Preparation method and application of macromolecular degradable master batch
A technology for degrading masterbatches and polymers, applied in the field of composite material production, can solve problems such as uncontrollable, accelerated molecular degradation, disordered molecular fragments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037]A polymer degradable masterbatch has a melt index of 3g / min (2.16kg, 190°C) and a melting range of 90°C; the degradable masterbatch has an aerobic degradation time t1 at 60°C and an anaerobic degradation time at 60°C The ratio t1 / t2 of t2 is 5, and the total content of metal ions with an atomic number greater than 30 in the degradable masterbatch is less than 100 ppm.
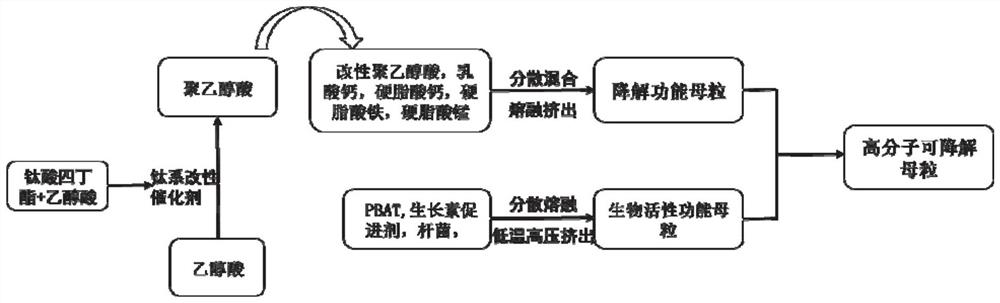
[0038] A kind of preparation method of macromolecule degradable masterbatch, its concrete steps are:
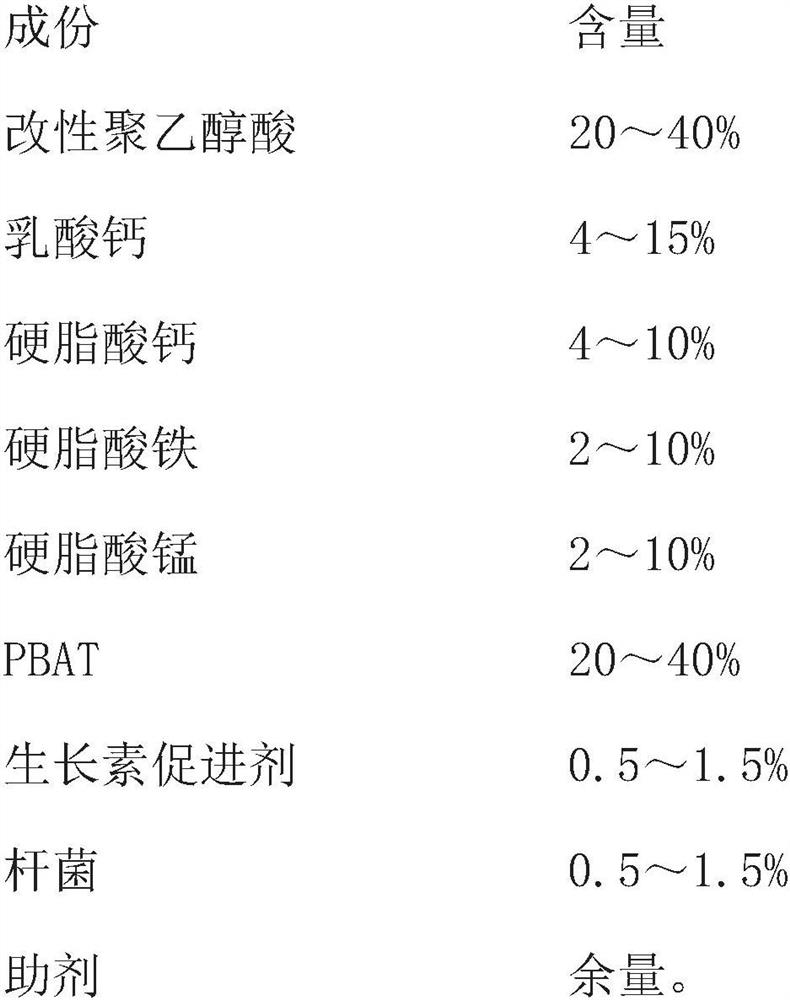
[0039] Its main components and content of described macromolecule degradable masterbatch are as follows:
[0040]
[0041] The preparation method of described macromolecule degradable master batch comprises the following:
[0042] (1) Preparation of modified polyglycolic acid
[0043] Glycolic acid is used as raw material and a titanium-based modified catalyst is used. First, the glycolic acid is esterified at 190-210 ° C. During the esterification process, nitrogen is used as a protective gas and t...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A polymer degradable masterbatch has a melt index of 30g / min (2.16kg, 190°C) and a melting range of 165°C; the aerobic degradation time t1 of the degradable masterbatch at 60°C and the anaerobic degradation time of 60°C The ratio t1 / t2 of t2 is 10, and the total content of metal ions with an atomic number greater than 30 in the degradable masterbatch is less than 100 ppm.
[0057] A kind of preparation method of macromolecule degradable masterbatch, its concrete steps are:
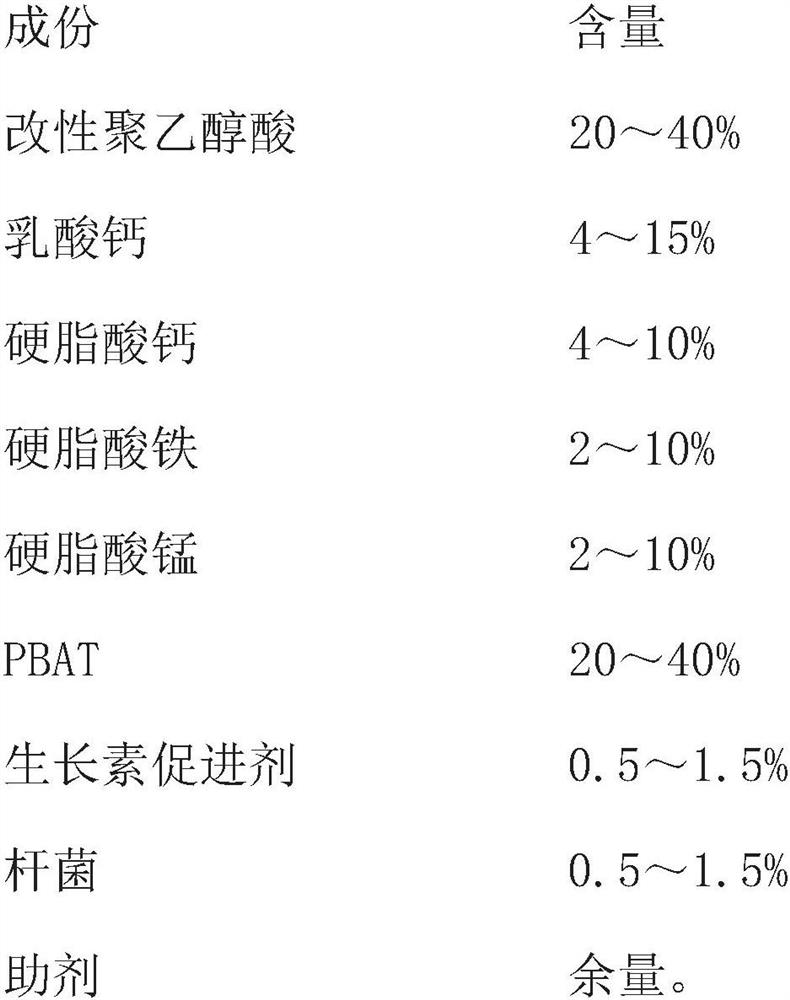
[0058] Its main components and content of described macromolecule degradable masterbatch are as follows:
[0059]
[0060] The preparation method of described macromolecule degradable master batch comprises the following:
[0061] (1) Preparation of modified polyglycolic acid
[0062] Glycolic acid is used as raw material and a titanium-based modified catalyst is used. First, the glycolic acid is esterified at 190-210 ° C. During the esterification process, nitrogen is used as a protective gas ...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A polymer degradable masterbatch has a melt index of 20g / min (2.16kg, 190°C) and a melting range of 135°C; the aerobic degradation time t1 of the degradable masterbatch at 60°C and the anaerobic degradation time of 60°C The ratio t1 / t2 of t2 is 8, and the total content of metal ions with an atomic number greater than 30 in the degradable masterbatch is less than 100 ppm.
[0076] A kind of preparation method of macromolecule degradable masterbatch, its concrete steps are:
[0077] Its main components and content of described macromolecule degradable masterbatch are as follows:
[0078]
[0079]
[0080] The preparation method of described macromolecule degradable master batch comprises the following:
[0081] (1) Preparation of modified polyglycolic acid
[0082] Glycolic acid is used as raw material and a titanium-based modified catalyst is used. First, the glycolic acid is esterified at 190-210 ° C. During the esterification process, nitrogen is used as a prot...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melt index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting range | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com