Container formation method of lead-acid storage battery for electric power system
A lead-acid battery and power system technology, applied in the field of storage batteries, can solve the problems of long formation charging cycle, poor battery cycle life, and poor formation consistency, so as to reduce the charging capacity and electrolyte density, improve battery life, and moderate acid density Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The specification and model of the lead-acid battery used is GFM-400, and the density of acid injection is 1.180g / cm3. The specific charging and discharging process is as follows:
[0038] S1. After the battery is injected with acid, let it stand for 2 hours;
[0039] S2. Charge with 0.05C10 for 3 hours;
[0040] S3, charging with 0.13C10 for 38 hours;
[0041] S4, charging with 0.06C10 for 6 hours;
[0042] S5, stand still for 1 hour;
[0043] S6. Discharge at 0.12C10 to an average cell voltage of 1.8V;
[0044] S7, charge with 0.13C10 for 10 hours;
[0045] S8, charging with 0.07C10 for 28 hours;
[0046] Among them, C10 represents the rated capacity of the lead-acid battery.
[0047] In this embodiment, by increasing the charging current in the high current stage, the electrochemical reaction rate on the pole plate is accelerated, the formation efficiency of the lead-acid battery is improved, and the formation time of the lead-acid battery is shortened.
[004...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The specification and model of the lead-acid battery used is GFM-400, and the acid injection density is 1.180g / cm 3 , the specific charging and discharging process is as follows:
[0051] S1. After the battery is injected with acid, let it stand for 2 hours;
[0052] S2. Charge with 0.06C10 for 4 hours;
[0053] S3, then charge with 0.12C10 for 32 hours;
[0054] S4, then charge with 0.08C10 for 10 hours;
[0055] S5. Stand still for 1 hour
[0056] S6, then discharge at 0.1C10 to an average cell voltage of 1.8V;
[0057] S7, then charge with 0.15C10 for 10 hours;
[0058] S8, and then charge at 0.1C10 for 28 hours;
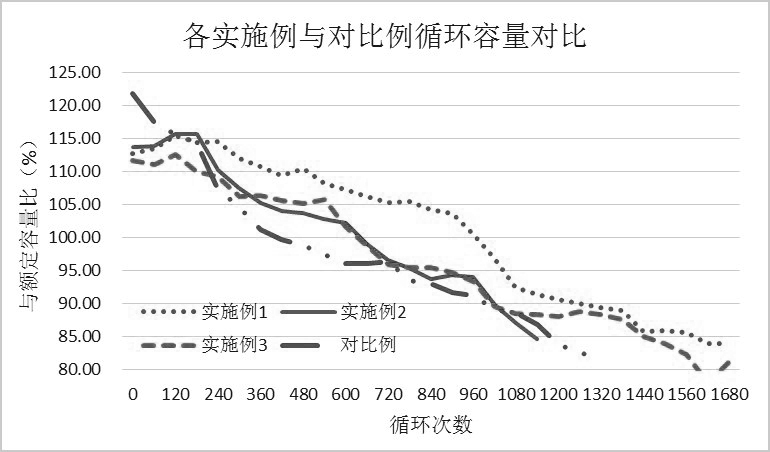
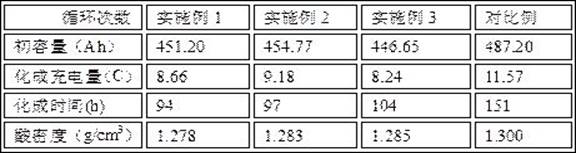
[0059] The initial capacity of the lead-acid battery was measured according to the "YDT799-2010 Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery for communication" standard, and the cycle life of the formed lead-acid battery was measured according to the 60%DOD cycle life test method, and recorded in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0061] The specification and model of the lead-acid battery used is GFM-400, and the acid injection density is 1.180g / cm 3 , the specific charging and discharging process is as follows:
[0062] S1. After the battery is injected with acid, let it stand for 2 hours;
[0063] S2. Charge with 0.05C10 for 4 hours;
[0064] S3, then charge with 0.14C10 for 30 hours;
[0065] S4, then charge with 0.06C10 for 9 hours;
[0066] S5, stand still for 1 hour;
[0067] S6, then discharge at 0.12C10 to an average cell voltage of 1.8V;
[0068] S7, and then charge with 0.13C10 for 10 hours;
[0069] S8, then charge with 0.05C10 for 40 hours;
[0070] The initial capacity of the lead-acid battery was measured according to the "YDT799-2010 Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery for communication" standard, and the cycle life of the formed lead-acid battery was measured according to the 60%DOD cycle life test method, and recorded in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com