Method for identifying plants by using DNA characteristic sequence
A DNA molecule and plant technology, applied in the field of plant identification using DNA characteristic sequences, can solve the problems of long development cycle, identification success rate of less than 80%, and heavy workload.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1, the establishment of the method for identifying plants using DNA signature sequences
[0048] The inventor of the present invention has established a method for using DSS to identify plants through a large number of experiments, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0049] 1. Obtaining DSS
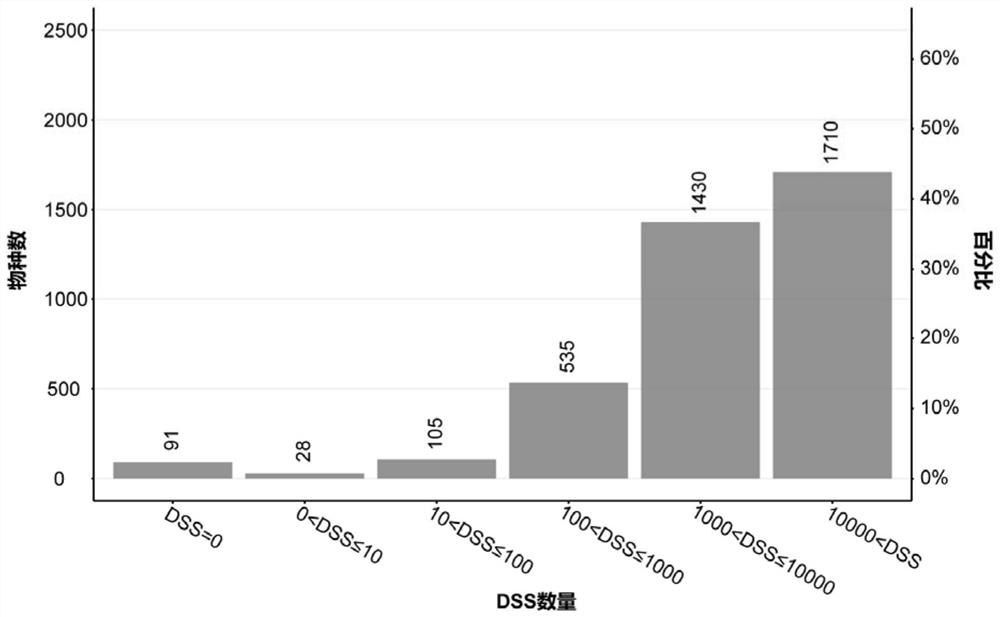
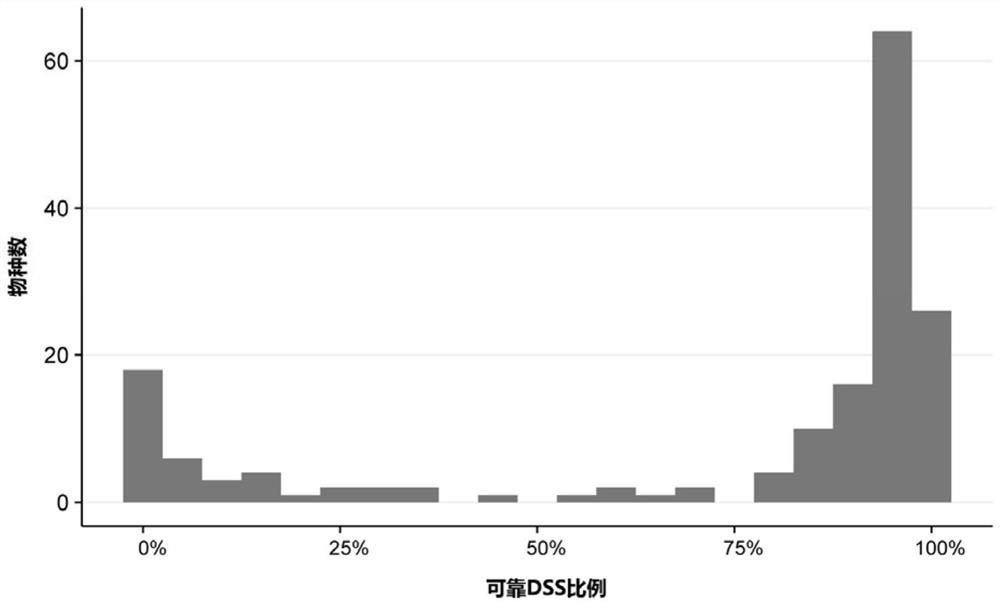
[0050] 1. Obtain 4356 chloroplast genome sequences of 3899 (plant) species from database download or analysis of large amounts of data.
[0051]3899个物种中具有代表性的500个分别为Solidago decurrens、Erycibeobtusifolia、Erycibeschmidtii、Syzygiumaromaticum、Panax ginseng、Illiciumverum、Murraya exotica、Murrayapaniculata、Senegalia catechu、Canavalia gladiata、Panax notoginseng、Saururus chinensis、Sparganiumstoloniferum、Berberis vernae、Berberis poiretii 、Berberis soulieana、Berberis wilsoniae、Zingiber officinale、Toxicodendron vernicifluum、Inula helenium、Bolbostemmapaniculatum、Pseudolarixamabilis、Smilax glabra、Callicarpa macrophylla、Sargentodoxa cuneata、Glycinemax、Gleditsia sinensis、Isatis ti...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Embodiment 2, the method for identifying Atractylodes macrocephala using DNA characteristic sequence
[0070] 1. Acquisition of Baizhu DSS
[0071] According to the method of step 1 in Example 1, Atractylodes macrocephala DSS was obtained.
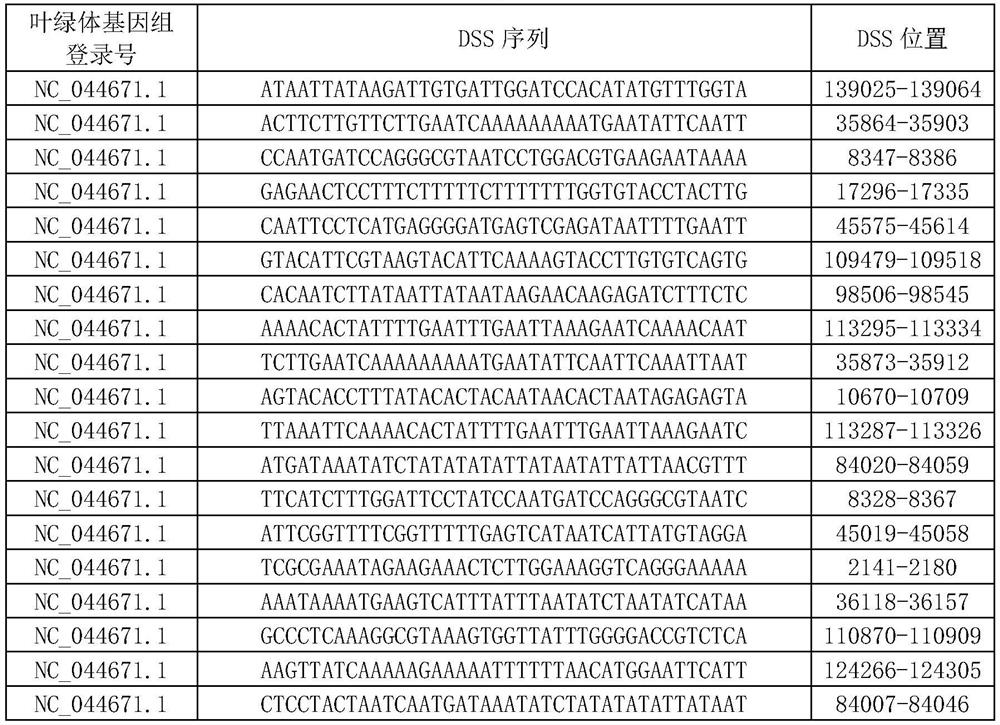
[0072] A total of 1327 DSS items of Atractylodes macrocephala were obtained, among which the first 100 items are shown in Table 1.
[0073] Table 1
[0074]
[0075]
[0076]
[0077] 2. Randomly select 5 pieces from the 1327 pieces of Atractylodes macrocephala DSS obtained in step 1, and design and synthesize primer pairs for amplifying the DSS according to the upstream and downstream 200 bp fragments of their positions in the genome.
[0078] The five selected Atractylodes macrocephala DSSs, the five primer pairs (composed of upstream primers and downstream primers) used to amplify the DSSs, and the length of the amplification products are shown in Table 2.
[0079] Table 2
[0080]
[0081]
[0082] Note: prime...
Embodiment 3
[0095] Embodiment 3, the method for identifying ginseng using DNA signature sequence
[0096] 1. Obtaining Ginseng DSS
[0097] Ginseng DSS was obtained according to the method of step one in Example 1.
[0098] A total of 5,927 ginseng DSSs were obtained, of which the top 100 are shown in Table 4.
[0099] Table 4
[0100]
[0101]
[0102]
[0103] 2. Five ginseng DSSs were randomly selected from the 5927 ginseng DSSs obtained in step 1, and primer pairs for amplifying the DSSs were designed and synthesized according to the upstream and downstream 200 bp fragments of their positions in the genome.
[0104] The five selected ginseng DSSs, the five primer pairs (composed of upstream primers and downstream primers) used to amplify the DSSs, and the length of the amplified products are shown in Table 5.
[0105] table 5
[0106]
[0107] 3. Use the 5 primer pairs synthesized in step 2 to identify Atractylodes macrocephala
[0108] The samples to be tested were 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com