A kind of waste lithium iron phosphate lithium replenishment restoration method and application
A waste lithium iron phosphate and repair method technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, phosphorus compounds, recycling technology, etc., can solve the problems of slow resynthesis process, low recovery efficiency, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve low cost and easy operation The effect of simple method and easy large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
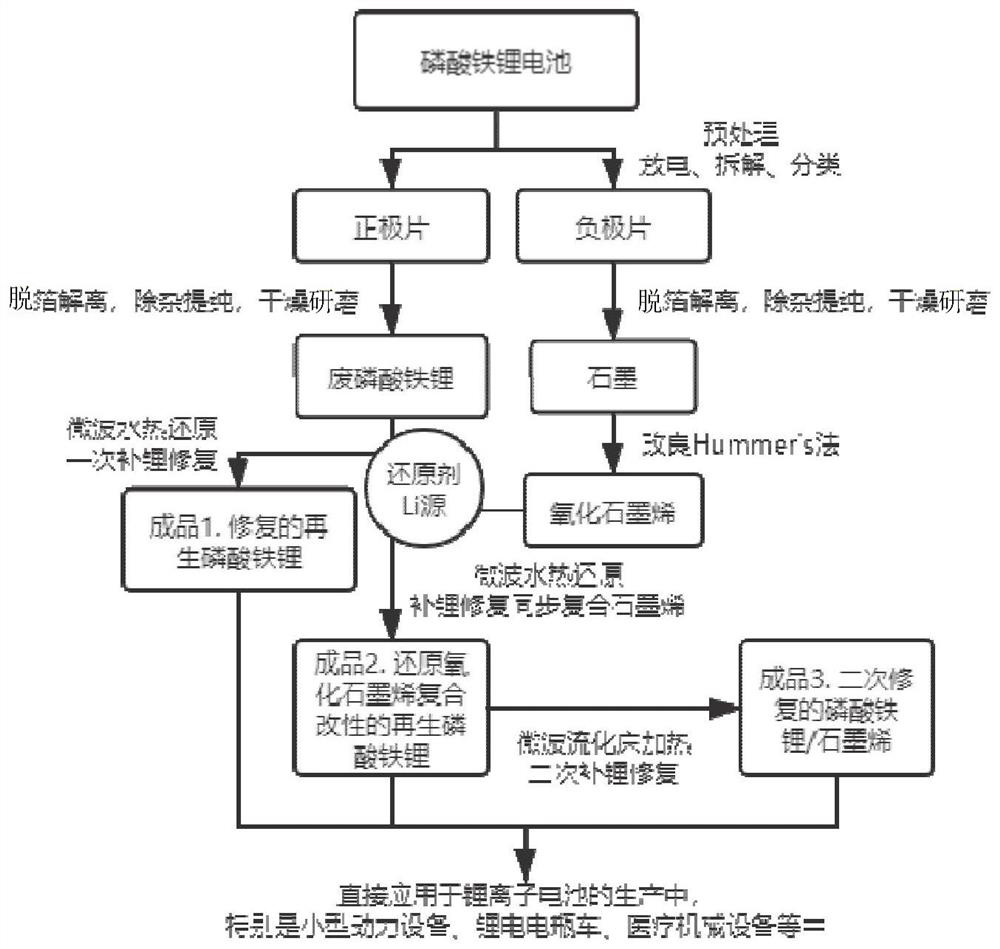
[0047] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate by supplementing lithium, comprising:
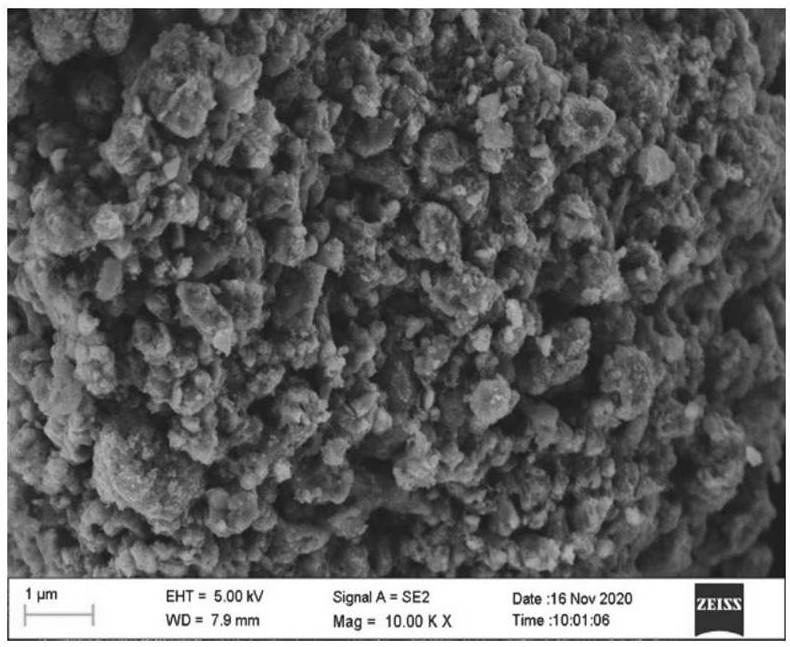
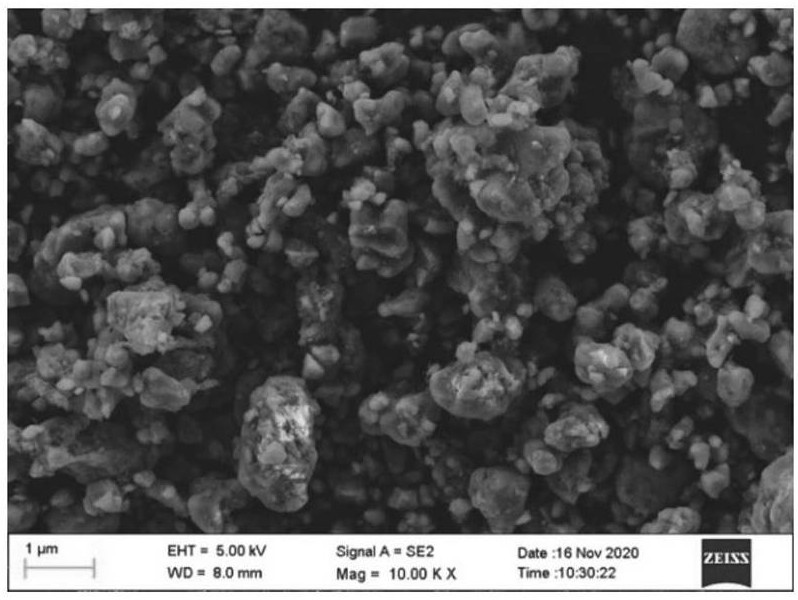
[0048] (1) Put waste LFP (such as figure 1 ) The battery was soaked in NaCl solution (10wt%) for 24h to discharge, and then manually dismantled, classified and recycled. The positive electrode sheet was calcined at 400 °C in a muffle furnace for 2 hours to separate the aluminum foil and the LFP material. The LFP material was peeled off and put into a ball mill for 6 hours to screen to obtain the LFP material with the expected particle size; the negative electrode sheet was peeled off and the copper foil was recovered. Graphene oxide material is obtained by treatment with modified Hummers method after graphite impurity removal.
[0049] (2) Pour the waste LFP powder into a beaker containing deionized water, and perform ultrasonic dispersion to form a suspension, wherein the solid-liquid ratio of the waste LFP powder and deionized water is 2:100; lithium hydroxide and citric acid ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate by supplementing lithium, comprising:
[0055] (1) The waste LFP battery was soaked in NaCl solution (10wt%) for 24h to discharge, and then manually dismantled, classified and recycled. The positive electrode sheet was calcined at 400 °C in a muffle furnace for 2 hours to separate the aluminum foil and the LFP material. The LFP material was peeled off and put into a ball mill for 6 hours to screen to obtain the LFP material with the expected particle size; the negative electrode sheet was peeled off and the copper foil was recovered. Graphene oxide material is obtained by treatment with modified Hummers method after graphite impurity removal.
[0056] (2) Pour the waste LFP powder into a beaker containing deionized water, and perform ultrasonic dispersion to form a suspension, wherein the solid-liquid ratio of the waste LFP powder and deionized water is 2:50; lithium hydroxide and glucose are added In the suspension, ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] A method for repairing waste lithium iron phosphate by supplementing lithium, comprising:
[0062] (1) The waste LFP battery was soaked in NaCl solution (10wt%) for 24h to discharge, and then manually dismantled, classified and recycled. The positive electrode sheet was calcined at 400°C in a muffle furnace for 2 hours to separate the aluminum foil and the LFP material. The LFP material was peeled off and put into a ball mill for 6 hours, and the LFP material with the expected particle size was obtained by screening; the negative electrode sheet was peeled off and the copper foil was recovered. Graphene oxide material is obtained by treatment with modified Hummers method after graphite impurity removal.
[0063] (2) Pour the waste LFP powder into a beaker containing deionized water, and perform ultrasonic dispersion to form a suspension, wherein the solid-liquid ratio of the waste LFP powder and deionized water is 2:50; lithium hydroxide and glucose are added In the su...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| power | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com