Ecological tissue culture container for factorial culture
A factory-like, tissue-culturing technology, applied in the field of plant tissue culture or micropropagation, can solve problems such as lack of pollution prevention, achieve the effects of saving materials and manpower, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
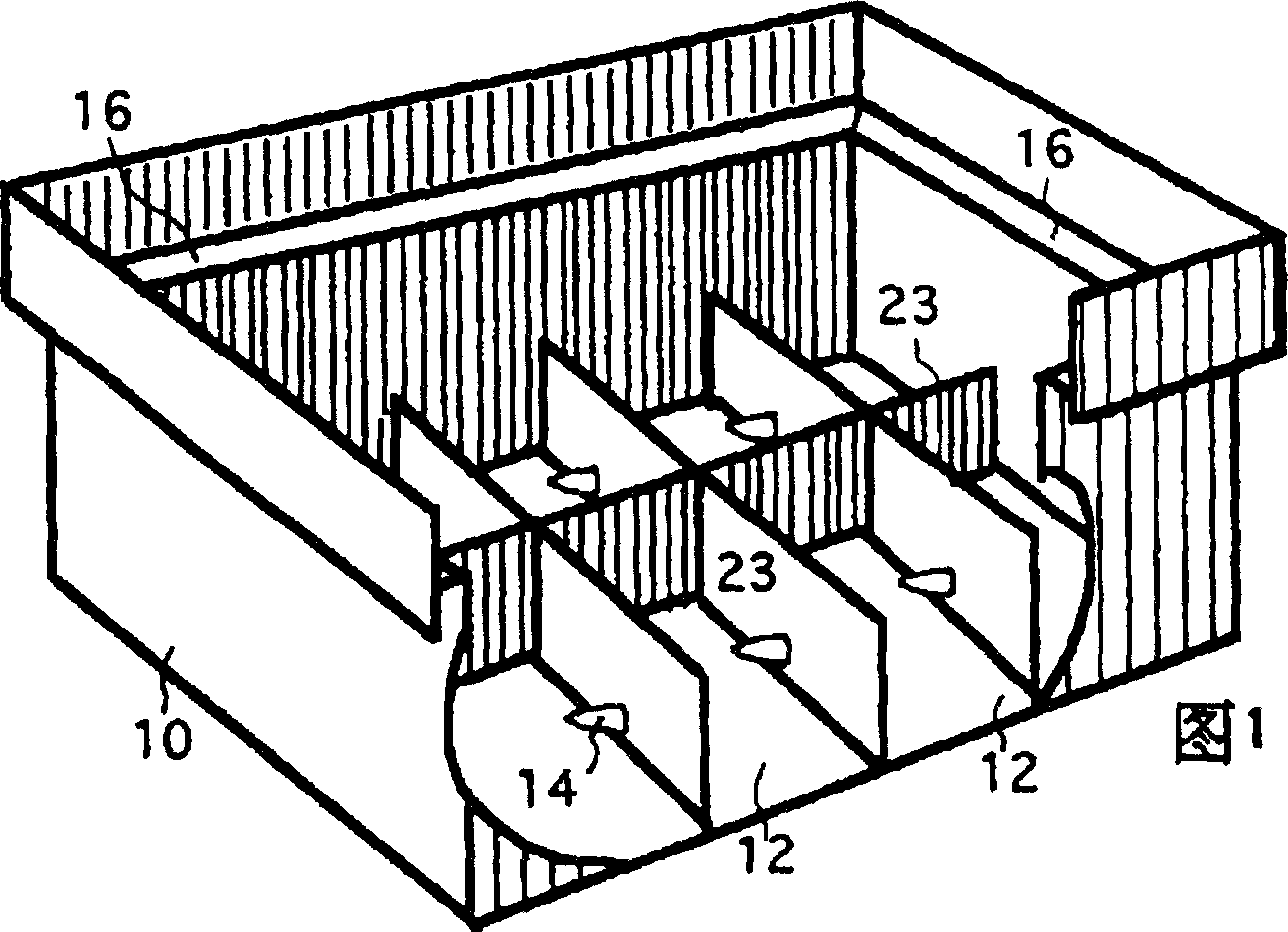
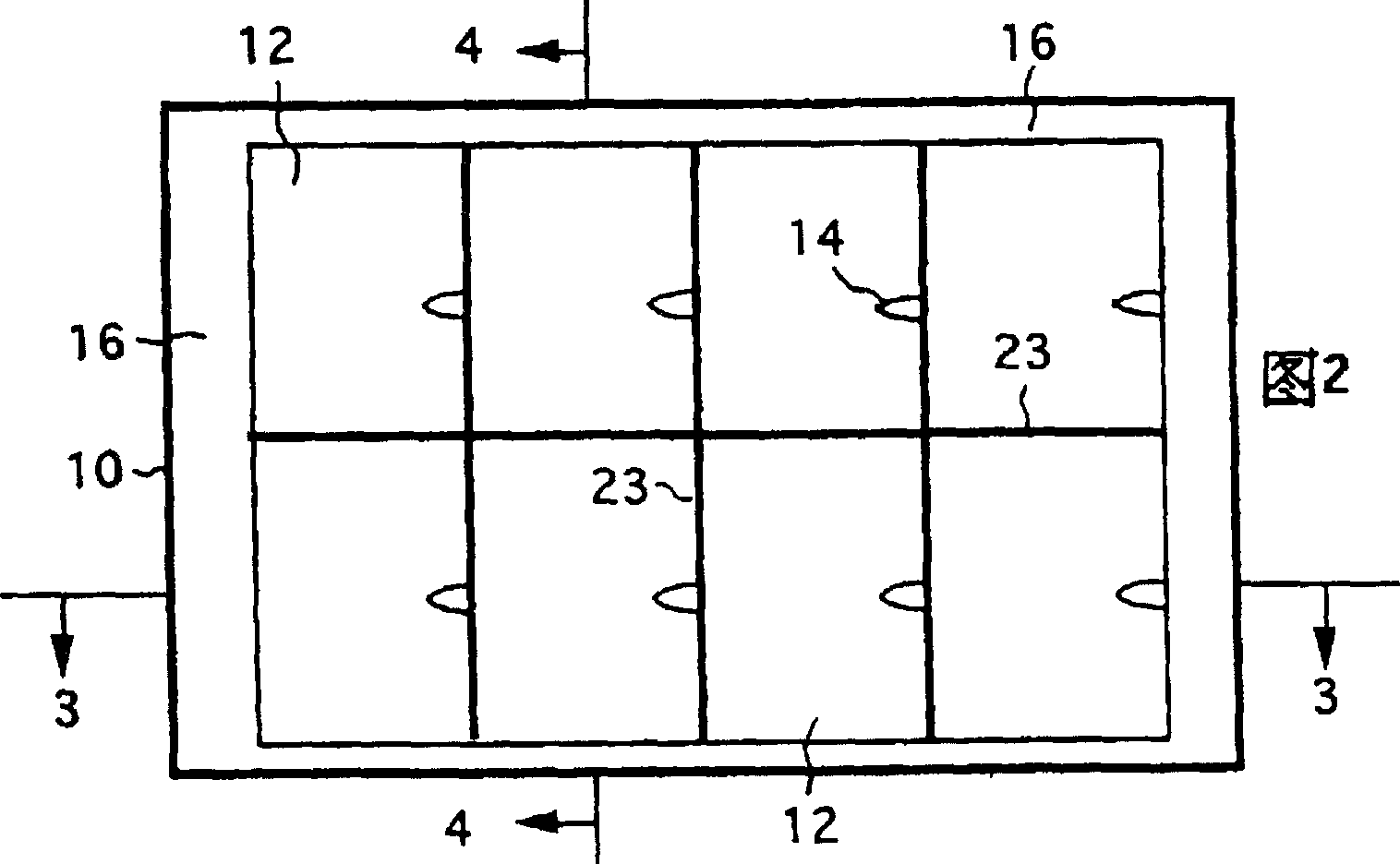
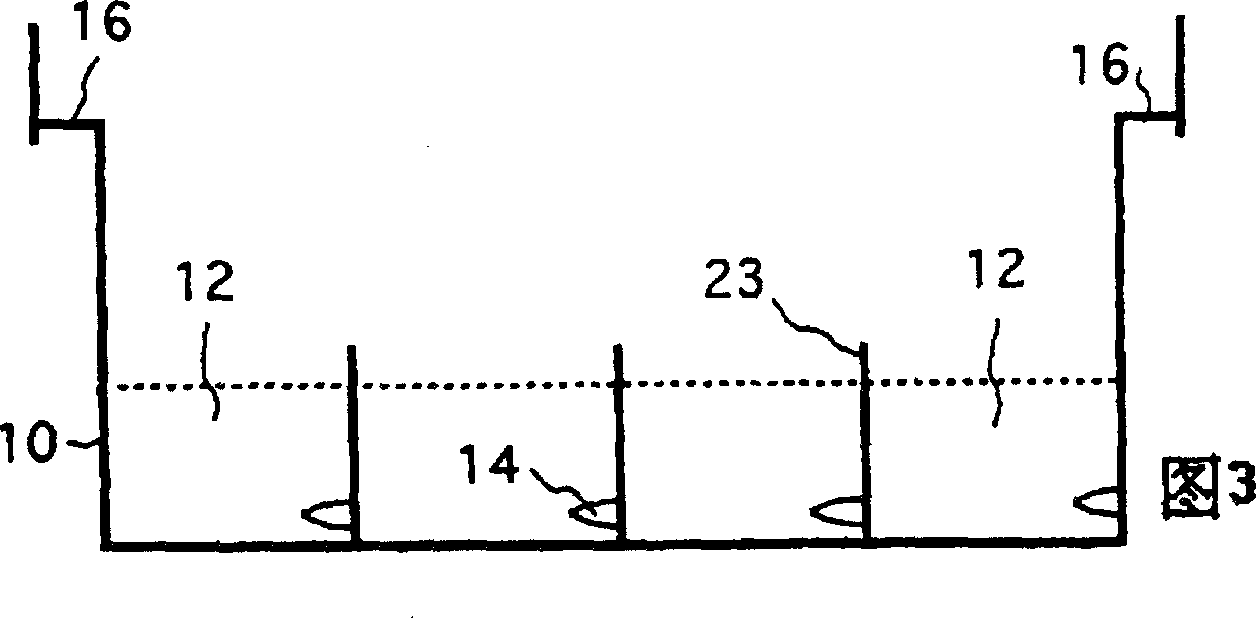
[0077]Embodiment 1, front and rear movable type: this type is a combined structure of two parts inside and outside, and the inner part can move back and forth in the outer part to control the water supply. The outer part 10 of the container contains a plurality of water storage compartments 12 with a plurality of protrusions or plugs 14 on the inner walls of the compartments. But the most important feature of the ecological tissue culture container is that there is a ring of blocking structure 16 on the outer part, so as to prevent the powder from slipping and forming a gap at the part where the powder contacts the container wall, thereby blocking the intrusion of microorganisms. The blocking structure 16 is stepped in this type (FIG. 1). The step is wider at both ends of the container and narrower at both sides, so that the inner part or culture medium carrier 18 hanging on the step can be pushed back and forth without leakage (see FIG. 2 ). The water storage compartment 12 ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Embodiment 2, up and down movable type: this type is a one-piece structure. It has a concave-convex bottom surface that can be pushed up and down. Its culture medium carrier 18 is not a single piece, but an integral part of the container (seeing Fig. 15 to Figure 19 ). The medium carrier 18 and its plurality of compartments 22 can be seen in plan view (FIG. 15). There is also an extension tube 20 for each compartment. There is a pipe 36 on the culture medium carrier, which needs to be sealed with common sealing material 37 after adding water. The section from line 16-16 shows more detail (Fig. 16), and all the components are inseparable as a whole.
[0085] The present embodiment also has many water storage compartments 12, and each compartment has an independent bottom surface and a partition wall not shared with adjacent rooms. Therefore, the water storage compartments are basically independent of each other, yet their centripetal ends are all covered. They are c...
Embodiment 3
[0088] Embodiment 3, solid water storage type: different from liquid water storage, this type uses solid water absorbing material 44 to absorb water storage liquid. Such materials as vermiculite, sand, perlite etc. They can absorb a considerable amount of water, and when the water is removed, their volume does not shrink much, and they will not sink due to the consumption of water.
[0089] The solid water storage type ecological tissue culture container is similar to the outer part of embodiment one. Below the stagnant structure, it is divided into several solid water storage compartments by compartment partition walls 23 . The above-mentioned solid water-absorbing material 44 is packed into and occupies most of the space of the water storage chamber. Medium 26 is placed on solid absorbent material (see Figure 22 and Figure 23 ), but not exceeding the height of the partition wall 23. In order to avoid excessive infiltration of medium components into the storage water, a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com