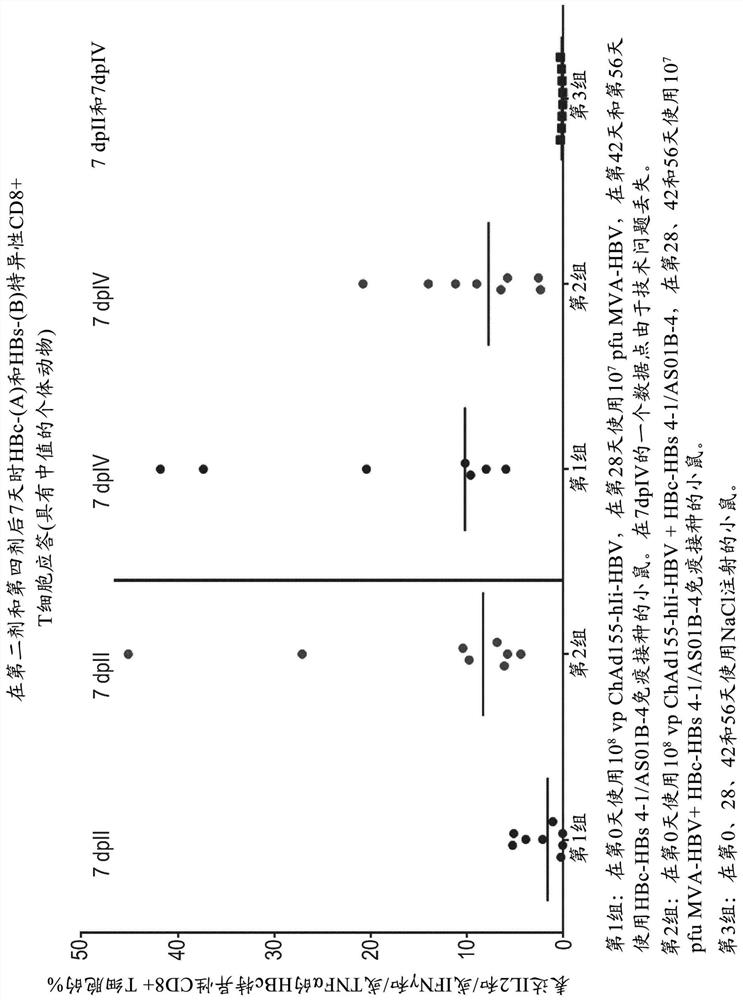
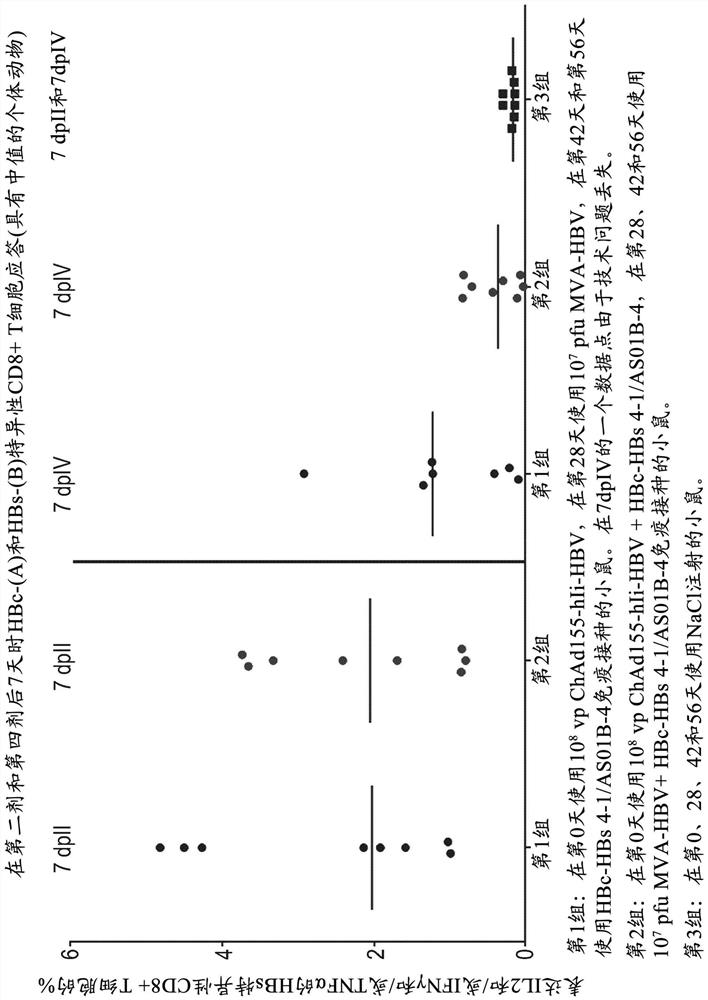
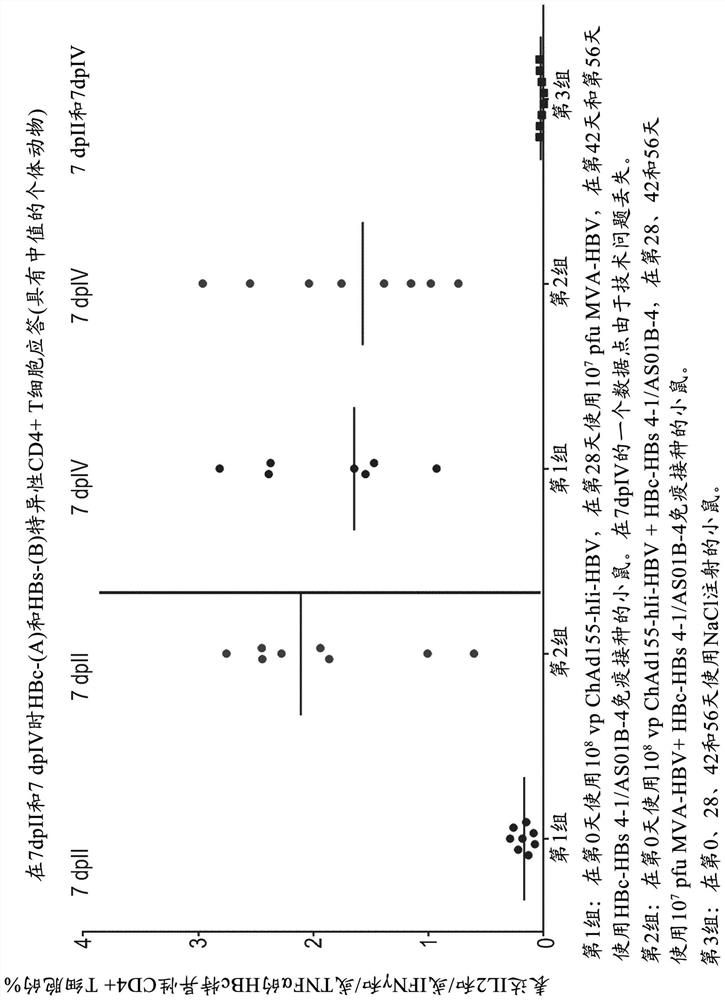
Hepatitis b immunisation regimen and compositions
A technology for hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis B, applied to a method and compositions used in such schemes and methods, field of immunization schemes for treating chronic hepatitis B
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0421] Example 1: Antisense suppression of HBV virus mRNA in HepG2.2.15 cells by MOE spacers
[0422] HepG2.2.15 cells are a widely used cell model for studying hepatitis B virus in vitro. In these cells, the HBV genome integrates into several sites in the cellular DNA. Cells were originally derived from the human hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2 and are characterized by stable HBV expression and replication in culture systems.
[0423] Antisense oligonucleotides were designed to target HBV viral nucleic acids and their effects on HBV mRNA were tested in vitro. Cultured HepG2.2.15 cells were transfected at a density of 25,000 cells per well using 15,000 nM antisense oligonucleotide electroporation. After a treatment period of approximately 24 hours, RNA was isolated from the cells and HBV mRNA levels were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. The viral primer probe set RTS3370 (forward sequence CTTGGTCATGGGCCATCAG, designated herein as SEQ ID NO: 17; reverse sequence CGGCTA...
Embodiment 2
[0435] Example 2: Tolerance of MOE spacers targeting HBV in BALB / c mice
[0436] BALB / c mice (Charles RiVer, MA) are a versatile model of mice frequently used for safety and efficacy testing. Mice were treated with antisense oligonucleotides selected from Example 1 above, and changes in the levels of various metabolic markers were assessed.
[0437] Each group of four BALB / c mice was subcutaneously injected with 50mg / kg of all the sequence numbers of WO2012 / 145697 SEQ ID NO: 83, SEQ ID NO: 224, SEQ ID NO: 88, SEQ ID NO: 103, SEQ ID NO: 20 , SEQ ID NO: 116, SEQ ID NO: 187, SEQ ID NO: 210, SEQ ID NO: 212, SEQ ID NO: 226, SEQ ID NO: 24, SEQ ID NO: 39, SEQ ID NO: 46, SEQ ID NO: 50, SEQ ID NO: 140, SEQ ID NO: 17, SEQ ID NO: 27, SEQ ID NO: 40 and SEQ ID NO: 74, twice a week for 3 weeks. A group of four BALB / c mice were subcutaneously injected with 50 mg / kg of an antisense oligonucleotide having the sequence CCTTCCCTGAAGGTTCCTCC (SEQ ID NO of WO2012 / 145697: 320), a 5-10-5 MOE spac...
Embodiment 3
[0454] Example 3: Effectiveness of MOE spacers targeting HBV in transgenic mice
[0455] Mice carrying HBV gene fragments were used (Guidotti, L.G et al. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6158-6169). Mice were treated with antisense oligonucleotides selected from the studies described above and their response in this model was assessed.
[0456] Each group of 6 mice was subcutaneously injected with 50 mg / kg of SEQ ID NO: 83, SEQ ID NO: 226, SEQ ID NO: 224, SEQ ID NO: 181, SEQ ID NO: 143 or SEQ ID NO: 145 (WO2012 / 145697) twice a week for 4 weeks. A control group of 10 mice were injected subcutaneously with PBS twice a week for 4 weeks. Mice were euthanized 48 hours after the last dose, and livers were collected for further analysis.
[0458] Using the primer probe set RTS3370, RNA was extracted from liver tissue for real-time PCR analysis of HBV DNA. DNA levels were normalized to picogreen. After RT-PCR analysis, HBV RNA samples were also assayed with pri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com