In-situ monitoring device and method for corrosion depth of high-temperature alloy
A high-temperature alloy, corrosion depth technology, applied in measuring devices, electromagnetic measuring devices, electromagnetic/magnetic thickness measurement, etc., can solve the problems of corrosion monitoring, limited testing equipment, inability to measure the corrosion and thinning of boiler tubes, etc., and achieve cost-saving. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
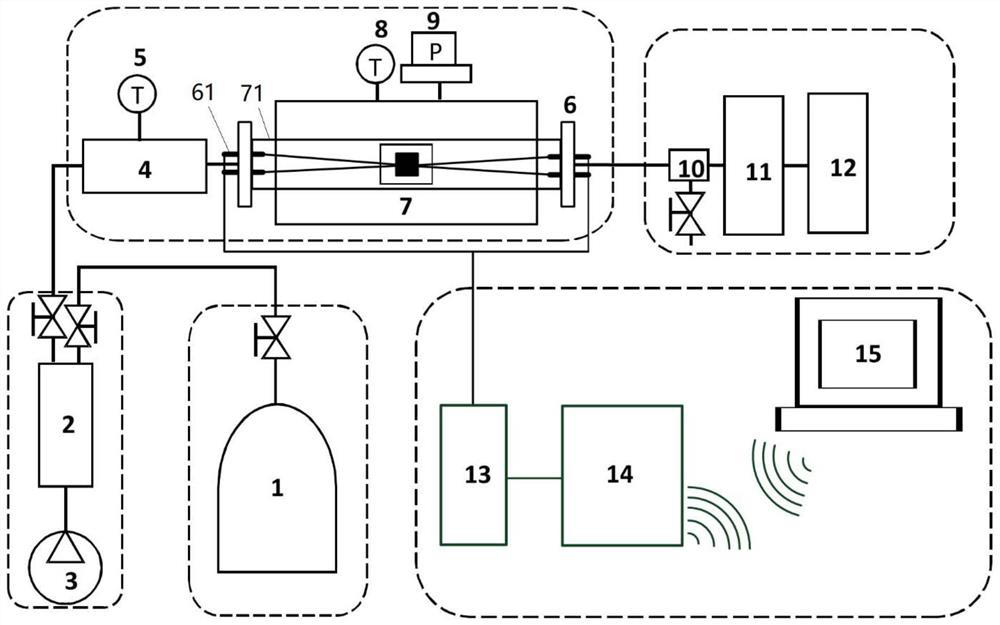
[0039] The high-temperature alloy to be tested is made of an alloy with the same material and preparation process as the alloy to be monitored on the heating surface. Taking the material of boiler tube P92 as an example, the in-situ monitoring of oxidation on the steam side is simulated. The air inlet and outlet seal vacuum electrode flanges 6 are two vacuum electrode flanges, and the vacuum electrode is connected to the digital micro-ohmmeter 14 using a four-wire method. 7 in the high-temperature reaction kettle is connected to the test piece and the vacuum electrode by high-temperature-resistant wires, and the connection method between the high-temperature-resistant wires and the sample is brazing. The digital micro-ohmmeter 14 controls and monitors the real-time corrosion data through the data terminal 15, and can convert the resistance data into corrosion depth data. When the corrosion depth exceeds a set value, an alarm prompt appears on the data terminal.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The high-temperature alloy to be tested is made of the same material and preparation process as the alloy to be monitored on the heating surface. Taking the Super304H material of the boiler tube as an example, the surface of the test piece is coated with coal ash, and the corrosion gas source is simulated flue gas. Gas corrosion in-situ monitoring. The air inlet and outlet seal vacuum electrode flanges 6 are two vacuum electrode flanges, and the vacuum electrode is connected to the digital micro-ohmmeter 14 using a four-wire method. 7 in the high-temperature reaction kettle is connected to the test piece and the vacuum electrode by high-temperature-resistant wires, and the connection method between the high-temperature-resistant wires and the sample is brazing. The digital micro-ohmmeter 14 controls and monitors the real-time corrosion data through the data terminal 15, and can convert the resistance data into corrosion depth data. When the corrosion depth exceeds a set...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com