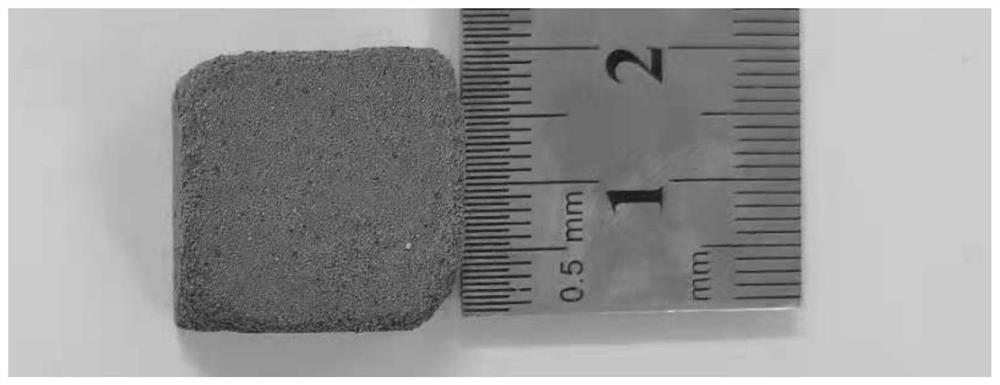
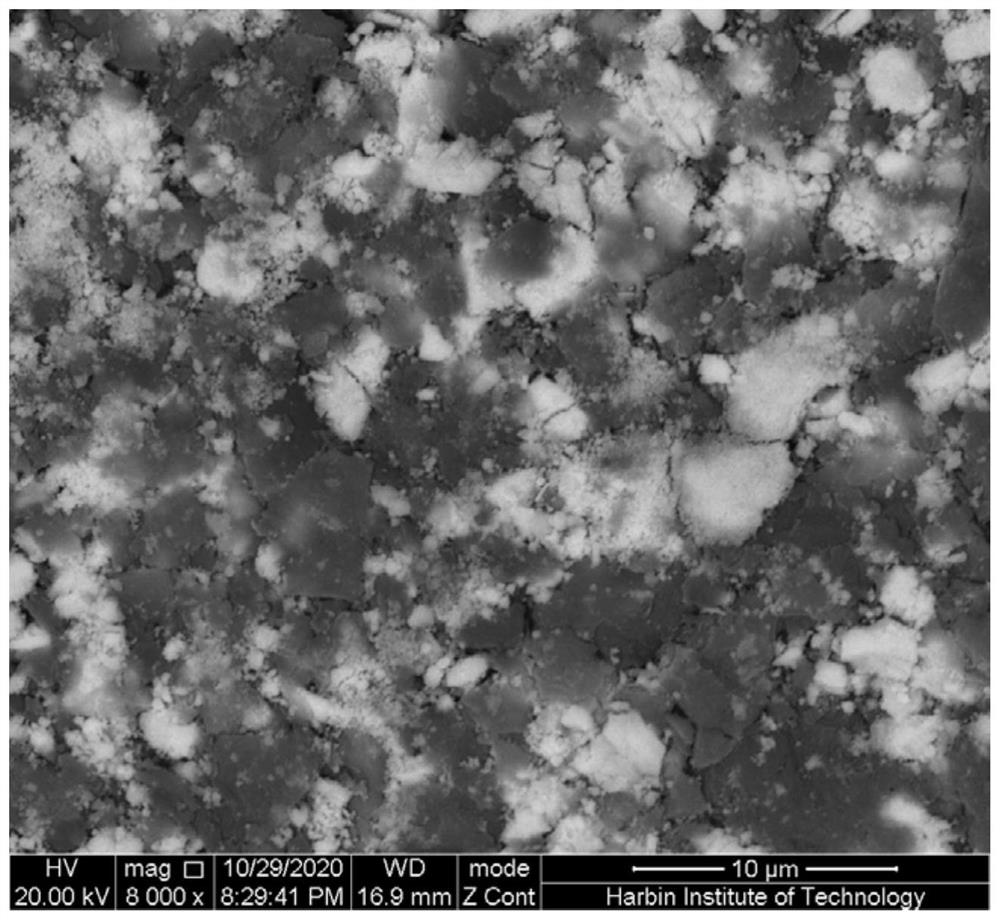
Pressureless sintering preparation method of three-dimensional porous structure
A three-dimensional porous, pressure vessel technology is applied in the field of preparation of three-dimensional porous structures, which can solve the problems of difficult cleaning of surface products, uneven distribution of pores, and high equipment costs, so as to ensure uniform distribution in a large area, avoid difficult cleaning, and simplify the production process. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
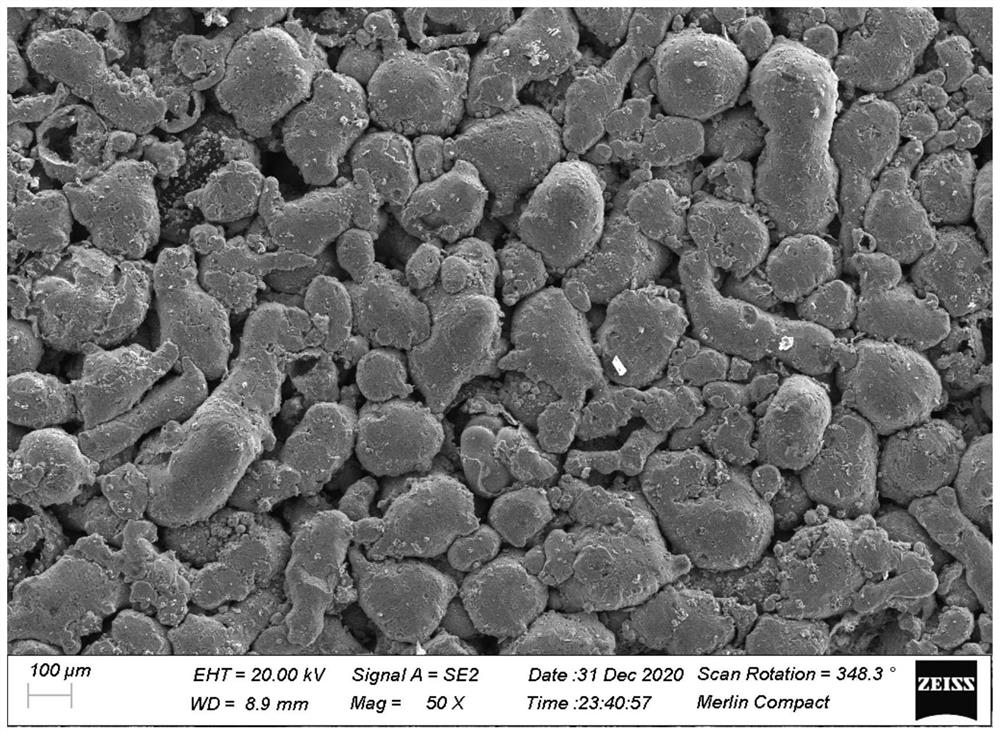
[0025] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, a method for preparing a three-dimensional porous structure without pressure sintering is carried out according to the following steps:
[0026] 1. Pretreatment of precursor powder:
[0027] Under the condition that the rotation speed is 100rpm-600rpm, ball mill the precursor powder, and filter after ball milling to obtain the pretreated powder;
[0028] The particle size of the pretreated powder is 100 mesh to 1000 mesh;
[0029] 2. Precursor curing:
[0030] Spread the pretreated powder evenly in a pressure vessel, and press it for 5s to 1000s under the condition of a pressure of 0.1MPa to 100MPa. After the pressing is completed, a block precursor is obtained;
[0031] 3. Pressureless sintering:
[0032] Put the bulk precursor in the heating furnace, and adjust the protective gas in the heating furnace to 10torr~1000torr, and then raise the temperature to 600℃~1500℃ at a rate of 5℃ / min~20℃ / min, and at a temperature of 600 Under th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the precursor powder described in step 1 is pure iron powder, pure tin powder, pure aluminum powder, pure zinc powder, silver-based solder, tin-based One or a mixture of brazing filler metals, aluminum-based brazing filler metals, silicon-based brazing filler metals and halogen salts. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the bottom surface area of the bulk precursor described in step 2 is 10mm 2 ~10m 2 , with a height of 1 mm to 100 mm. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com