Automatic screening method, system and device for gene editing sites and storage medium
An automatic screening and gene editing technology, applied in the field of gene editing, can solve problems such as no change in gRNA protein expression, incomplete information sources, and unsatisfactory effects, and achieve automation, high cutting efficiency, and strong specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0094] Implementation Mode 1: Frameshift Knockout Scheme
[0095] (1) Determine the knockout region
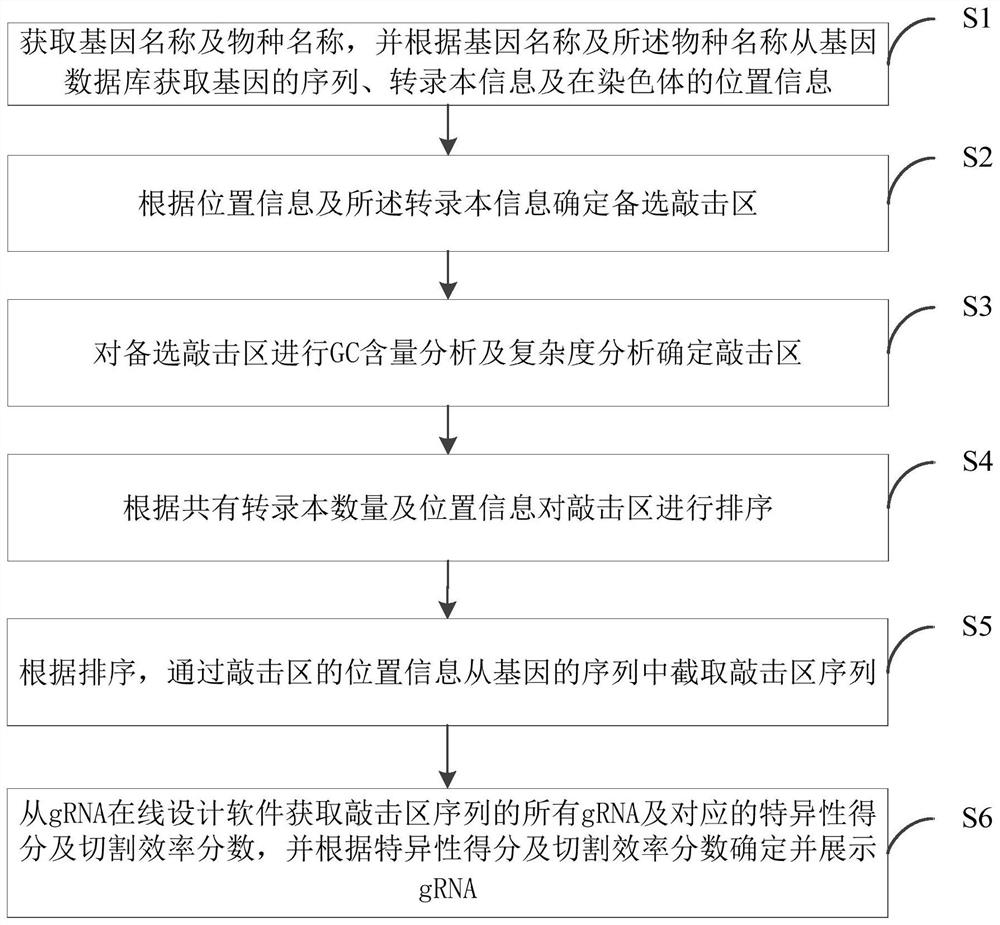
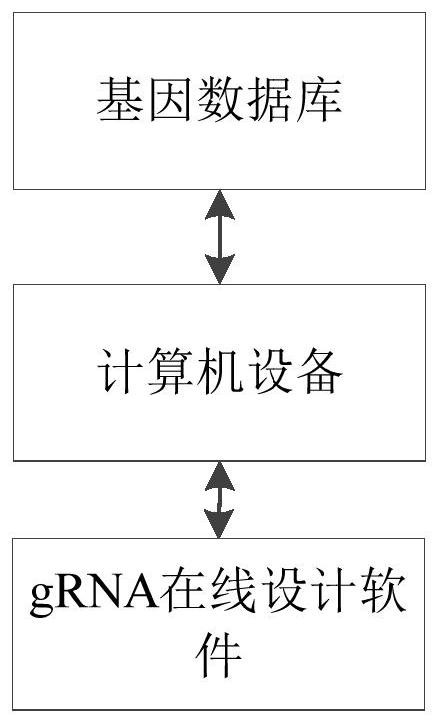
[0096] S111. Determine whether the target gene is suitable for designing a knockout scheme. The specific method is as follows: obtain the position of the target gene on the chromosome from Ensembl, and search whether there are other genes in the segment where the target gene is located on the chromosome according to this position; if there are other genes, continue to obtain these genes that overlap with the target gene Types of other genes, if the other genes are protein-coding genes, then the target gene is not suitable for designing a knockout scheme.
[0097] S112. Preprocessing the transcript of the target gene. The specific method is: obtain the transcript information of the target gene from Ensembl, and exclude non-coding protein transcripts and incomplete transcripts.
[0098] S113. Find out the protein coding region of each transcript, that is, CDS. The specific m...
Embodiment approach 2
[0108] Embodiment 2: Small fragment knockout scheme
[0109] (1) Determine the knockout region
[0110] S121. Determine whether the target gene is suitable for designing a knockout scheme. The specific method is as follows: obtain the position of the target gene on the chromosome from Ensembl, and search whether there are other genes in the segment where the target gene is located on the chromosome according to this position; if there are other genes, continue to obtain these genes that overlap with the target gene Types of other genes, if the other genes are protein-coding genes, then the target gene is not suitable for designing a knockout scheme.
[0111] S122. Preprocessing the transcript of the target gene. The specific method is: obtain the transcript information of the target gene from Ensembl, and exclude non-coding protein transcripts and incomplete transcripts.
[0112] S123. Find out the protein coding region of each transcript, that is, CDS. The specific method...
Embodiment approach 3
[0129] Implementation Mode 3: Large Fragment Knockout Solution
[0130] (1) Determine the knockout region
[0131] S131. Determine whether the target gene is suitable for designing a knockout scheme. The specific method is as follows: obtain the position of the target gene on the chromosome from Ensembl, and search whether there are other genes in the segment where the target gene is located on the chromosome according to this position; if there are other genes, continue to obtain these genes that overlap with the target gene Types of other genes, if the other genes are protein-coding genes, then the target gene is not suitable for designing a knockout scheme.
[0132]S132. Preprocessing the transcript of the target gene. The specific method is: obtain the transcript information of the target gene from Ensembl, and exclude non-coding protein transcripts and incomplete transcripts.
[0133] S133. Find out the protein coding region of each transcript, that is, CDS. The speci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com