Non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectification converter and control method
A non-isolated, converter technology, applied in the non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifier converter and control field, can solve the problem that the current-conducting capability of the buck switching device cannot be fully utilized, the current-conducting path devices are many, and the unsuitable Cost requirements and other issues, to achieve the effect of reducing restrictions, low loop on-resistance, and reducing the difficulty of control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
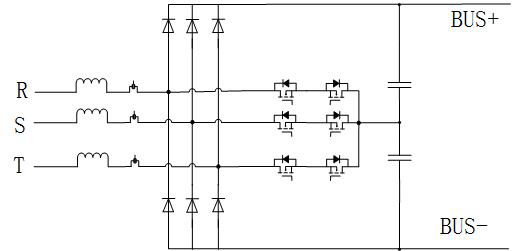
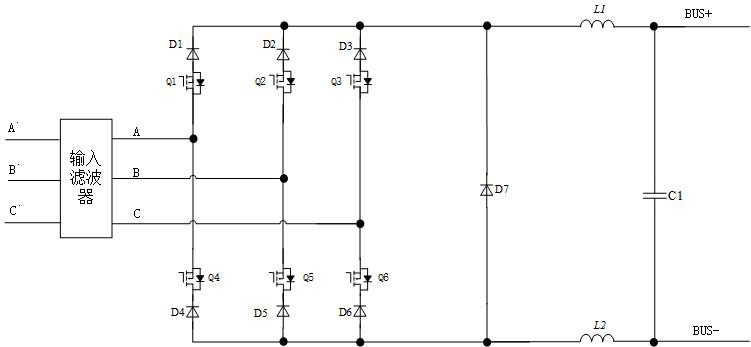
[0053] Such as Figure 4 As shown, a non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifier converter includes an input rectifier bridge group, a step-down switch unit and an energy storage freewheeling unit; the input rectifier bridge group includes first to third rectifier bridges FB1~ FB3, the first to third rectifier bridges FB1 to FB3 each include four diodes, and the four diodes are connected in series in pairs in the same direction to form two bridge arm groups with the same function, and the two bridge arm groups are connected in parallel to form Two AC input ports, that is, the midpoint of two diodes connected in series in the bridge arm group, a rectified output positive terminal, that is, the cathode of the bridge arm group, and a rectified output negative terminal, that is, the anode of the bridge arm group; the step-down switch The unit includes the thirteenth to the eighteenth diodes D13~D18 and the first to the sixth switch tubes Q1~Q6, and the energy storage freewheelin...
Embodiment 2
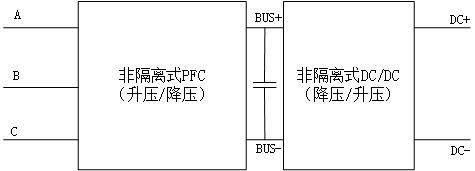
[0093] Such as Figure 16 As shown, Embodiment 2 proposes a modified embodiment based on Embodiment 1, including at least two non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifier converters as described in Embodiment 1, each non-isolated The three-phase buck-boost rectifier converters are connected in parallel, and the working phases of the first to sixth switching tubes Q1~Q6 of each non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifier converter are interleaved according to 1 / N high-frequency switching cycles , where N is the total number of parallel non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifier converters.
[0094] The control method of embodiment 2 is the same as that of embodiment 1. Through the "high" and "middle" mode PWM drive signal control methods described in embodiment 1, N non-isolated three-phase buck-boost rectifiers connected in parallel can be respectively The converter is controlled, and the working phases of the first to sixth switching tubes Q1~Q6 of the N parallel-conne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com