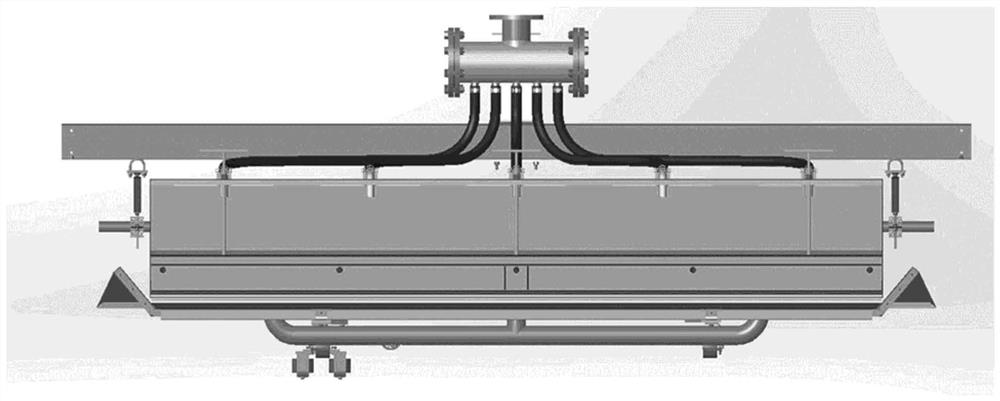
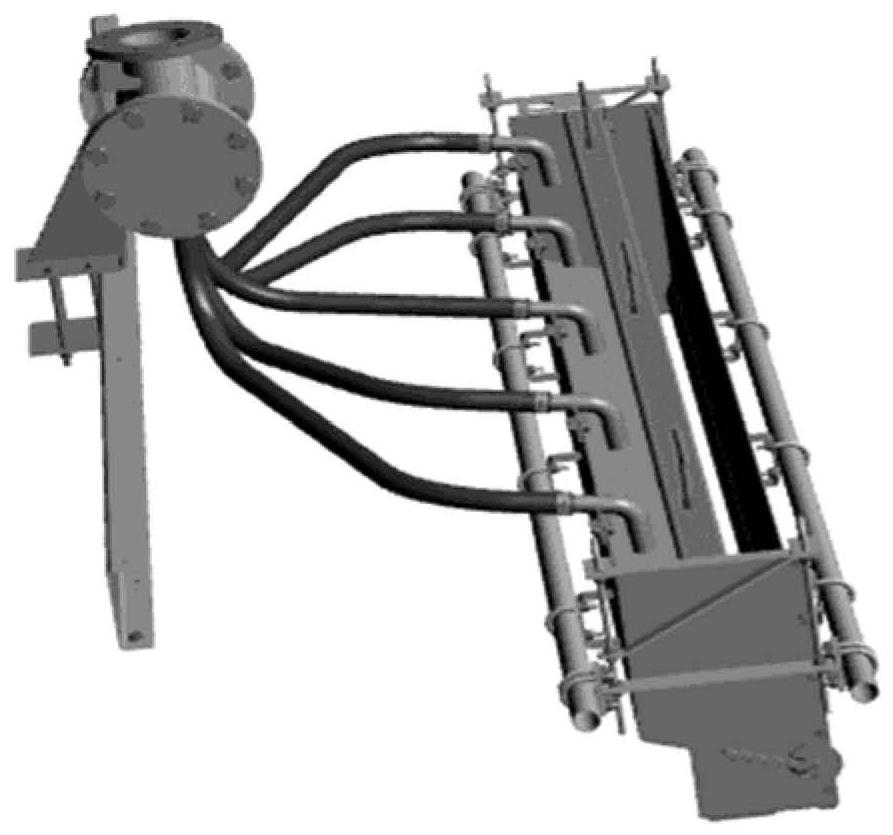
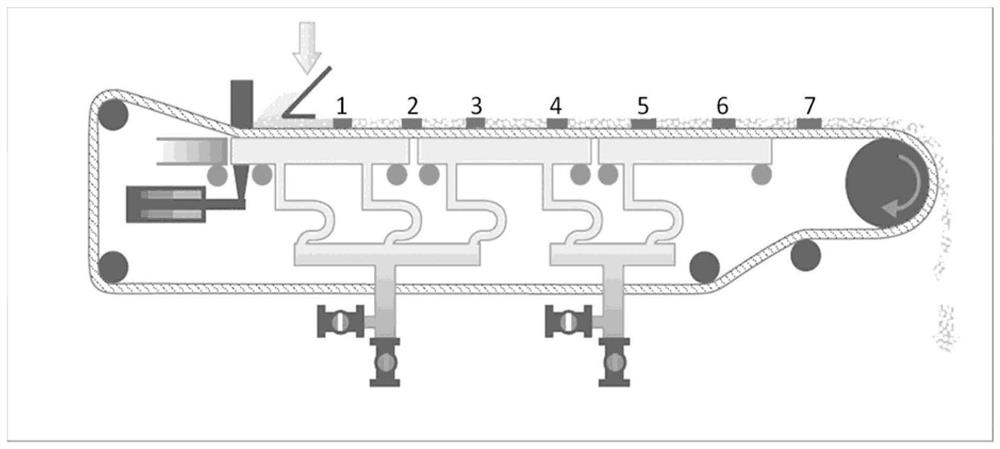
Process and system for increasing the solids content of microfibrillated cellulose
A solid content, cellulose technology, applied in the direction of drying solid materials without heating, post-treatment modification of cellulose pulp, drying solid materials, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Preparation of microfibrillated cellulose
[0127] MFC is commercially available and commercialized as "Exilva" based on cellulose pulp from Norway spruce (softwood). The starting solids content of the microfibrillated cellulose used for solvent removal was 2%.
[0128] MFC is available in two different qualities called Microfibrillated Cellulose P and Microfibrillated Cellulose F. The difference between microfibrillated cellulose P and microfibrillated cellulose F is mainly related to the size of the microfibril aggregates and thus to the 3D network properties. Microfibrillated cellulose "F" has higher Brookfield viscosity, surface area (water retention) and higher tensile strength than microfibrillated cellulose "P". Although these differences are not relevant to the working of the present invention, the removal of solvent from these two different microfibrillated cellulose materials shows that the method according to the present invention is applicable to differe...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Solvent removal (dehydration) of 2% MFC "F" in a laboratory scale system according to the invention
[0131] 2% MFC "F" was conditioned overnight in a heating cabinet.
[0132] Figure 5 It is shown how the choice of porous substrate (tape) and temperature affects the filtration capacity.
[0133] In a specific example, the following porous substrates were tested: Valmet S5111-L1, Valmet S2121-L2K2, Safar Tetex DLW 07-8435-SK010, Maro S35, Maro S25.
[0134] Vacuum set to 450mbar
[0135] Filtration time 220 seconds
[0136] Filter cake thickness: 6-7mm (about 70g)
[0137] Dry content measured after drying the filter cake in a heating cabinet at 105°C
[0138] Visual observation of the filtrate and calculation of yield from dry content measurements showed no discernible loss of fibrils through the substrate.
Embodiment 3
[0140] The Effect of pH Value on Filtration Capacity
[0141] Figure 6 Shows how choice of pH affects filterability
[0142] Solvent removal (dehydration) of 2% MFC "F" performed in a laboratory scale setup.
[0143] 2% MFC "F" was conditioned overnight in a heating cabinet.
[0144] Vacuum set to 450mbar
[0145] Porous substrates tested: Valmet S4152-l2K2 and Valmet S4152-L2K2-M7
[0146] Filter time 180 and 220 seconds
[0147] Filter cake 6-7mm (about 70g)
[0148] Dry content measured after drying the filter cake in a heating cabinet at 105°C
[0149] Visual observation of the filtrate and calculation of yield from dry content measurements showed no discernible loss of fibrils through the substrate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com