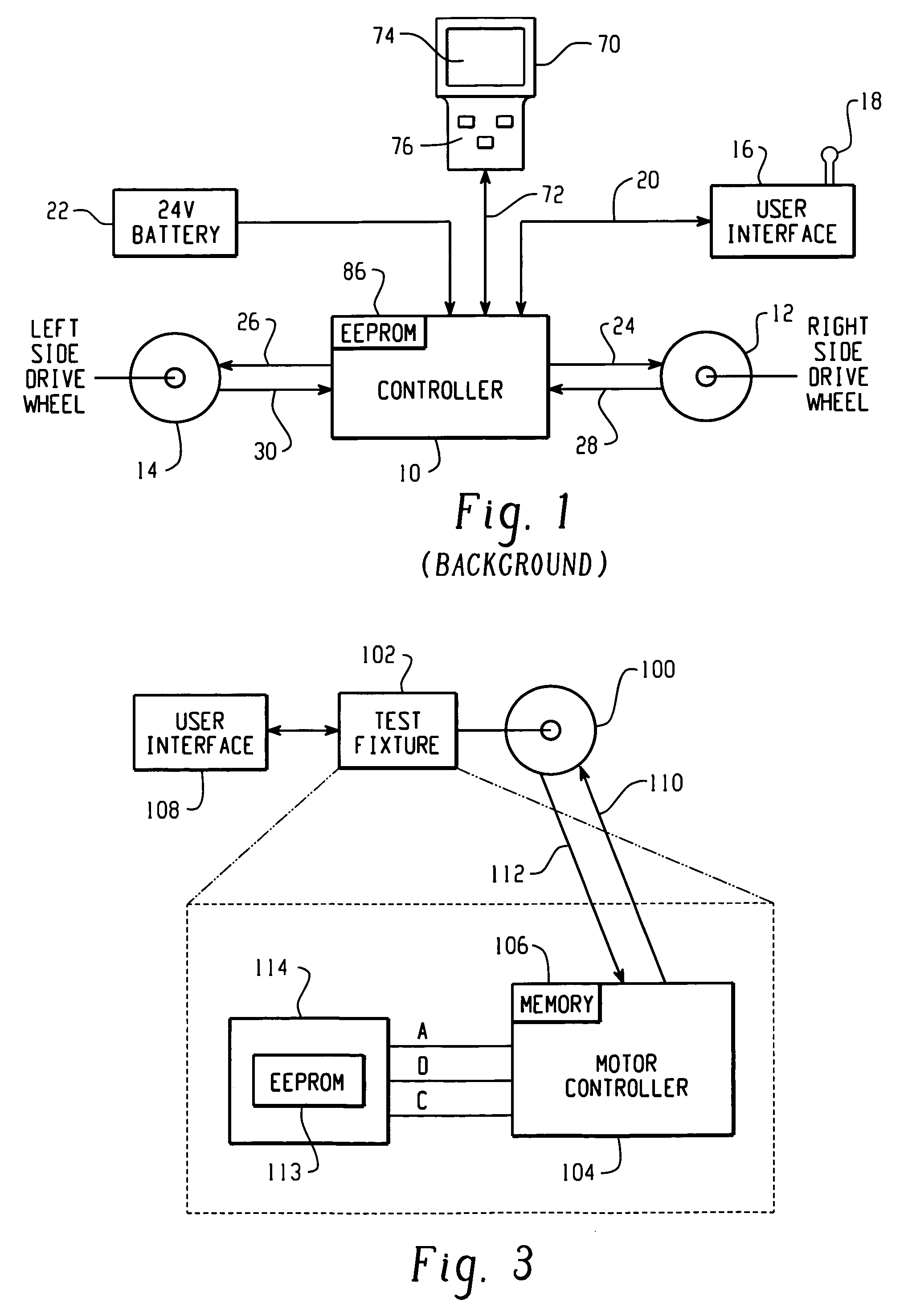
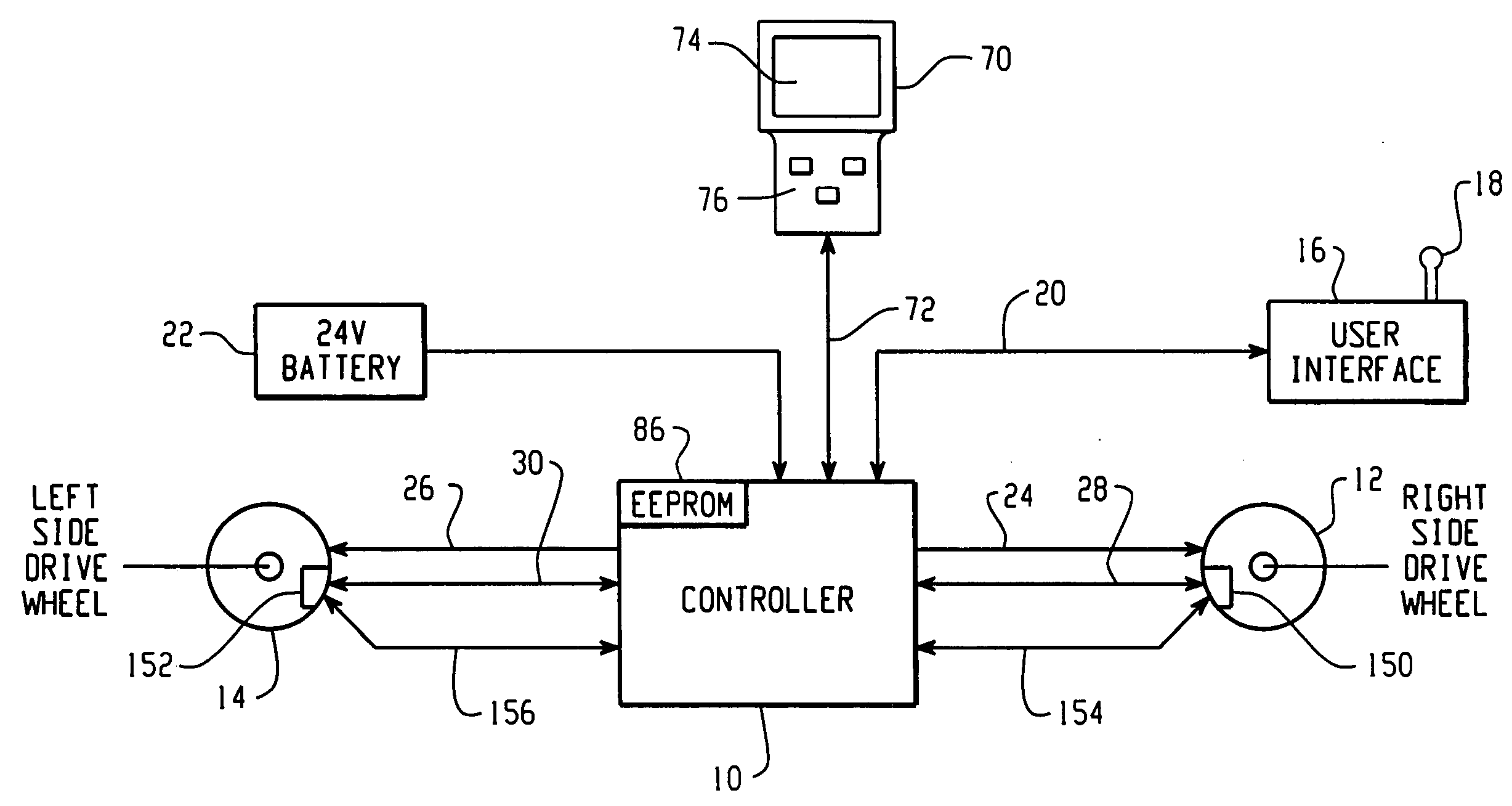
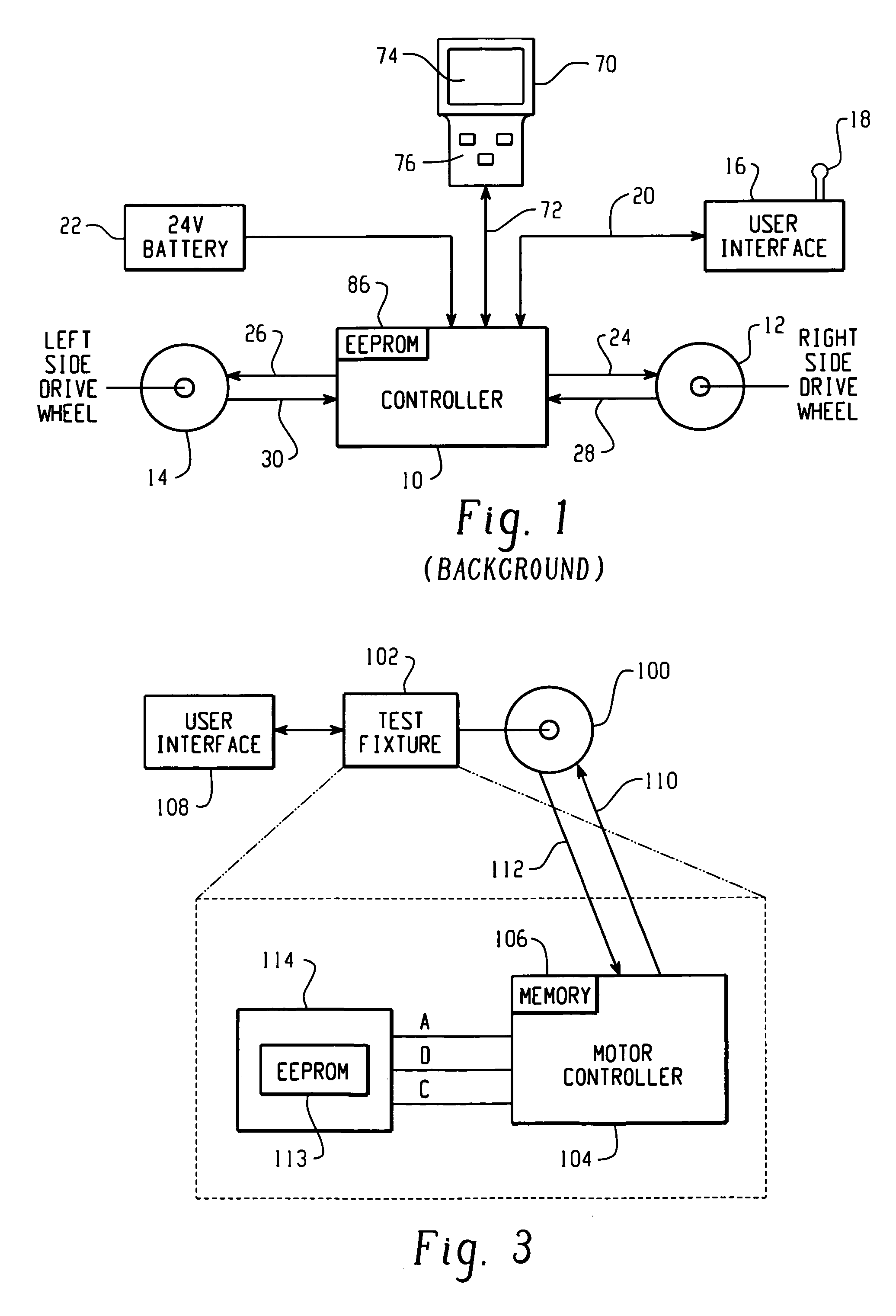
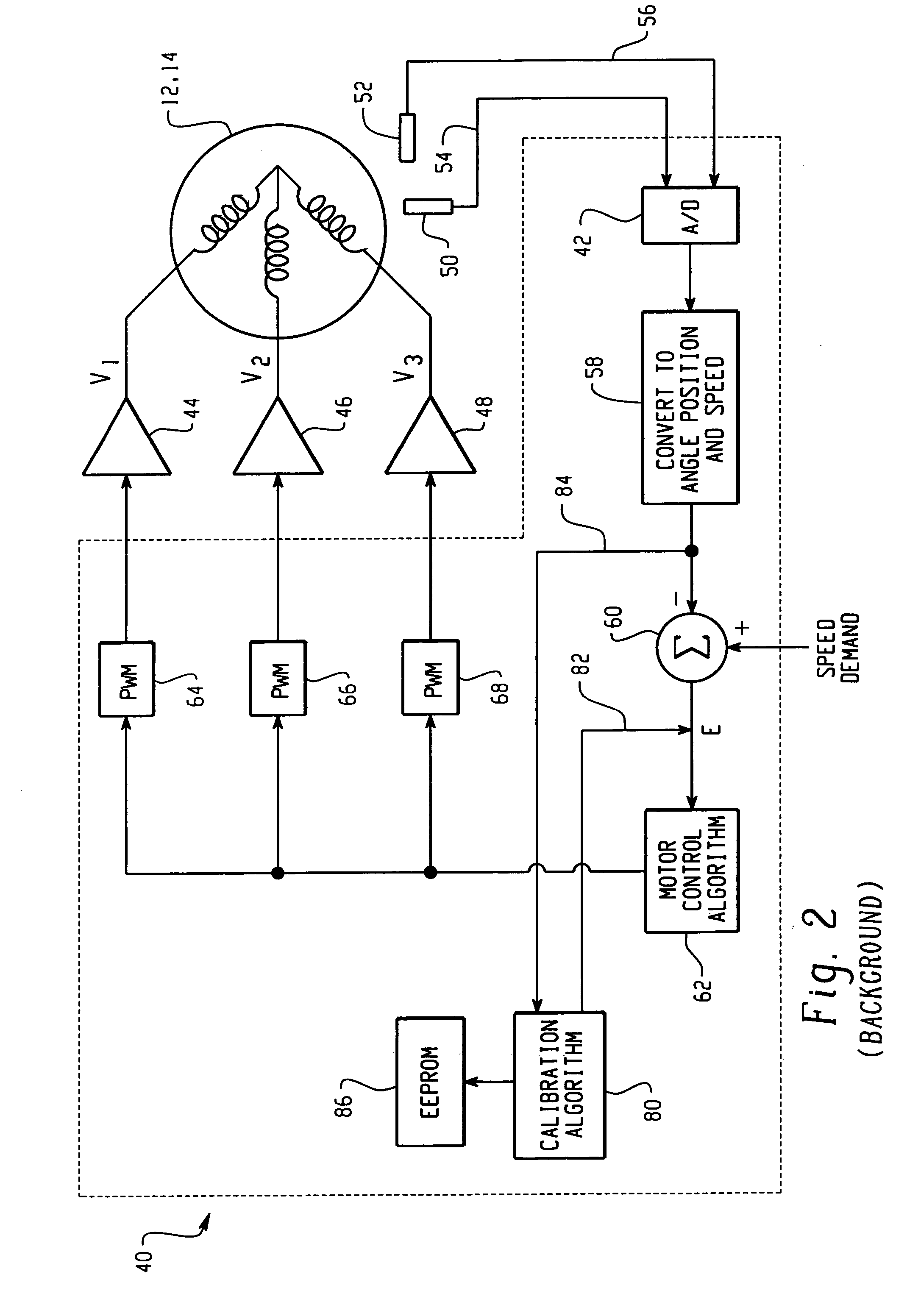
Method and apparatus for embedding motor error parameter data in a drive motor of a power driven wheelchair
InactiveUS6989642B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlMode controlEngineering
A drive motor assembly for a power driven wheelchair comprises: a stator housing for containing field coils of a stator of the motor assembly; at least one sensor disposed in the stator housing for sensing rotation of the motor; a memory storing motor error parameter data including data of errors of the at least one sensor, the memory being embedded in the stator housing; and a connection for accessing the error parameter data of the memory from the stator housing. The motor error parameter data may be accessed from the embedded memory of the drive motor by a programmed motor controller for use in controlling the drive motor. Also, the motor error parameter data may be embedded in the drive motor by the steps of: controlling the motor through at least one predetermined drive pattern; sensing motor rotation during the drive pattern and generating signals representative thereof; deriving error parameter data of the drive motor from the generated signals; programming a memory with the derived error parameter data; and embedding the memory in the drive motor.
Owner:INVACARE CORP
Weight loading system for fitness equipments
ActiveUS20170173396A1Increase load capacitySimple structureElectric motor controlWound field motor controlMotor driveMotor control
A weight loading system for fitness equipments includes a fitness equipment support, a rally rope, a motor, a motor driving and a motor control unit. The motor is a permanent magnet brushless DC motor with an external rotor structure, and the motor includes a stator mounted onto the fitness equipment support and an external rotor sheathed on the stator and rotatable with respect to the stator, and the rally rope is wound around the external rotor of the motor, and an end of the rally rope is coupled to the external rotor of the motor, and the other end of the rally rope is coupled to the power driving mechanism of the fitness equipment; the power driving mechanism is provided for driving the external rotor of the motor through the rally rope to rotate and generate a rally, and the motor control unit controls the motor to rotate in an opposite direction through the motor driving module, so as to produce a load force opposite to the rally. The weight loading system for fitness equipments structure is simple, lightweight, and achieves the effect of a stepless weight control.
Owner:NINGBO JADA HEALTH TECH
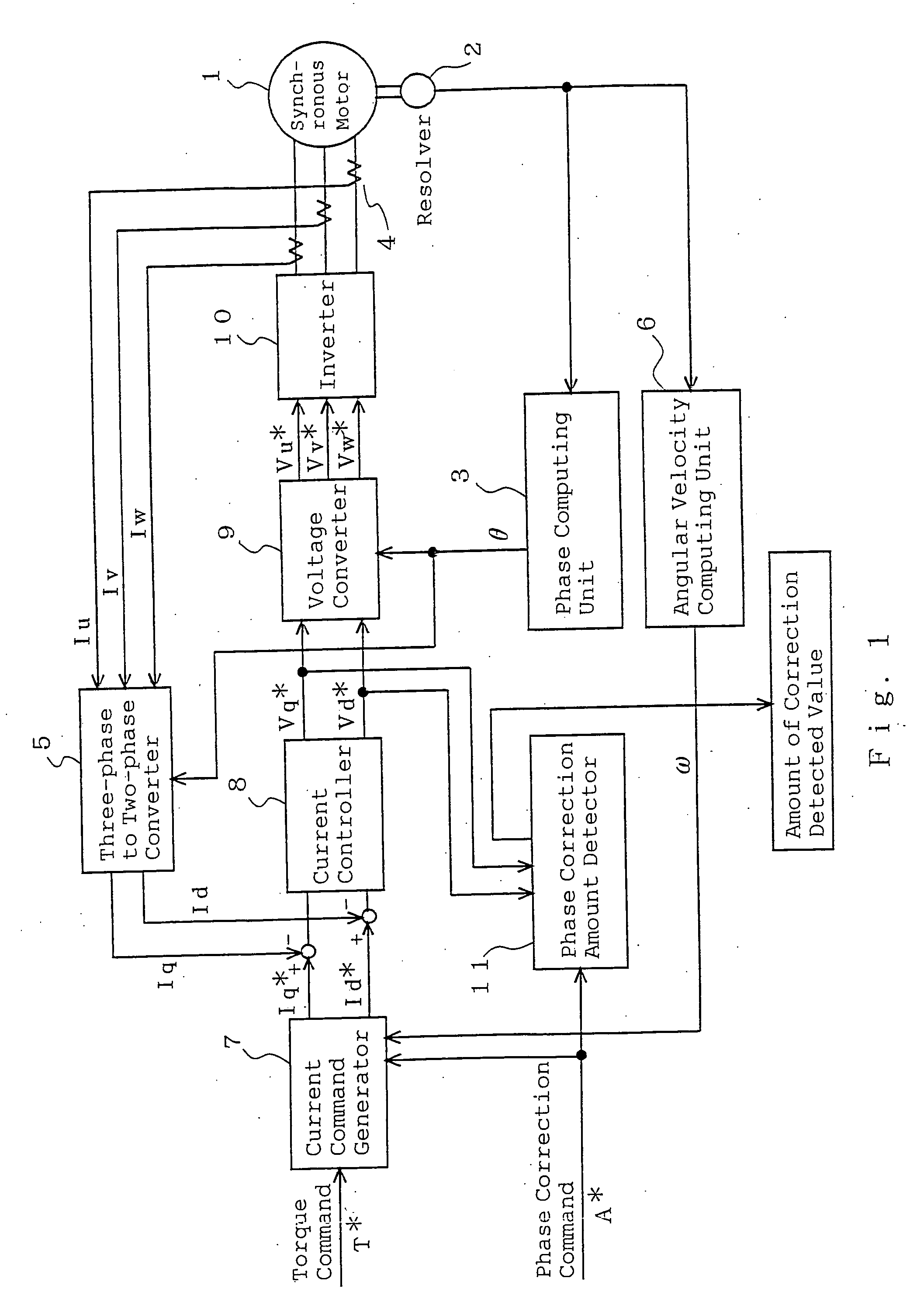
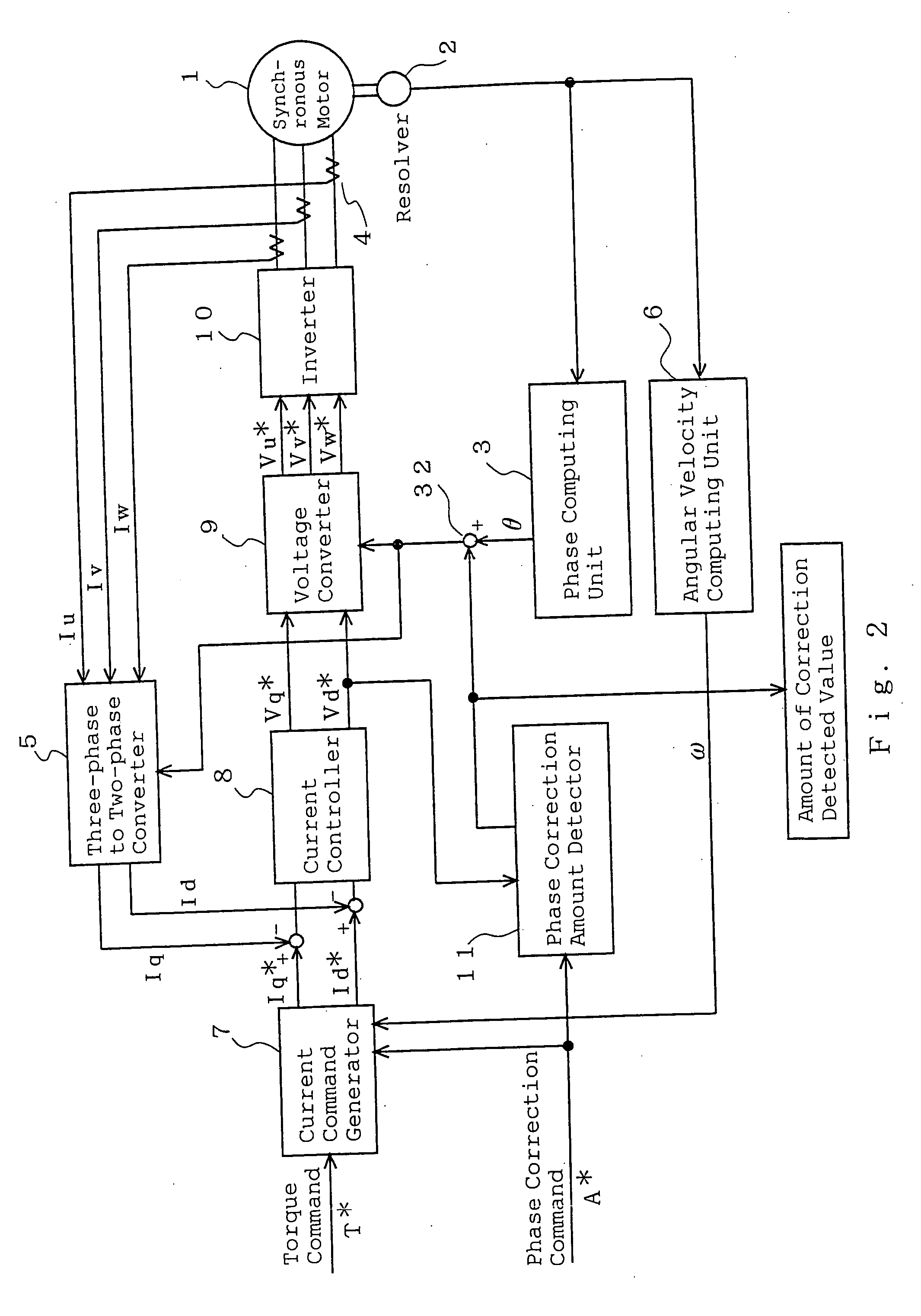
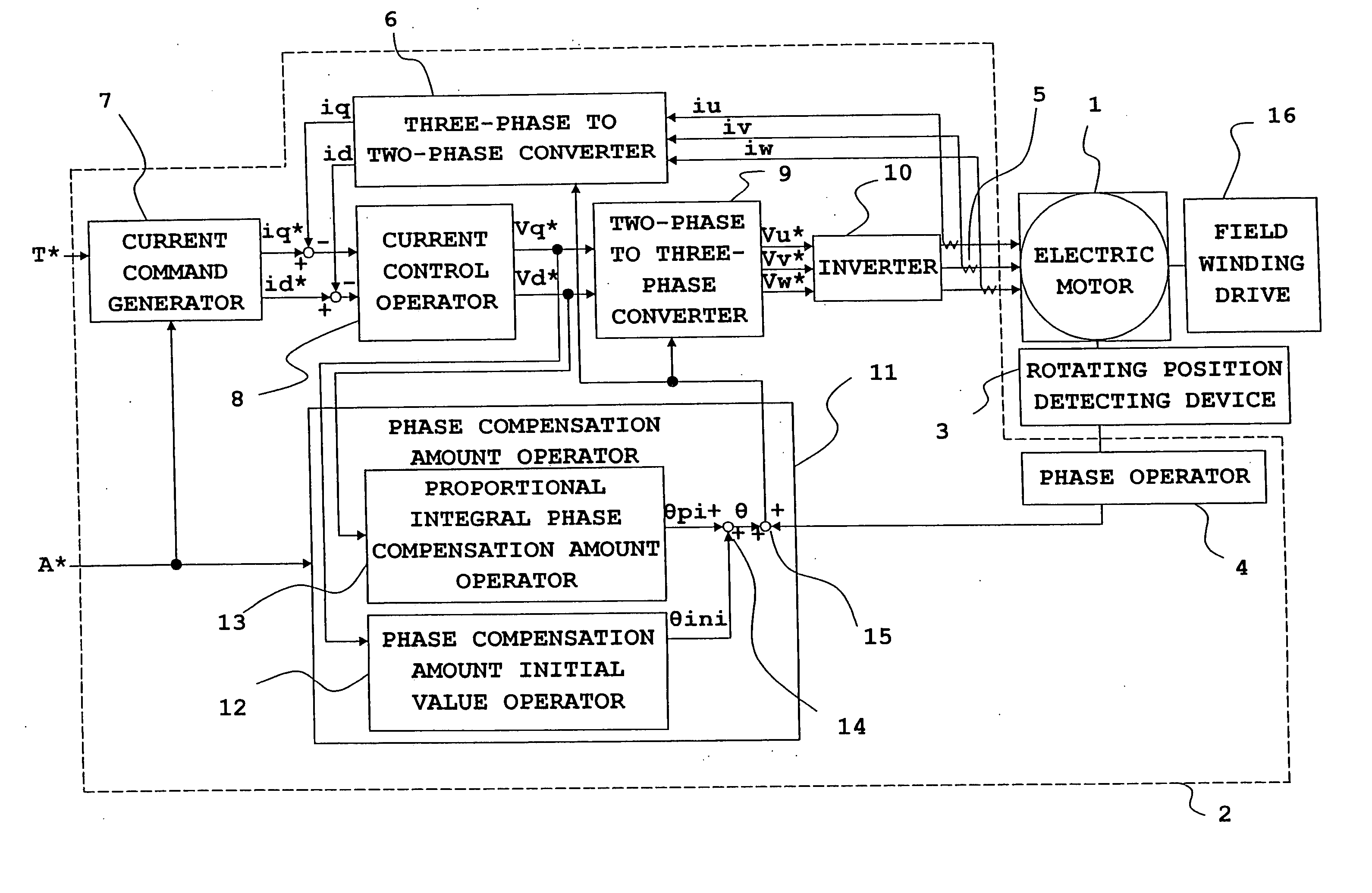
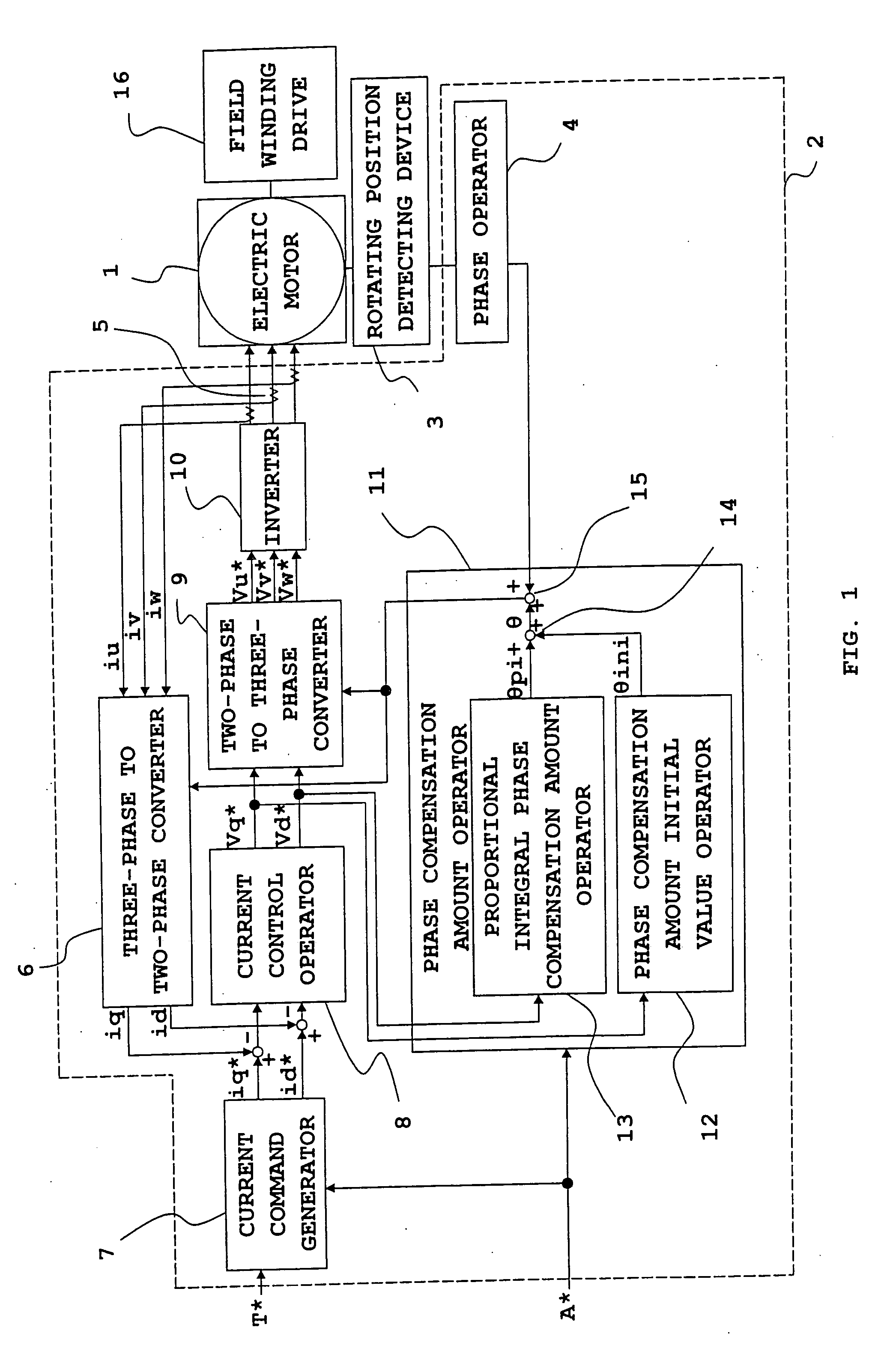
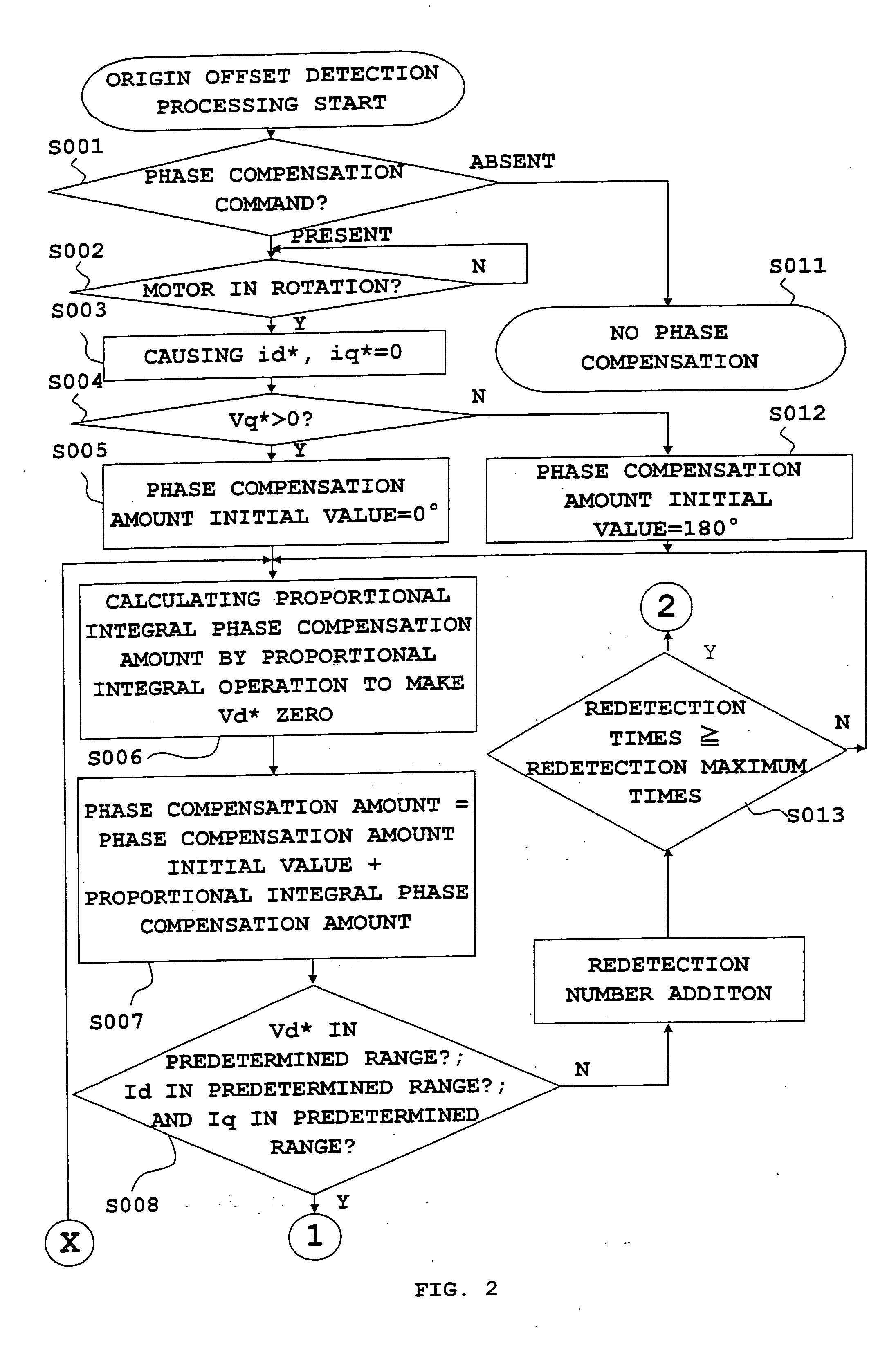
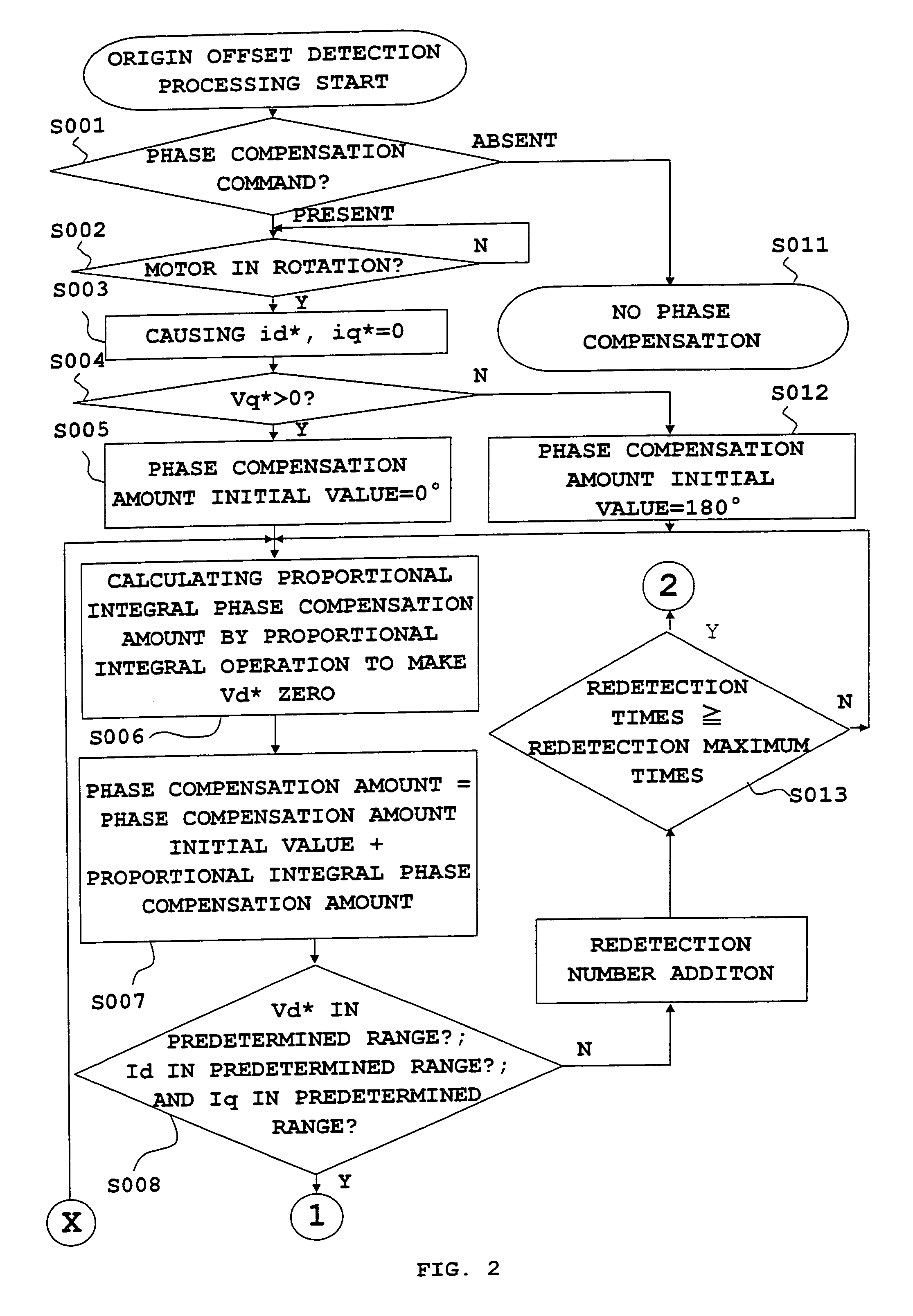
Origin offset calculation method of rotational position detecting device of electric motor and motor control device using the calculation method
ActiveUS20060012328A1Improve calculation accuracyImprove detection accuracyDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlLocation detectionSynchronous motor
An inverter that executes a d q-axis control of a three-phase synchronous motor needs a rotational position sensor that detects rotational positions of an electric motor for mutual conversion between two-phase and three-phase. An angle error of this rotational position sensor affects accuracy in the d q-axis control, so that it is necessary to make a compensation with accuracy. In the conventional method, however, there is a problem of occurrence of an ignorable error due to influence of noise. An origin offset calculation method according to the invention includes a first process of forcibly making d q-axis current command values zero; a second process of multiplying a magnetic flux component voltage command value at this time by a proportional integral gain; and a third process of storing a rotational position sensor phase error when a magnetic flux component voltage command value becomes zero being a result of the second process.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Electromagnetic motor
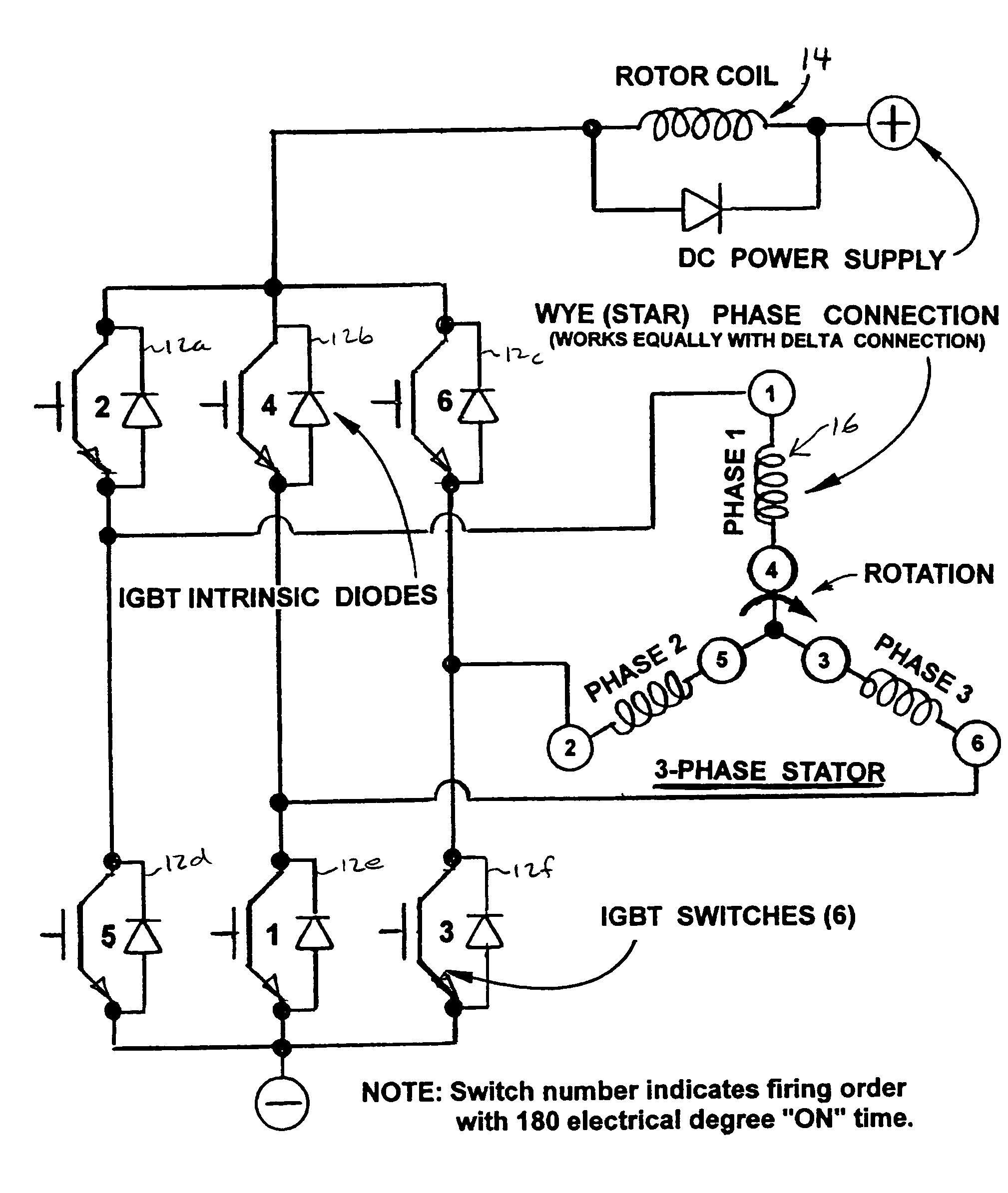
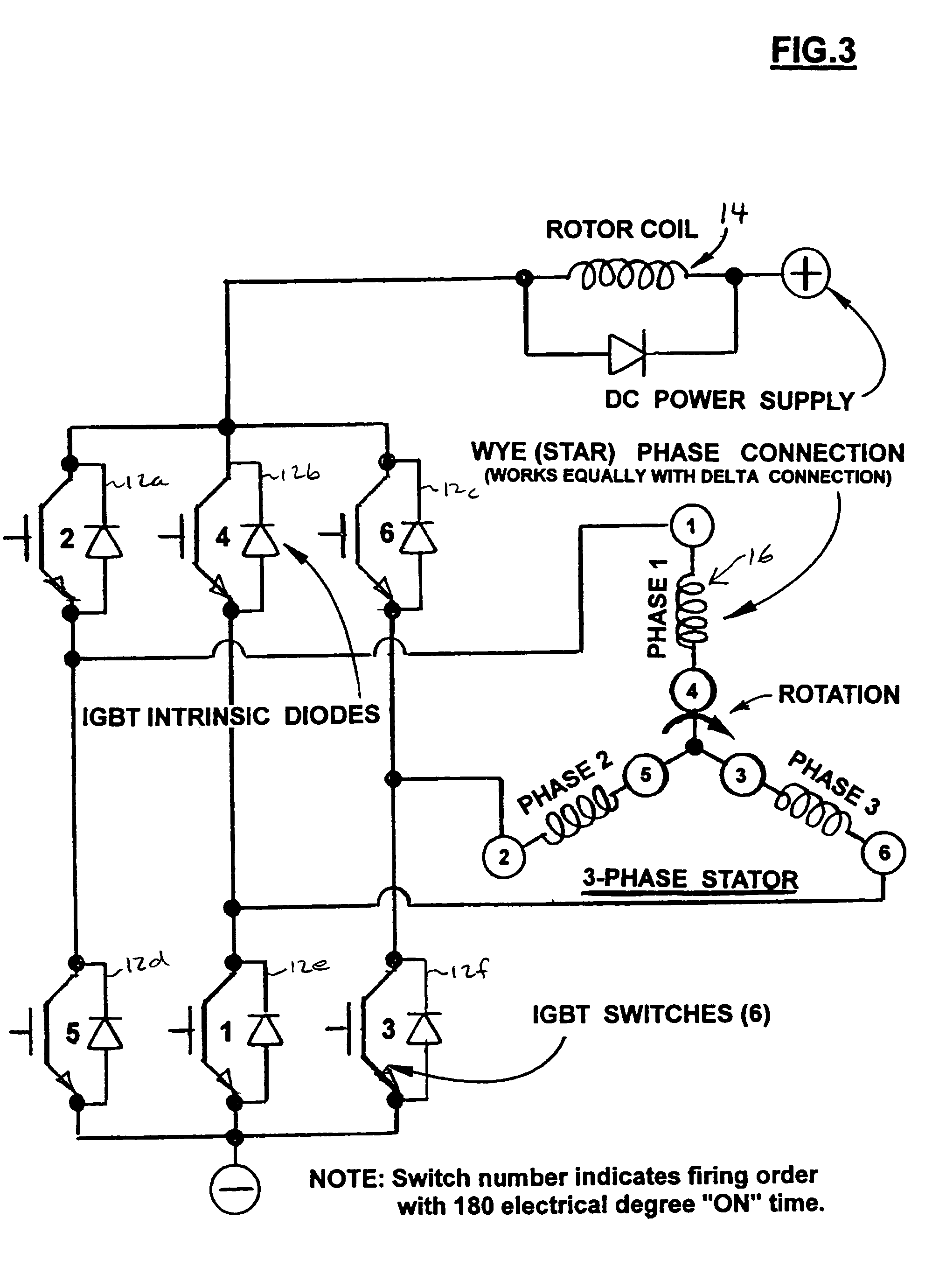
InactiveUS20050073281A1Efficient productionEffectively doubles iron utilizationSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlStator coilMagnetic field
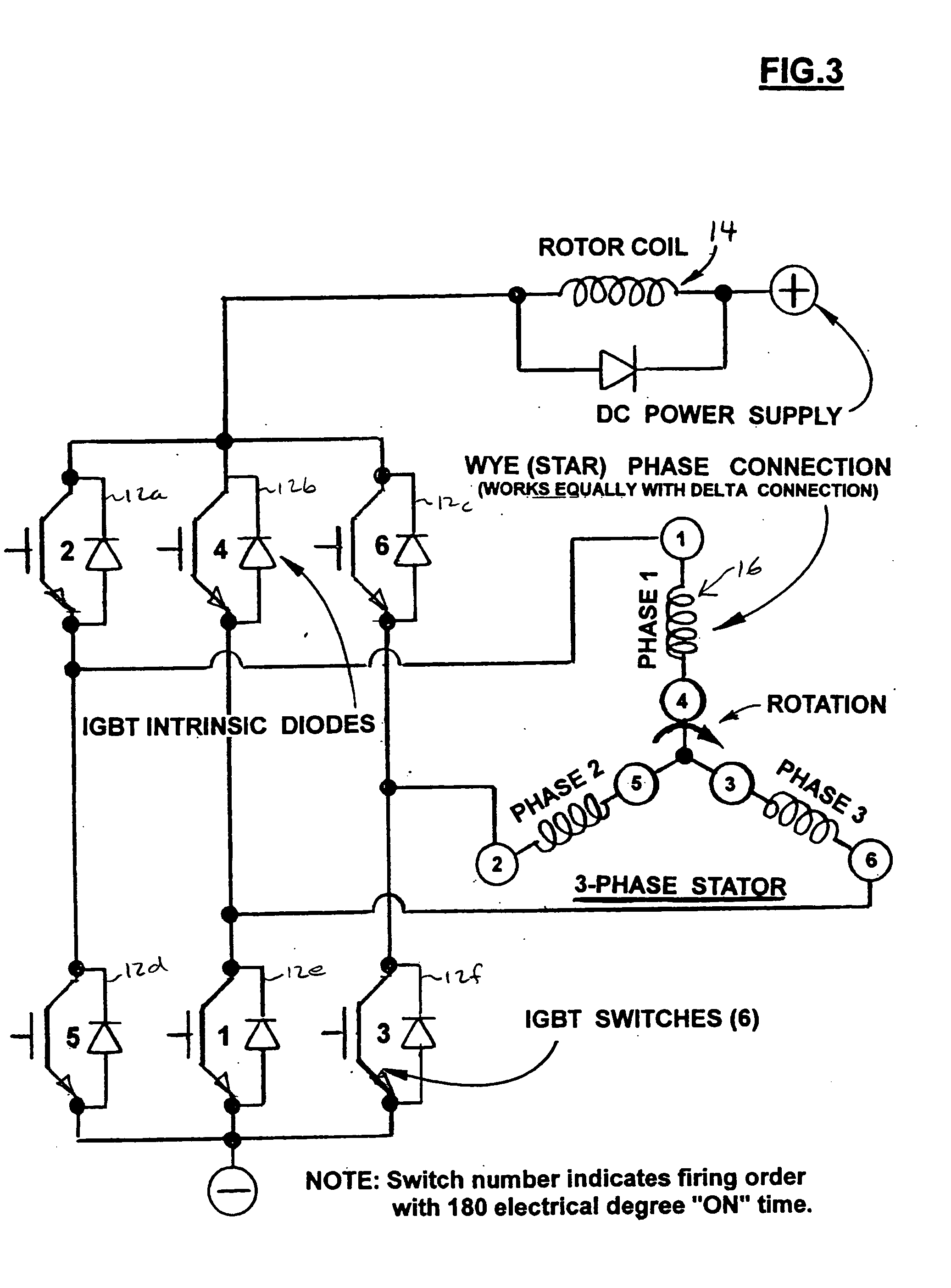
An electromagnetic motor with increased torque. The motor has a rotor coil configured to generate a magnetic field. At least two stator coils are connected in series with the rotor coil. Each of the stator coils is configured to generate a respective magnetic field. The motor further includes a plurality of switches configured to generate the magnetic field in each of the respective rotor and stator coils. The switches are configured to generate the magnetic field in the stator coils such that the rotor coil rotates in response thereto. By having the rotor and stator coils connected in series, the torque of the motor is increased.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY POWER SYST
Power converter for electric rotating machine
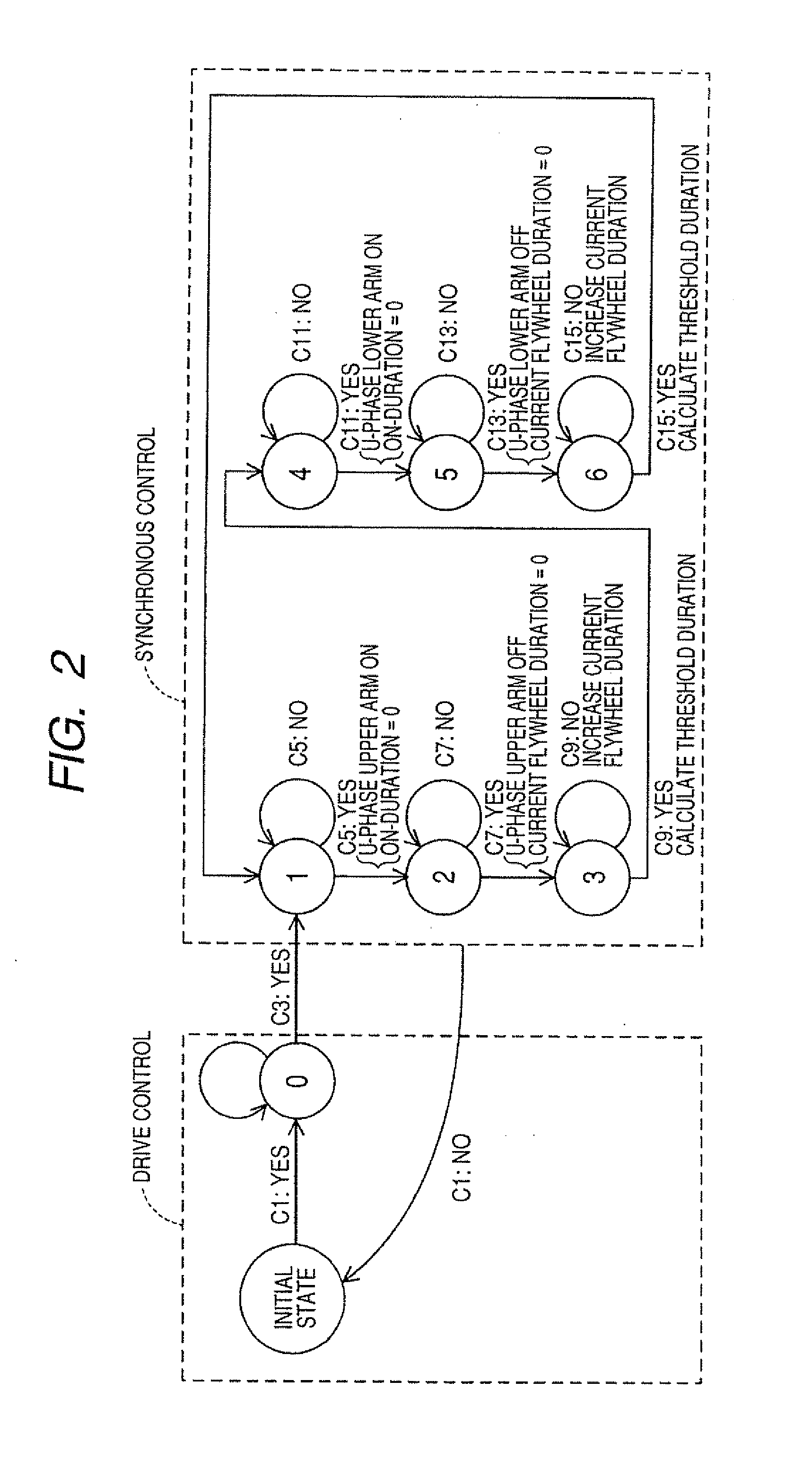
ActiveUS20110006710A1Simple structureEnsure reliabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersAc-dc conversion without reversalTransient stateFreewheel
A power converter for an electric rotating machine is provided which is designed to ensure a desired length of a current flywheel duration in which current is permitted to freewheel from the electric rotating machine even if the power converter is in a transient state or subjected to an unexpected change. The power converter is equipped with a controller and a switching circuit which is disposed between a power supply and windings of the electric rotating machine. The switching circuit has switches grouped into an upper and a lower arm. The controller works to control an off-operation of one of the switches of one of the upper and lower arm so as to produce a desired length of the current flywheel duration following turning off of the one of the switches, thereby minimizing a loss of rectification and avoiding the backflow of current from the power supply to the windings.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electromagnetic motor
InactiveUS7034499B2Effectively doubles iron utilizationDoubling of torqueSingle-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersStator coilPhysics
An electromagnetic motor with increased torque. The motor has a rotor coil configured to generate a magnetic field. At least two stator coils are connected in series with the rotor coil. Each of the stator coils is configured to generate a respective magnetic field. The motor further includes a plurality of switches configured to generate the magnetic field in each of the respective rotor and stator coils. The switches are configured to generate the magnetic field in the stator coils such that the rotor coil rotates in response thereto. By having the rotor and stator coils connected in series, the torque of the motor is increased.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY POWER SYST
Method and apparatus for embedding motor error parameter data in a drive motor of a power driven wheelchair
A drive motor assembly for a power driven wheelchair comprises: a stator housing for containing field coils of a stator of the motor assembly; at least one sensor disposed in the stator housing for sensing rotation of the motor; a memory storing motor error parameter data including data of errors of the at least one sensor, the memory being embedded in the stator housing; and a connection for accessing the error parameter data of the memory from the stator housing. The motor error parameter data may be accessed from the embedded memory of the drive motor by a programmed motor controller for use in controlling the drive motor. Also, the motor error parameter data may be embedded in the drive motor by the steps of: controlling the motor through at least one predetermined drive pattern; sensing motor rotation during the drive pattern and generating signals representative thereof; deriving error parameter data of the drive motor from the generated signals; programming a memory with the derived error parameter data; and embedding the memory in the drive motor.
Owner:INVACARE CORP
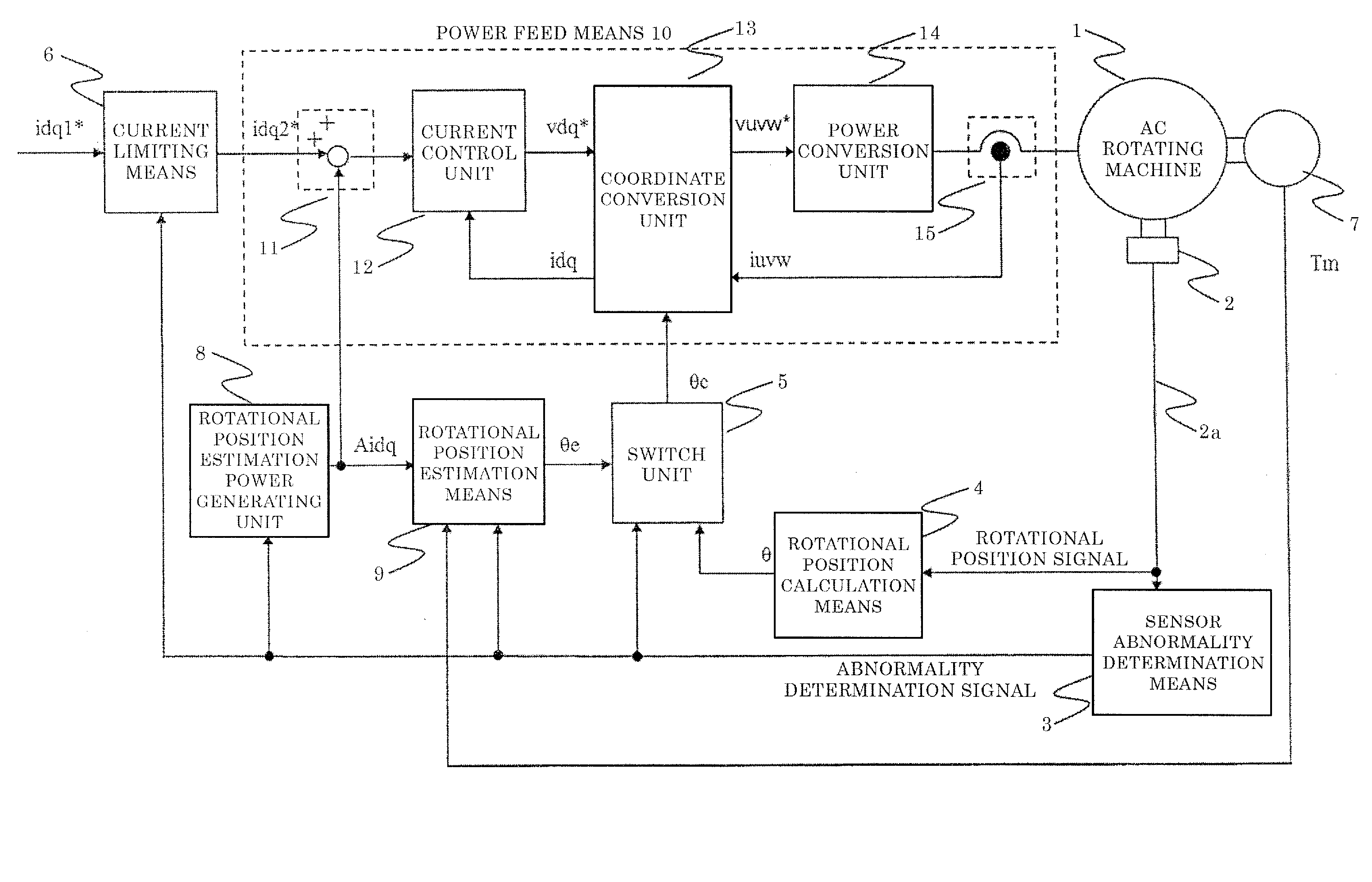
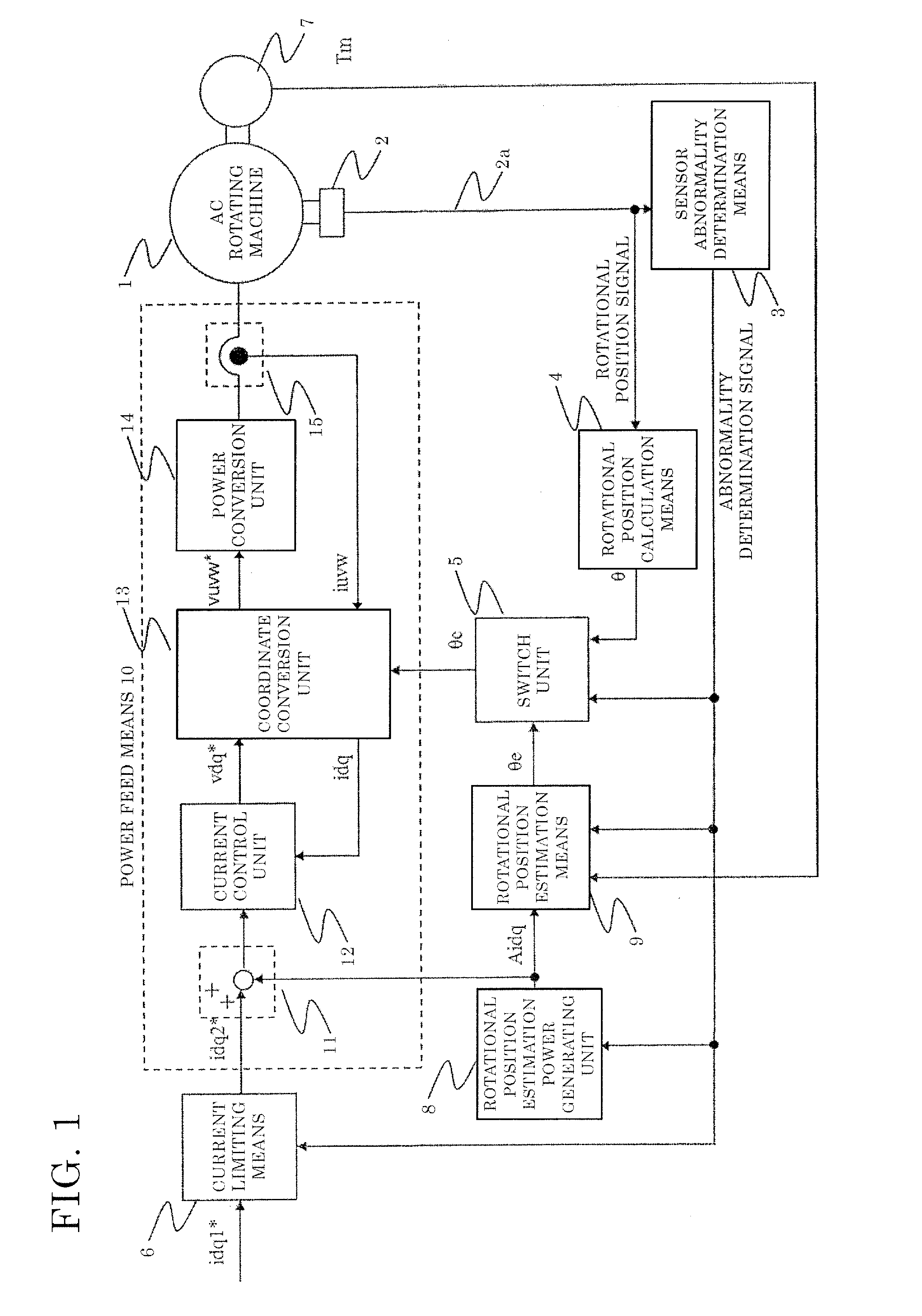
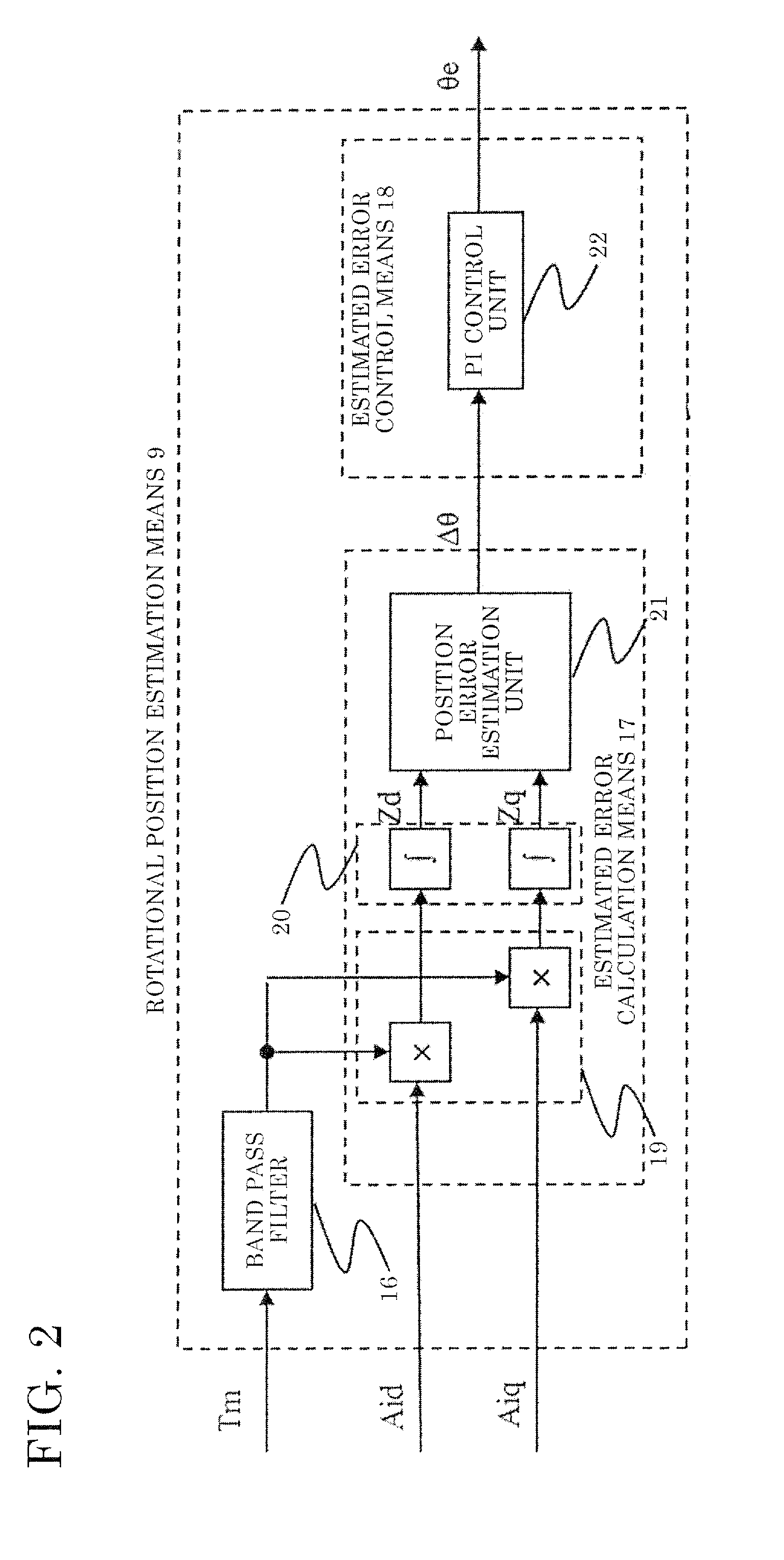
Ac rotating machine control device and electric power steering device equipped with same
ActiveUS20160329849A1Minimize periodWeakening rangeElectric motor controlVector control systemsElectric power steeringDriving current
This AC rotating machine control device includes: power limiting means 6 for limiting drive power supplied for driving the AC rotating machine; and power feed means 10 for, when sensor abnormality determination means 3 determines that the rotational position sensor is abnormal, on the basis of the estimated rotational position, supplying the AC rotating machine with power obtained by adding rotational position estimation power supplied for the rotational position estimation means 9 to estimate the rotational position, to the drive power limited by the power limiting means, wherein the power limiting means 6 limits drive current at least during a predetermined period since the sensor abnormality determination means 3 determines that the abnormality occurs until estimated error of the estimated rotational position falls within a predetermined range.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Rotor excitation method and device of synchronous motor
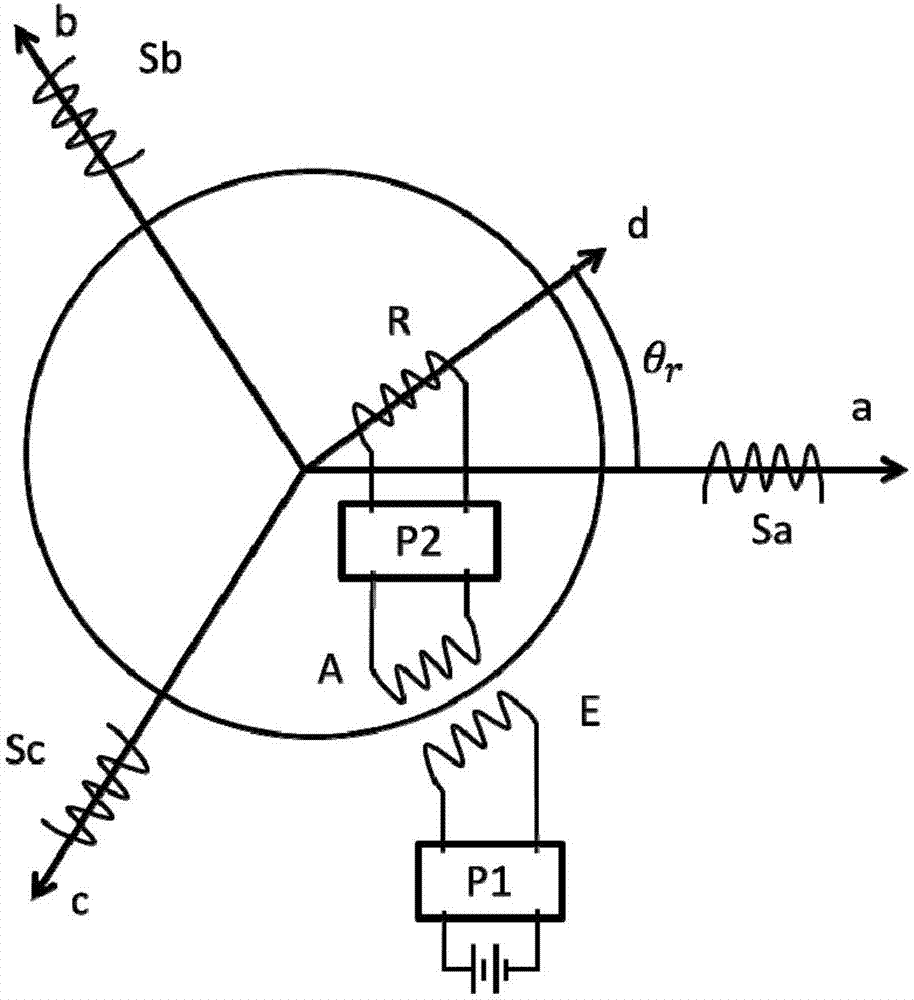
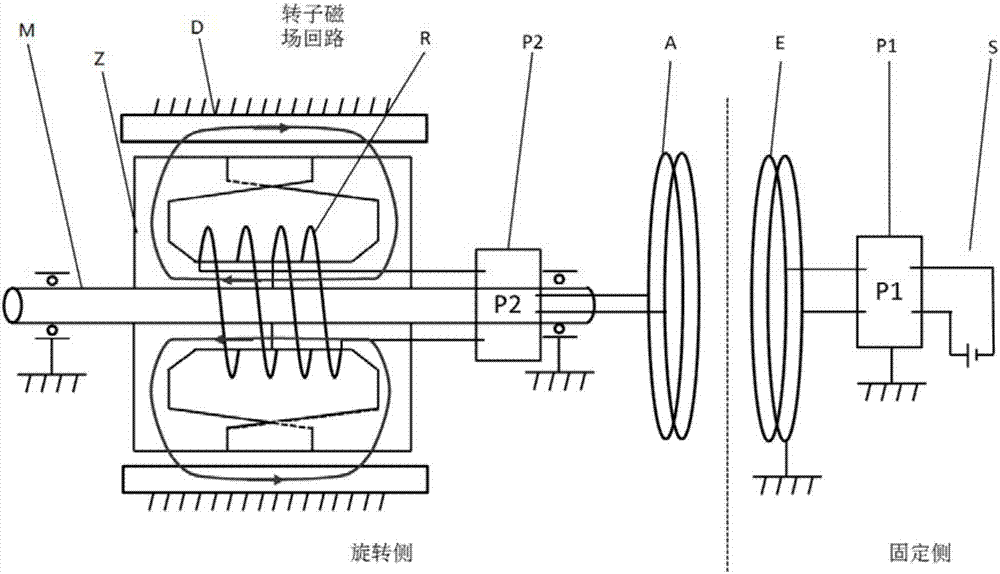
InactiveCN107104613AStable structureRequirements are easy to implementTransformersCircuit arrangementsSynchronous motorExcitation current
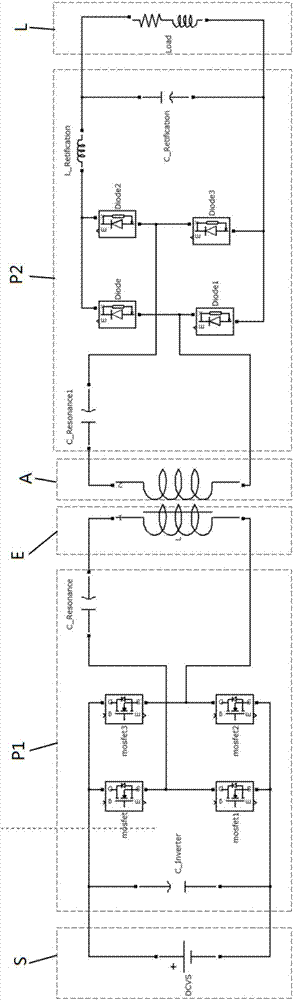
The invention relates to a rotor excitation method and device of a synchronous motor. According to the method, electric energy of a DC / AC power supply is transmitted to a rotor excitation winding in a non-contact mode by employing a resonant wireless electric energy transmission mode, so that rotor electrical excitation or hybrid electrical excitation is achieved. The device comprises an emission end and a receiving end, wherein the emission end is fixedly combined with an engine base, the receiving end synchronously rotates with a rotor and is connected with the rotor excitation winding, the emission end comprises a resonant excitation circuit, an emission end compensation circuit and an emission coil which are connected, the receiving end comprises a receiving coil, a receiving end compensation circuit and rectification conversion circuit which are connected, the rectification conversion circuit is connected with the rotor excitation winding, and the resonant excitation circuit comprises a power input interface and is used for inputting the electric energy from the power supply and continuing to simulate the emission coil and the emission end compensation circuit to work in a resonant state. Compared with the prior art, the device has the advantage of a reliable structure, wireless excitation can be achieved, and an excitation current can be adjusted to satisfy the running demand of the motor under various working conditions.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Idle-stop restart control system
ActiveUS20110049880A1Range of detection of induced is inducedExpand the scope of detectionHybrid vehiclesAC motor controlSynchronous motorControl system
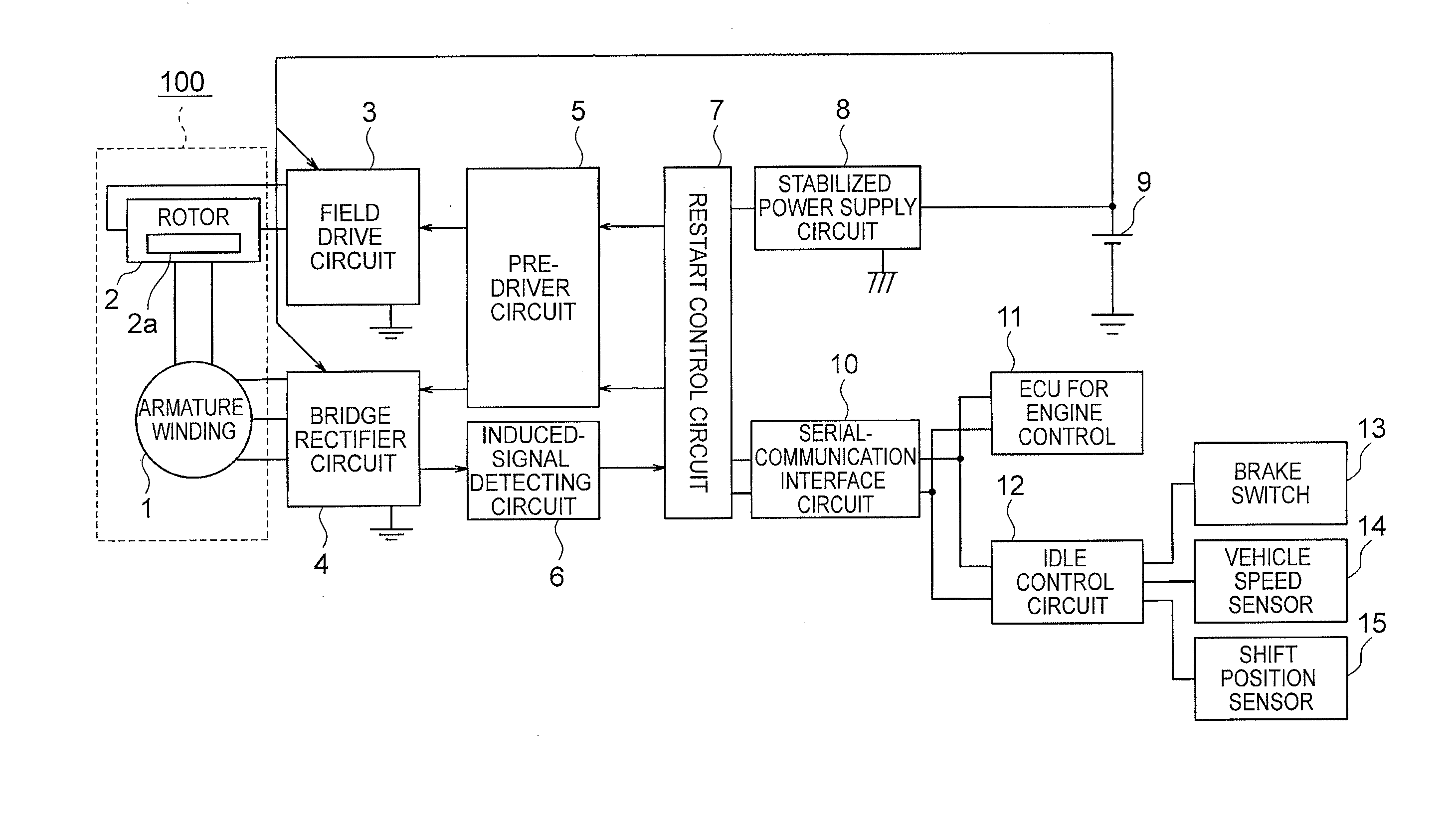
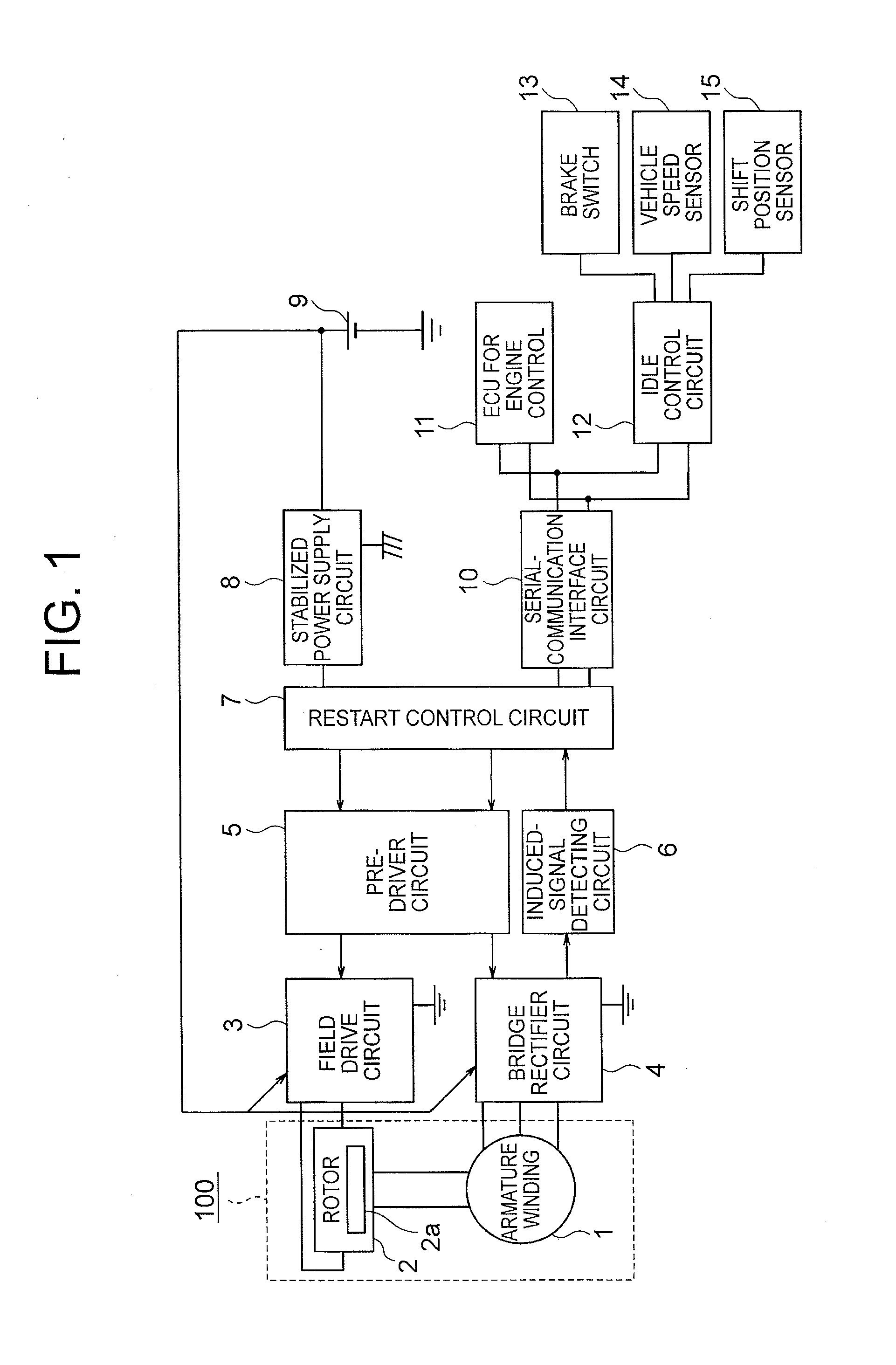
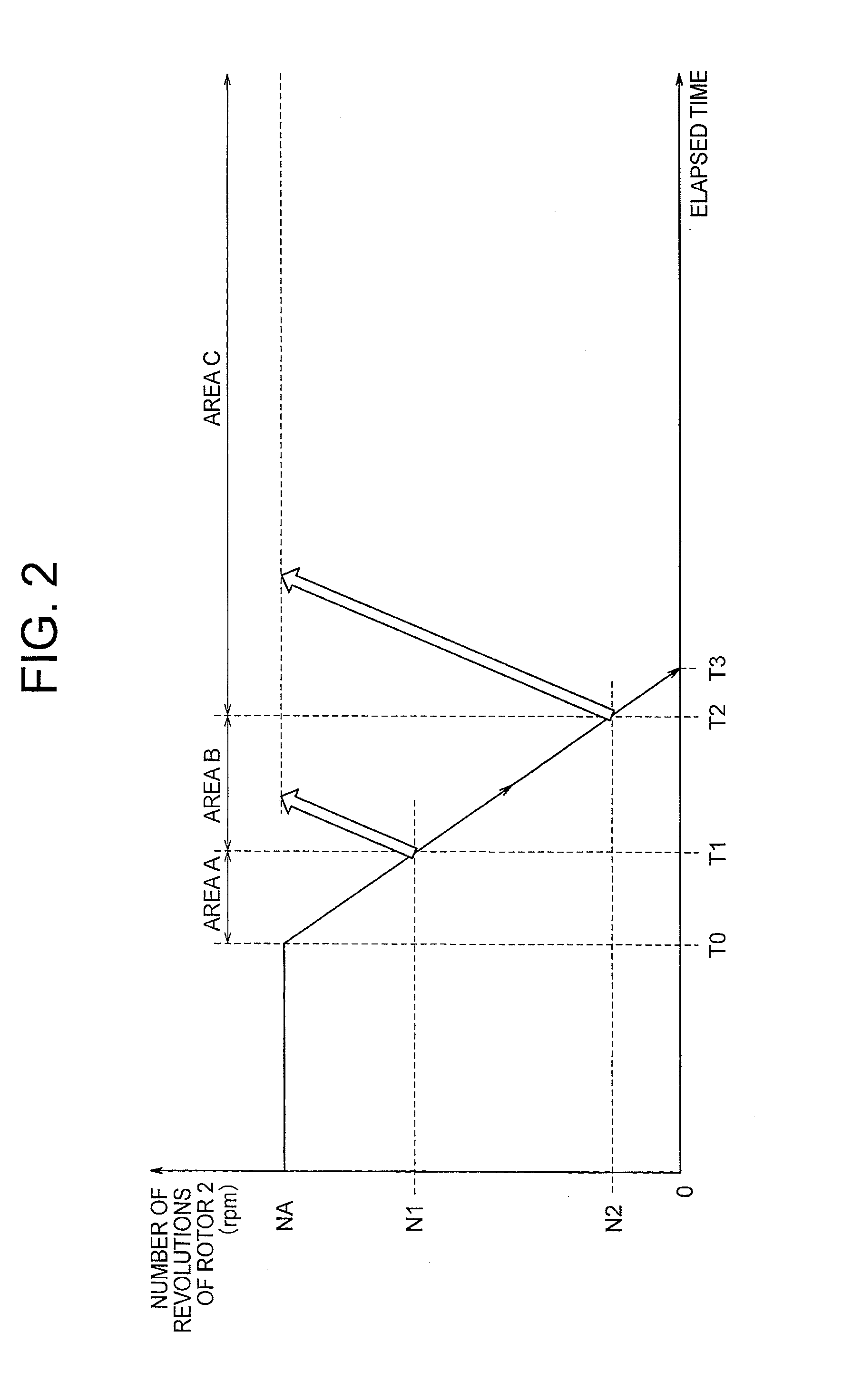
The idle-stop restart control system includes: a sensorless synchronous motor-generator which operates as a generator and a starting motor; an induced-signal detecting circuit for detecting an induced signal output from an armature winding; a field drive circuit for controlling energization of a field winding; and a restart control circuit output, to the field drive circuit, a drive signal for controlling the energization of the field winding to amplify the induced signal while calculating the number of revolutions and an angular position of a rotor based on the detected induced signal when an engine stop command is input and a level of the detected induced signal is equal to or less than a predetermined value and output the drive signal for controlling the energization of the armature winding to restart the engine based on the calculated number of revolutions and angular position of the rotor when a restart command is input.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
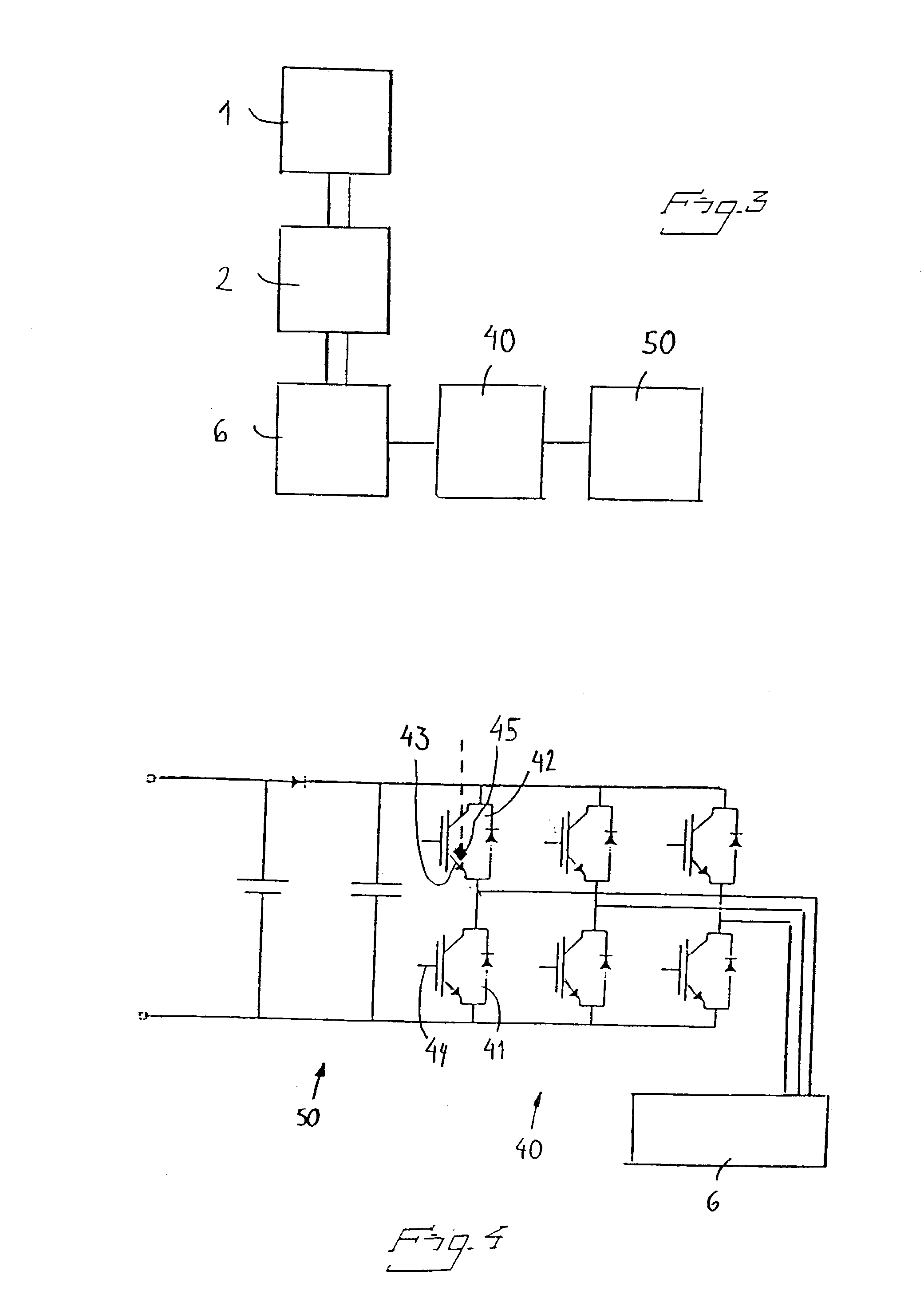
Electric circuit breaker, as well as plant, use and method where such is used
InactiveUS20030150841A1Reduce energy costsReduce in quantityWound field motor controlHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectrical devicesEngineering
The invention relates to an electric circuit breaker. The circuit breaker comprises at least one mobile contact with operating means (2) for operating the same. An electric motor (6) is arranged for driving the operating means (2). The motor (6) is powered from a current source (50) via a current converter (40). According to the invention, the motor (6) and / or current converter (40) are greatly under-dimensioned in relation to the output the current converter is designed to deliver. This is possible because the operating duration is so brief. Under-dimensioning results in extensive cost-savings. The invention also relates to an electric plant equipped with such a circuit breaker. The invention further relates to the use of such a circuit breaker and a method for breaking electric current in the corresponding fashion.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
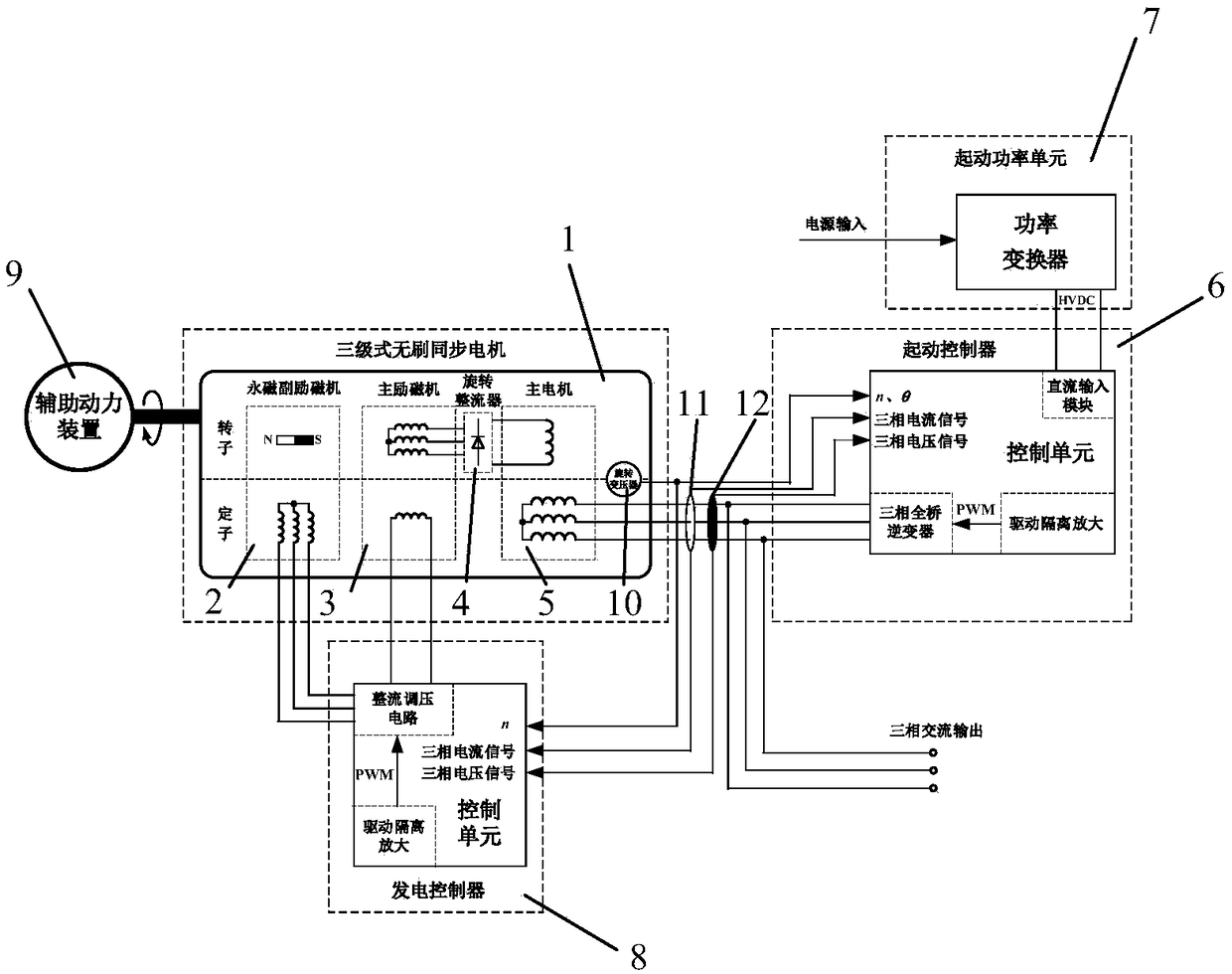
Staged start control system and method of three-stage brushless synchronous motor
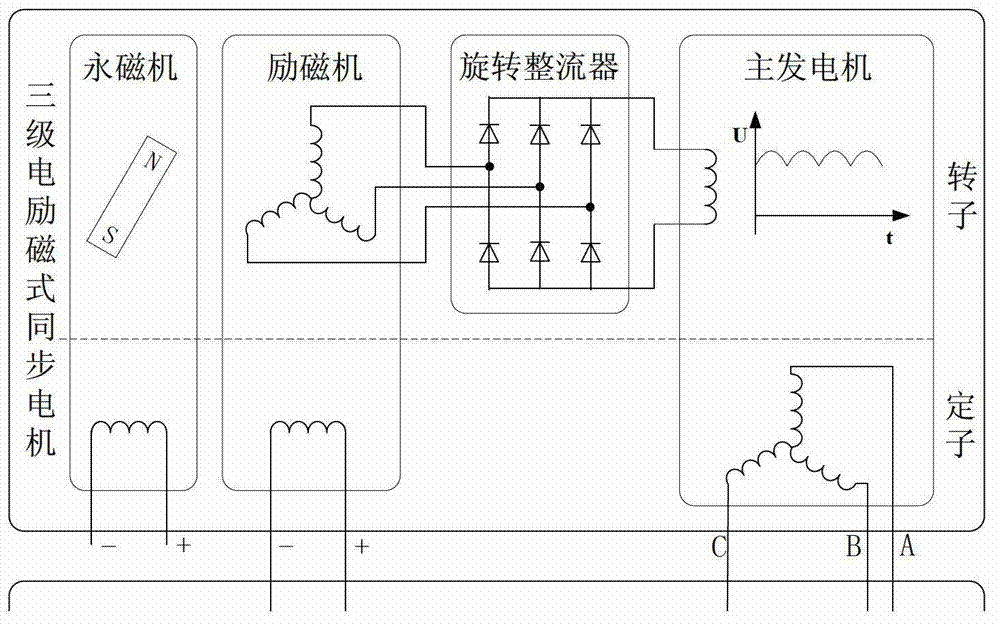
InactiveCN108964532AReduce volumeReduce weightWound field motor controlStarter arrangementsSynchronous motorAlternating current
The invention discloses a staged start control system and method of a three-stage brushless synchronous motor. The three-stage brushless synchronous motor is composed of a permanent-magnet auxiliary exciter, a main exciter, a rotary rectifier and a main generator, a starting controller, a starting power unit and a power generation controller. The main exciter, the rotary rectifier and the main generator are connected in sequence. The starting controller leads alternating currents to an armature winding of the main generator at the starting stage of a starting power generation system and a reluctance torque is generated; and starting of the system at a zero-rotating speed is realized by the reluctance torque. When the motor obtains a certain rotating speed, the power generation controller leads direct currents to an excitation coil of the main exciter to provide excitation currents for the main generator, so that the current amplitude value to the armature winding of the main generatorby the starting controller is reduced substantially during the follow-up acceleration process. On the basis of the start control method, multiplexing of the power generation controller is realized; and the starting controller only needs one set of three-phase inverters to realize the starting function, so that the complexity of the whole system is reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Origin offset calculation method of rotational position detecting device of electric motor and motor control device using the calculation method
ActiveUS7023170B2Improve calculation accuracyImprove detection accuracyAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersLocation detectionSynchronous motor
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
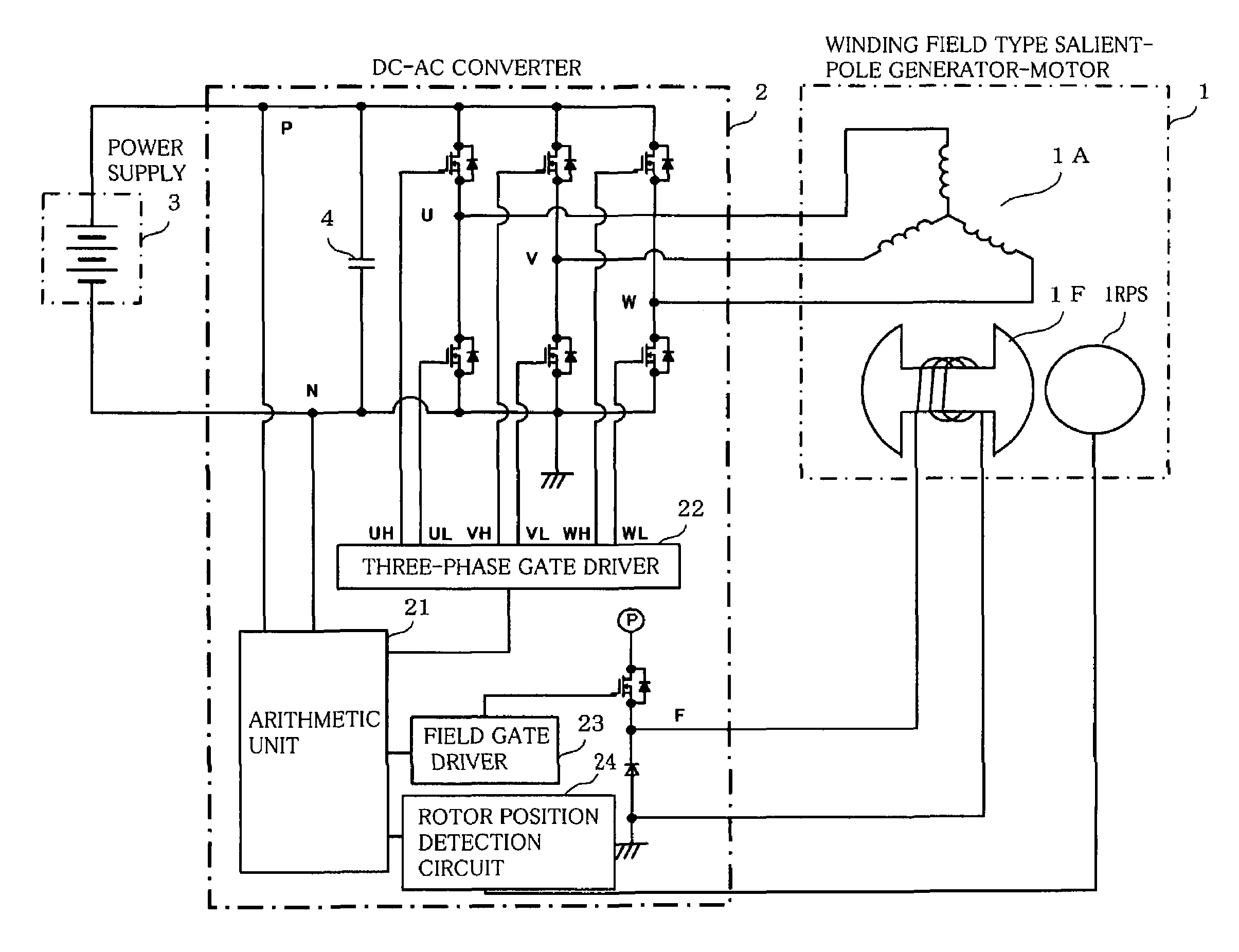
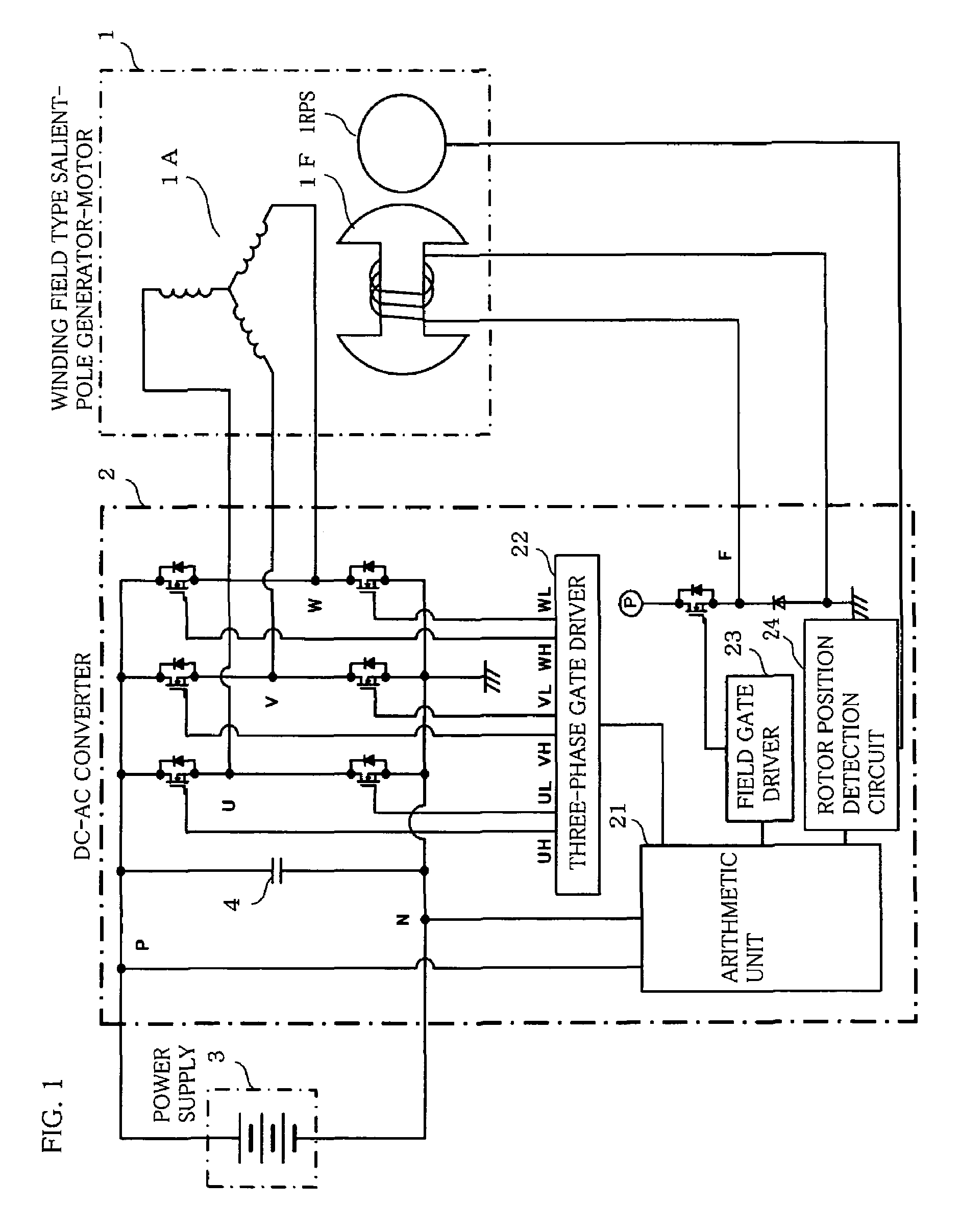
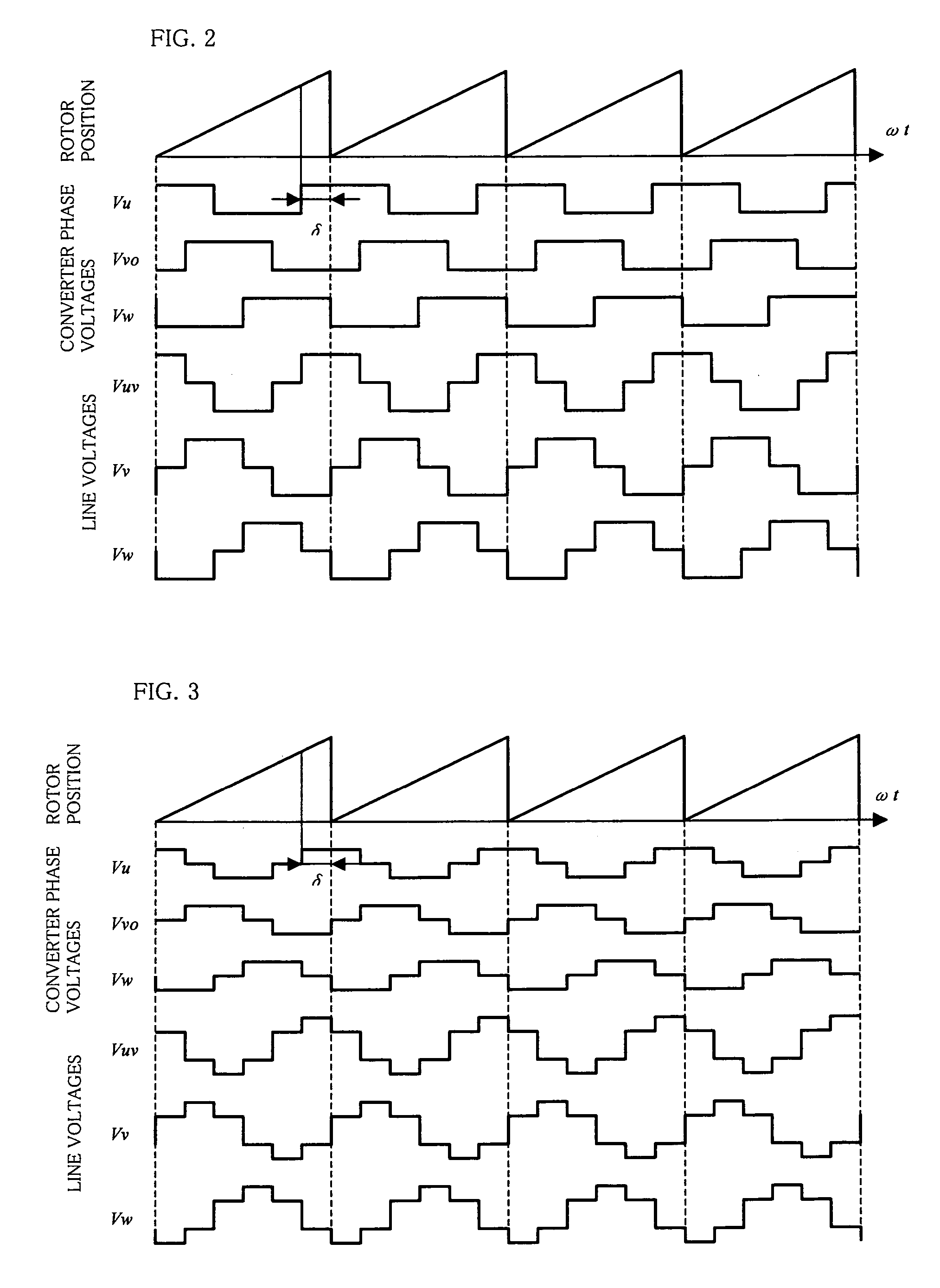
Vehicular generator-motor control apparatus
ActiveUS7723933B2Increase torqueAC motor controlSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor controlDc ac converter
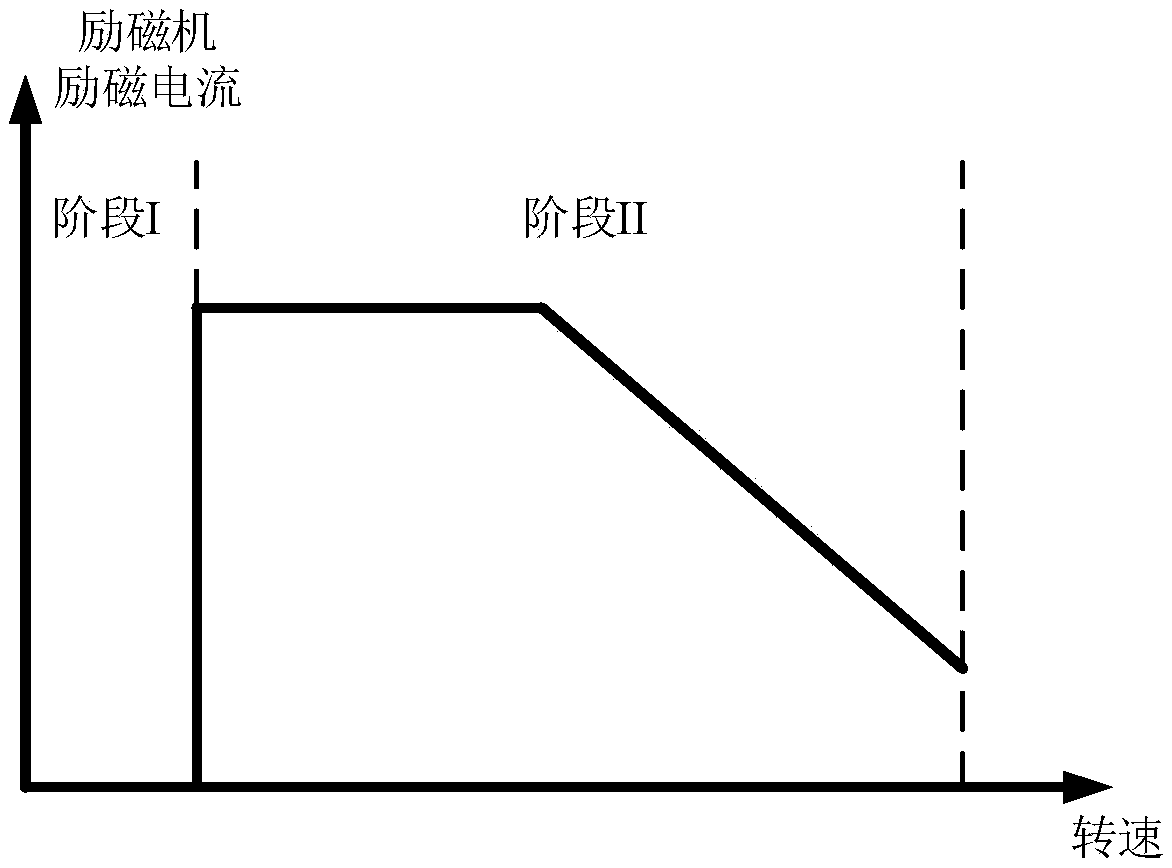
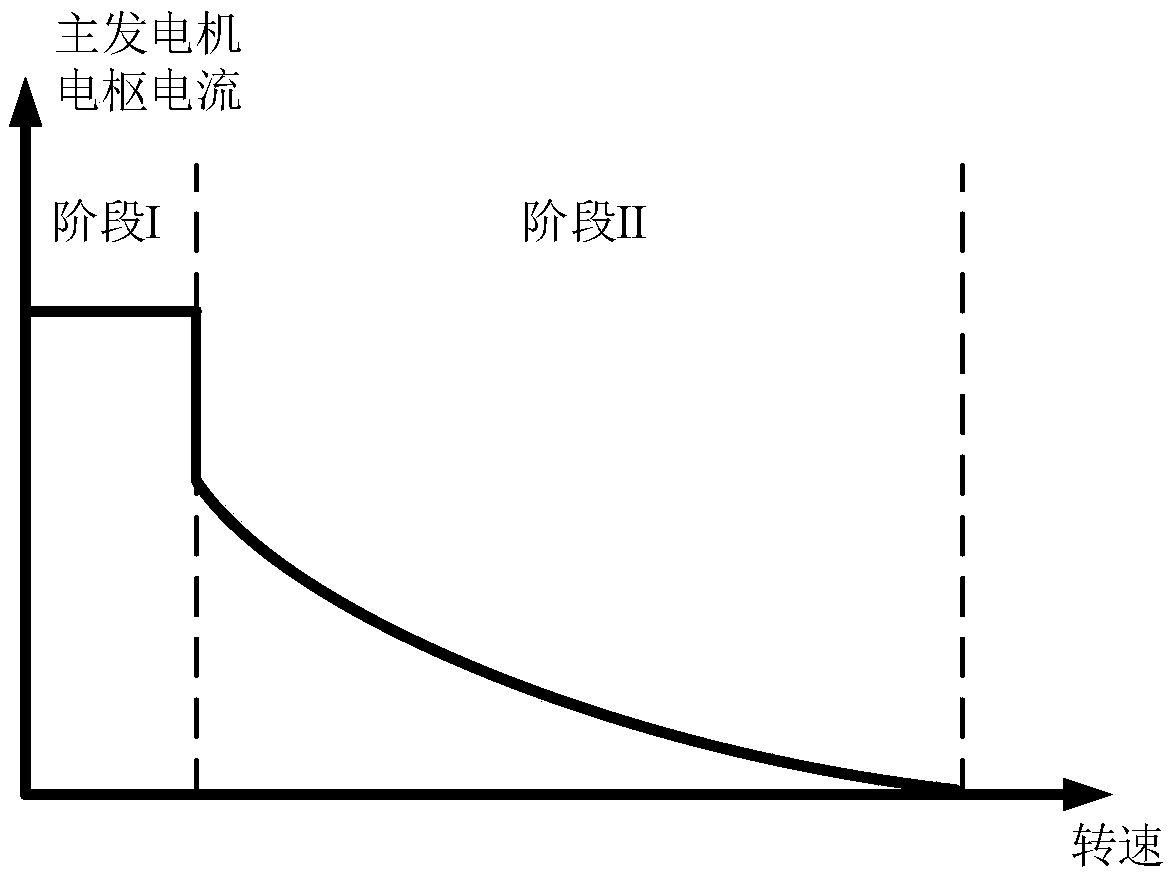
A vehicular generator-motor control apparatus wherein a winding field type salient-pole generator-motor 1 (in FIG. 1) for a vehicle is subjected to a conduction control by a DC-AC converter 2, characterized in that a stator 1A of the vehicular winding field type salient-pole generator-motor 1 is energized by rectangular wave voltages at those conduction start angles δ of respective phases of the stator 1A which are shifted a predetermined angle relative to a rotor position, and that the conduction start angles δ of the respective phases change substantially continuously in accordance with an input voltage of the DC-AC converter 2 and a revolution speed of the generator-motor 2.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Excitation-varied synchronous motor MTPA (Maximum Torque Per Ampere) control method based on fitting of binary quadratic function
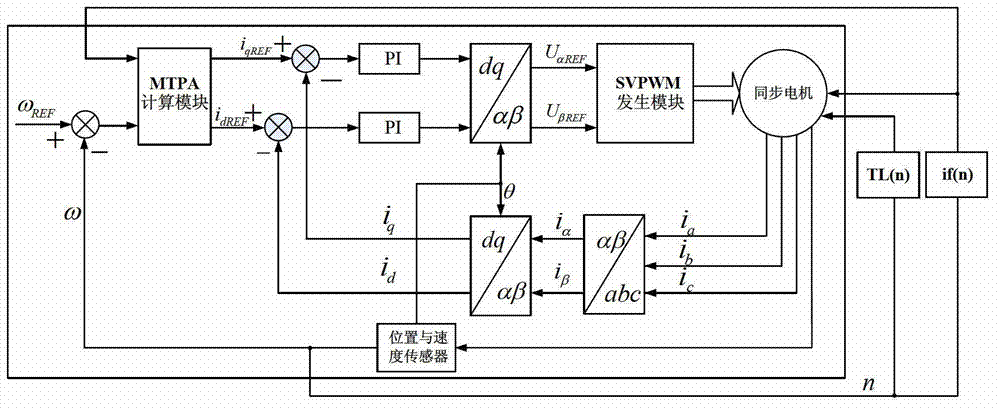
InactiveCN102857159ASolve hard-to-get problemsThe fitting method is simple and effectiveSingle motor speed/torque controlWound field motor controlMaximum torqueSynchronous motor
The invention relates to an excitation-varied synchronous motor MTPA control method based on fitting of a binary quadratic function, and provides a method for carrying out rectangular axis current function fitting by the binary quadratic function aiming at a rectangular axis current calculating module in a control structure graph (3), and the method comprises the following steps of: respectively fitting the rectangular axis current functions into the binary quadratic functions about Te and psi f, and finally finishing controlling of maximum torque per ampere of the excitation-varied synchronous motor. The excitation-varied synchronous motor MTPA control method based on fitting of the binary quadratic function has the following beneficial effects: (1), the problem that the rectangular axis current function is difficultly acquired in the MTPA controlling of the excitation-varied synchronous motor is solved by carrying out rectangular axis current function fitting through a fitting method of the binary quadratic function; and (2), the method of the binary quadratic function in the method adopted by the invention is simple and effective, and compared with the other two-dimensional look-up table methods, the method has the superiorities of good fitting degree and small occupied memory.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
Switch reluctance motor system based on double-bus split current sampling
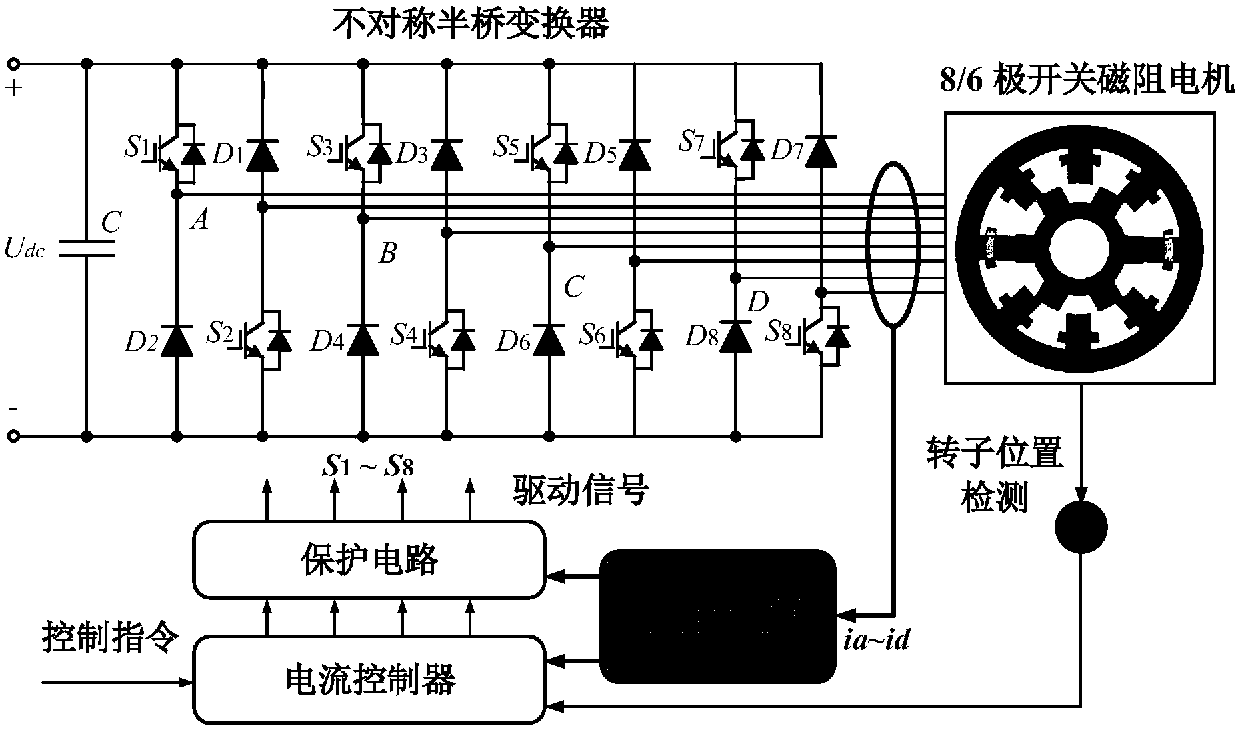
ActiveCN107659229ASimple methodReliable methodAC motor controlWound field motor controlMagnetic reluctanceCurrent sensor
The invention discloses a switch reluctance motor system based on double-bus split current sampling. On the basis of a traditional asymmetric half-bridge converter, an upper bus and a lower bus are split and connected, and two current sensors are adopted to respectively detect the current information of the upper bus and the current information of the lower bus. One bus current comprises current information of two phases, and the other bus current comprises current information of the other two phases. By combining the turn-on interval information of each phase winding, the excitation current in each phase conduction interval can be effectively obtained, and therefore current control is carried out. The excitation current of each phase winding in the turn-on interval can be detected by onlytwo current sensors, and the number of current sensors traditionally used is reduced by one half. According to the scheme, pulse injection is not needed for each phase and extra hardware equipment isnot needed. The excitation current of each phase can be obtained directly according to the double-bus sampling current and the turn-on information of each phase. The method is simple and reliable andis easy to implement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnet flux amount estimation device, abnormal demagnetize determination device, synchronous motor driving device, and electric motor car
ActiveCN104009684ACommutation monitoringAC motor controlSynchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
The invention refers to a magnet flux amount estimation device, abnormal demagnetize determination device, synchronous motor driving device, and electric motor car. According to one embodiment, a magnet flux amount estimation device includes a magnetic pole position detector configured to detect a magnetic pole position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor including a permanent magnet within a rotor; an inductance-equivalent value determination module configured to determine an inductance-equivalent value of a d-axis corresponding to a determined magnetic pole direction; and a magnet flux amount estimator configured to calculate an estimation value of a magnet flux amount of the permanent magnet, based on the inductance-equivalent value.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electronic controller for electric power steering
InactiveUS20150274197A1Further reducedLow costMotor/generator/converter stoppersCasings with connectors and PCBElectric power steeringElectronic controller
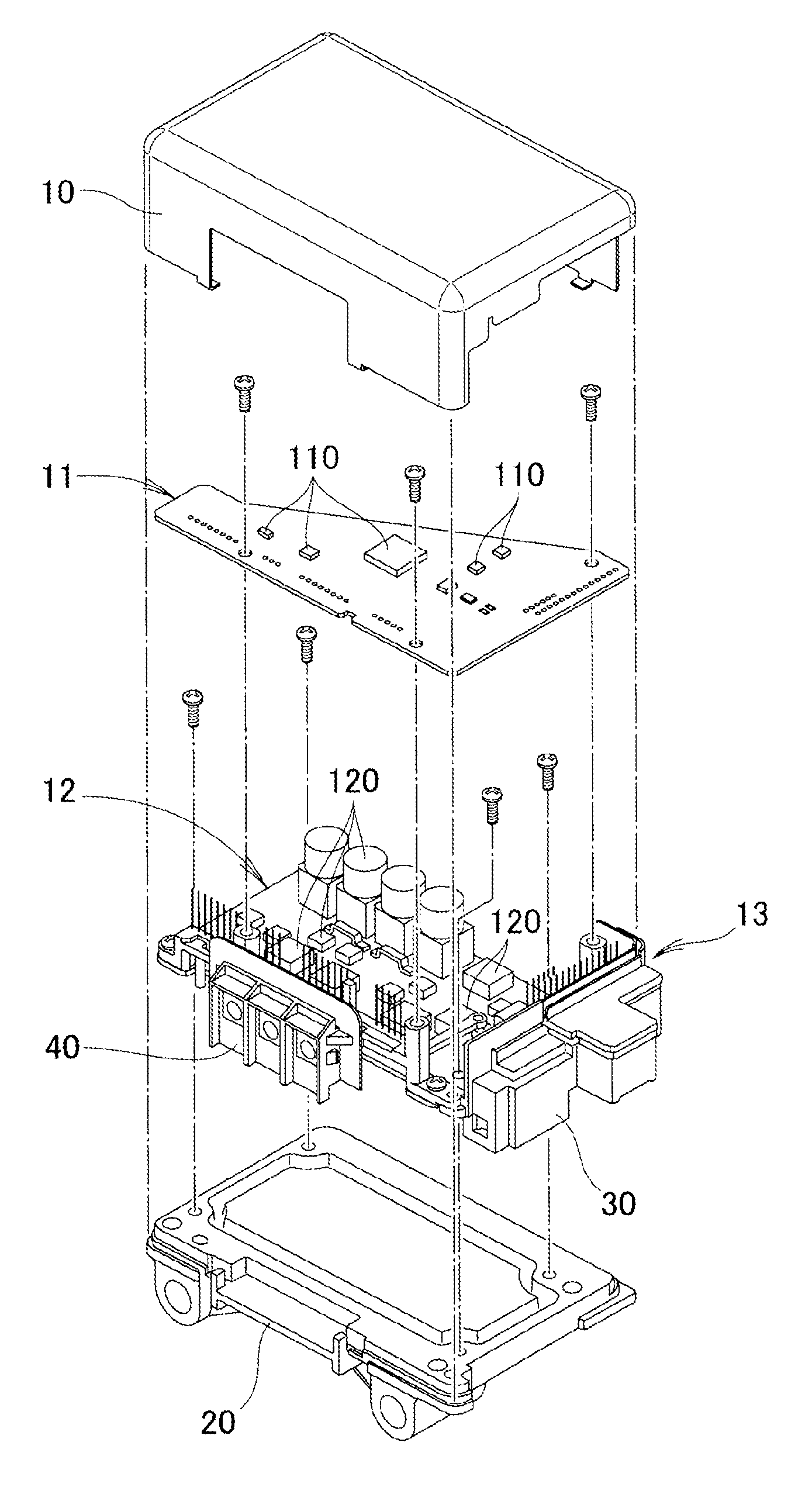
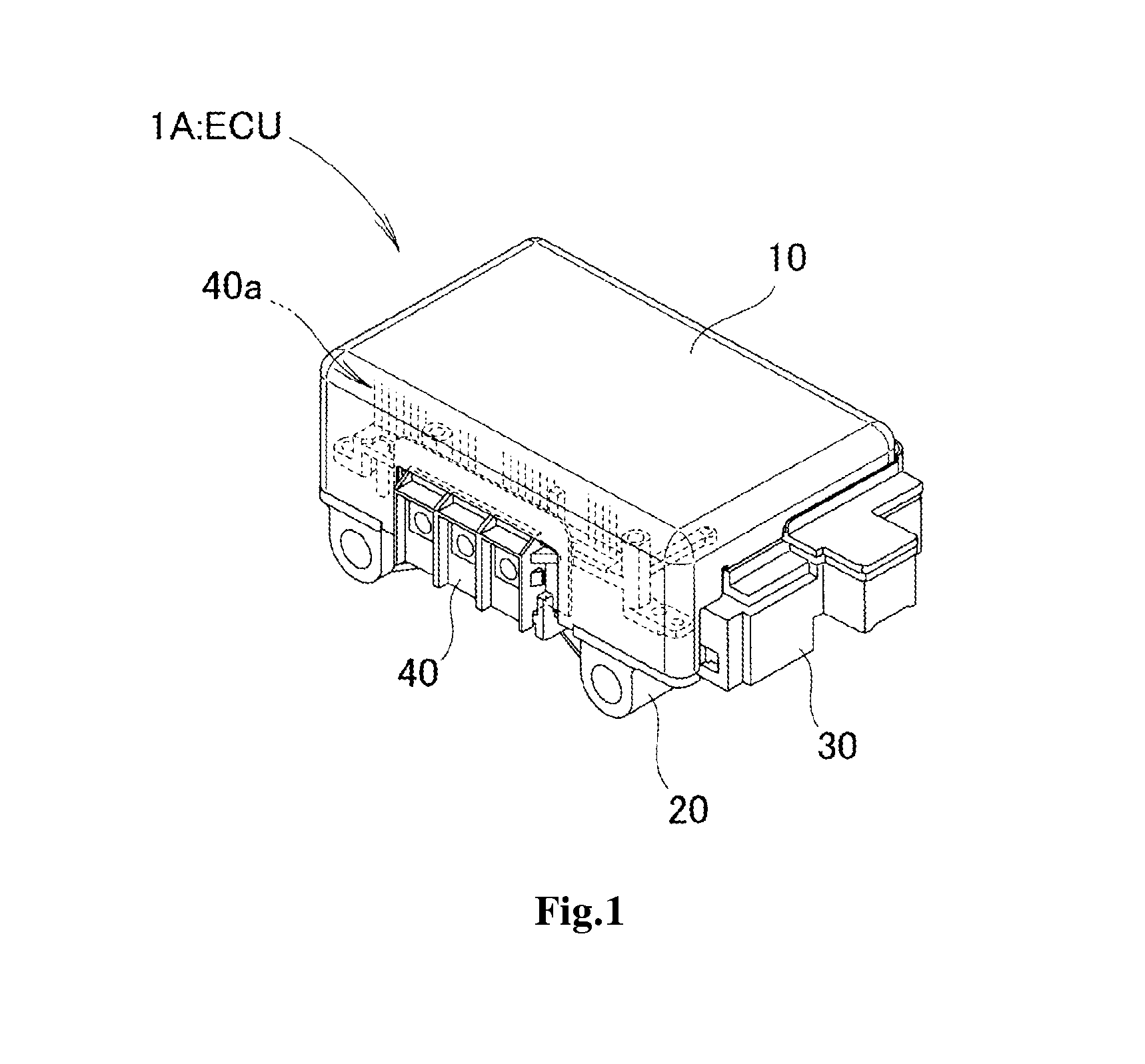
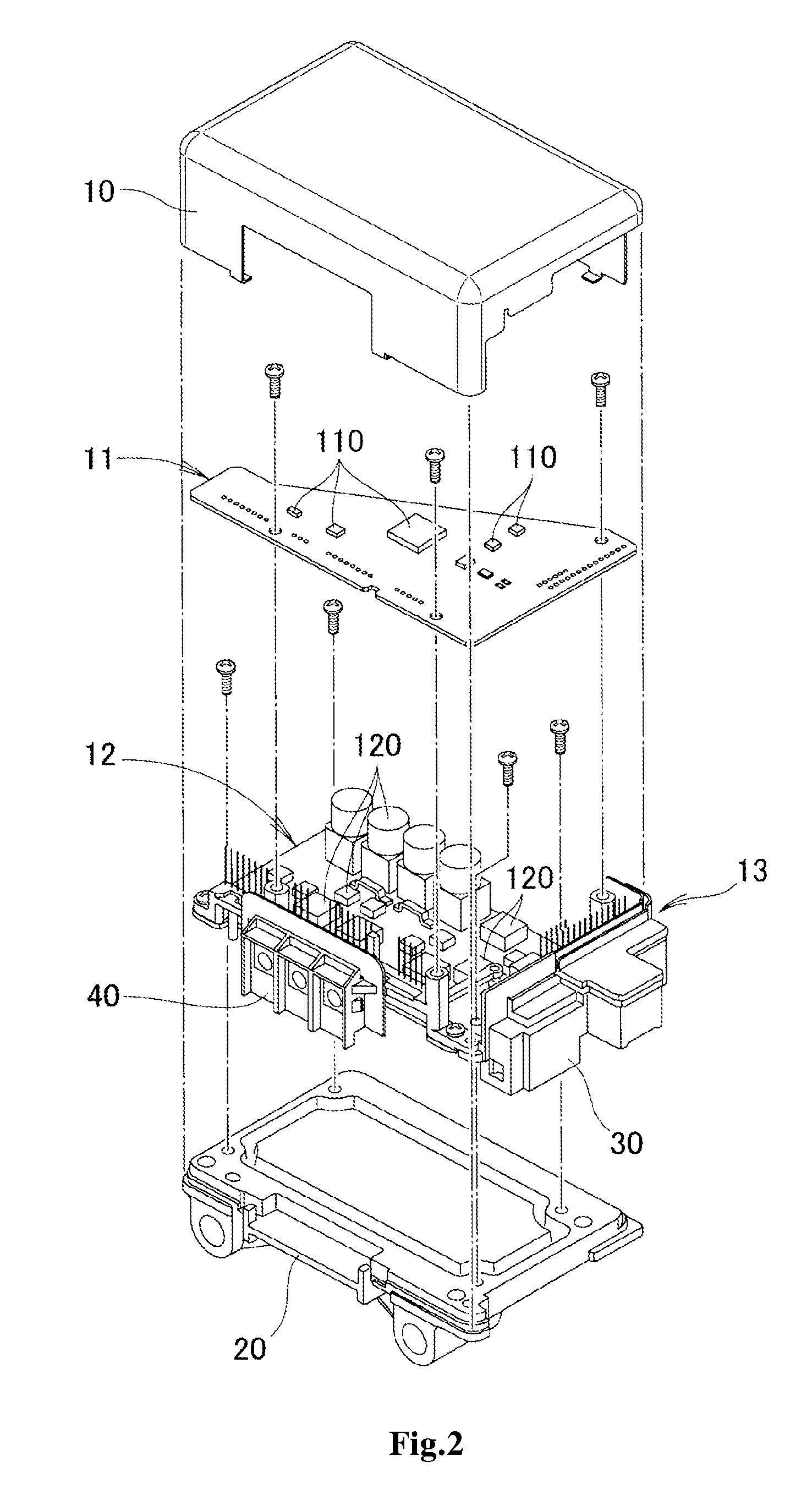
An electronic controller for electric power steering includes a first board, a second board, an insert molded component, a heat sink, and a protective cover. First surface-mounted components are mounted on the first board. Second surface-mounted components having a higher tolerant current capacity than that of the first surface-mounted components are mounted on the second board. The insert molded component includes connectors mounted at a first end portion of the second board and mounted at a second end portion located vertically to the first end portion. The heat sink externally radiates heat transferred from the second surface-mounted component to the second board. The protective cover is fixed to the heat sink to cover the first board and the second board on which the insert molded component is mounted.
Owner:NIDEC ELESYS
Adjustment method of rotor position detection of synchronous motor
ActiveUS7388346B2Improve performanceHigh positioning accuracyAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlProduction rateLocation detection
To obtain an adjustment method of rotor position detection of a synchronous motor with excellent productivity. An adjustment method of rotor position detection of a synchronous motor, wherein a synchronous motor having a stator wound around a stator coil and a rotor provided with magnetic poles, and a rotational position detector having a sensor rotor fixed to the rotor and a sensor stator disposed opposite to the sensor rotor for detecting a rotational position of the rotor are provided, and wherein an amount of deviation between the rotational position of the synchronous motor determined from an output of the rotational position detector and an actual rotational position of the synchronous motor is adjusted, the method comprising: a step of detecting the amount of deviation during rotation of the synchronous motor; and a step of mechanically adjusting a relative position between the rotational position detector and the synchronous motor based on a detected value of the amount of deviation, is provided.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
A magnetic gear system and method for reducing transmission of torque pulsation
InactiveCN105993126AWound field motor controlPermanent-magnet clutches/brakesMagnetic polesPole piece
A system comprises an input member, an output member, a magnetic gear connecting the input member to the output member and control means arranged to control the flow of power from the input member to the output member. The magnetic gear comprises a first set of magnetic poles, a second set of magnetic poles, and a set of pole pieces arranged to modulate the magnetic field between the first set of magnetic poles and the second set of magnetic poles. The control means comprises means for reducing the transmission of torque pulsation and / or oscillation from the input member to the output member.
Owner:MAGNOMATICS LTD
Method and apparatus for initialization and operation of field-commutated motors and machines incorporating field-commutated motors
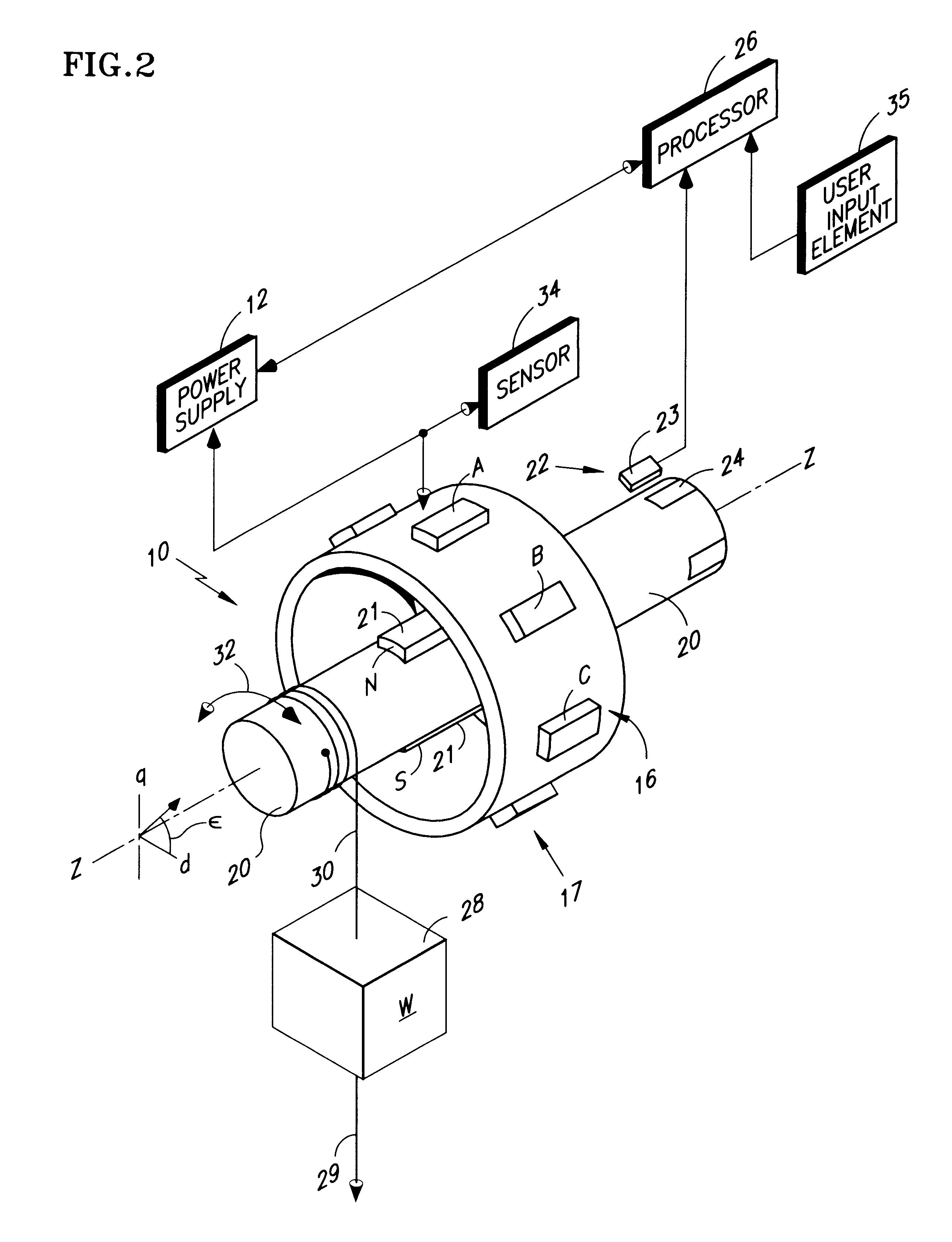
InactiveUS6211634B1Save effortShorten the timeCommutation monitoringSynchronous motors startersUser inputCurrent sensor
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for calibrating a field-commutated motor (10) when under load, wherein initializing the motor (10) refers to relating data representative of the angle of the rotor in an uncalibrated coordinate system to a coordinate system having a known relationship to the excitation coils (17), typically mounted with the stator (16). The angular data can then be used for exciting the excitation coils (17) in the proper sequence and with the proper timing to obtain the desired speed, torque, direction or rotation, etc. of the motor (10). Test voltages having a known orientation are applied to one of the stator and the rotor, (whichever mounts the excitation coils (17)), and the angle of the rotor produced by the application of each of the test voltages noted. An equation is disclosed for determining an error angle between the uncalibrated and the known coordinate system as a function of the angles of the rotor produced by application of the test voltages. Apparatus for practicing the invention can include a processor (26), a power supply (12), and user input element (35) and a voltage and / or current sensor (35). The processor (26) can include appropriate means for executing the disclosed method steps.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Electric circuit breaker, as well as plant, use and method where such is used
InactiveCN1416585ASwitch power arrangementsWound field motor controlElectrical devicesElectric power
The invention relates to an electric circuit breaker. The circuit breaker comprises at least one mobile contact with operating means (2) for operating the same. An electric motor (6) is arranged for driving the operating means (2). The motor (6) is powered from a current source (50) via a current converter (40). According to the invention, the motor (6) and / or current converter (40) are greatly under-dimensioned in relation to the output the current converter is designed to deliver. This is possible because the operating duration is so brief. Under-dimensioning results in extensive cost-savings. The invention also relates to an electric plant equipped with such a circuit breaker. The invention further relates to the use of such a circuit breaker and a method for breaking electric current in the corresponding fashion.
Owner:ABB (SCHWEIZ) AG
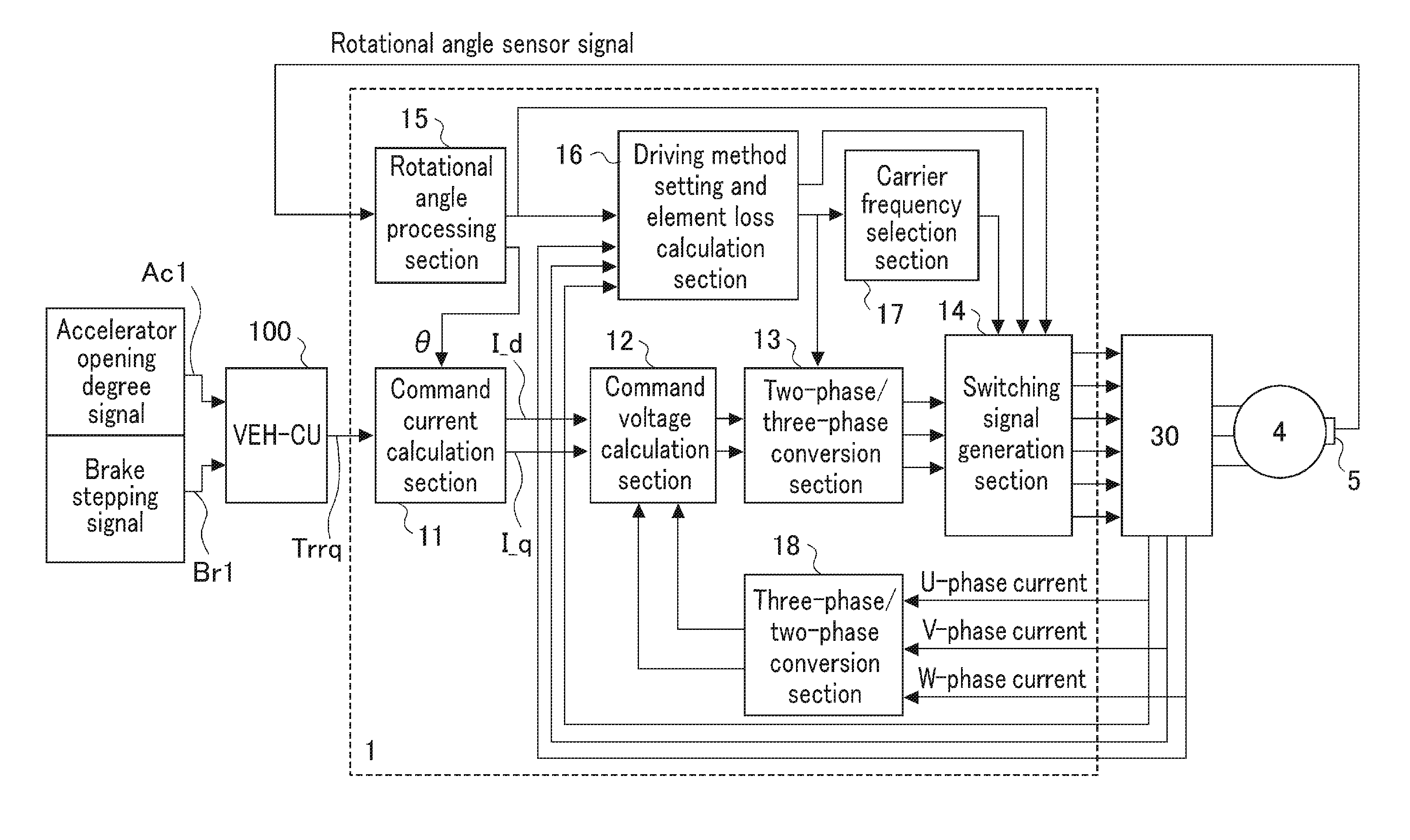
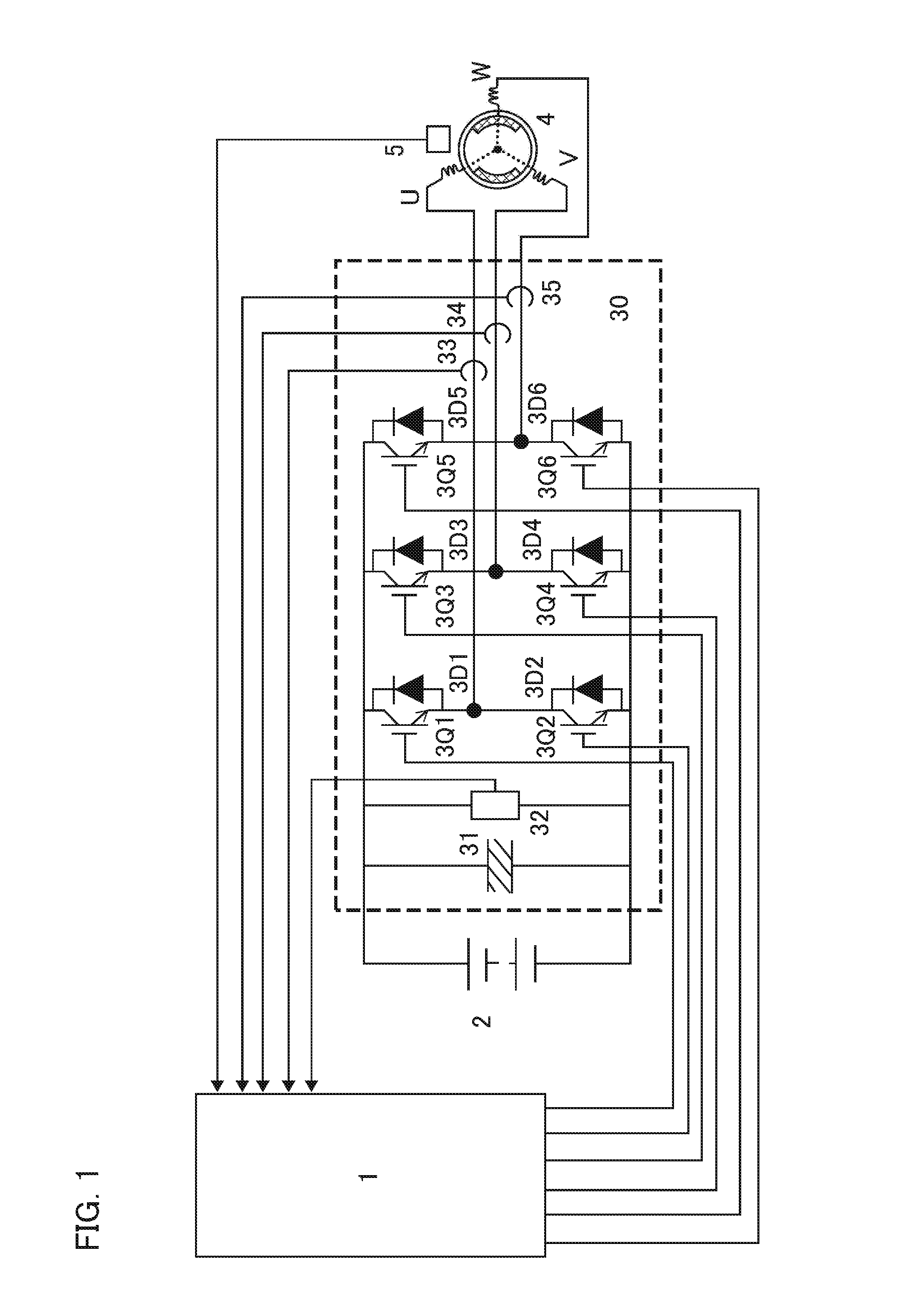
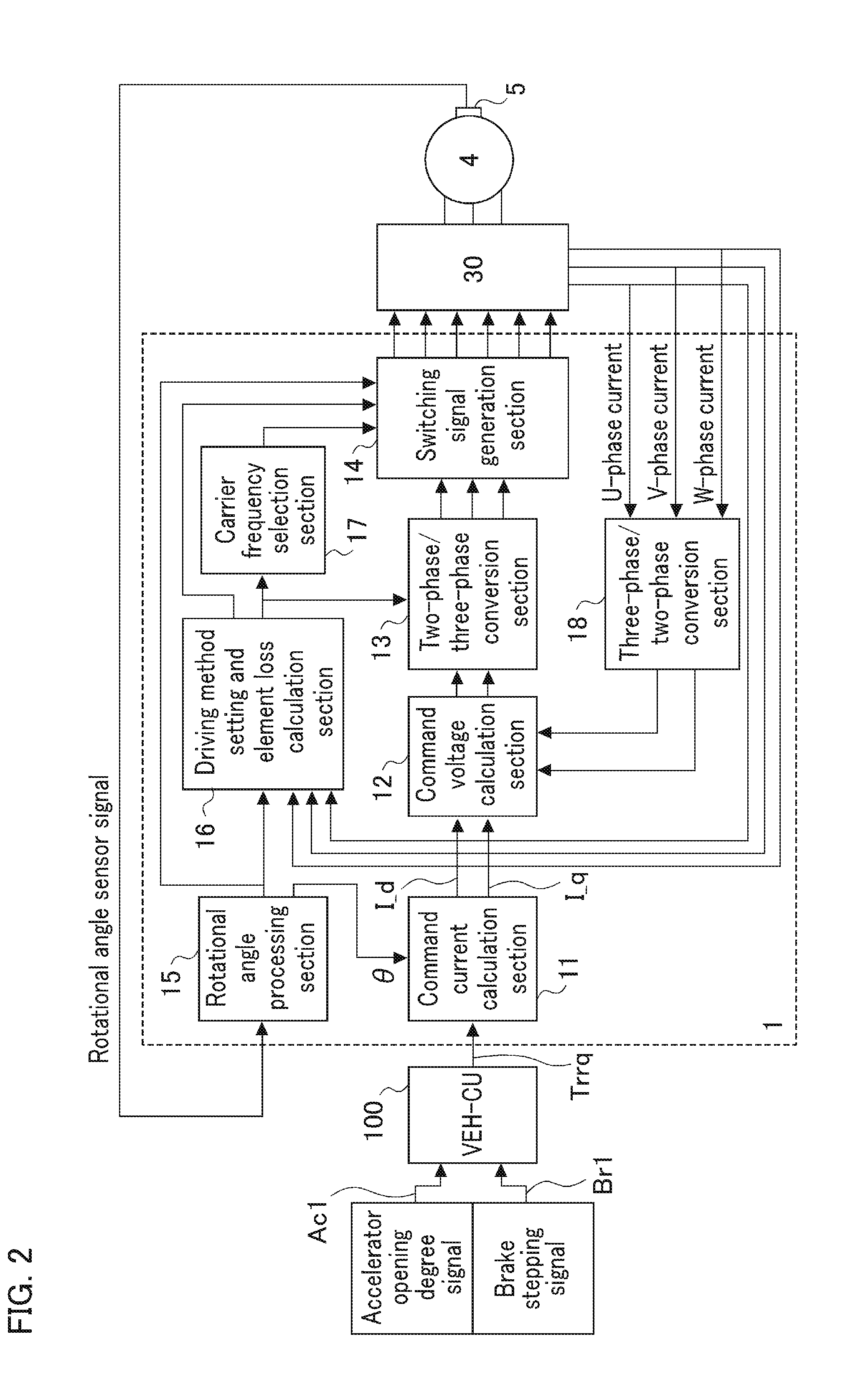
Electric motor control device
ActiveUS20160329856A1Suppresses noise generationReduce power lossAC motor controlElectric motor controlSwitching signalEngineering
An electric motor control device drives a power converter (30) by two-phase modulation drive based on calculation of a driving method setting and element loss calculation section (16) when an electric motor (4) is equal to or less than a predetermined rotational speed; and switches switching signals from a switching signal generation section (14) to switch a switching operation of the switching elements when a loss integrated value of a first switching element with a large switching loss or a second switching element exceeds a predetermined value.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for measuring position and speed of rotor of electrically excited synchronous motor and control device
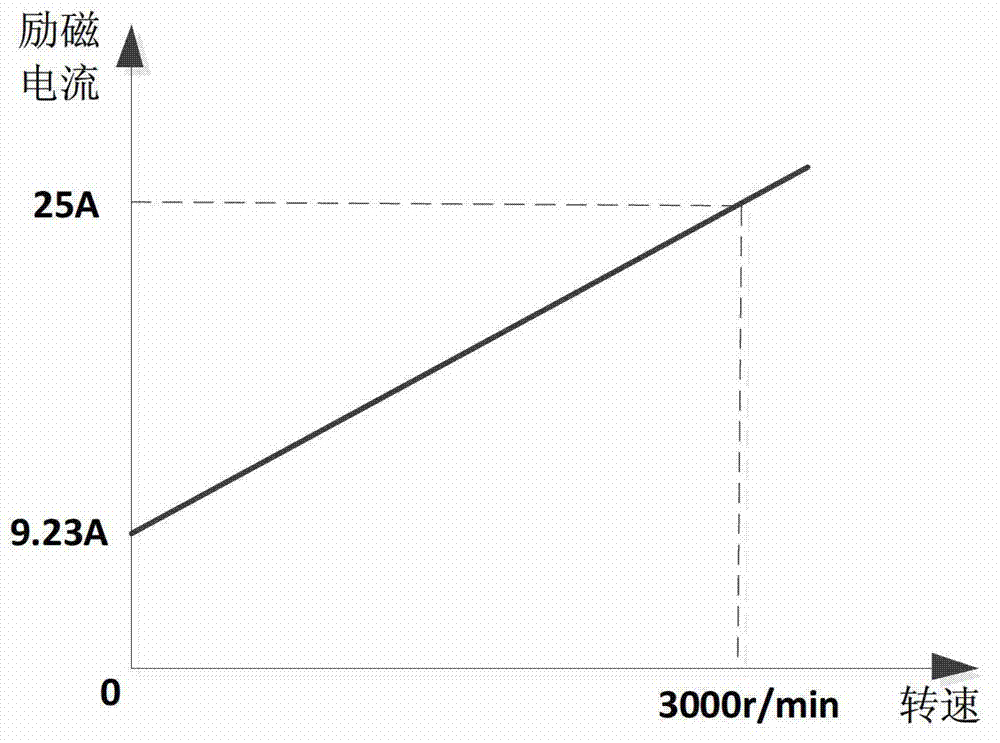
InactiveCN101977000AControl speedGood control effectSingle motor speed/torque controlWound field motor controlSynchronous motorTransformer
The invention discloses a method for measuring position and speed of a rotor of an electrically excited synchronous motor and a control device, and belongs to the measurement method and a control device for the synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps of: injecting a high-frequency voltage signal at the U phase of a stator of the electrically excited synchronous motor; generating a high-frequency pulsating magnetic field by the high-frequency voltage signal, wherein a high-frequency potential signal induced in a rotor winding by the high-frequency pulsating magnetic field also changes along with position change of the motor rotor; acquiring the signal by a voltage transformer and determining the position of the rotor and the rotation speed of a synchronizer; feeding the measured rotor position signal and rotation speed signal back to a controller; and accurately controlling the speed of the electrically excited synchronous motor by the controller according to a given signal. The method and the device have the advantages that: the device is not provided with a mechanical speed sensor; by using the electromagnetic structure of the synchronous motor, the rotation speed of the motor is directly measured by injecting the high-frequency signal at one phase of the stator; and the composition of the system is simplified, and the reliability of the system and the accuracy for the speed control are improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH +1
Method and device for determining phase currents and an excitation current of an electrical machine, and motor system
InactiveUS20160197569A1Robust and cost-effective electricalMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlPhase currentsElectric machine
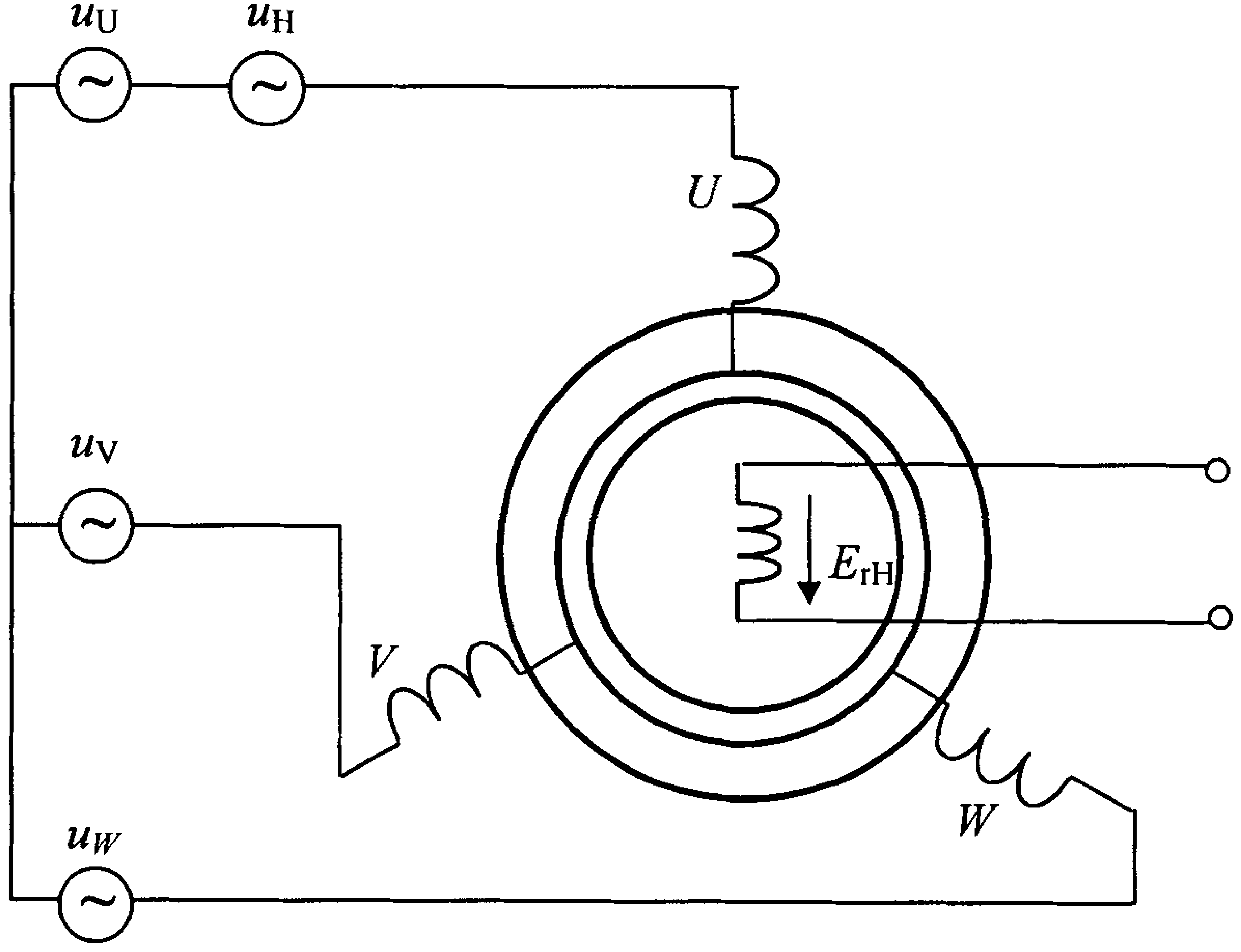
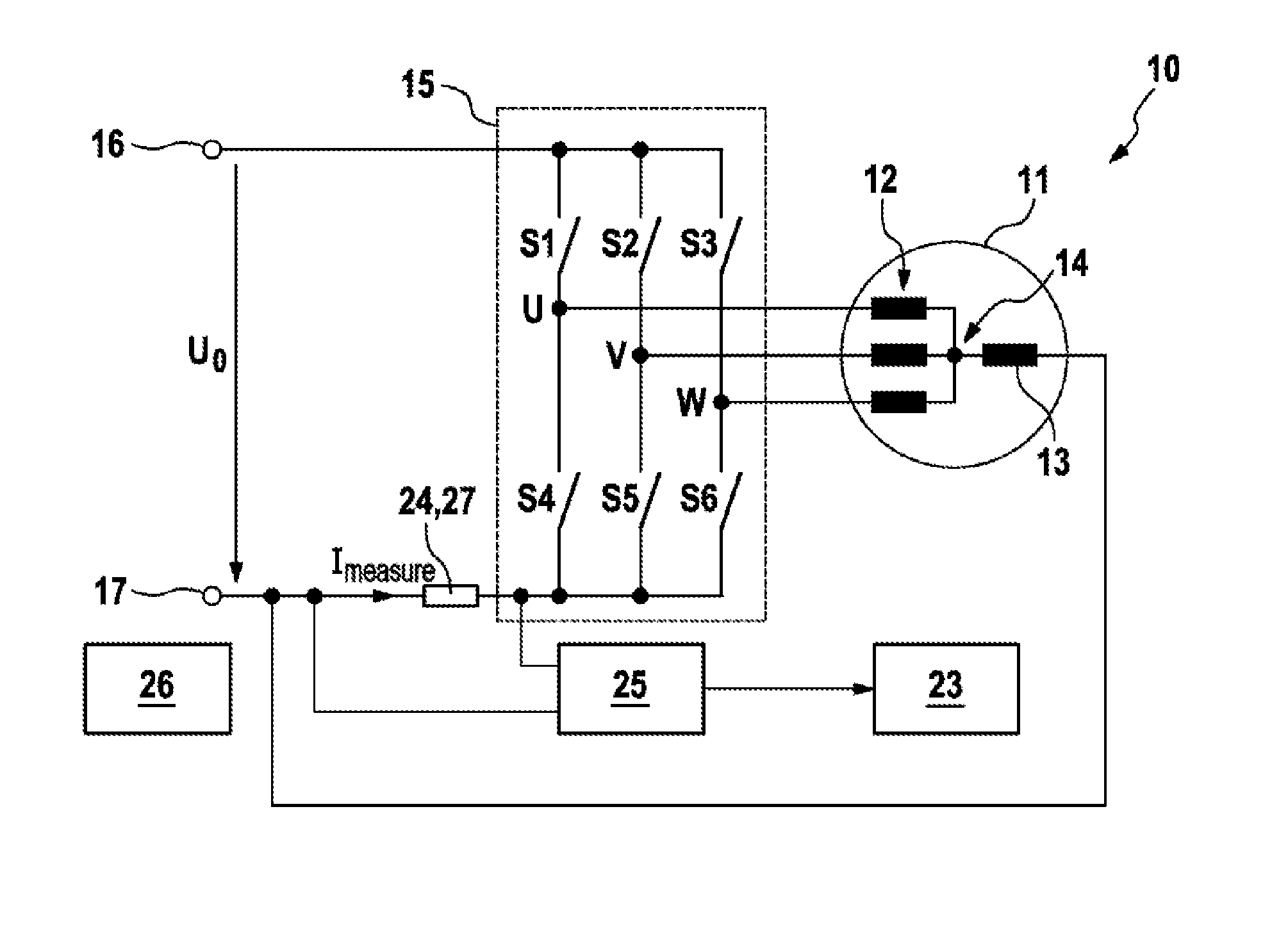
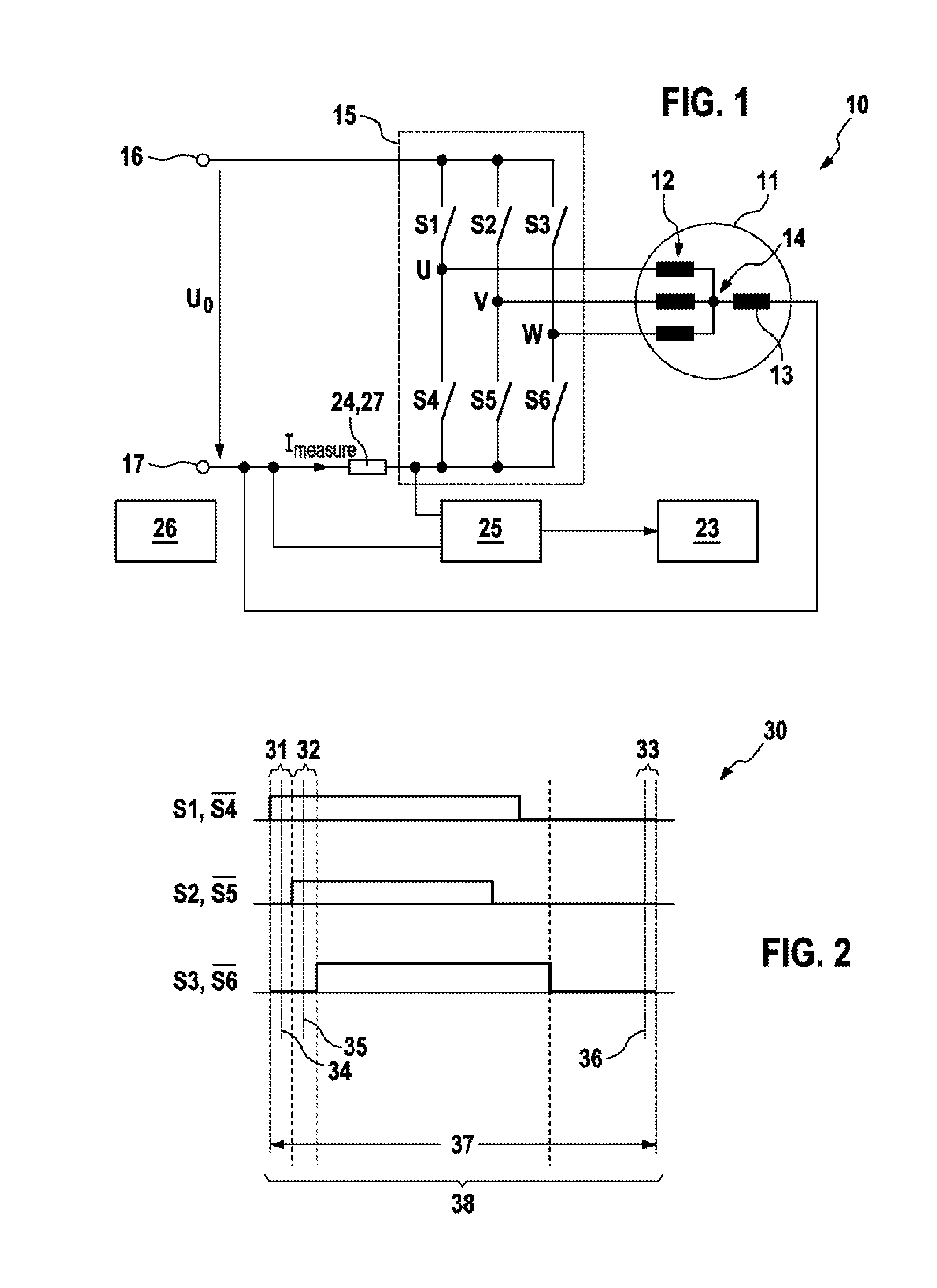
The invention relates to a method for determining the phase currents through phase windings (12) and an excitation current through an excitation winding (13) of an electrical machine (11), wherein an excitation winding (13) is connected between a star point (14) of the phase windings (12) and a defined reference potential, the method comprising the following steps: —periodic driving of the electrical machine (11) with a predefined pulse pattern (30); —determining a respective measurement current (Imess) in a plurality of temporal measuring windows (31, 32, 33) of a measuring period (37), wherein the measurement currents (Imess) correspond to currents through one of the phase windings (12) and through one or more parallel connections of a plurality of the phase windings (12); and —determining the phase currents and the excitation current by evaluating the measurement currents (Imess) determined during the measuring period (37).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Motor driving system and vehicle
ActiveCN111510030AReduce weightReduce volumeAc-dc conversion without reversalCharging stationsMultiplexingElectric machine
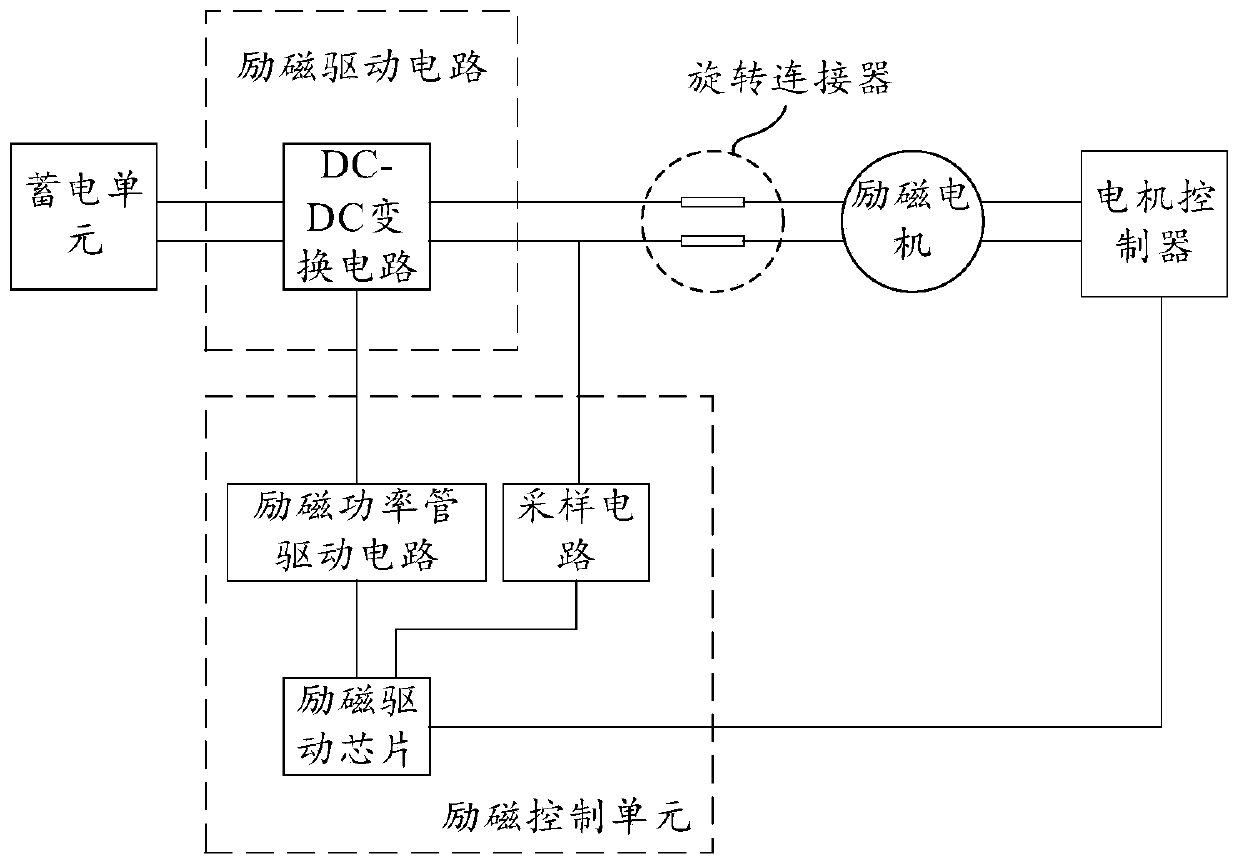
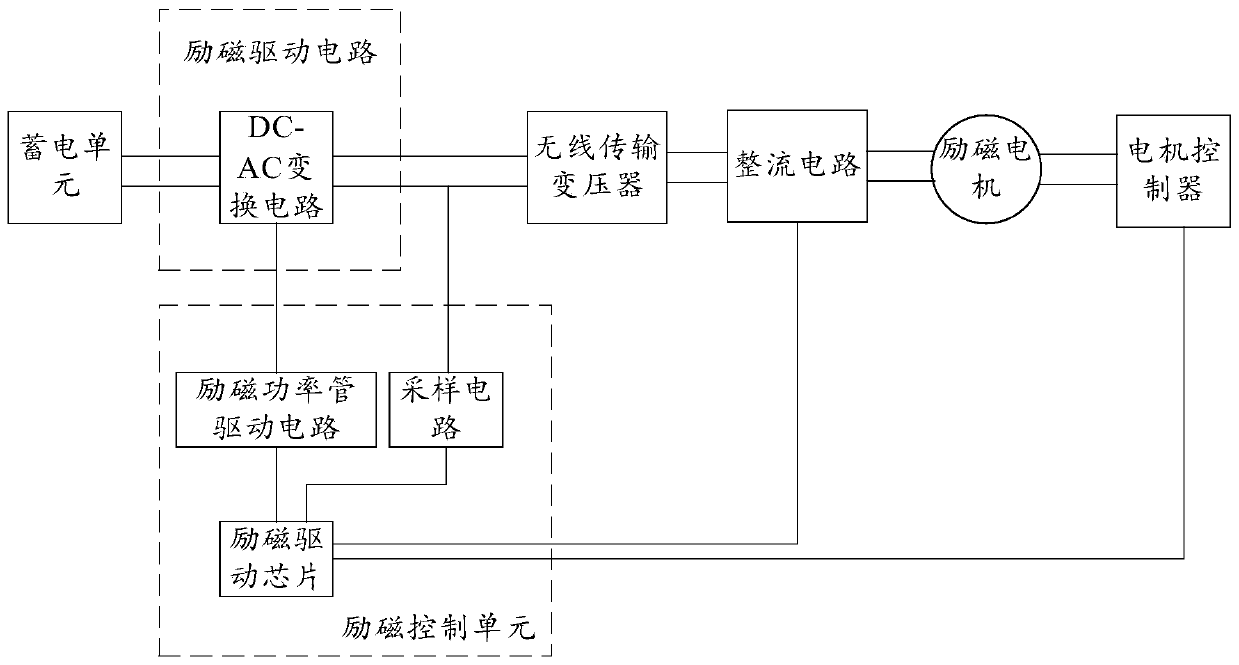
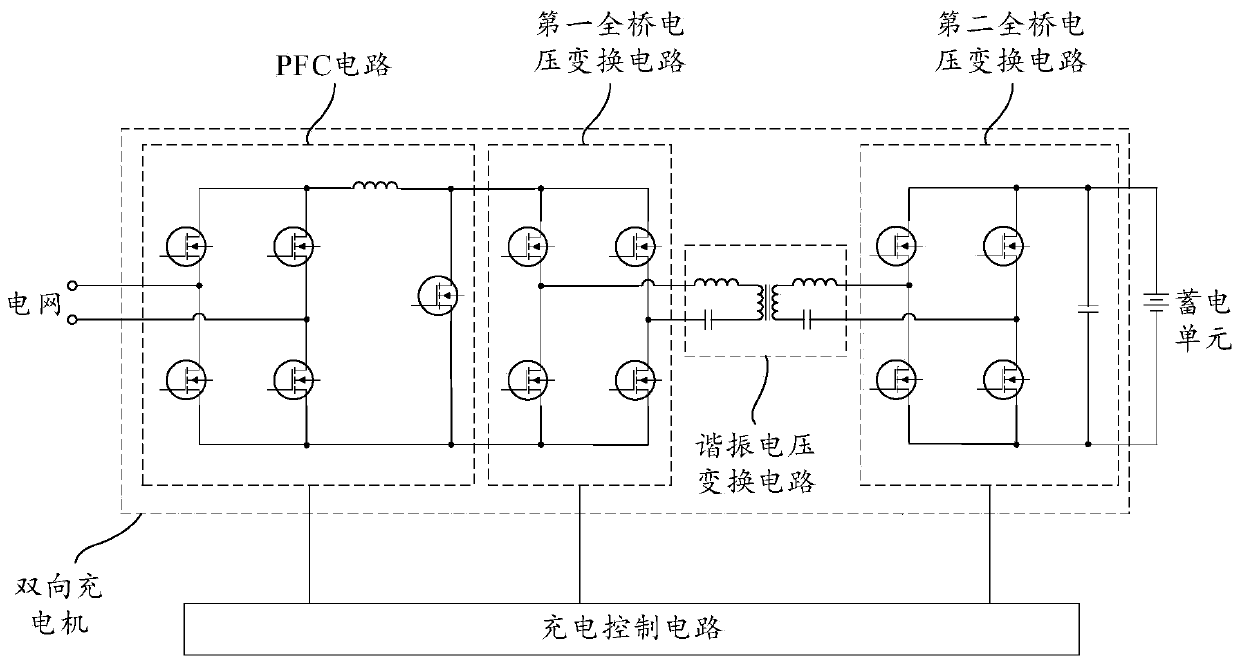
The invention provides a motor driving system and a vehicle, relates to the technical field of vehicle control, and can simplify the structure of the motor driving system and reduce the cost. The motor driving system comprises a bidirectional charger, an excitation driving assembly and a motor controller, wherein the bidirectional charger comprises a power factor correction circuit, a first voltage conversion circuit, a first transformer and a second voltage conversion circuit; a power storage unit is electrically connected to a second port of the second voltage conversion circuit; the excitation driving assembly is electrically connected to a multiplexing node through a first switch unit, the multiplexing node is located between the power factor correction circuit and the first voltage conversion circuit, and the excitation driving assembly is used for driving the excitation motor.
Owner:HUAWEI DIGITAL POWER TECH CO LTD
Synchronous motor and electric driving system
InactiveCN1835349AReduce vibrationAC motor controlSingle motor speed/torque controlSynchronous motorExcitation current
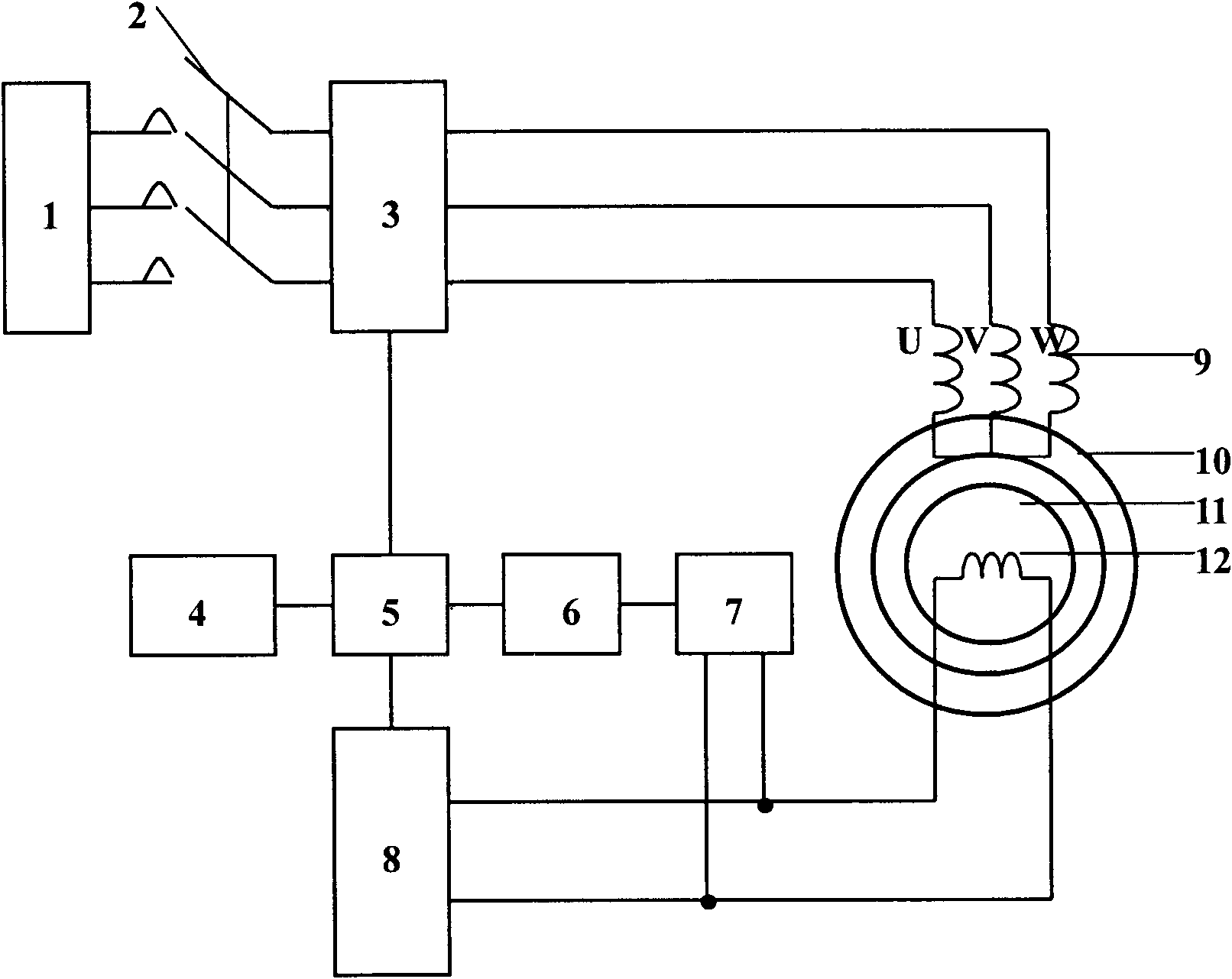
The invention relates to a synchronous motor with low vibrations and an electric driving system using the motor. A field-coil synchronous motor (100) comprises a stator (103) and a rotor (110) rotatably supported at the inner peripheral side of the stator (103) with a gap left relative to the stator (103). The stator (103) has a stator coil (106) supplied with electric power while being controlled such that driving torque is reduced as a rotation speed of the rotor (110) increases, and the rotor (110) has a field coil (113a, 113b) supplied with a field current while being controlled such that the field current is reduced as the rotation speed of the rotor (110) increases. The rotor (110) is a tandem claw-pole rotor comprising plural pairs of N- and S-claw poles (111a, 112a; 111b, 112b) disposed side by side in an axial direction, and the plural pairs of claw poles (111a, 112a; 111b, 112b) of said tandem claw-pole rotor are relatively shifted from each other in a circumferential direction.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Control method of electrically excited doubly salient pole motor based on torque closed-loop suppression of torque ripple
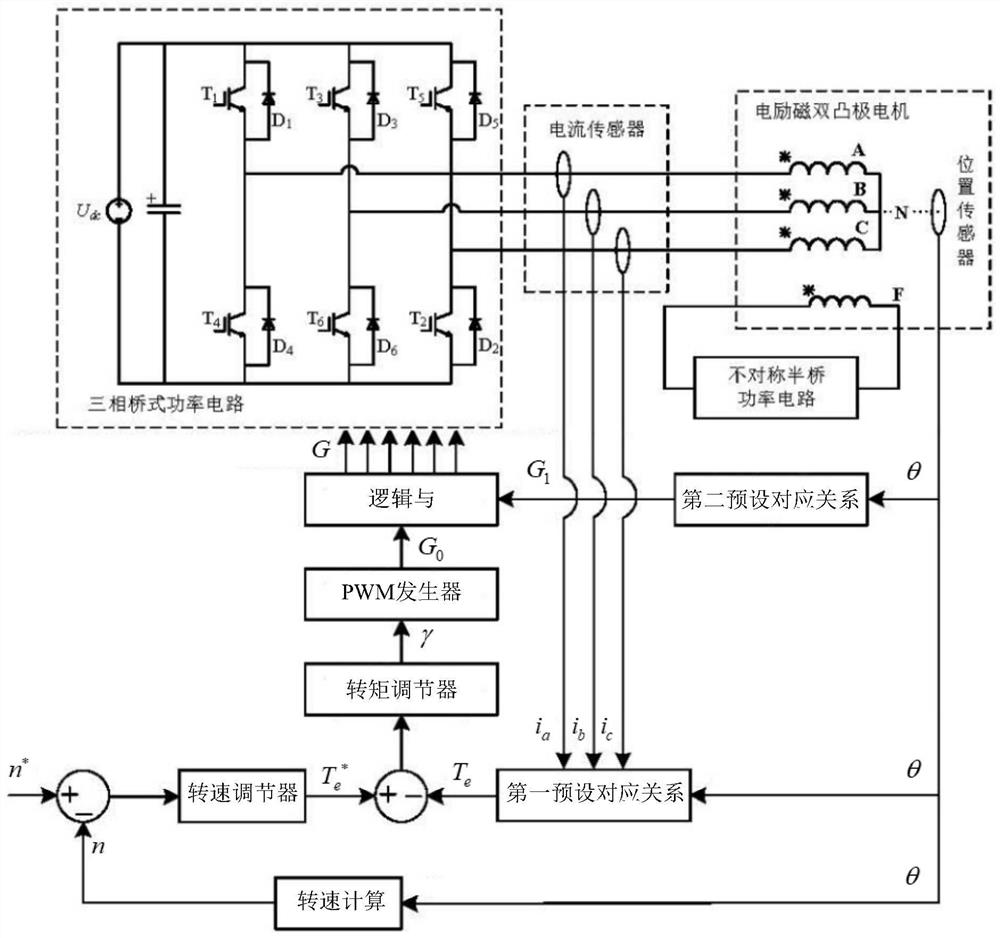
ActiveCN113411014BNo effect on output torqueOutput torque will not decreaseTorque ripple controlAC motor controlControl signalElectric machine
The invention discloses a control method for an electrically excited double salient pole motor based on a torque closed-loop suppression of torque ripple, and relates to the field of an electrically excited double salient pole motor. Fixed value, the motor torque feedback value is determined by the motor rotor position and the phase current values of the three phase windings, and the first control signal with a predetermined duty cycle is generated according to the motor torque given value and the motor torque feedback value, according to the first The two preset correspondences determine the second control signal corresponding to the rotor position of the motor, and the drive signal is generated by the first control signal and the second control signal to drive all the power tubes in the three-phase bridge power circuit. This method adopts a torque closed-loop instead The current closed loop directly controls the output torque of the motor, which can effectively suppress the torque ripple in the commutation and non-commutation stages, and the control structure is relatively simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com