Stator permanent magnet switch reluctance generator
A reluctance generator and permanent magnet switch technology, applied in the direction of synchronous machines, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of large resistance and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of small running resistance, high mechanical strength, and simple and compact structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
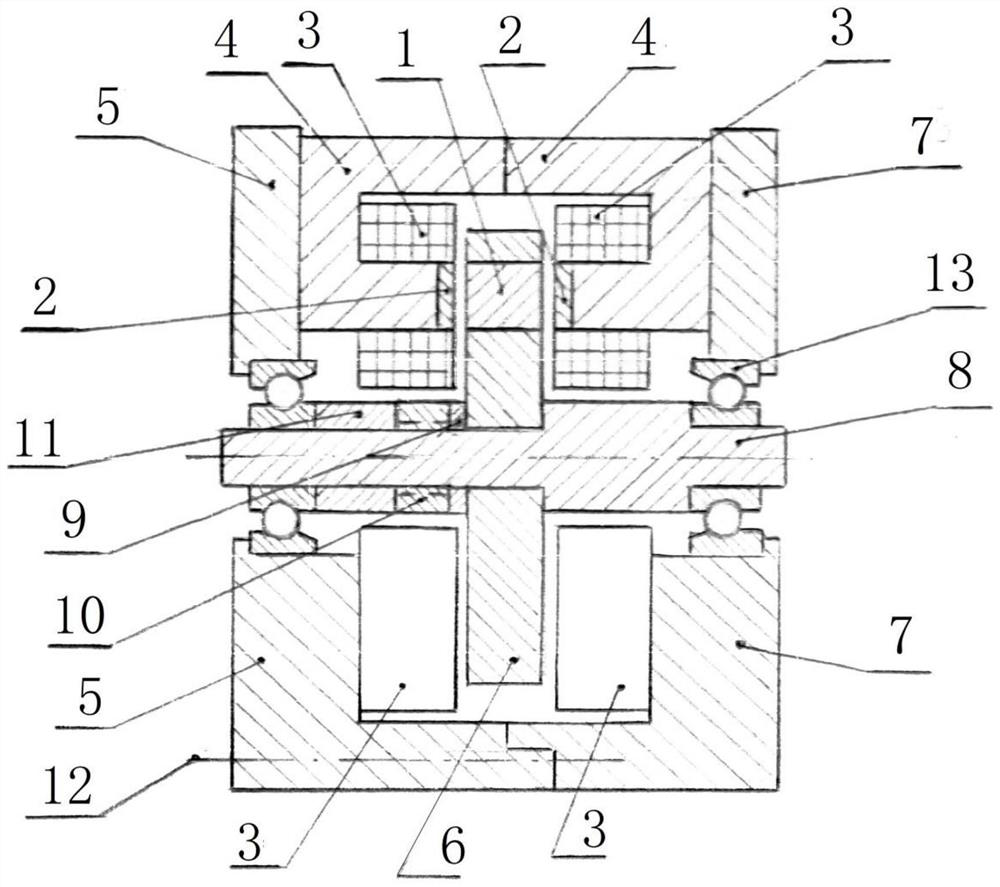
[0043] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, a plurality of stator cores 4 are respectively fixed in the axial grooves of the left end cover 5 and the right end cover 7, which can be bonded with high-strength adhesives or welded by laser welding. The permanent magnet sheet 2 fixed by adhesive bonding or laser welding, the concentrated winding 3 is respectively fixed on the two opposite stator cores 4, the groove of the rotor disk 6 is inlaid with the magnetic block 1, and the rotor disk 6 is made of high-strength It is made of non-magnetic steel. In this application, it is made of 316L material. The magnetic block 1 is pasted with high-strength adhesive or fixed by laser welding. The number of permanent magnet pieces 2 on each pair of stator cores 4 is the number of stator pole pairs. The number of magnetic blocks 1 on the rotor disk 6 is the number of magnetic poles of the rotor. In this embodiment, the ratio of the number of stator pole pairs to the number of rotor poles is 2:...
Embodiment 2
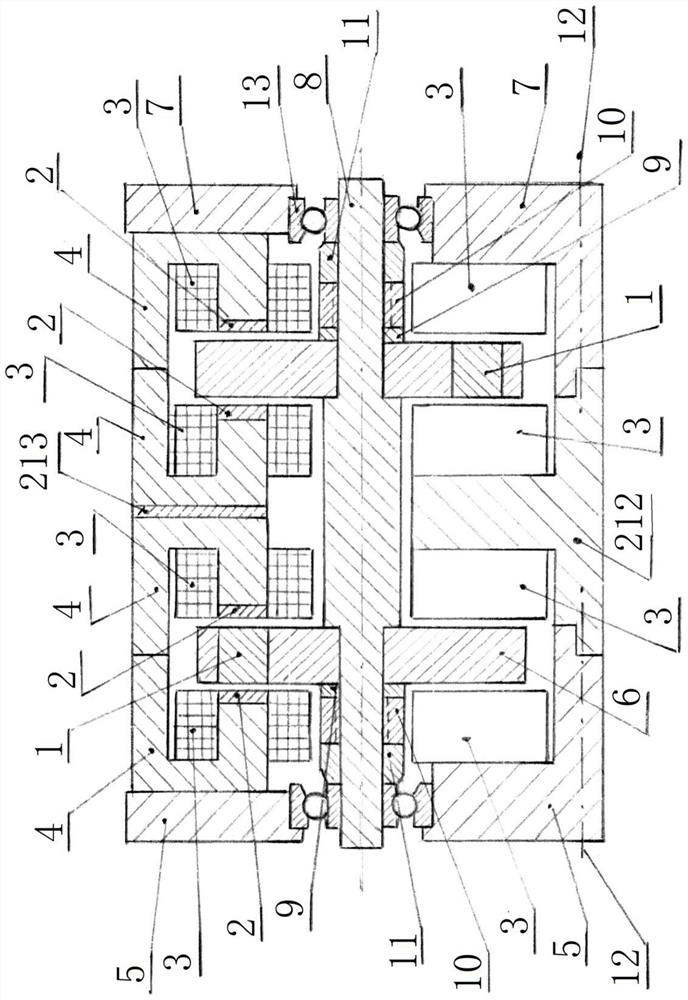
[0046] Embodiment 2: as figure 2 As shown, it is a double-disk axial magnetic field stator permanent magnet switched reluctance generator. The number of magnetic poles on the rotor disk 6 is consistent with the logarithm of the number of magnetic poles on the stator core 4, and the magnetic pole phase between the two rotor disks is used. The difference is 180 degrees to ensure that the induced voltage phase difference between the two stator cores 4 is 180 degrees, and the formed one-way feedback circuit is consistent with the embodiment 1.
[0047] Because there are two rotor disks 6 and two sections of stator cores 4, all the left end cover 5 and the right end cover 5 are connected with the middle housing 212. Since the stator cores 4 at both ends are divided into two phases, their magnetic circuits cannot be correlated, so the two Between the section stator iron core 4, there is a magnetic isolation sheet 213, and the concentrated winding 3 is also doubled, and the lock was...
Embodiment 3
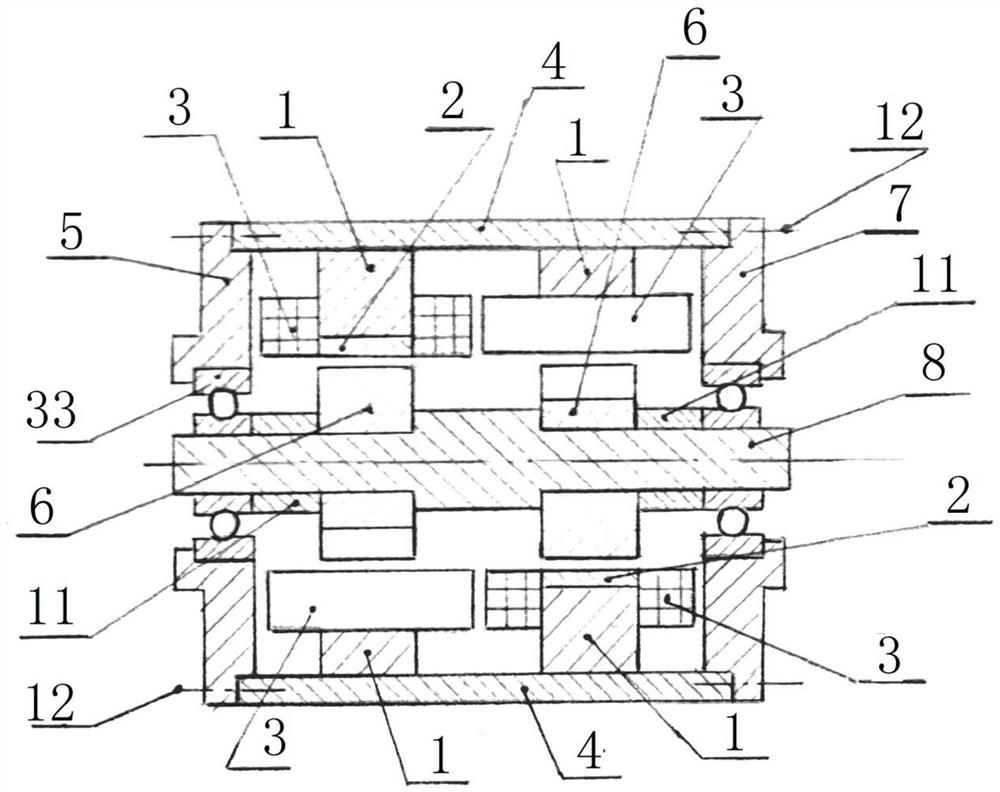
[0048] Embodiment 3: Radial magnetic field permanent magnet stator switched reluctance generator, the number of magnetic poles of the rotor disk 6 is consistent with the number of stator magnetic poles, and the magnetic pole phase difference between the two rotor disks 6 is 180 degrees to ensure that the two sections of stator iron The induced voltage phase difference between the cores 4 is 180 degrees, or the magnetic pole phase difference between the two rotor disks 6 is 0 degrees, and the magnetic pole phase difference between the two stator cores 4 is 180 degrees.
[0049] The two sections of stator core 4 are all installed in a housing 34, and bearings are arranged on the end covers 35 at both ends to support the rotating shaft. Since it is not an axial magnetic field, deep groove ball bearings can be used. The permanent magnet sheet 2 is fixed by bonding agent or laser welding, the concentrated winding 3 is installed on the stator core 4, and the rotor disk 6 is directly ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com