A dispersion-optimized bend-insensitive optical fiber
A bend-insensitive, optical fiber technology, applied in clad optical fibers, multi-layer core/clad optical fibers, optics, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in meeting the requirements of bending loss, avoid excessive bending loss, and optimize the dispersion coefficient. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1~10
[0055] Embodiment 1-1~10 G657A2 standard optical fiber
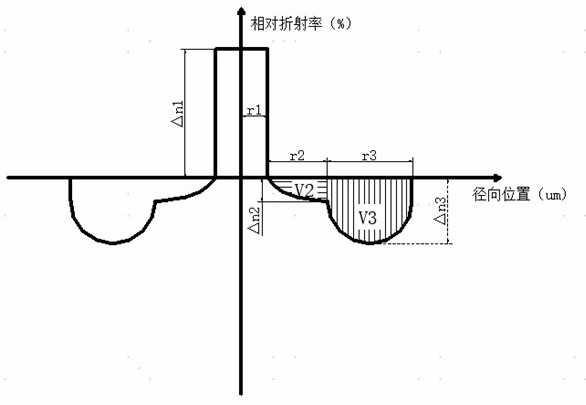
[0056] The geometric dimensions and refractive index parameters adopted by the G657A2 standard optical fiber are shown in the table below;
[0057]
[0058]
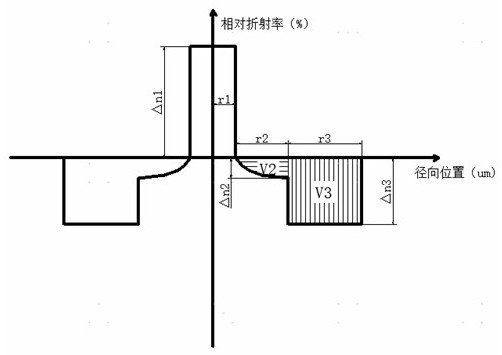
[0059] The relative refractive index difference change curve of the transitional depressed cladding can be expressed as:
[0060]
[0061] in is the distance from a point in the transitional depressed cladding to the boundary of the core cladding, is the distribution index, is the refractive index of the core layer relative to pure silica, that is, its relative refractive index difference, is the refractive index of the depressed cladding relative to pure silica, that is, its relative refractive index difference, is the transitional sag cladding width.
[0062] After testing, the attenuation of the G657A2 standard optical fiber provided in Examples 1-1~10 at a wavelength of 1310nm is less than or equal to 0.330dB / km; the attenuation at a waveleng...
Embodiment 2-1~10
[0072] Embodiment 2-1~10 G657B3 standard optical fiber
[0073] The geometric dimensions and refractive index parameters adopted by the G657B3 standard optical fiber are shown in the table below;
[0074]
[0075]
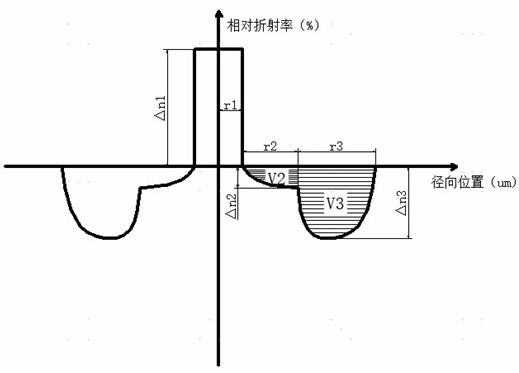
[0076] The refractive index variation curve of the transitional depressed cladding can be expressed as:
[0077]
[0078] in is the distance from a point in the transitional depressed cladding to the boundary of the core cladding, is the distribution index, is the refractive index of the core layer relative to pure silica, is the refractive index of the depressed cladding relative to pure silica, is the transitional sag cladding width.
[0079] After testing, the attenuation of the G657B3 standard optical fiber provided in Examples 2-1~10 at a wavelength of 1310nm is less than or equal to 0.330dB / km; the attenuation at a wavelength of 1383nm is less than or equal to 0.284 dB / km; Less than or equal to 0.190dB / km; attenuation at a wavelength of 16...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com