Application of rapamycin or tumor necrosis factor alpha in preventing and/or treating diseases associated with mesenchymal stem cell injury
A mesenchymal stem cell, rapamycin technology, applied in the prevention and/or treatment of diseases related to mesenchymal stem cell damage, rapamycin or tumor necrosis factor α, can solve problems such as ignorance and affecting BMMSC function , achieve the effect of improving function, reducing bone loss and reducing bone density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] The general experimental method that embodiment 1 present invention relates to
[0090] 1. Experimental materials
[0091] (1) ANIMAL. Female C57BL / 6J and B6.129S-Tnftm1Gk1 / J (TNFα- / -), B6.129S7-Ifngtm1Ts / J (IFNγ- / -), B6.129S2-Il6tm1Kopf / J (IL-6- / -), B6 .129S-TNFαsf1atm1ImxTNFαsf1btm1Imx / J(TNFα- / -), B6.Cg-Tg(Prrx1-cre)1Cjt / J(Prx1-Cre) and B6.Cg-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm9(CAG-tdTomato)Hze / J Mice were purchased from Jackson Lab and maintained at least 10 backcrosses in the C57BL / 6J background. Age-matched female littermates were used in all experiments. Female immunocompromised nude mice (Beige nu / nuXIDIII) were purchased from Harlan.
[0092] (2) Animal model, that is, hindlimb unloading. Mice were randomly divided into three groups: control group, unloading group and rapamycin-treated group. Mice in the unloaded group were subjected to continuous hindlimb suspension for 2 weeks. Hindlimb unloading was performed as previously described (Egawa et al., 2015). Briefly, the ta...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2. TNFα is required to maintain BMMSC homeostasis through a TNF receptor-independent pathway.
[0111] 1. Experimental materials
[0112] (1) ANIMAL. Please refer to the experimental materials in Part 1 of Example 1.
[0113] 2. Experimental method
[0114] Please refer to the experimental method (1)-(15) of the second part of Example 1.
[0115] 3. Experimental results
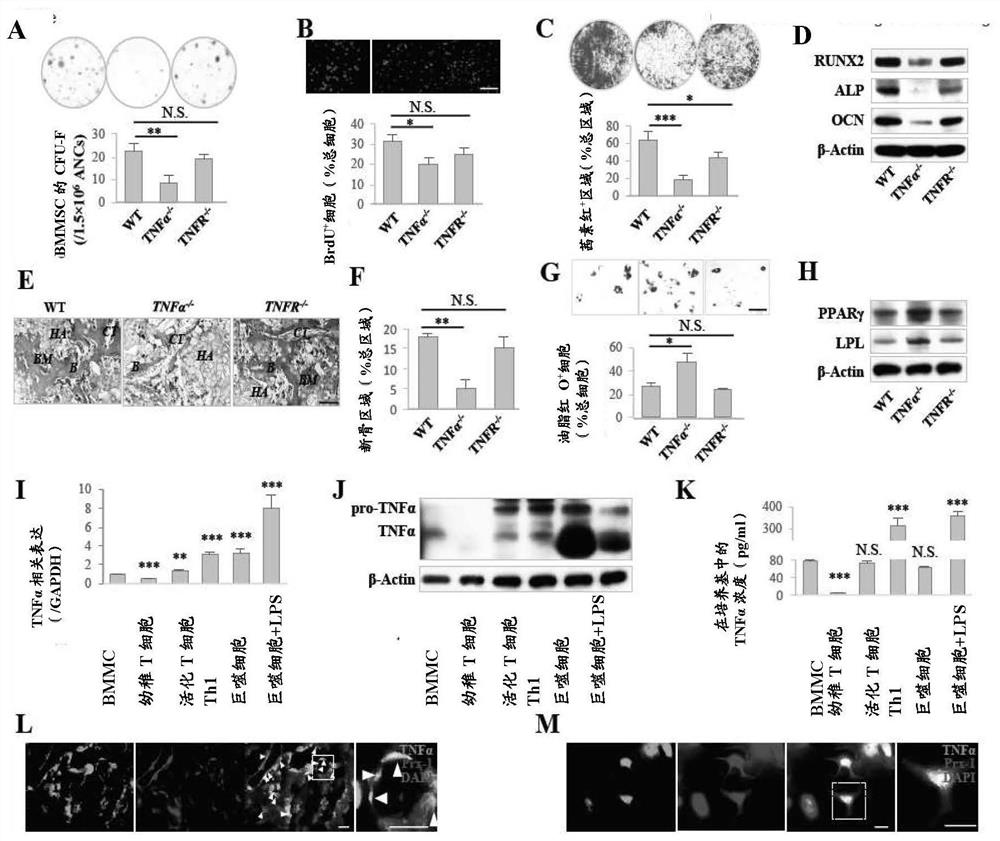
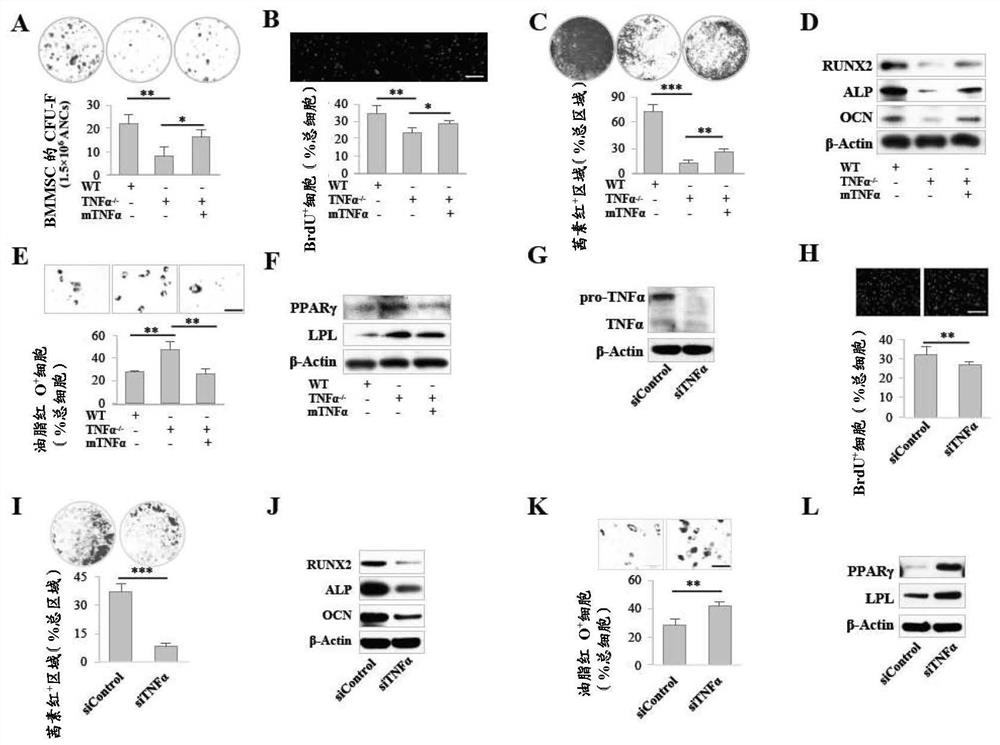
[0116] To examine whether MSC-produced cytokines could modulate stem cell properties in BMMSCs, TNFα knockout (TNFα- / -), interferon-γ knockout (IFNγ- / -) and interleukin-6 knockout (IL- 6- / -) mice were used as a cytokine-deficient model to examine BMMSC function. found that TNFα- / -, but not IFNγ- / - and IL-6- / -, BMMSCs showed significantly reduced colony-forming unit fibroblast numbers (CFU-F; figure 1 A and Figure 8 A) and significantly reduced proliferation rate as assessed by toluidine blue staining and BrdU labeling assays, respectively ( figure 1 B and Figure 8 B). When cultured ...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3. Endocytic TNFα inhibits mTOR activation by binding to mTOR complex 2.
[0123] 1. Experimental materials
[0124] (1) ANIMAL. Please refer to the experimental materials in Part 1 of Example 1.
[0125] 2. Experimental method
[0126] Please refer to the experimental method (1)-(15) of the second part of Example 1.
[0127] 3. Experimental results
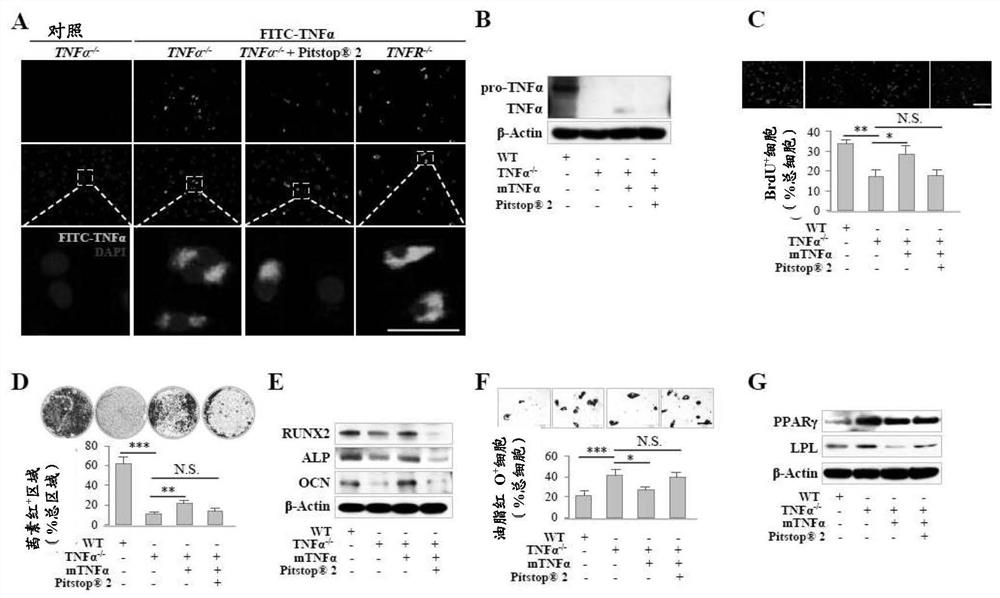
[0128] Since TNFα protein was detected in TNFα- / - BMMSC lysates after mTNFα treatment, as analyzed by Western blot ( Figure 9 B and 3B) Assessed, it is hypothesized that mTNF[alpha] can be internalized by endocytosis. To test this hypothesis, TNFα- / - BMMSCs were treated with FITC-tagged mTNFα (FITC-TNFα), followed by immunofluorescence (IF) microscopy to detect FITC-TNFα in the cytoplasm; it mainly surrounds the nuclear region ( image 3 A). Furthermore, FITC-tagged TNFα was detected in TNFα- / - BMMSCs, suggesting that TNFα endocytosis is independent of TNF receptors ( image 3 A). Next, apply the CMst inh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com