MMC-based pseudo-random code fault location method and system
A technology of fault distance measurement and pseudo-random code, which is applied in the direction of fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, fault detection by pulse reflection method, etc., to achieve the effect of eliminating power and pulse width, large time-bandwidth product, and excellent autocorrelation characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
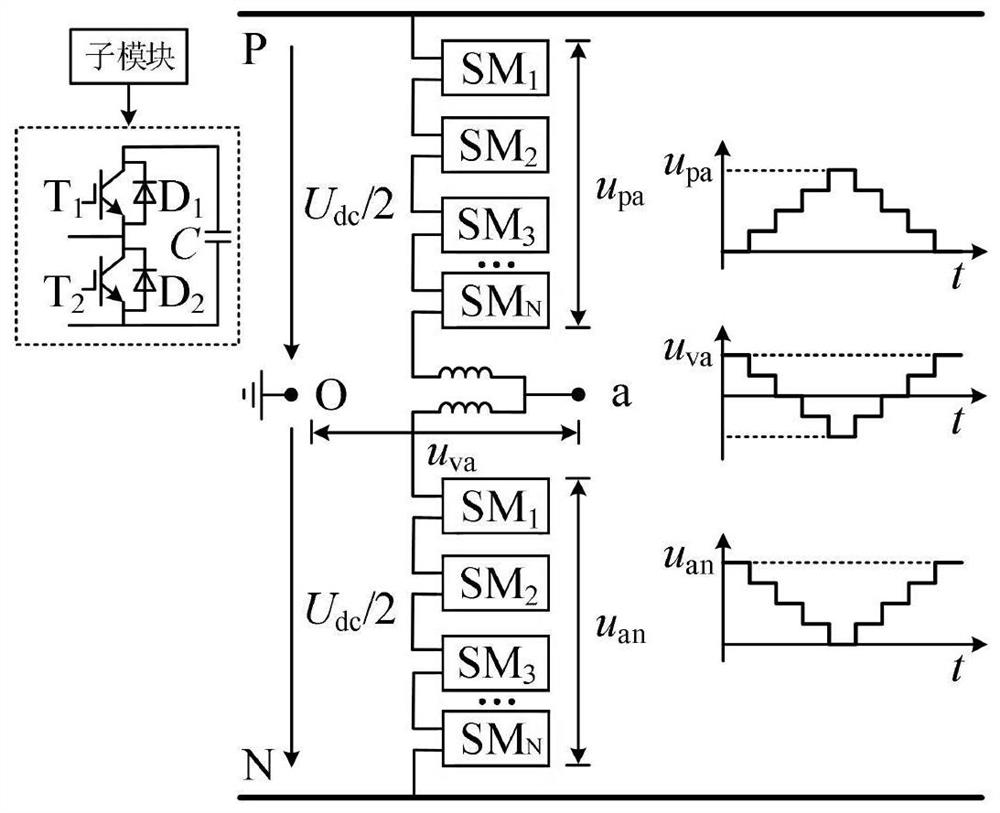
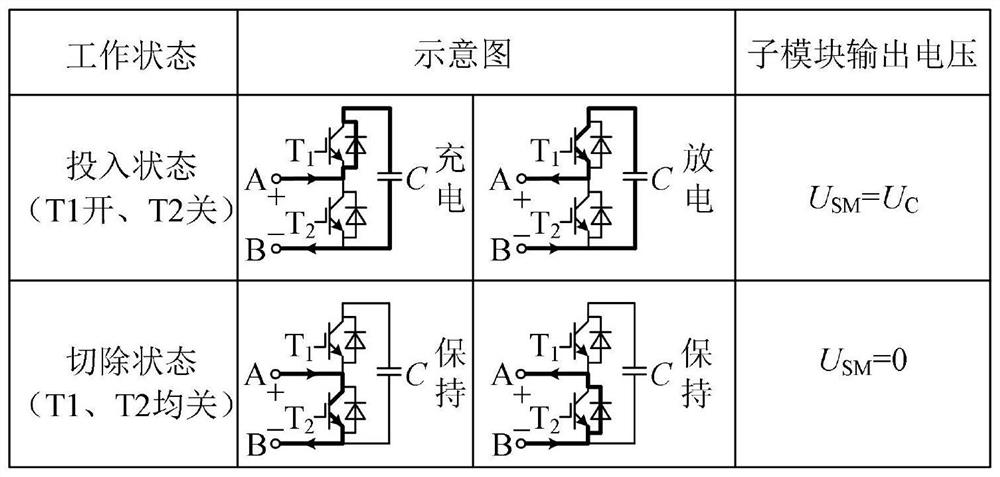
[0049] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the topology structure of the modular multilevel converter (MMC), including the positive pole P and the negative pole N of the DC bus. There are upper and lower bridge arms between the DC buses. The arm is connected to the negative pole N of the busbar, the junction of the upper and lower bridge arms is node a, and the node a is connected to the upper and lower bridge arms respectively through inductance; point O is the equivalent neutral point, u vais the output voltage on the AC side of phase A. Both the upper and lower bridge arms are equipped with a number of series-connected half-bridge sub-modules (Half Bridge SM, HBSM). The sub-modules include two series-connected IGBTs (T1, T2), and T1 and T2 are respectively equipped with anti-parallel diodes D1, D2, T1, T2 are connected in parallel with capacitor C after being connected in series. The first output terminal of the sub-module is located on the line connecting the emitter ...
Embodiment 2
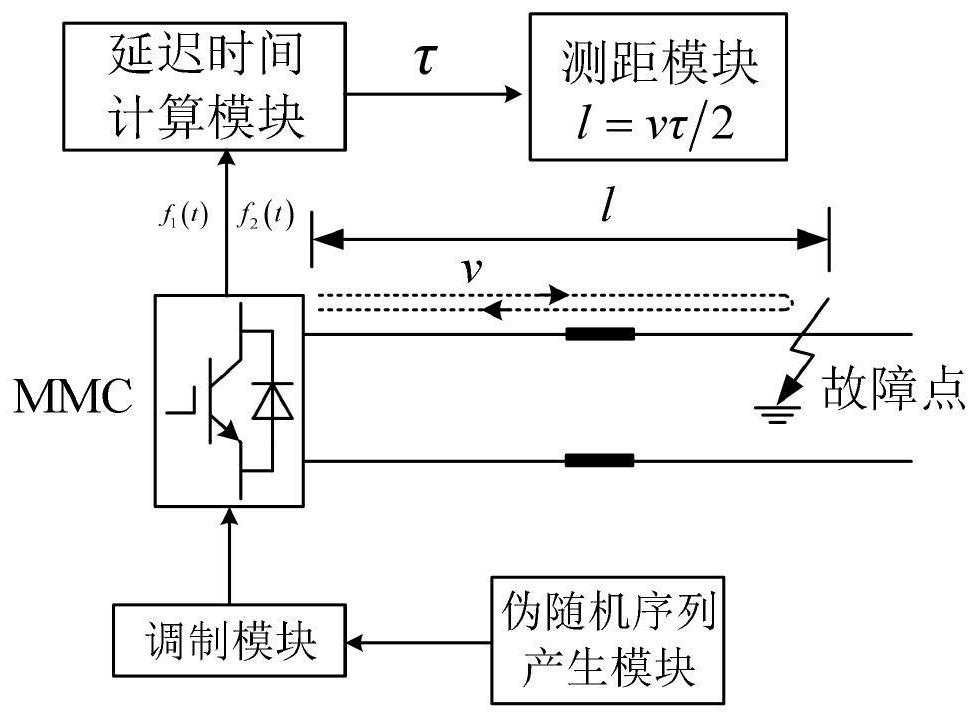
[0083] Such as figure 1 As shown, a pseudo-random code fault ranging system based on MMC includes a pseudo-random sequence generation module, a modulation control module, a delay time calculation module, and a ranging module;
[0084] The pseudo-random sequence generation module generates m-sequence signals; the modulation control module receives the m-sequence signals and controls the MMC DC side voltage to follow the m-sequence signals to switch between two levels; the delay time calculation module receives the MMC DC side voltage signals and reflected wave signals And calculate the delay time between the MMC DC side voltage signal and the reflected wave signal; the ranging module receives the delay time signal and calculates the distance between the fault point and the MMC terminal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com