PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) pulse width dynamic adjustment and neutral-point balance method based on current observer
A current observer and dynamic adjustment technology, applied in electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve problems such as current coupling, disordered harmonics, and insufficient adjustment capability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
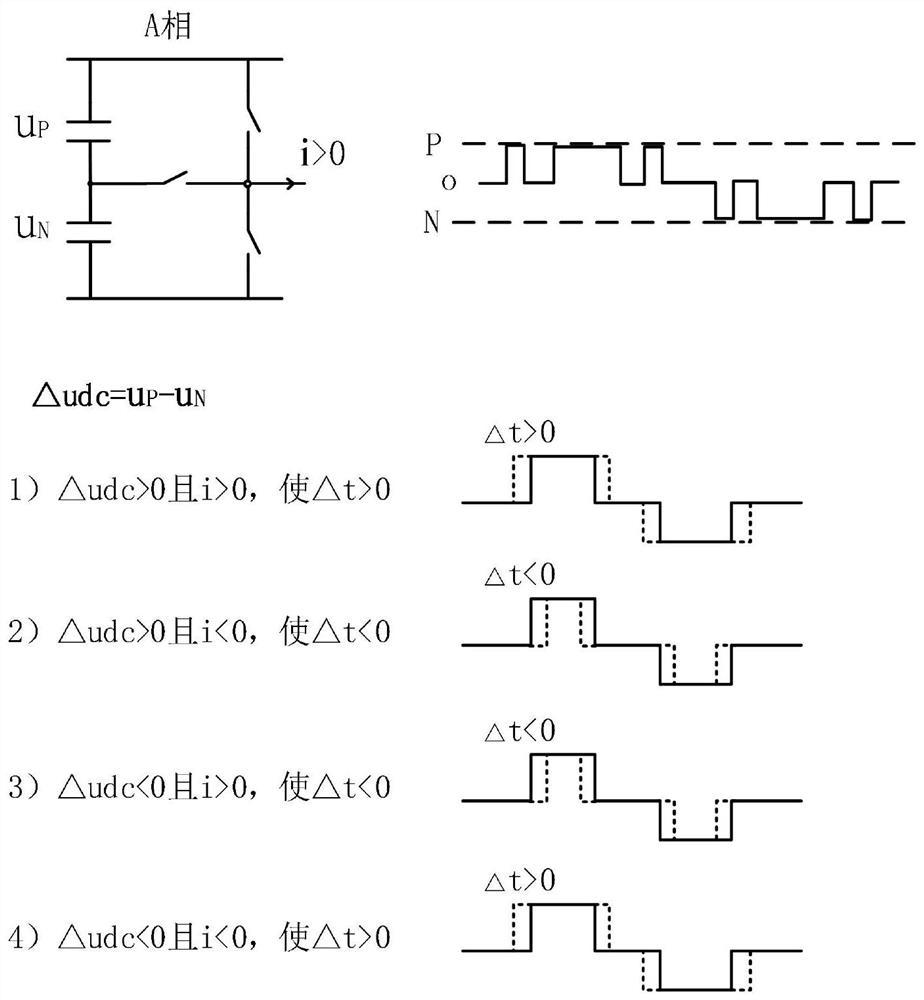
[0058] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the usual PWM modulation strategy uses the carrier wave to compare with the triangular wave to produce PWM modulated pulses. This modulation method has the advantage of simplicity and ease when the harmonics are not large at high carrier ratios, but the ratio harmonics are large at low carrier ratios.
[0059] Such as Figure 6 As shown, the optimized PWM modulation strategy obtains a set of switching angles through offline numerical calculation to achieve the minimum output harmonics. However, the optimal PWM strategy cannot be directly used in high-performance systems such as vector control, because it will cause PWM disorder and system overcurrent in dynamics.
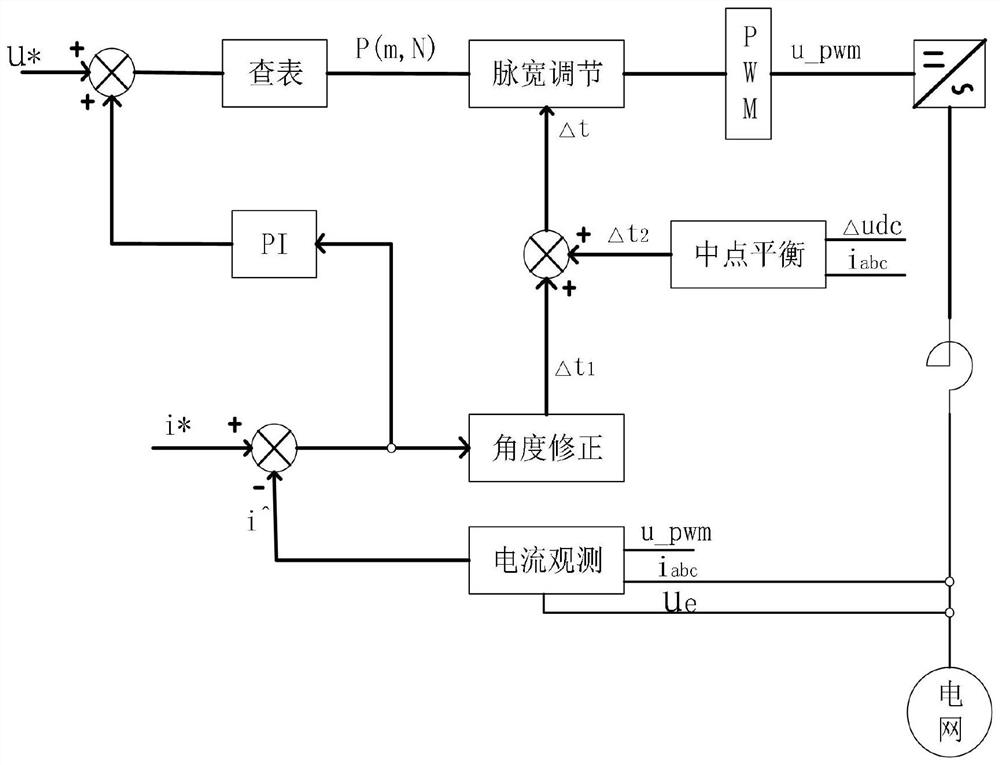
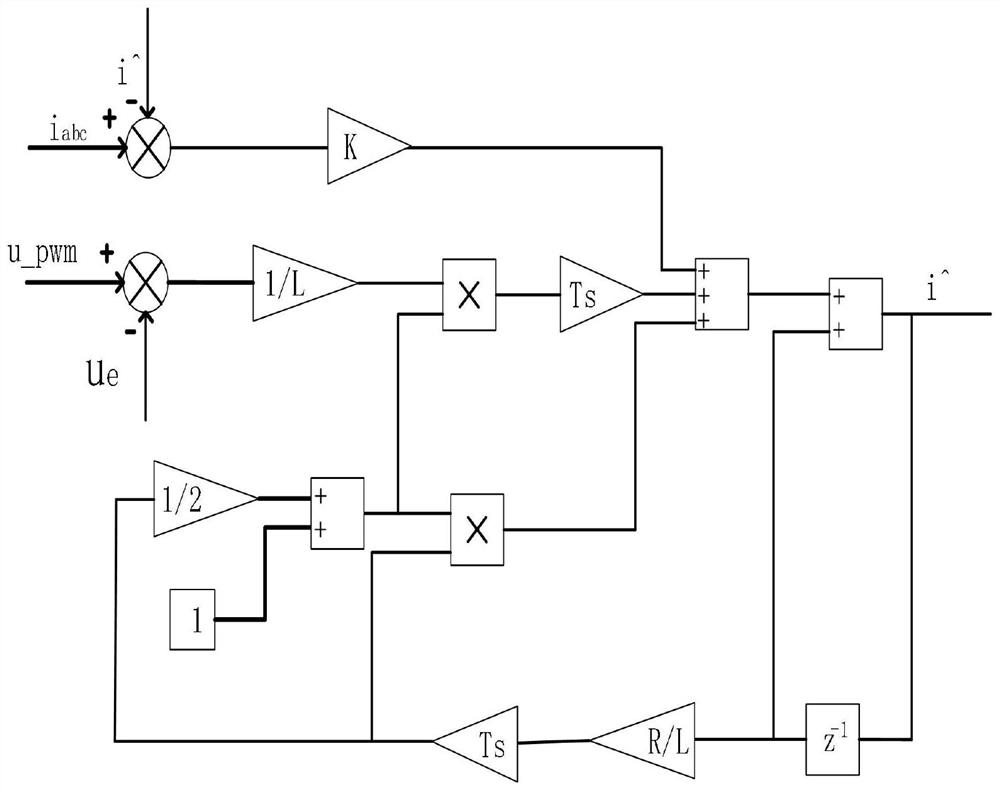
[0060] PWM pulse width dynamic adjustment and midpoint balance method based on current observer, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com