Light emitting diode and preparation method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and second subs, applied in electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor heat dissipation, chip burn, uneven chip heat dissipation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
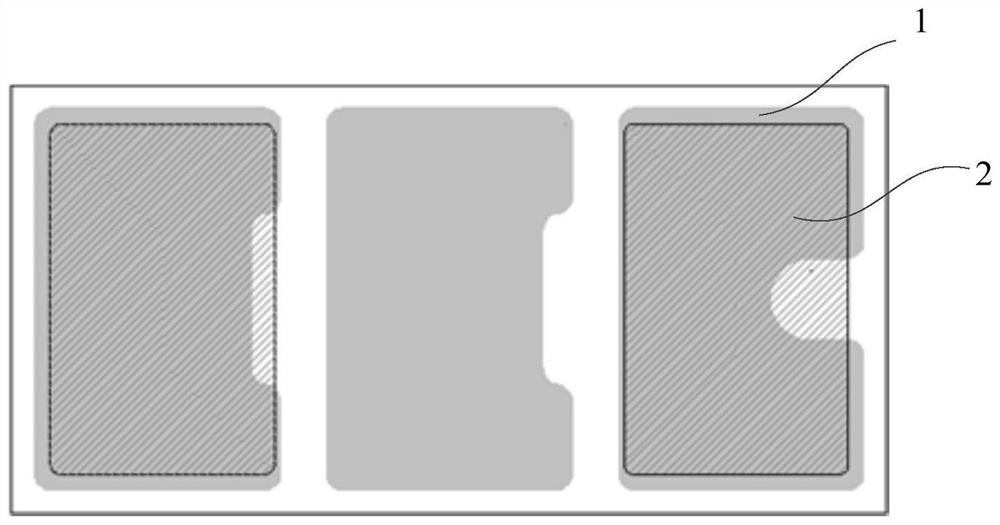
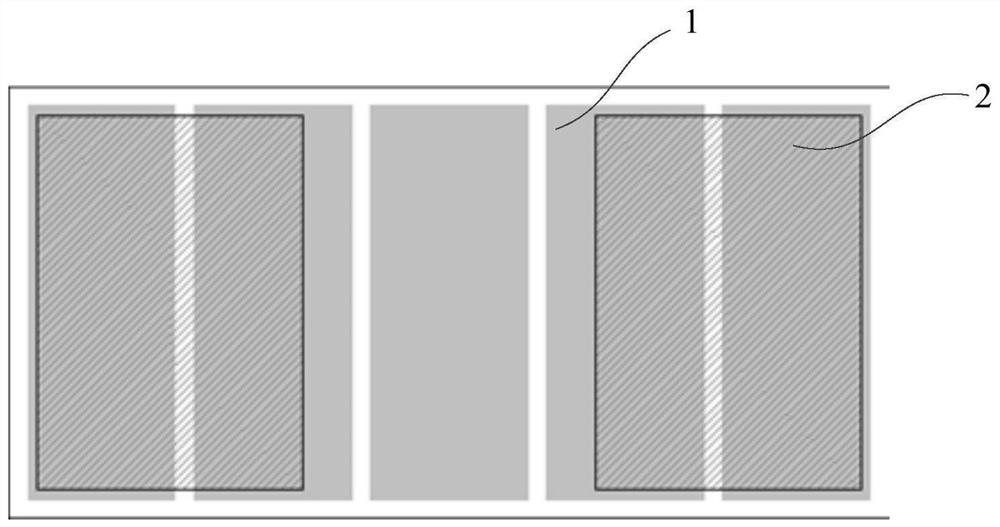
[0064] The light emitting diode provided in this embodiment includes several sub-chips, a first pad, a second pad and other pads, wherein several sub-chips are electrically connected, and adjacent sub-chips are separated by grooves, and at least one sub-chip includes The first semiconductor layer, the active layer and the second semiconductor layer, and the plurality of sub-chips include the first sub-chip, the second sub-chip and at least one other sub-chip except the first sub-chip and the second sub-chip; the first The pad is electrically connected to the second semiconductor layer of the first sub-chip, the second pad is electrically connected to the first semiconductor layer of the second sub-chip, at least one other sub-chip has one other pad, and the other pad is connected to the second semiconductor layer of the second sub-chip. At most one of the first pad or the second pad is electrically connected. Therefore, in the light emitting diode of the present invention, oth...
Embodiment 2
[0079] This embodiment provides a light-emitting diode, which is the same as Embodiment 1 and will not be repeated here. The difference lies in:
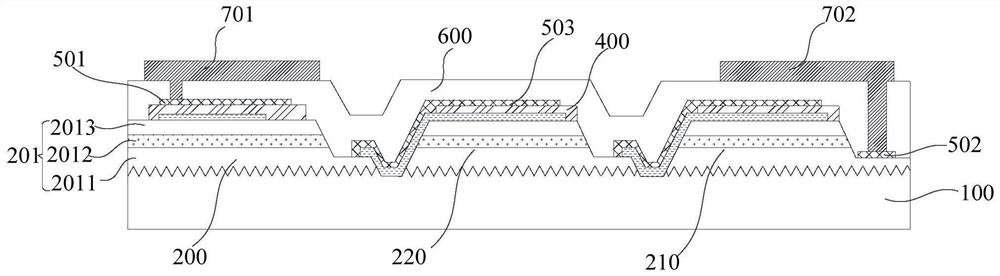
[0080] refer to Figure 7 , the other pads 703 are electrically connected to each other sub-chip through the heat conduction portion 800 disposed in the through hole 603 of the other pad on the reflective layer 600 . Specifically, one end of the heat conduction part 800 is connected to other pads 703 through other heat dissipation vias 603 , and the other end is connected to the epitaxial layer of another sub-chip 220 ; at this time, the other pads 703 and the heat conduction part 800 are both conductive materials. Optionally, a heat dissipation layer 900 is also provided between the heat conduction portion 800 and the epitaxial layers of other chiplets 220 , and the material of the heat dissipation layer 900 is also heat conduction metal. Optionally, the cross-sectional area of the heat dissipation layer 900 is greater than the ...
Embodiment 3
[0083] This embodiment also provides a method for preparing a light-emitting diode, referring to Figure 8 , 4a -4b and 5a-5h; including:
[0084] S101: Obtain several sub-chips that are electrically connected to each other, and adjacent sub-chips are separated by trenches; wherein at least one sub-chip includes at least a first semiconductor layer, an active layer, and a conductive layer opposite to the first semiconductor layer. The epitaxial layer formed by the second semiconductor layer, the several sub-chips include the first sub-chip 200, the second sub-chip 210 and at least one other sub-chip 220 except the first sub-chip 200 and the second sub-chip 210;
[0085] Specifically, a substrate 100 is provided, and the substrate 100 can be one of a sapphire substrate, a silicon carbide substrate, a gallium nitride substrate, a gallium arsenide substrate, a silicon substrate, etc. Forming the epitaxial layer comprising the first semiconductor layer, the active layer and the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com