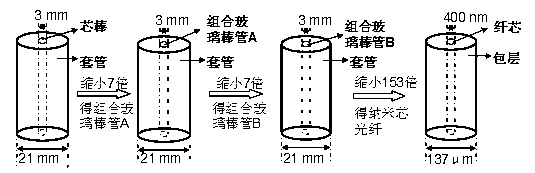
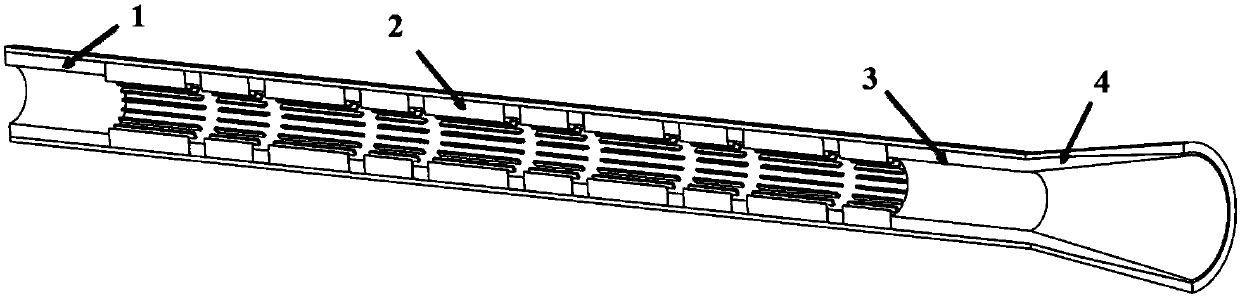
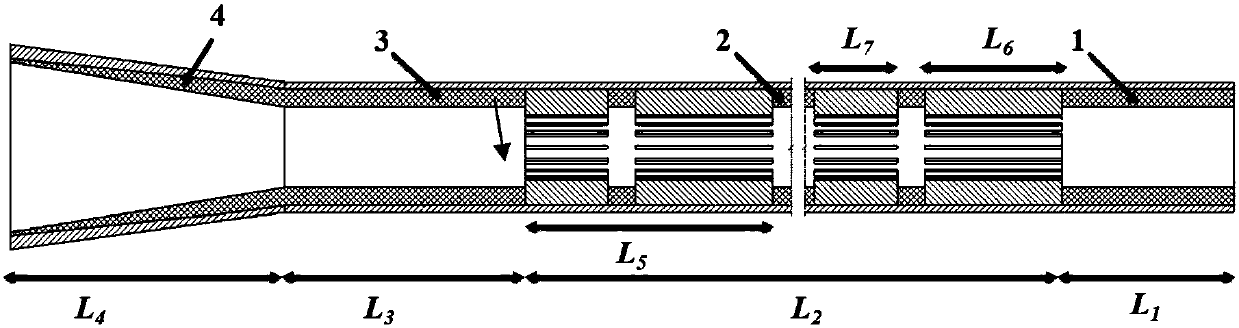
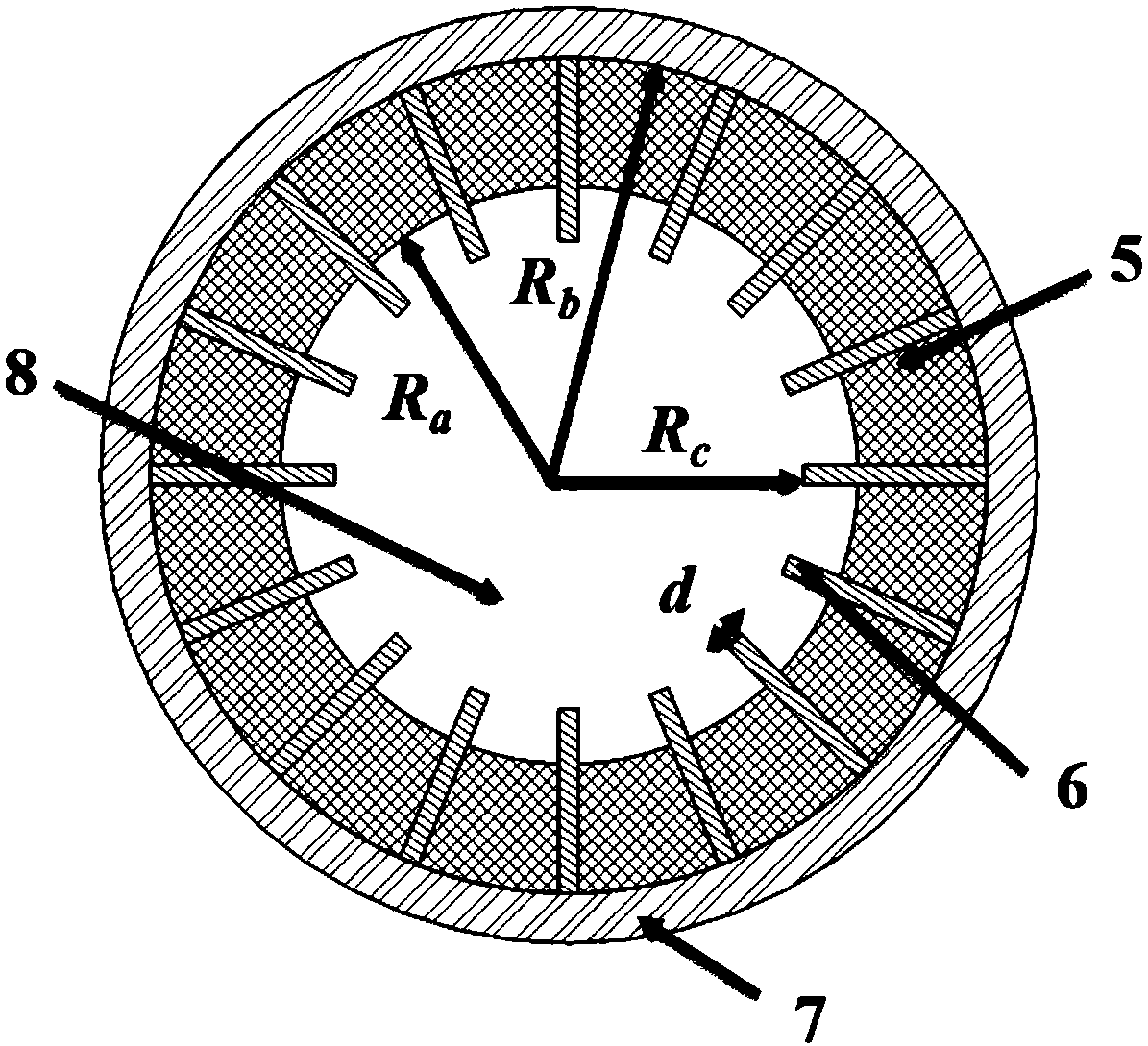
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Waveguide dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
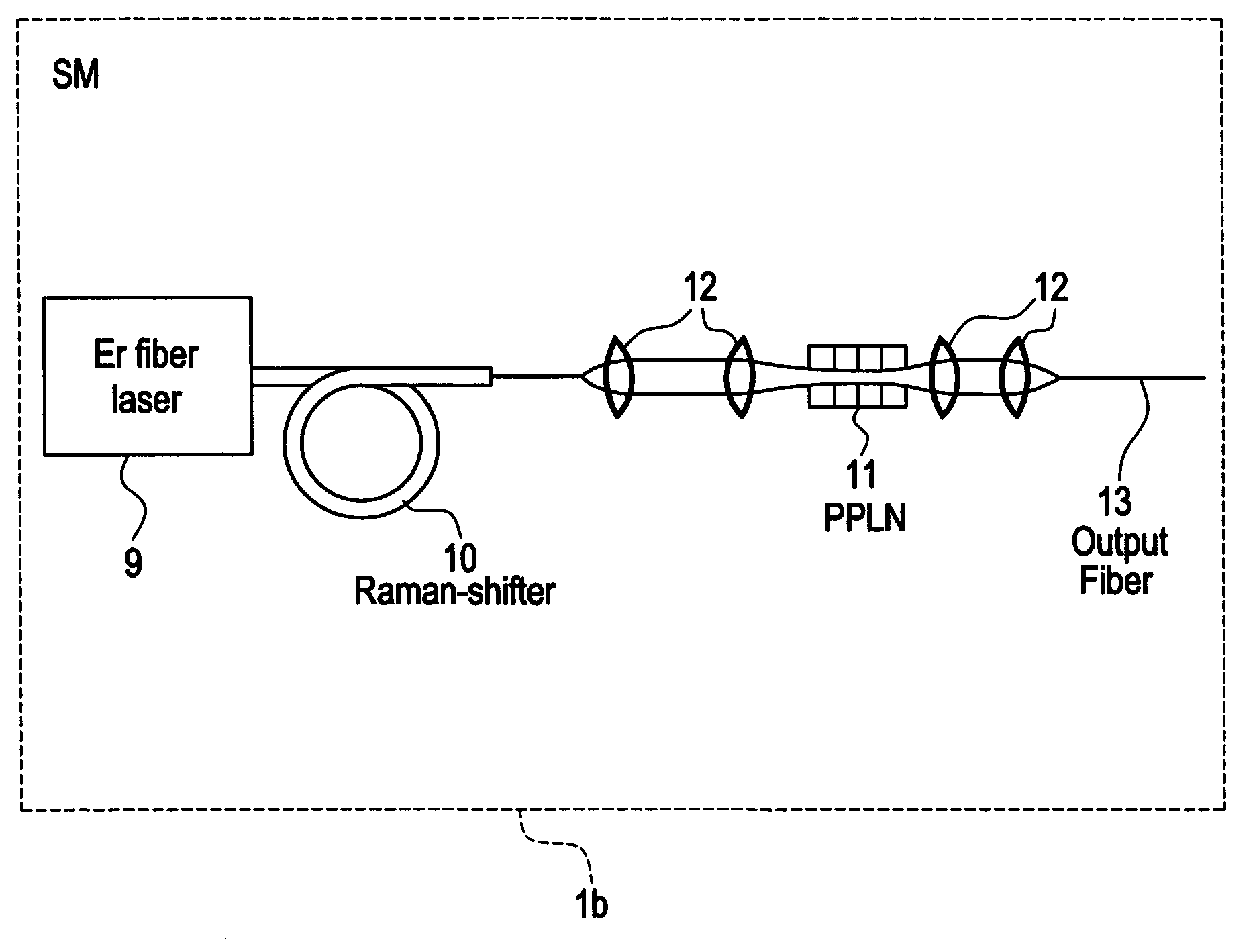
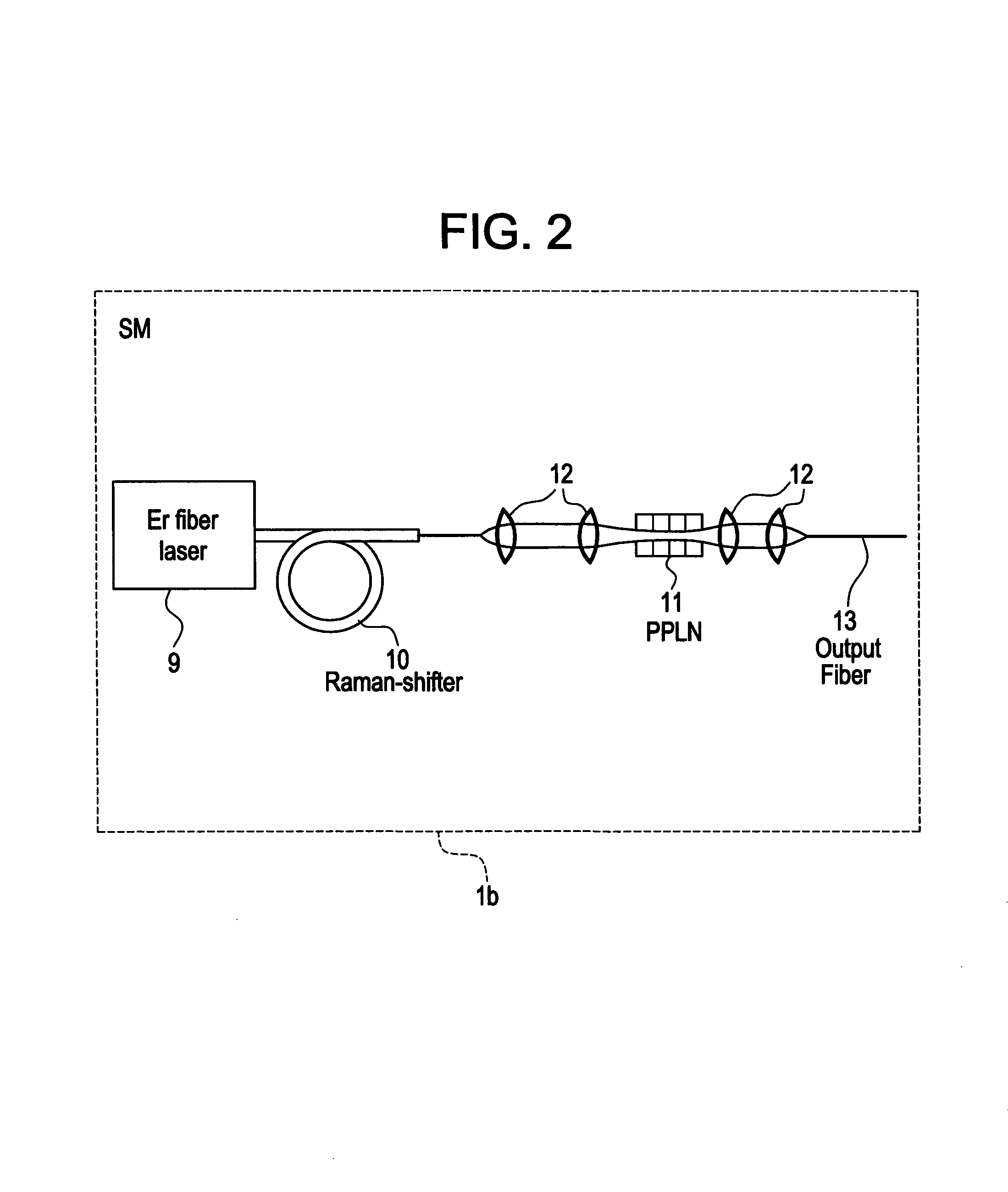
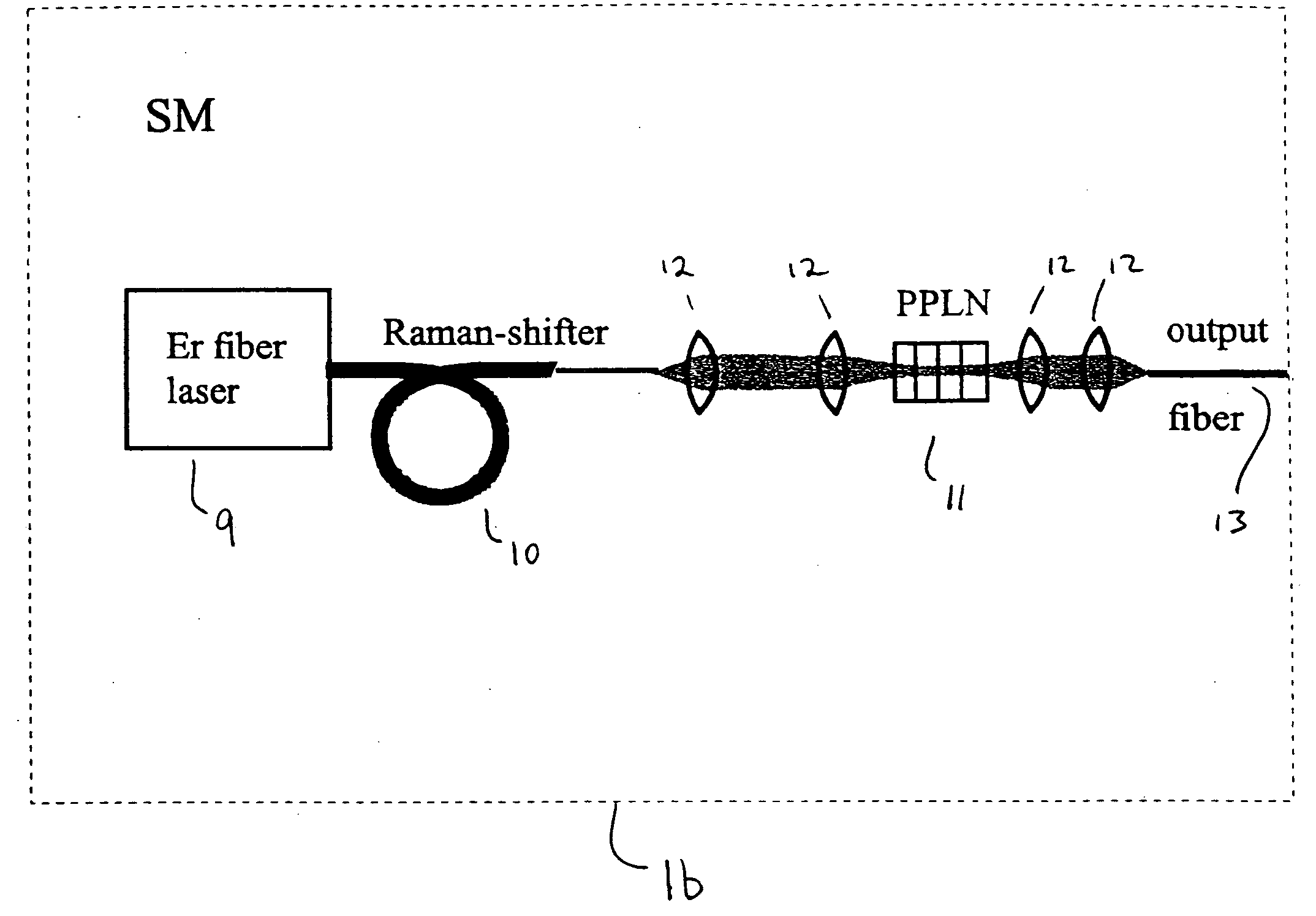
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS7167300B2High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Modular, high energy, widely-tunable ultrafast fiber source
InactiveUS20050163426A1High peak and high average powerReduce noiseLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreHigh peakHigh energy
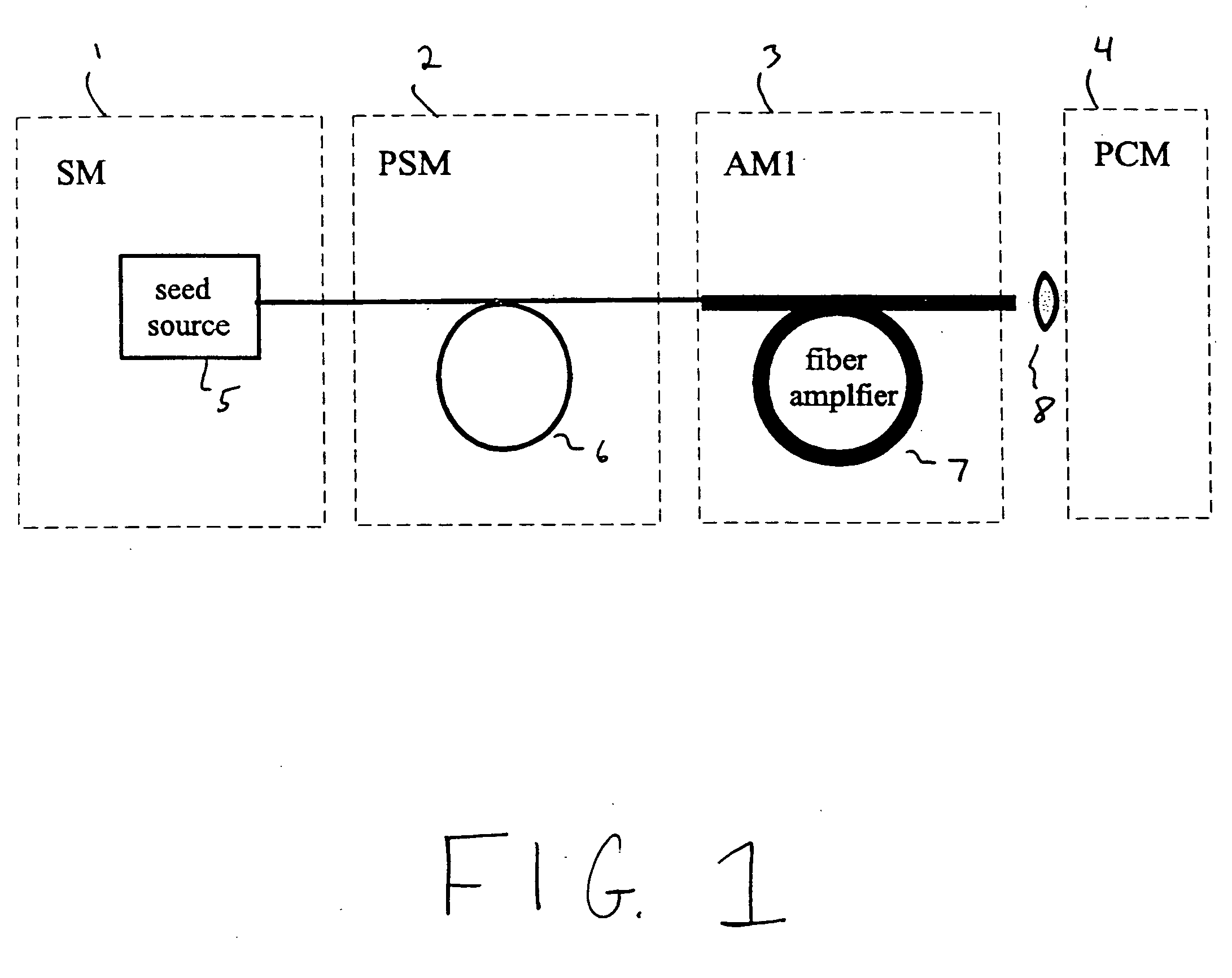
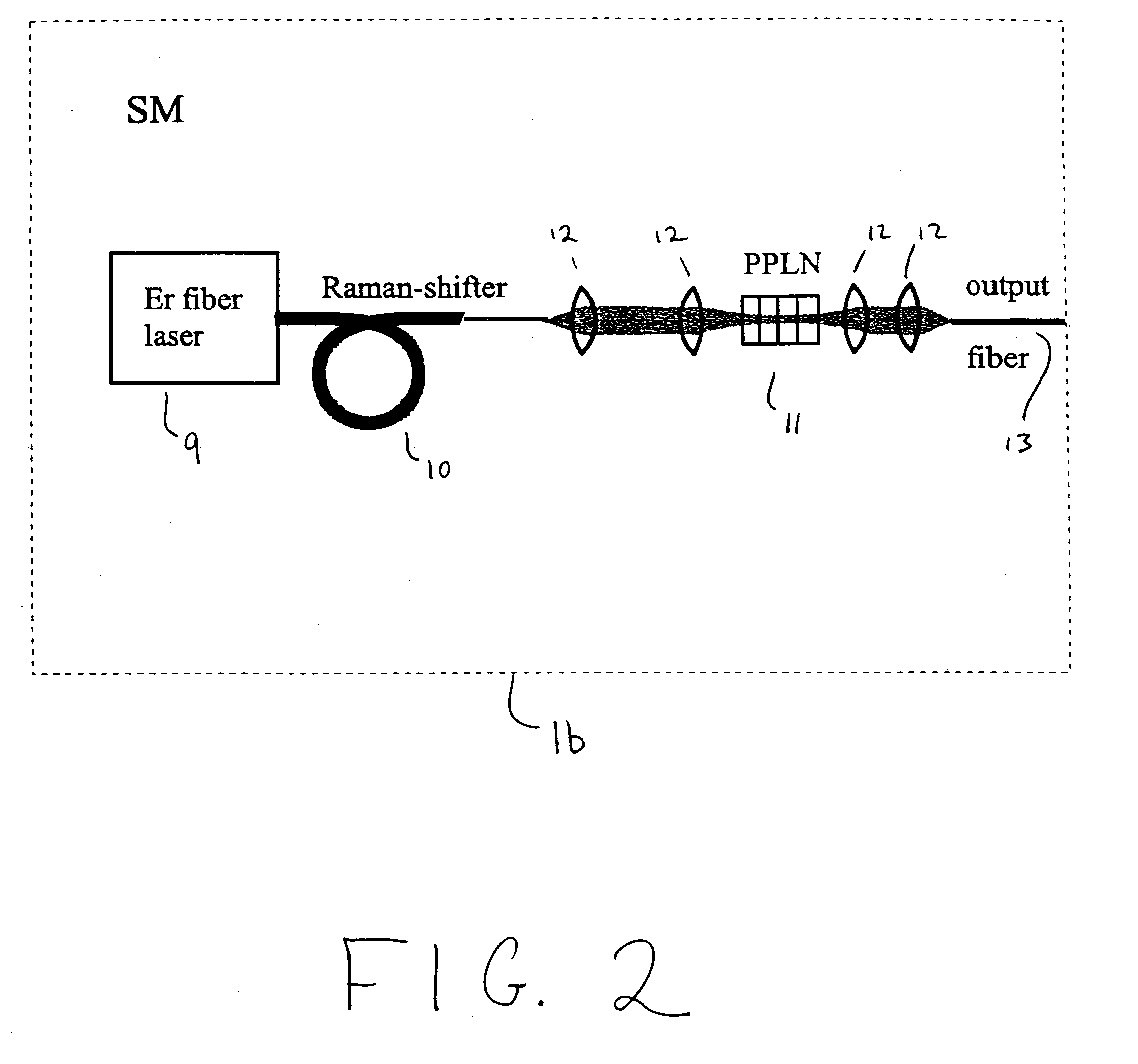
A modular, compact and widely tunable laser system for the efficient generation of high peak and high average power ultrashort pulses. Modularity is ensured by the implementation of interchangeable amplifier components. System compactness is ensured by employing efficient fiber amplifiers, directly or indirectly pumped by diode lasers. Peak power handling capability of the fiber amplifiers is expanded by using optimized pulse shapes, as well as dispersively broadened pulses. Dispersive broadening is introduced by dispersive pulse stretching in the presence of self-phase modulation and gain, resulting in the formation of high-power parabolic pulses. In addition, dispersive broadening is also introduced by simple fiber delay lines or chirped fiber gratings, resulting in a further increase of the energy handling ability of the fiber amplifiers. The phase of the pulses in the dispersive delay line is controlled to quartic order by the use of fibers with varying amounts of waveguide dispersion or by controlling the chirp of the fiber gratings. After amplification, the dispersively stretched pulses can be re-compressed to nearly their bandwidth limit by the implementation of another set of dispersive delay lines. To ensure a wide tunability of the whole system, Raman-shifting of the compact sources of ultrashort pulses in conjunction with frequency-conversion in nonlinear optical crystals can be implemented, or an Anti-Stokes fiber in conjunction with fiber amplifiers and Raman-shifters are used. A particularly compact implementation of the whole system uses fiber oscillators in conjunction with fiber amplifiers. Additionally, long, distributed, positive dispersion optical amplifiers are used to improve transmission characteristics of an optical communication system. Finally, an optical communication system utilizes a Raman amplifier fiber pumped by a train of Raman-shifted, wavelength-tunable pump pulses, to thereby amplify an optical signal which counterpropogates within the Raman amplifier fiber with respect to the pump pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Optical compensator array for dispersive element arrays
InactiveUS20060159395A1Reduce temperature sensitivityCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCylindrical lensOptics
An array of dispersive arrangements, for example an array of waveguide dispersive elements, is compensated with a set of optical compensators such as wedges or pairs of cylindrical lenses. The optical compensators are selected to achieve a pre-defined dispersion profile across the array of waveguide dispersive elements. The optical compensators can make corrections for fabrication errors or other errors in an optical system that includes the array of waveguide dispersive elements. A particular application is found in waveguide selective switches.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Planar waveguide dispersion compensator
InactiveUS6636662B1Compensation for dispersionEasy to integrateCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePhase shiftedPath length
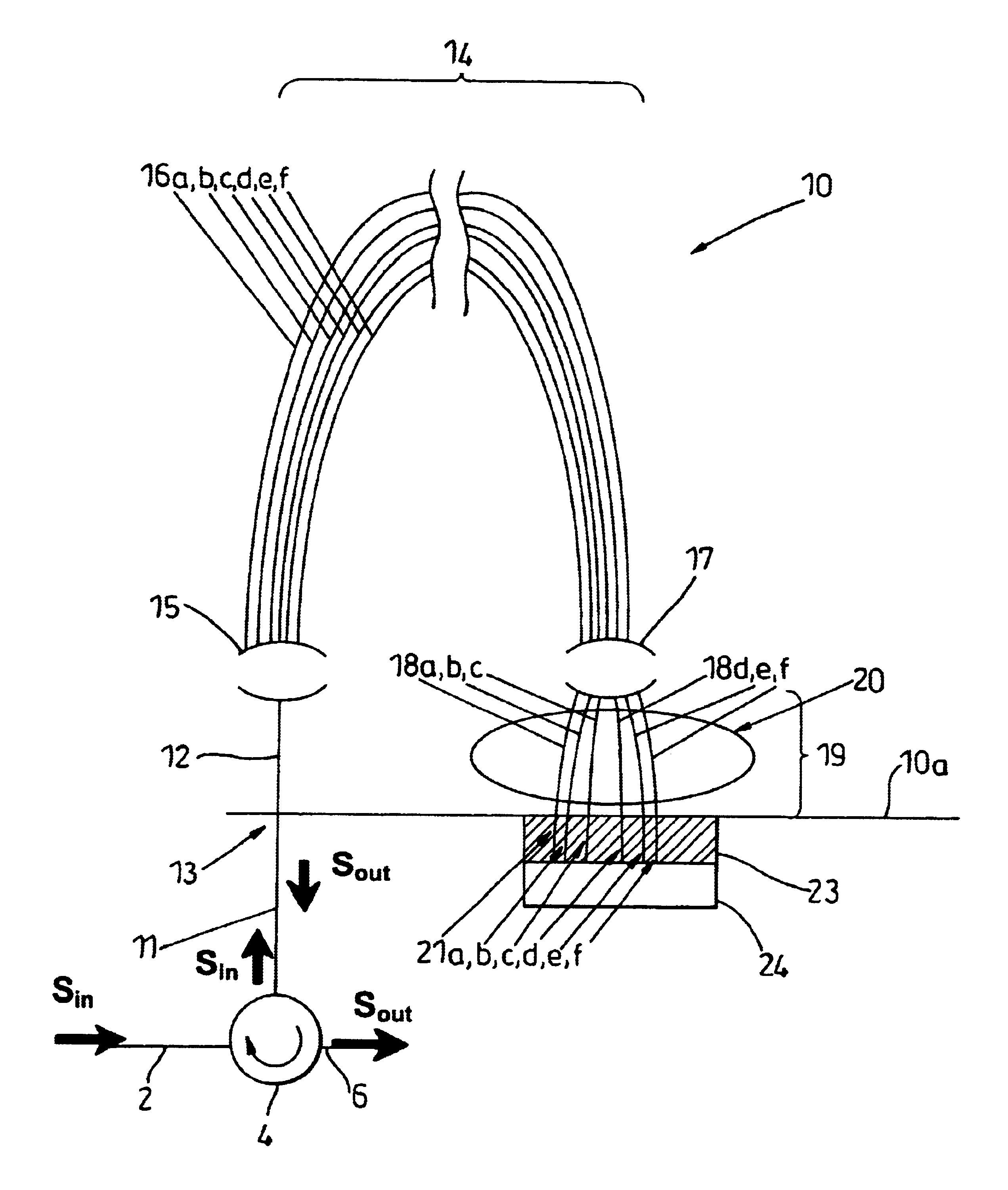
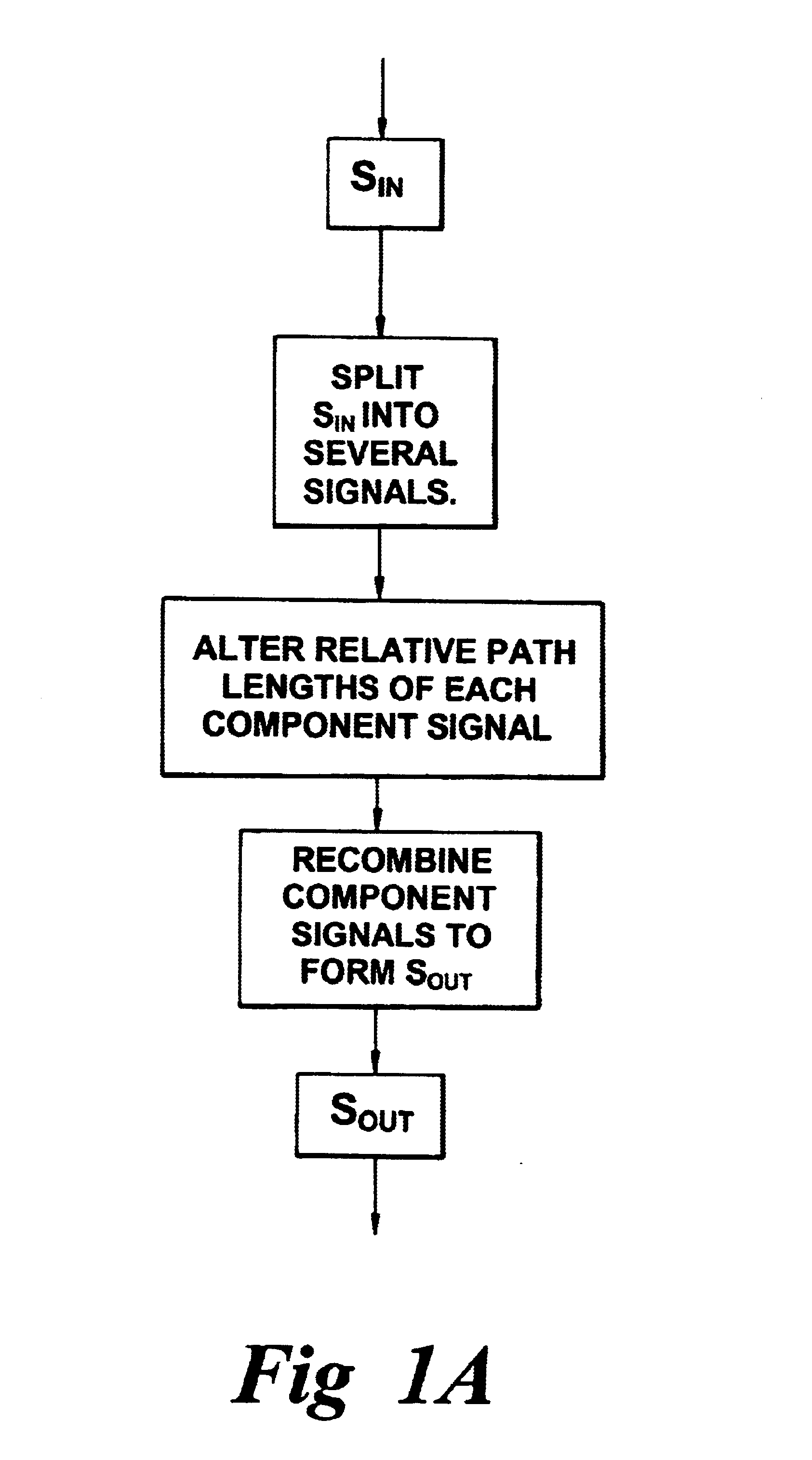
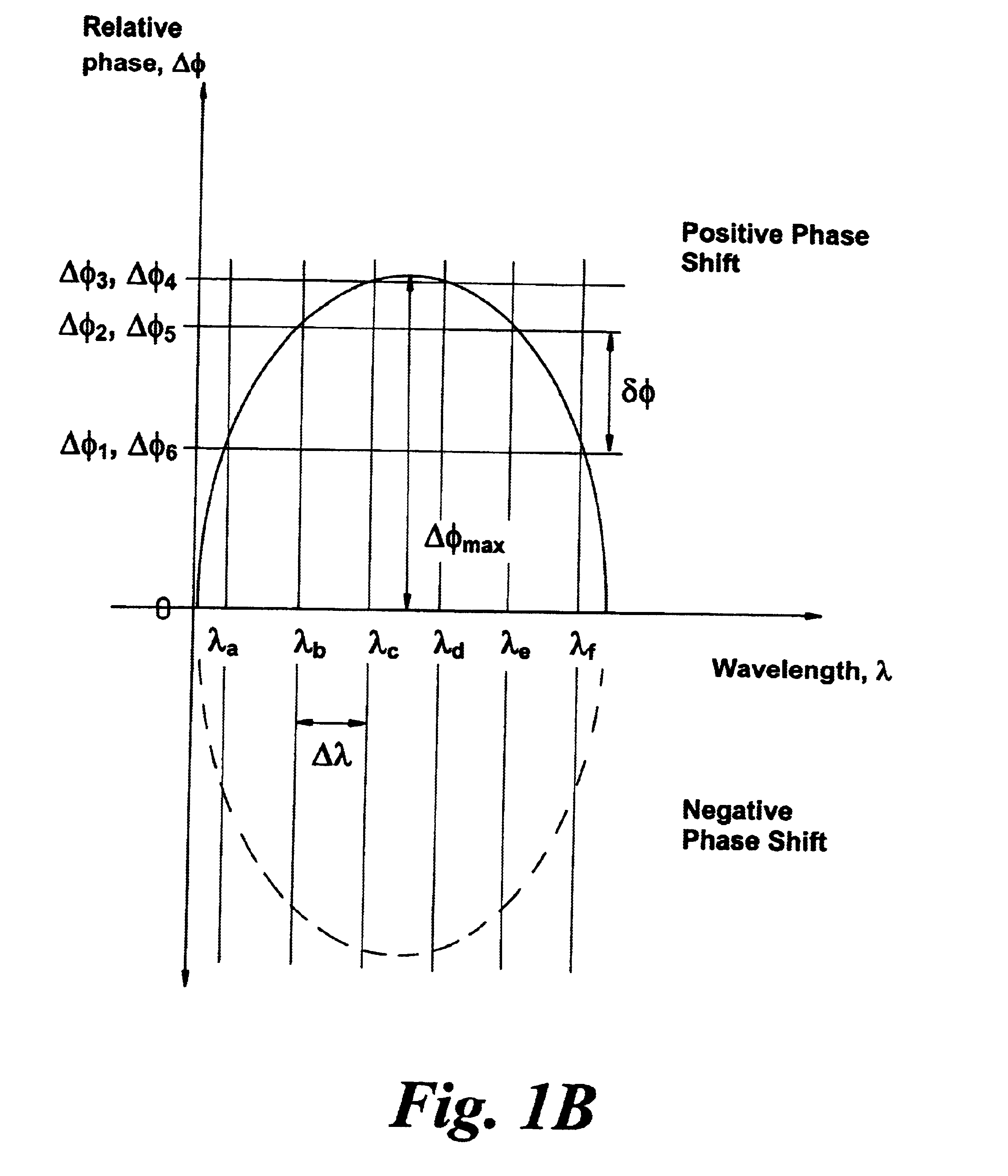
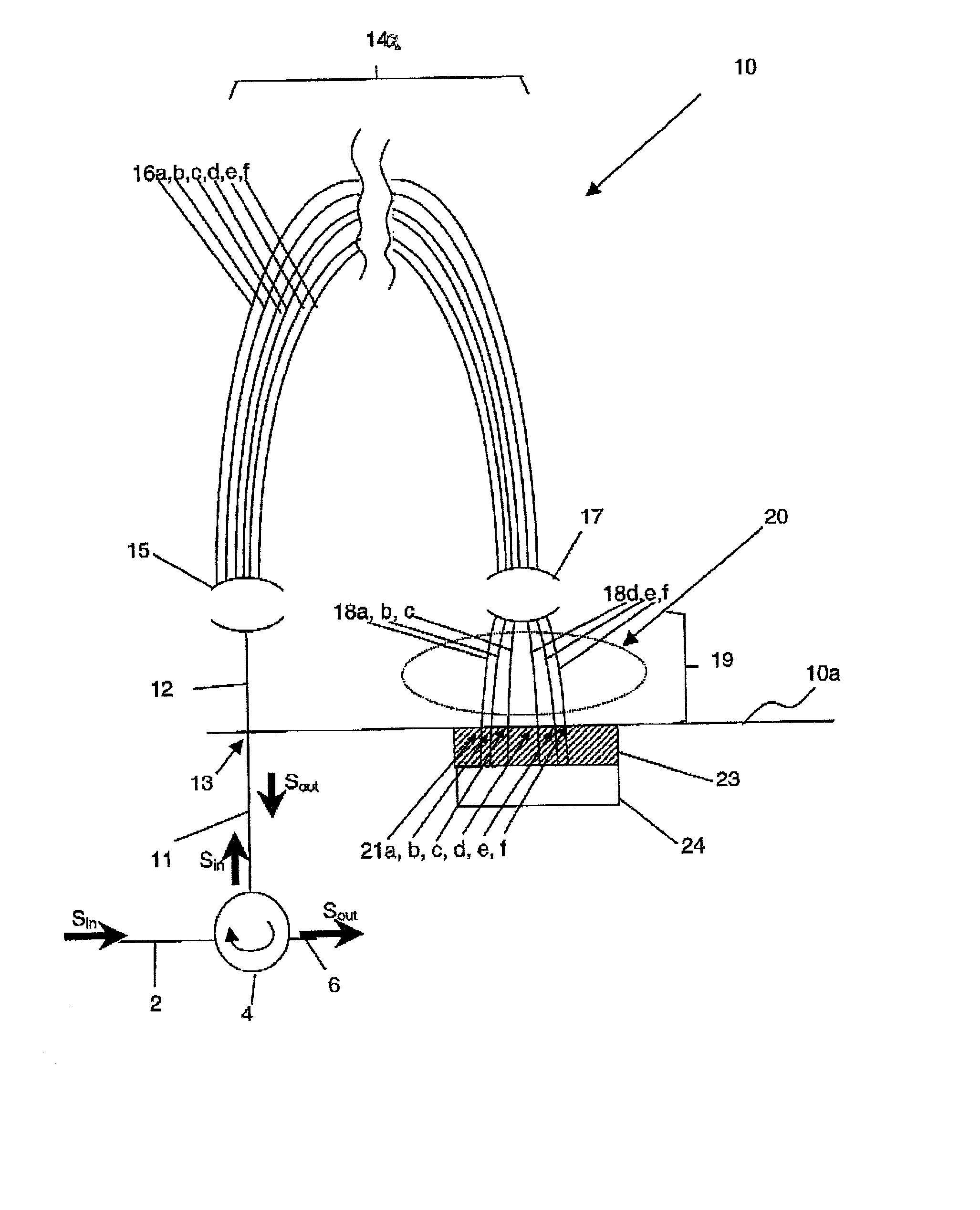
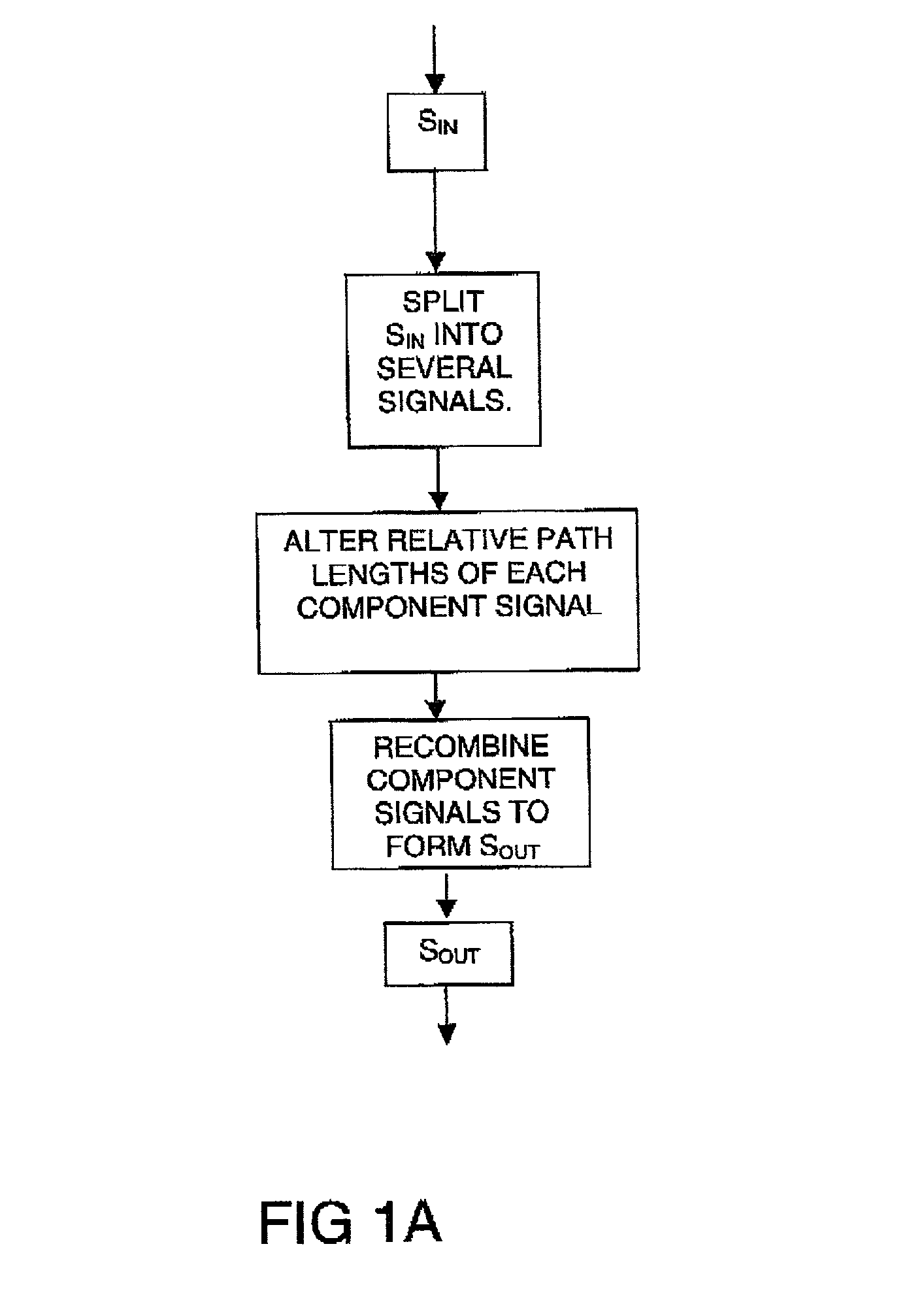
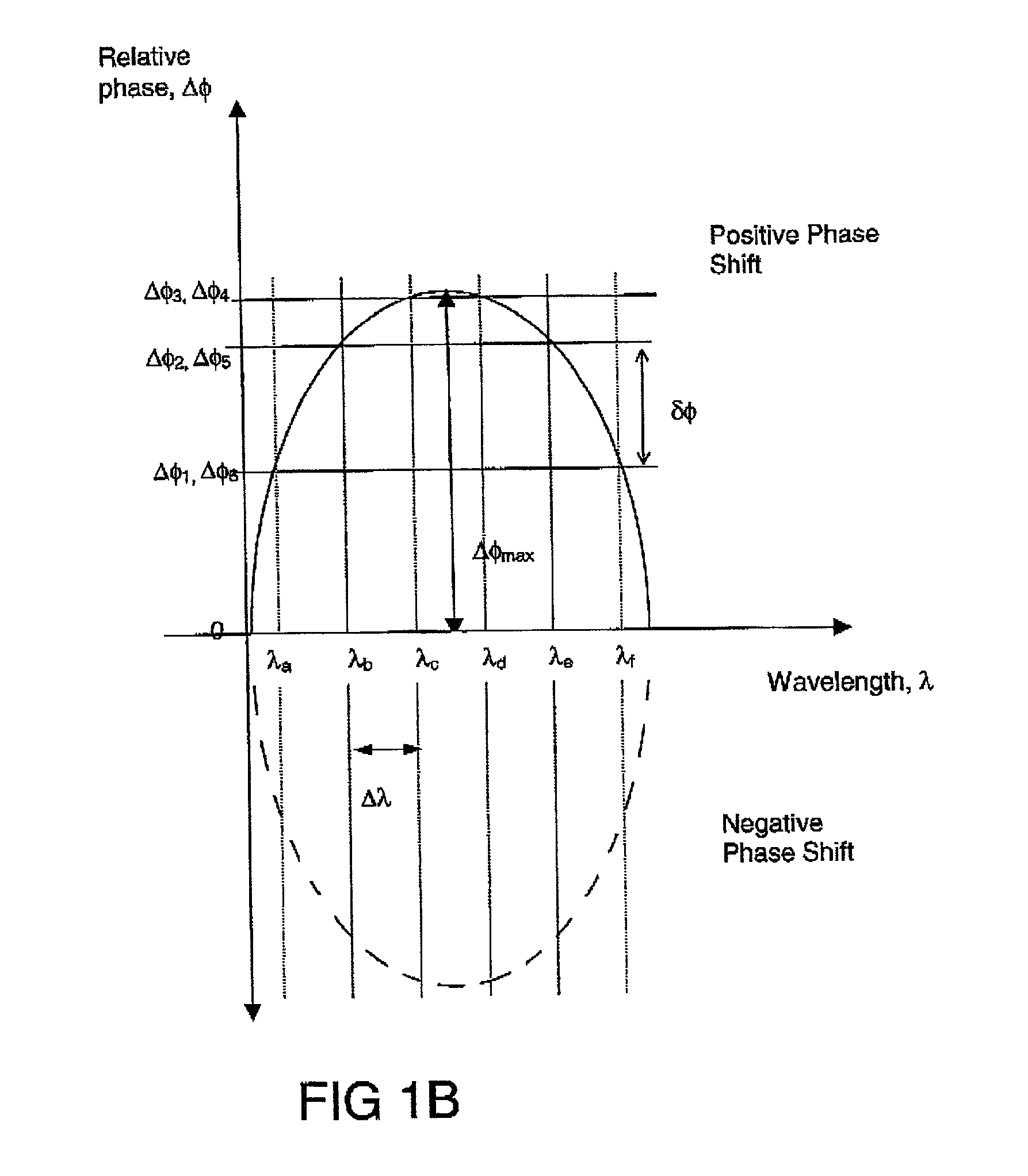
A planar dispersion compensator for an optical signal is provided. The compensator decomposes an inputted optical signal into N component signals separated by a fractional wavelength deltalambda. Each component signal has its path-length adjusted to induce a sufficient phase shift between input and output to change the group delay of the optical signal when recombined from each of the component signals. In this manner, pulse broadening can be compensated by selectively varying the induced phase shifts to produce the desired level of opposite group delay.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Planar waveguide dispersion compensator
A planar dispersion compensator for an optical signal is provided. The compensator decomposes an inputted optical signal into N component signals separated by a fractional wavelength deltalambda. Each component signal has its path-length adjusted to induce a sufficient phase shift between input and output to change the group delay of the optical signal when recombined from each of the component signals. In this manner, pulse broadening can be compensated by selectively varying the induced phase shifts to produce the desired level of opposite group delay. Portions of the substrate of the planar waveguide are removed to improve thermal responsiveness of the path-length adjustment means.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Planar waveguide dispersion compensator
InactiveUS20020102052A1Coupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePath lengthPulse broadening
A planar dispersion compensator for an optical signal is provided. The compensator decomposes an inputted optical signal into N component signals separated by a fractional wavelength deltalambd. Each component signal has its path-length adjusted to induce a sufficient phase shift between input and output to change the group delay of the optical signal when recombined from each of the component signals. In this manner, pulse broadening can be compensated by selectively varying the induced phase shifts to produce the desired level of opposite group delay. Portions of the substrate of the planar waveguide are removed to improve thermal responsiveness of the path-length adjustment means.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Ultrasonic guided wave propagation mechanism and detection method of defects in resin-based plywood with sudden change in thickness
InactiveCN102288683AHigh precisionSuppression of guided wave dispersion effectsProcessing detected response signalUltrasound attenuationElement model
The invention relates to an ultrasonic guided wave propagation mechanism and a detection method for defects in a resin-based plywood with a sudden change in thickness. The present invention adopts the finite element method to establish a dynamic finite element model of the resin-based plywood with a sudden change in thickness, and studies the propagation mechanism of the ultrasonic guided wave and the action mechanism between the ultrasonic guided wave and the defect in the resin-based plywood with a sudden change in thickness through the model. , proposed an ultrasonic guided wave inspection method for internal defects of resin-based plywood based on a dynamic finite element model with sudden changes in thickness. The ultrasonic guided wave dynamics finite element model can predict the ultrasonic guided wave signal at any point in the laminate, and the defect reflection echo signal can be extracted from the received signal, so that the size and position of the defect in the resin-based laminate with a sudden change in thickness can be analyzed information. In order to accurately predict the defect signal, the attenuation model of the composite plate is added to the established finite element model, and the optimized guided wave excitation technology is used to suppress the dispersion effect and mode conversion effect of the guided wave, which improves the accuracy of the detection method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Systems and methods for fiber optic parametric amplification and nonlinear optical fiber for use therein
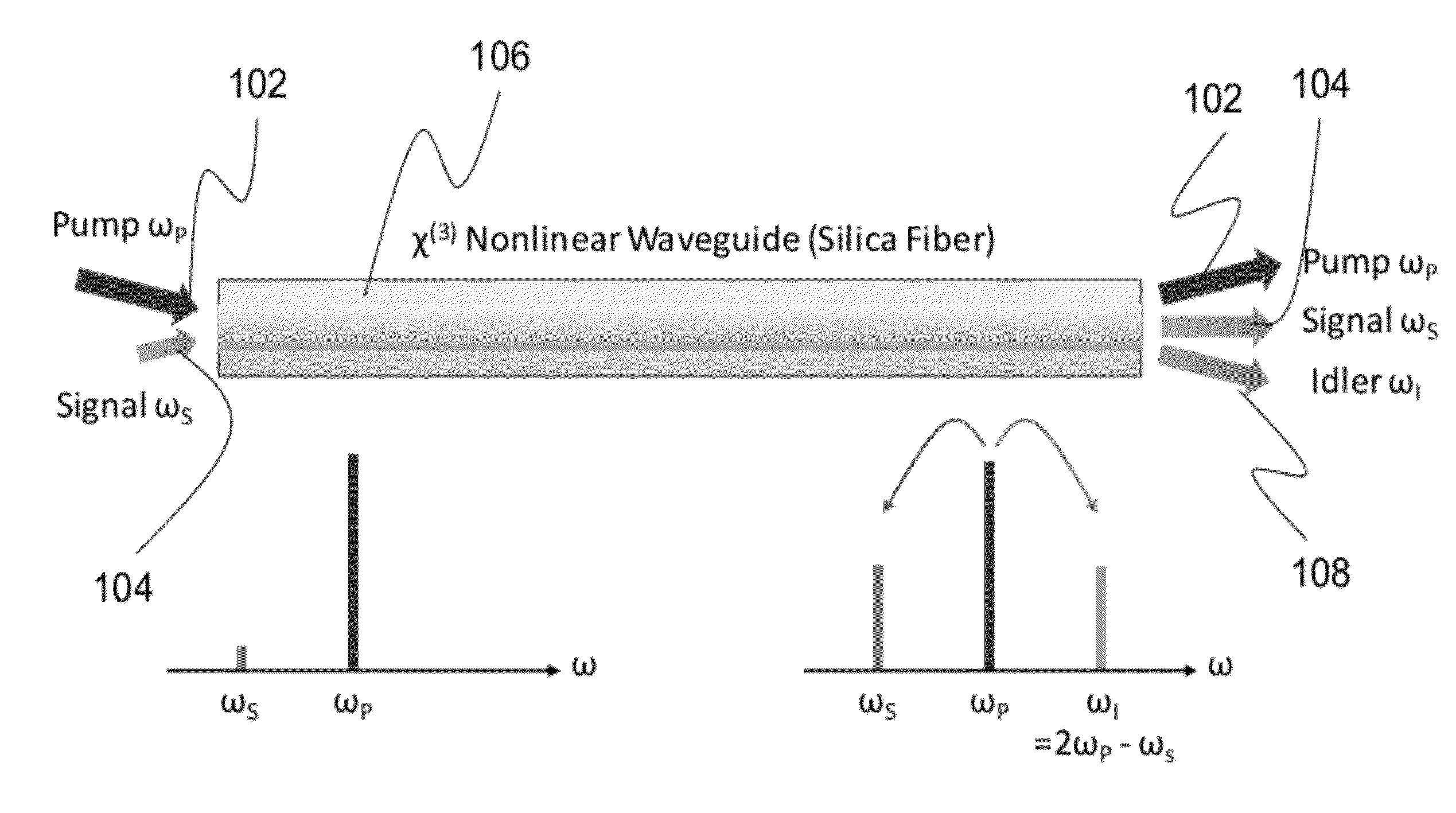
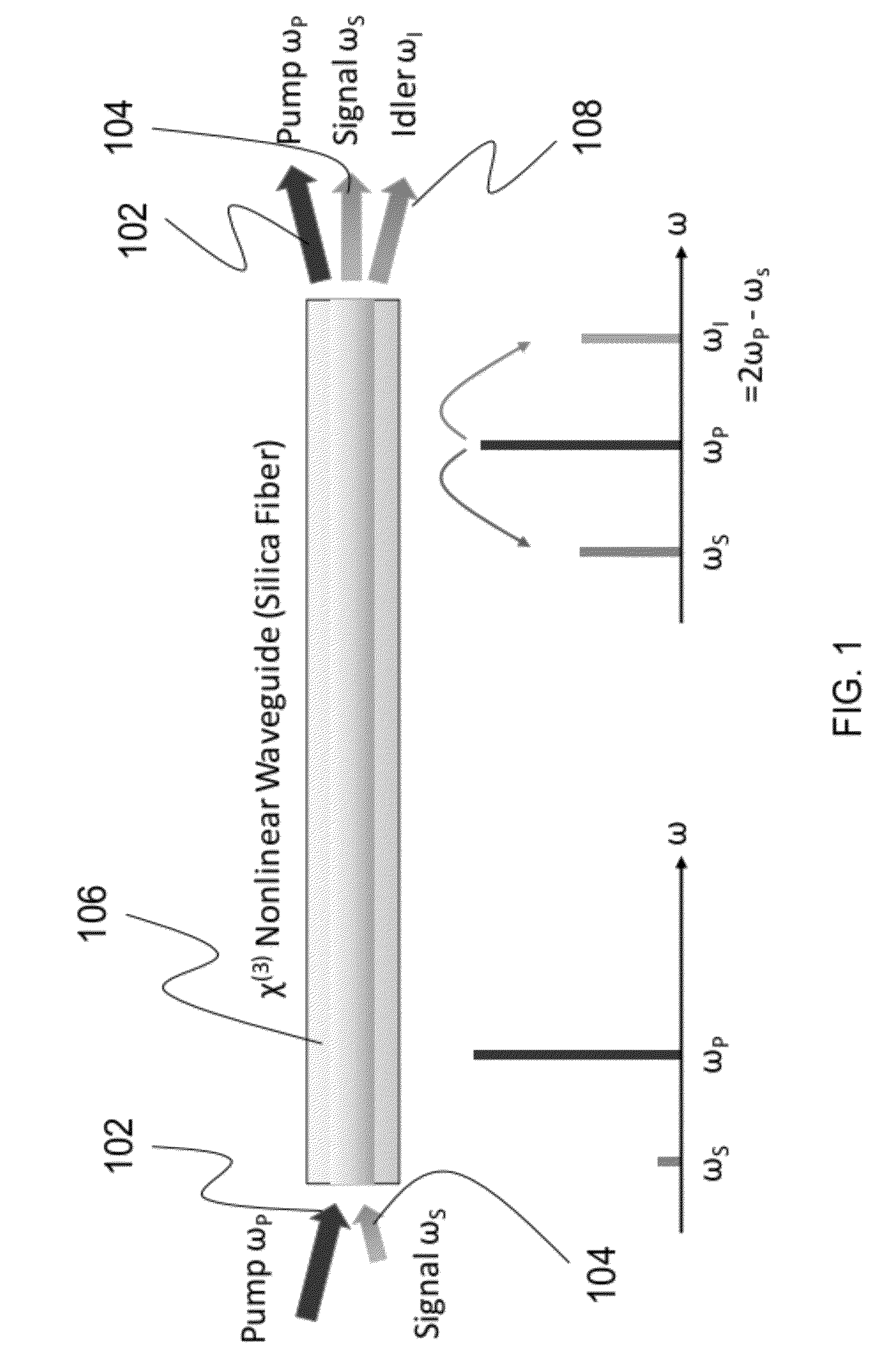
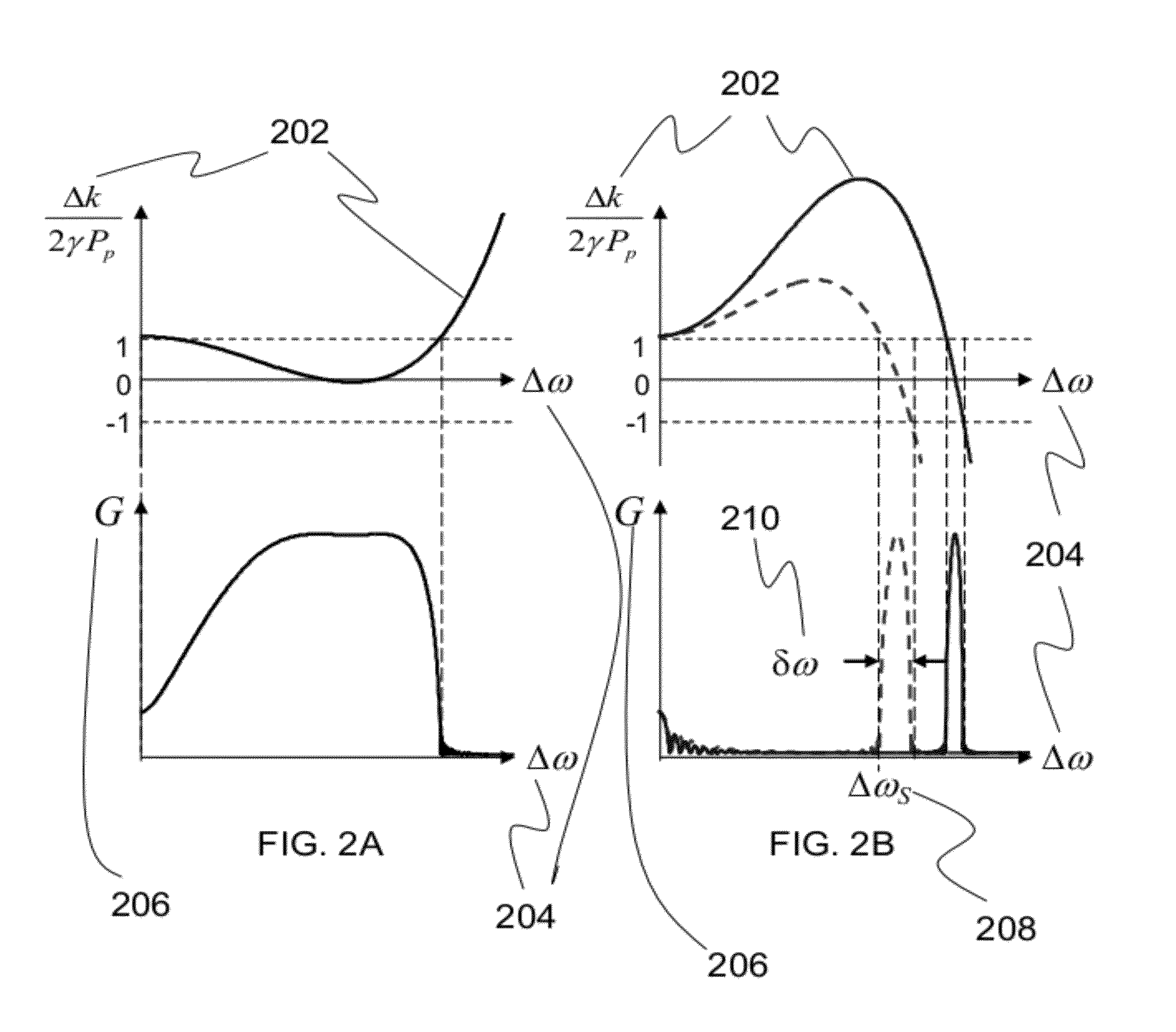
ActiveUS8482847B2Precise physical propertySlow changeLaser detailsSpectrum investigationFiber optical parametric amplifierLight source
A high confinement nonlinear optical fiber is provided along with methods of parametric amplification for use thereof. The nonlinear optical fiber may include a plurality of concentric layers which are configured to provide different guiding regimes to low-frequency and high-frequency components through transverse geometry and refractive index profiling, thus reducing waveguide dispersion. The resulting optical fiber provides a parametric device with phase-matching in any spectral region of interest, such that a fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) implementing the optical fiber can amplify in any spectral window of interest. A narrow-band FOPA configured to minimize phase mismatching is also provided for use with the optical fiber, and may be implemented as a light source or a monochromator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Long-distance micro/nano-core glass optical fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103011607AStructural size controllableHigh precisionGlass making apparatusHost materialRefractive index
The invention provides a long-distance micro / nano-core glass optical fiber and a preparation method thereof. The invention mainly comprises the aspects of optical fiber matrix material, rare-earth doping, refringence of core wrap, dimensions of core wrap, casing, multistep stretching method and the like. The micro / nano-core glass optical fiber has the characteristics of low optical loss, large-proportion evanescent wave transmission, large waveguide dispersion and the like. The preparation method has the advantages of high accuracy, controllable structural dimensions and the like, and can be used for preparing long-distance micro / nano-core glass optical fibers. The invention can be well applied to design and preparation of long-distance micro / nano-core glass optical fibers, and provides a feasible design and preparation technique of a long-distance micro / nano-core glass optical fiber.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Novel wideband dielectric loaded gyro traveling wave tube high frequency system
ActiveCN107591306AFix workSolve power problemsTransit-tube coupling devicesDielectricLinear amplification
The invention discloses a novel wideband dielectric loaded gyro traveling wave tube high frequency system, and belongs to the technical field of microwave, millimeter wave and terahertz devices. The system comprises pre-bunching section, a linear amplification section, a nonlinear amplification section and an output gradual change section which are sequentially connected, and is characterized in that the pre-bunching section, the linear amplification section, the nonlinear amplification section and the output gradual change section comprise a metal circular waveguide shell and an annular lossless dielectric loading waveguide which is loaded in a mode of attaching to the circular waveguide inner wall, the linear amplification section is uniformly provided with rectangular lossy dielectric pieces in the angular direction, and the lossy dielectric pieces are distributed in a periodic manner along the axial direction. Dispersion characteristics of the whole high frequency structure are changed through loading the lossless dielectric waveguide, an electron beam curve and a waveguide dispersion curve are enabled to meet resonance conditions within a wide frequency band range, and wideband operating characteristics are ensured; and meanwhile, a gradually changing output structure is adopted, so that a problem of low output power brought about by low gain of a high frequency point is solved. The system disclosed by the invention not only can meet wideband operating requirements, but also can provide high microwave power output within the frequency band range.
Owner:四川杰诺创科技有限公司
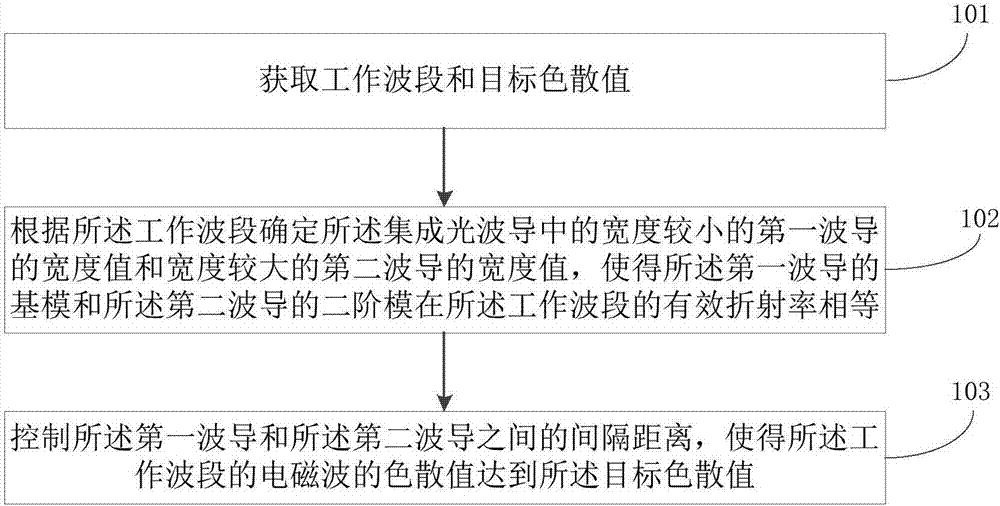
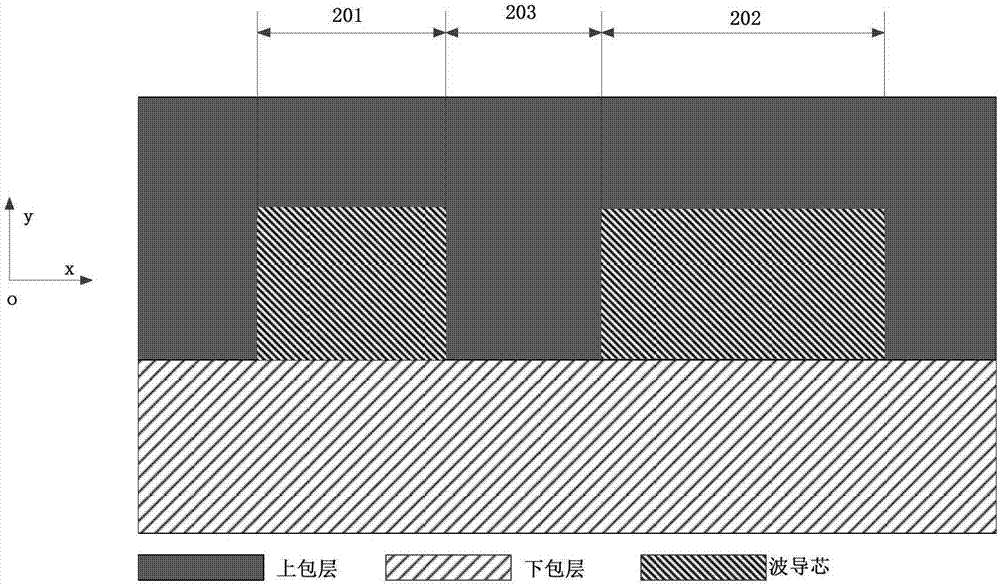
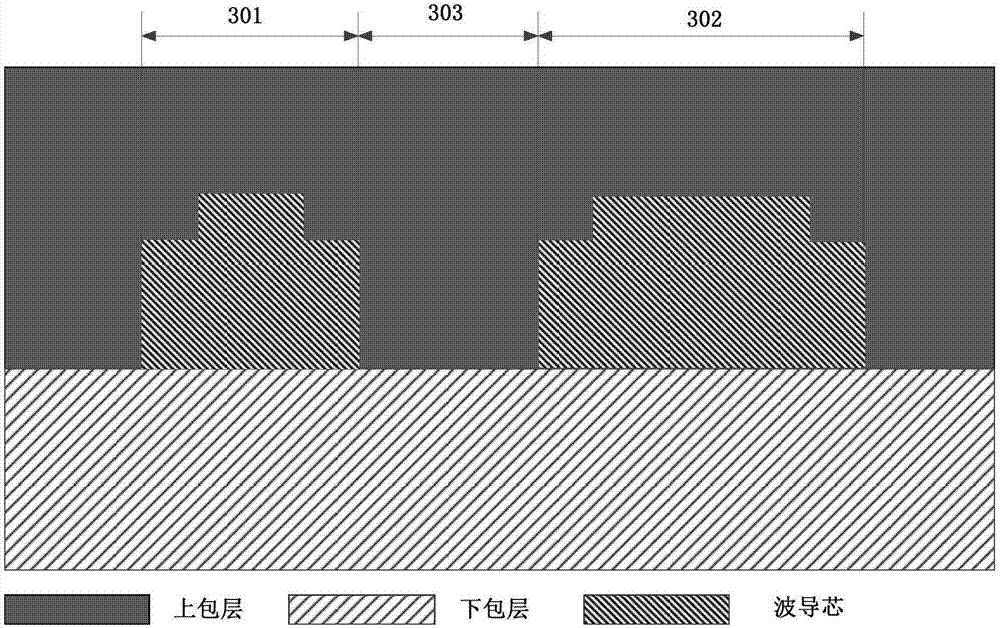
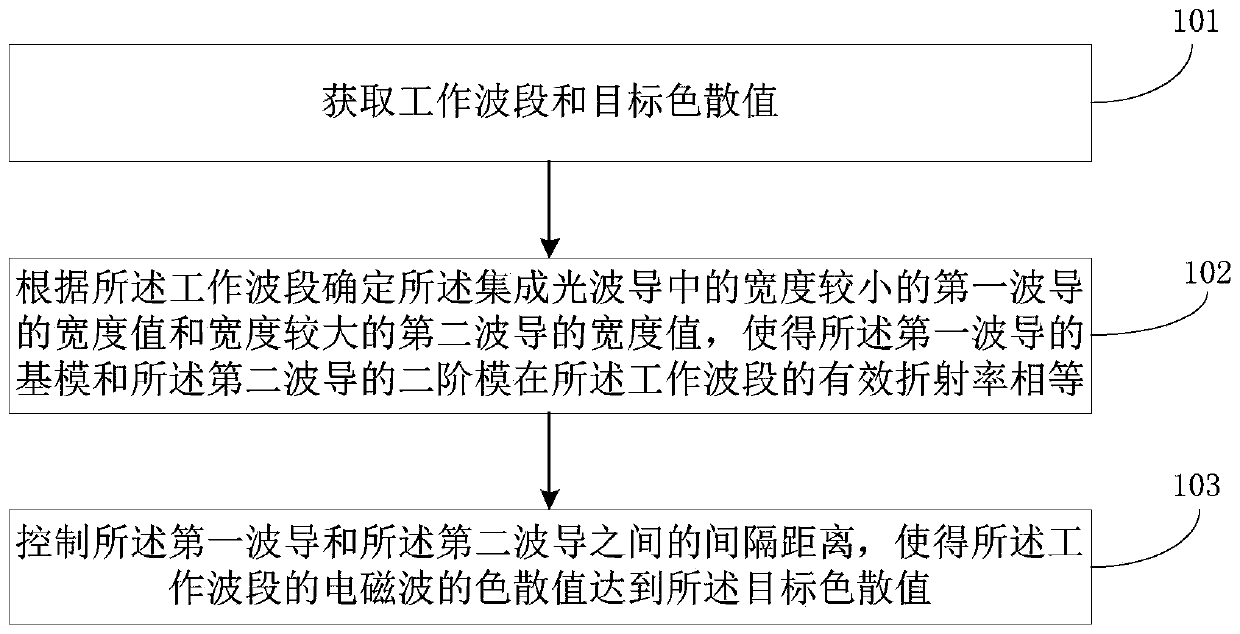
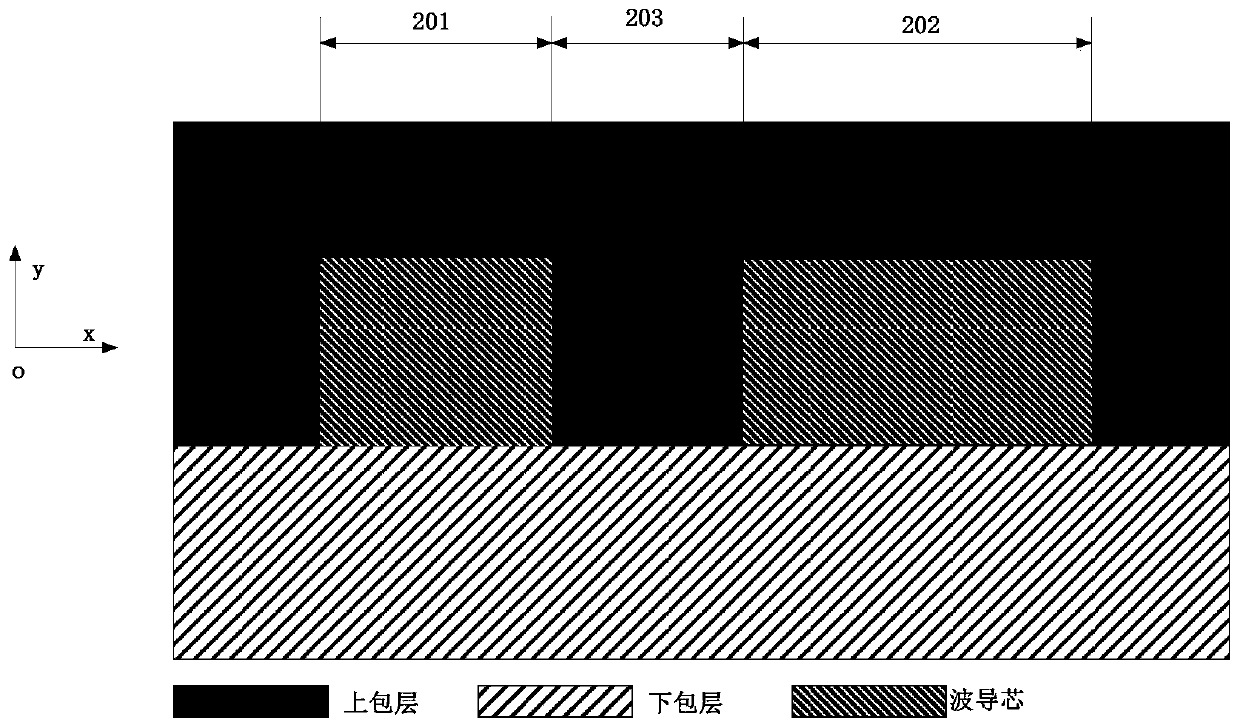
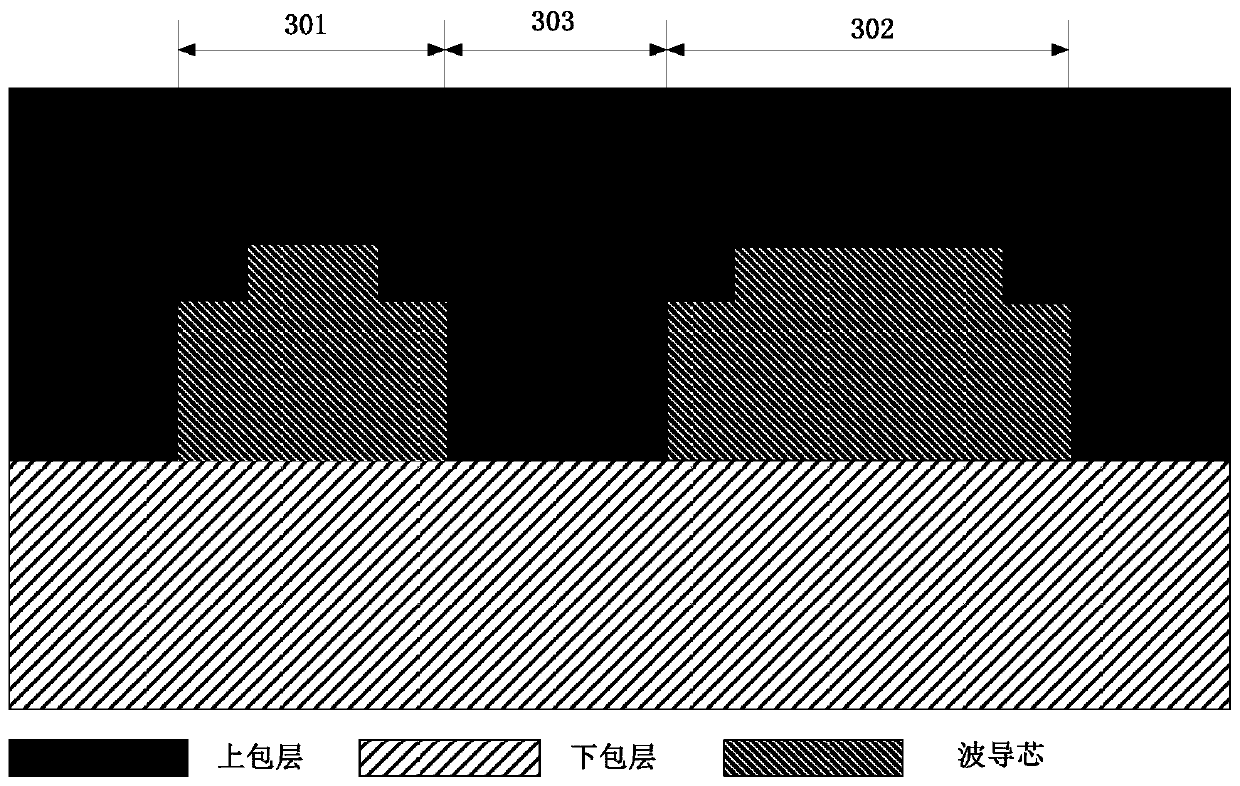
Chromatic dispersion control method for integrated optical waveguide and integrated optical waveguide
The embodiment of the invention discloses a chromatic dispersion control method for an integrated optical waveguide and an integrated optical waveguide. According to the control method, respective width values of a first waveguide and a second waveguide are controlled according to an operating waveband, so that effective refractive indexes of a fundamental mode of the first waveguide and a second-order mode of the second waveguide are equal at the operating waveband; and a coupled chromatic dispersion value reaches a target chromatic dispersion value based on control of the spacing distance between the first waveguide and the second waveguide. On the basis of a mode coupling principle, chromatic dispersion value controlling is realized by adjusting the width space between waveguide cores. Compared with the traditional method for optical waveguide dispersion control based on the waveguide cross section shape and dimension, the chromatic dispersion control method disclosed by the invention has no special requirement on the process and has high compatibility because only the parameters of the integrated optical waveguide at the width dimension need to be adjusted. The chromatic dispersion control method can be applied to most of application occasions including the technical field of fables design.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
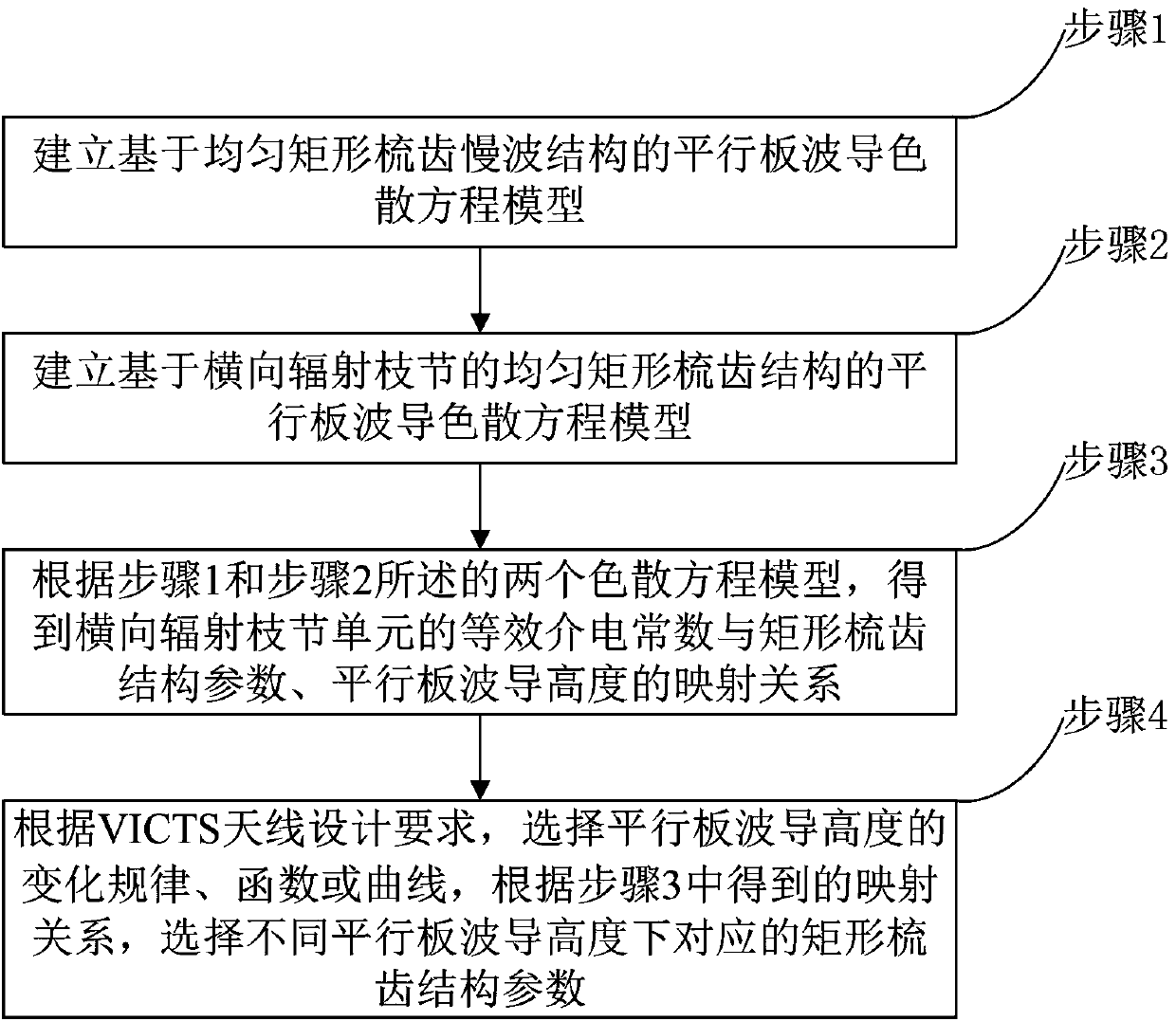
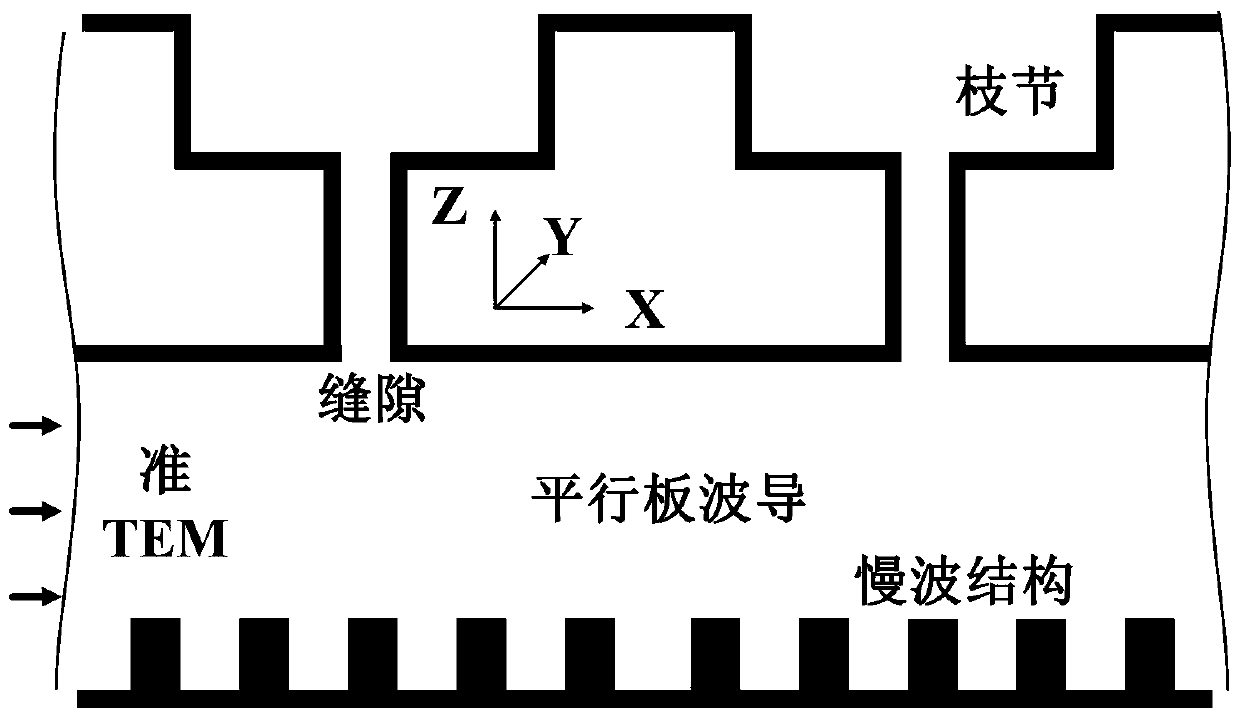
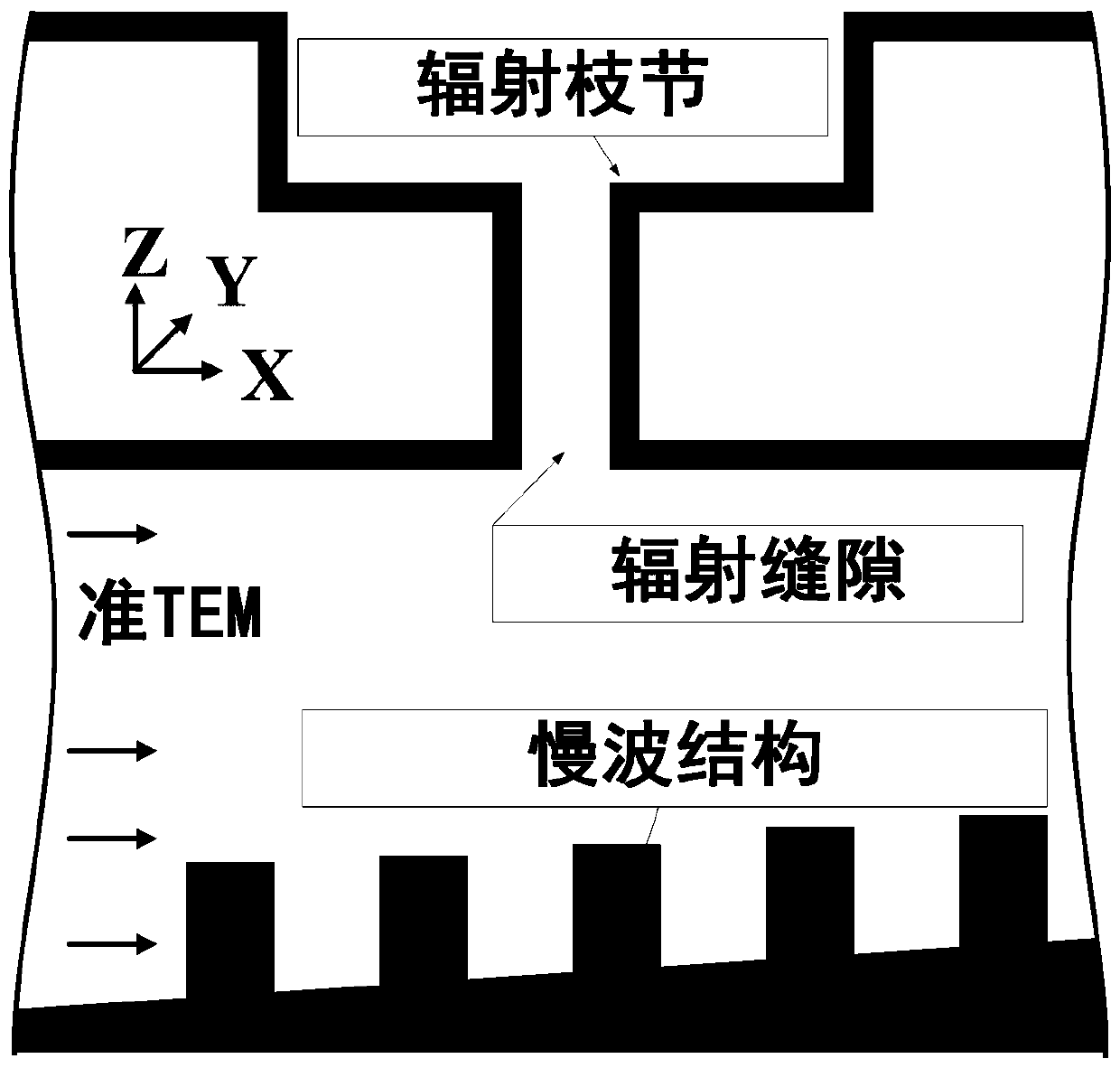
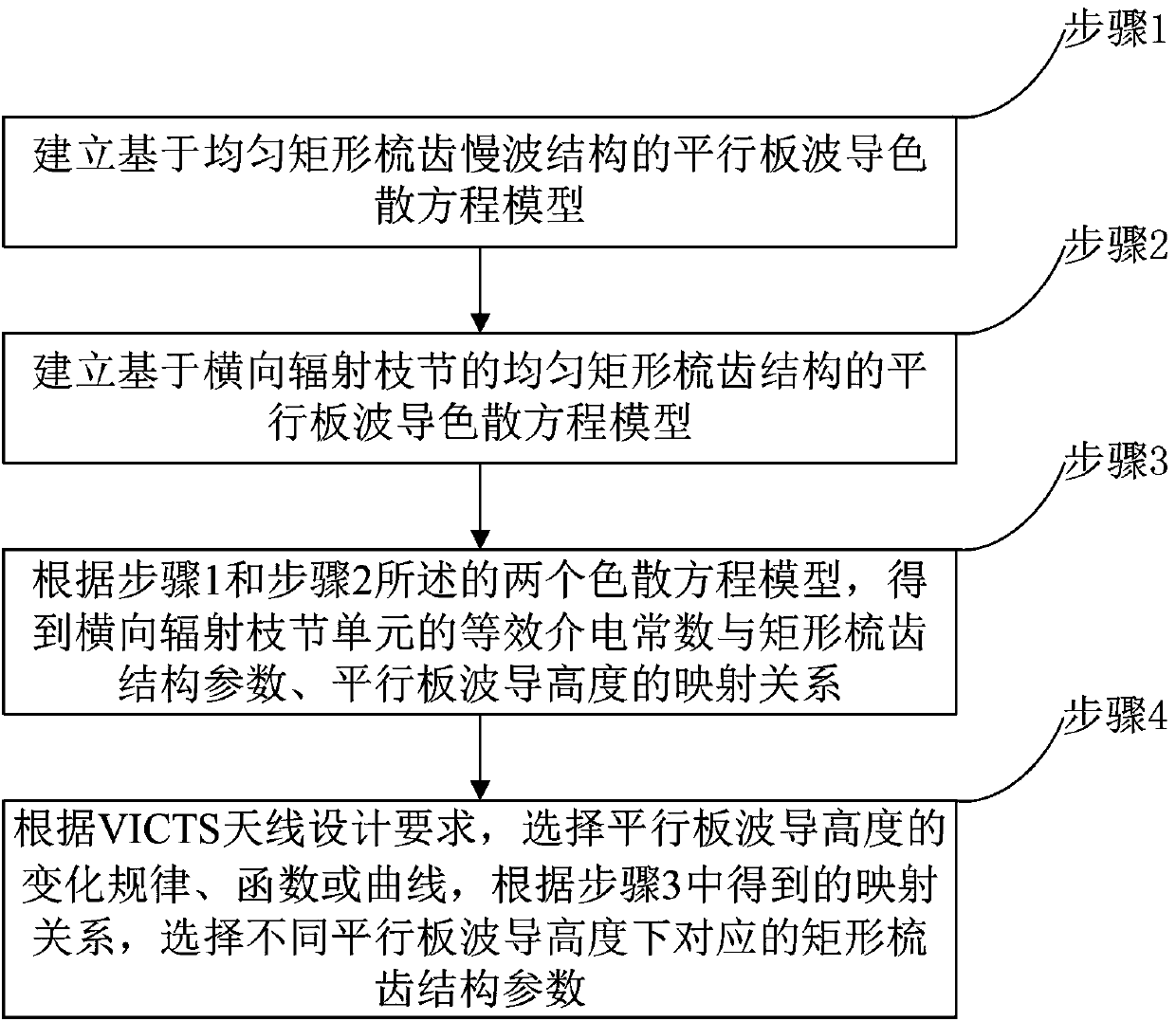
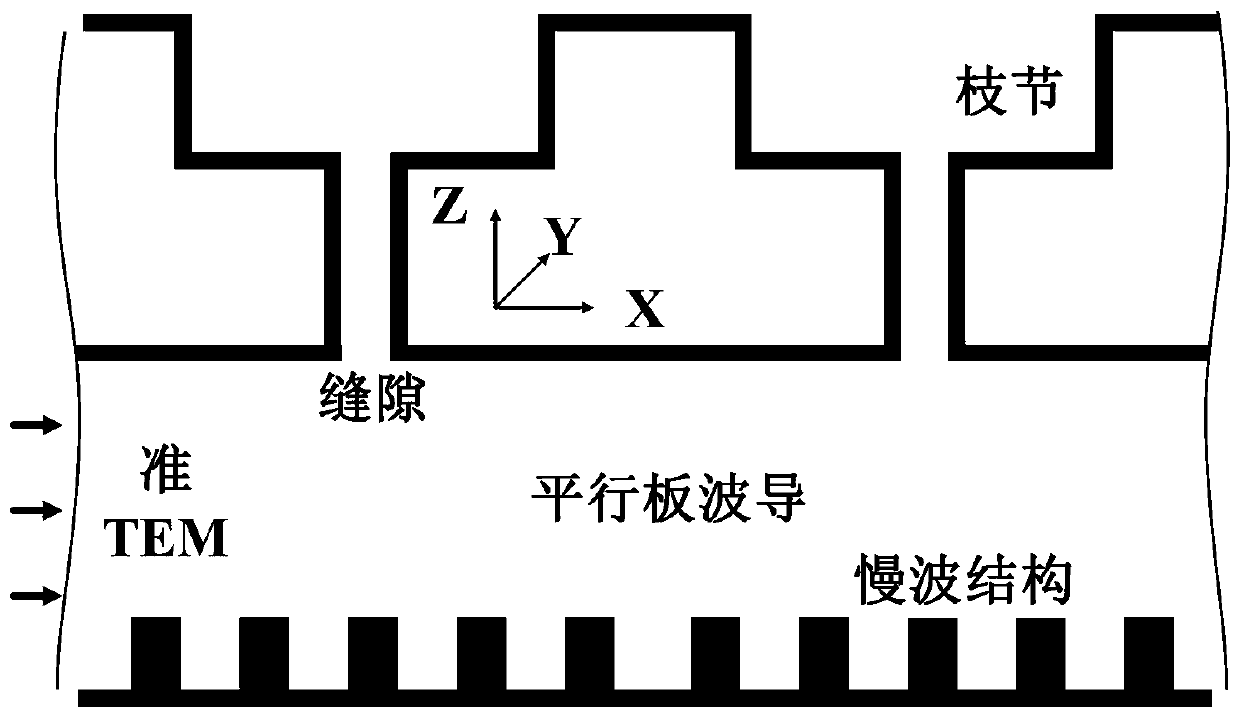
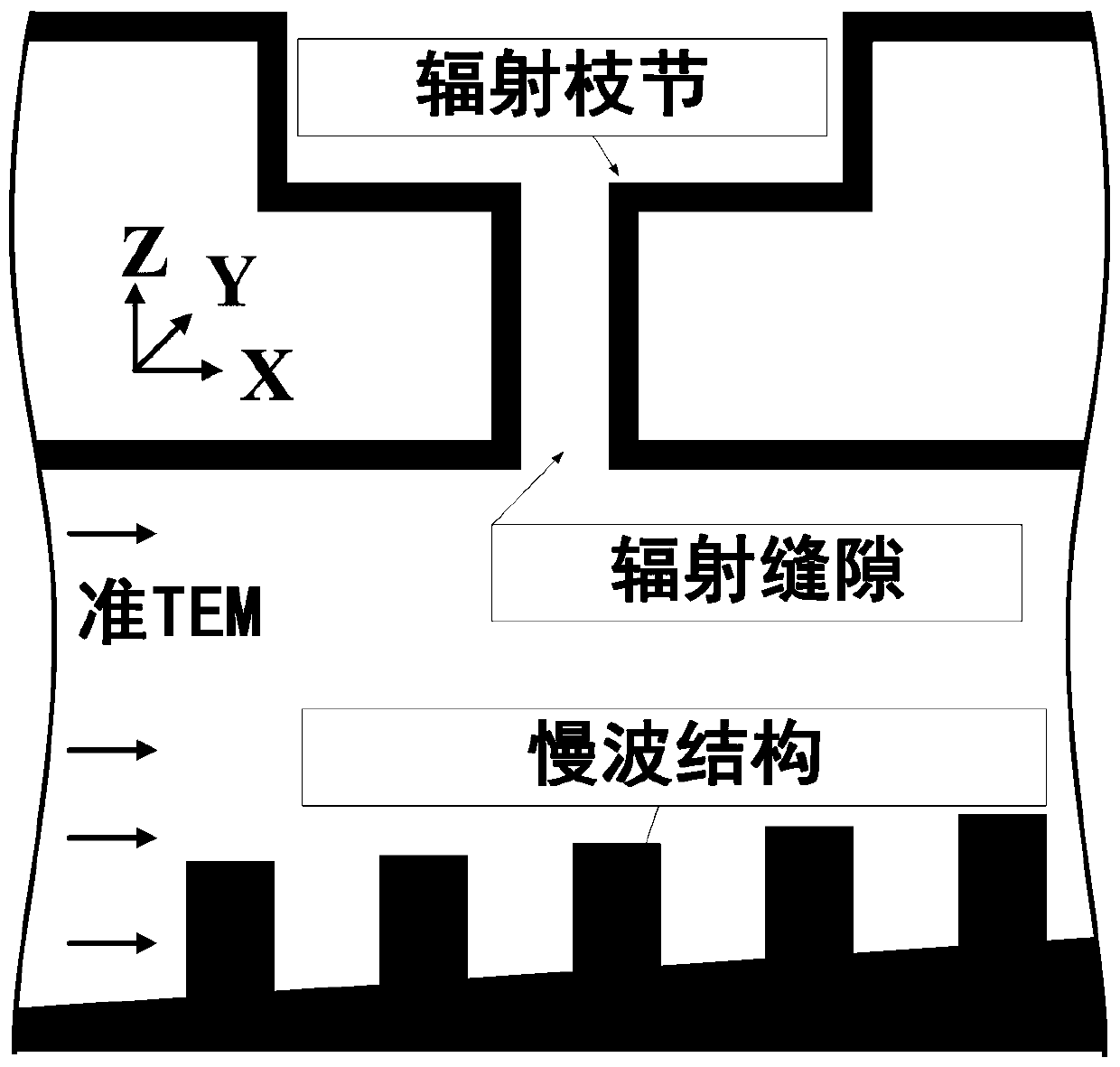
Method for designing slow wave structure of CTS antenna and VICTS antenna
ActiveCN108073770AImprove radiation efficiencySidelobe level does not deteriorateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAntenna designWave structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication antennas, and particularly relates to a method for designing a slow wave structure of a CTS antenna and a VICTS antenna. Firstly, a parallel plate waveguide dispersion equation model based on a uniform rectangular comb tooth slow wave structure is established to establish a parallel-plate waveguide dispersion equation model with a uniform rectangular comb tooth structure based on horizontal radiation branching; according to the two dispersion equation models, obtaining a mapping relationship between an effective dielectricconstant of a horizontal radiation branching unit and rectangular comb tooth structure parameters and the height of a parallel plate waveguide; finally according to the VICTS antenna design requirements, choosing a variation rule, function or curve of the height of the parallel plate waveguide, and according to the obtained mapping relationship, selecting the corresponding rectangular comb toothstructure parameters under different parallel plate waveguide heights. According to the method for designing the slow wave structure of the CTS antenna and the VICTS antenna, by the nonlinear design on rectangular comb teeth which are of the slow wave structure in the VICTS antenna, while array optimization is achieved, it is ensured that parameters such as the gain of the antenna and the standing-wave ratio do not deteriorate or even are improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU +1
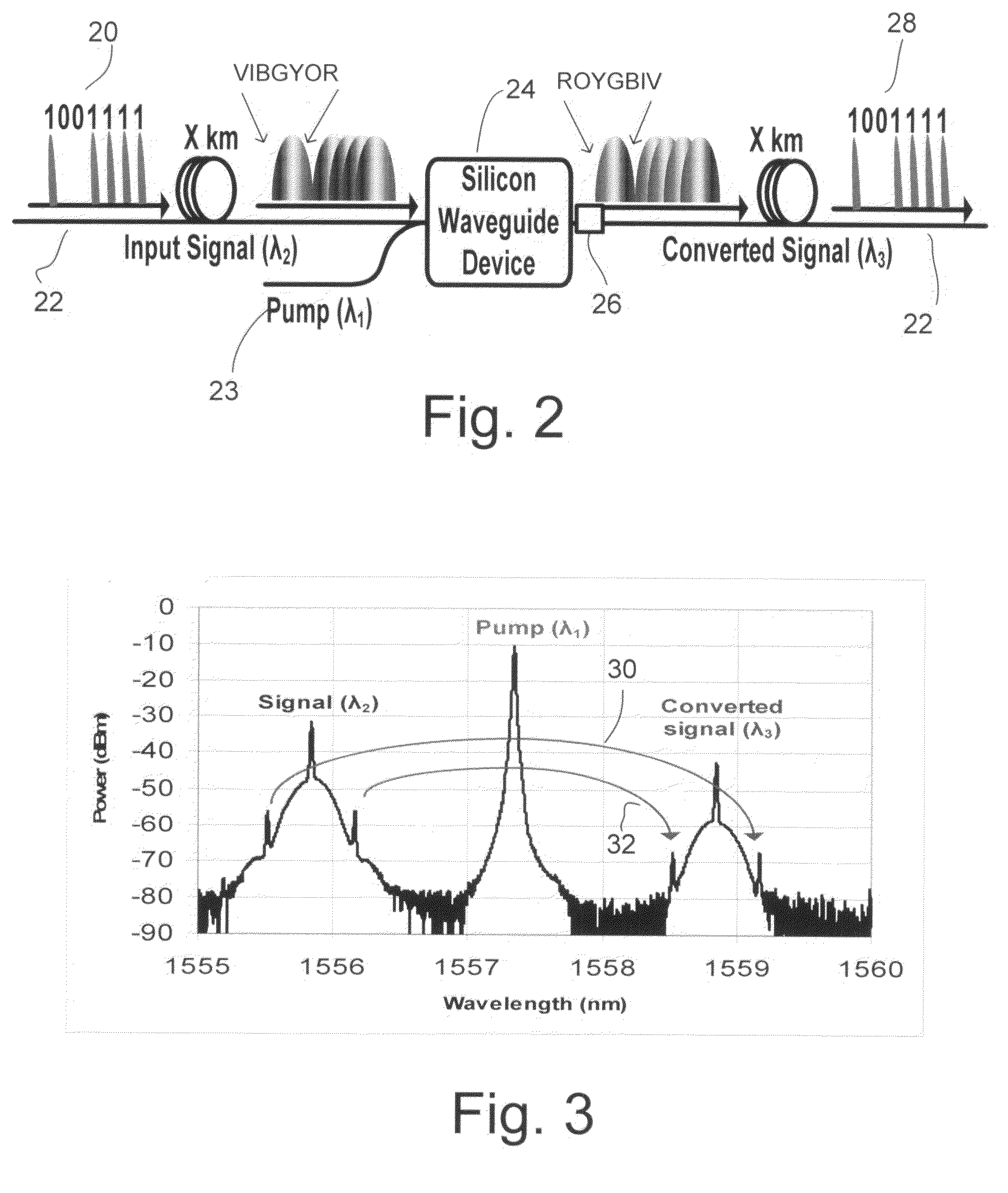
Silicon waveguide dispersion compensator using optical phase conjugation
InactiveUS20080240651A1Coupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionOptical phase conjugationWaveguide
In the absence of using any chromatic dispersion compensation technique, it may be difficult to detect the transmitted data over long distances at the receiving end. Embodiments utilize the optical phase conjugation (OPC) property in silicon waveguides to compensate chromatic dispersion effect in optical fibers.
Owner:RONG HAISHENG +2
Impulse optical spectrometer based on optical fiber dispersion and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101464189AIncrease the sampling intervalImprove spectral resolution dataSpectrum investigationCoupling light guidesAcousto-optical spectrometerFiber chromatic dispersion
The invention discloses a pulse spectrograph based on optical fiber dispersion and a measuring method thereof. A section of optical fiber characterized by large material dispersion and small mode dispersion and waveguide dispersion is taken as a spectrum light-splitting device with a simple optical system and no adjustable mechanism; and the spectral resolution can be adjusted by changing the length of the optical fiber or the sampling time interval of a data acquisition system. By utilizing a simplex photodetector to measure spectrum without a scanning mechanism, the spectrograph has the advantages of simple structure, good measuring consistency, and low requirements for working conditions. The invention is applicable to the measurement of the spectrums of pulsed light signals, such as pulsed laser fluorescence spectrum measurement, pulsed laser Raman spectral measurement and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Design method of slow wave structure of cts antenna and victs antenna
ActiveCN108073770BImprove radiation efficiencySidelobe level does not deteriorateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAntenna designWave structure
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite communication antennas, and particularly relates to a method for designing a slow wave structure of a CTS antenna and a VICTS antenna. Firstly, a parallel plate waveguide dispersion equation model based on a uniform rectangular comb tooth slow wave structure is established to establish a parallel-plate waveguide dispersion equation model with a uniform rectangular comb tooth structure based on horizontal radiation branching; according to the two dispersion equation models, obtaining a mapping relationship between an effective dielectricconstant of a horizontal radiation branching unit and rectangular comb tooth structure parameters and the height of a parallel plate waveguide; finally according to the VICTS antenna design requirements, choosing a variation rule, function or curve of the height of the parallel plate waveguide, and according to the obtained mapping relationship, selecting the corresponding rectangular comb toothstructure parameters under different parallel plate waveguide heights. According to the method for designing the slow wave structure of the CTS antenna and the VICTS antenna, by the nonlinear design on rectangular comb teeth which are of the slow wave structure in the VICTS antenna, while array optimization is achieved, it is ensured that parameters such as the gain of the antenna and the standing-wave ratio do not deteriorate or even are improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU +1
Terahertz porous fiber evanescent wave sensing device
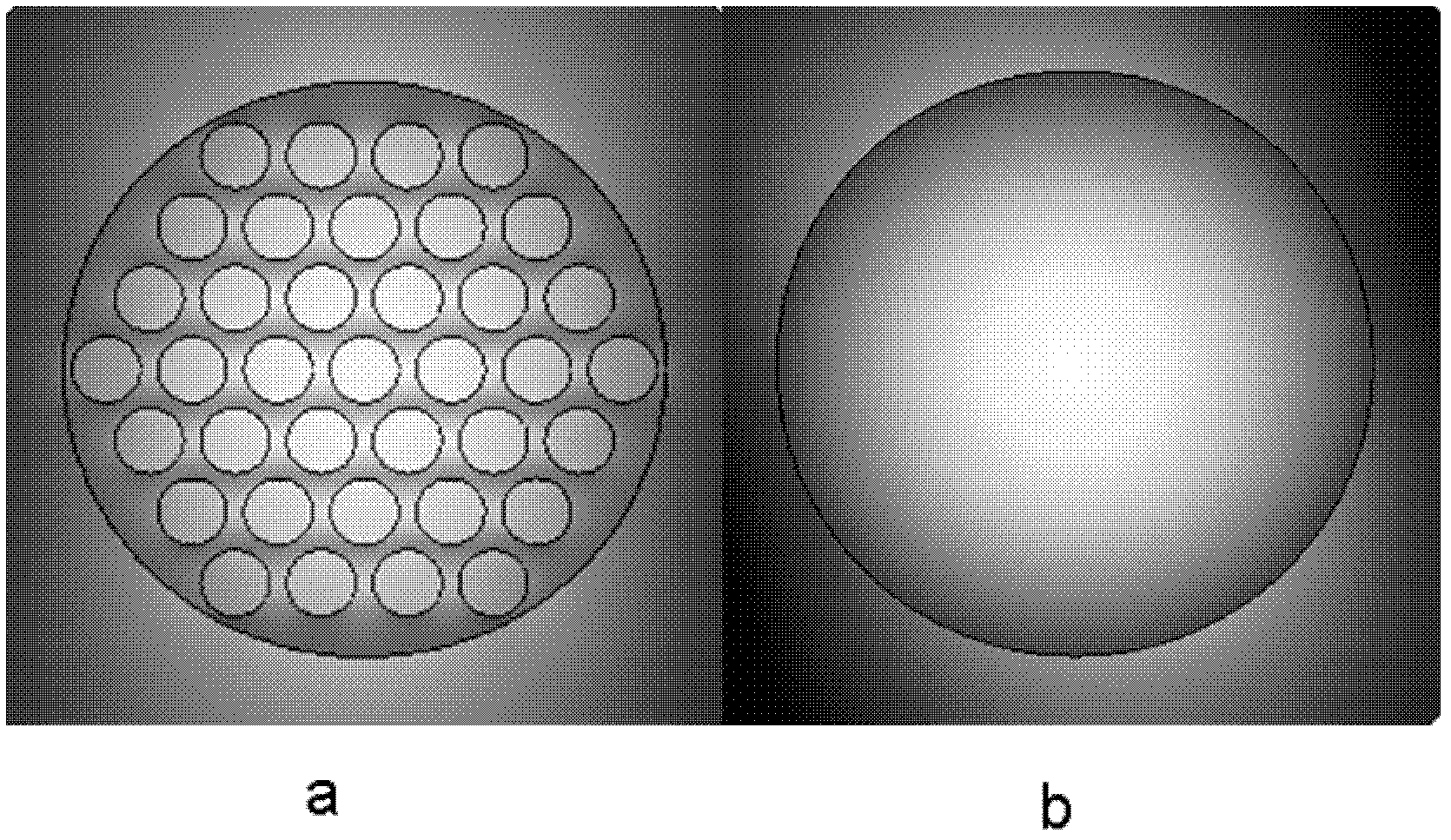
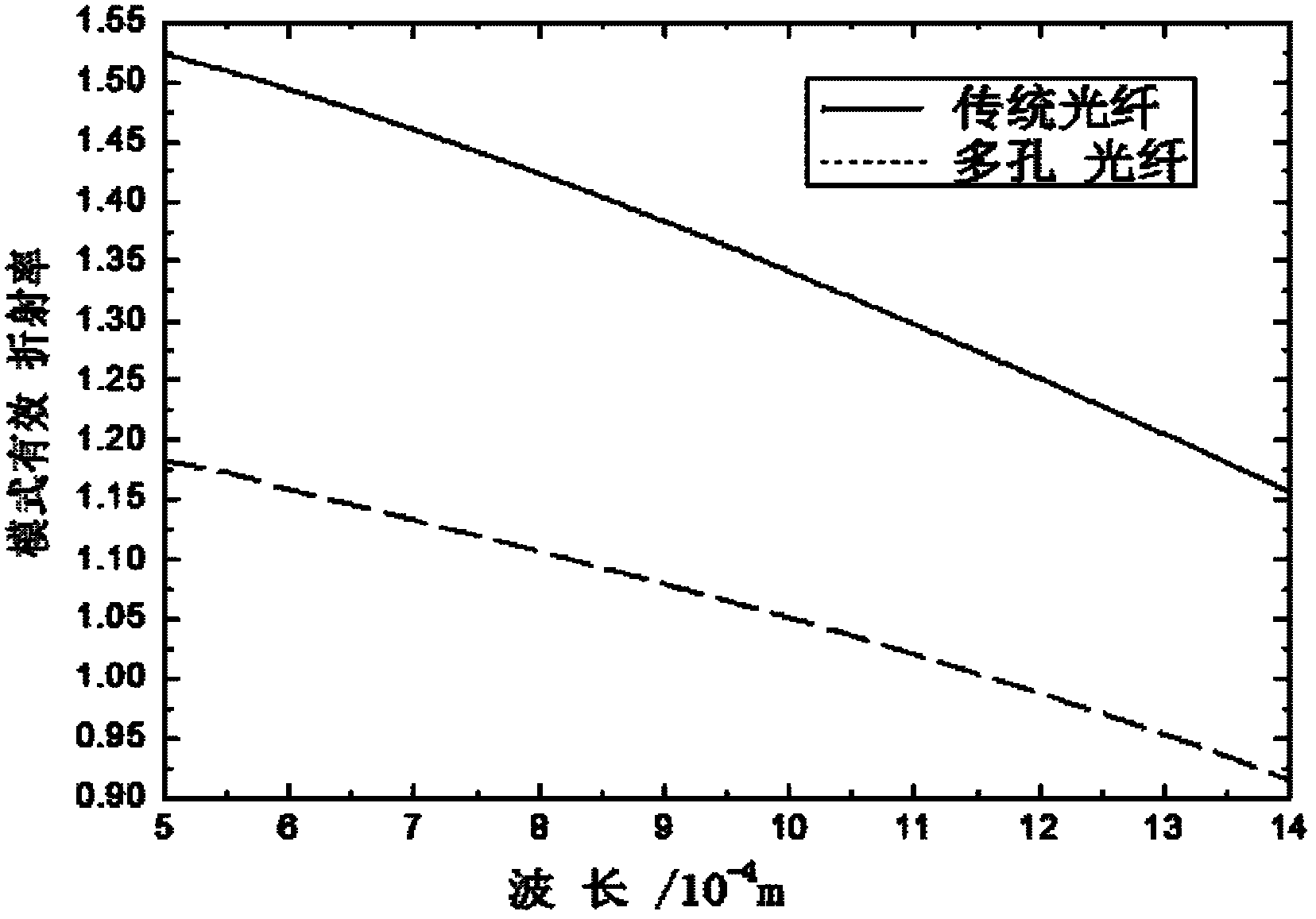
InactiveCN102607610ALower effective refractive indexReduce absorption lossCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFluorescenceMechanical reliability
Disclosed is a terahertz fiber evanescent wave sensing device. A fiber core is made of a polymethyl methacrylate material, sub-wavelength air holes which are axially arrayed in a regular-triangularly periodic manner are uniformly distributed in the fiber core, a cladding consists of to-be-detected gas or to-be-detected liquid positioned on the outside of the fiber core, and the sensing characteristic is realized by the aid of evanescent waves at an interface of the fiber core and the cladding. The terahertz porous fiber evanescent wave sensing device has the advantages that a series of sub-wavelength air holes which are axially arrayed in the regular-triangularly periodic manner are additionally disposed in the solid fiber core of the sensing device, the effective refractivity of a fundamental mode is effectively reduced, absorption loss and waveguide dispersion of the material are reduced, relative sensitivity is improved, a fiber can be used as a sensor probe without any treatment when used for sensing the evanescent waves, mechanical reliability is high, processing cost is low, detection time is relatively shortened when the sensing device is used for a sensing area positioned on the outside of the fiber, the surface of the fiber can be treated conveniently when the fiber is used for biological fluorescent detection, and reliability of the probe cannot be affected.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Tunable light wave guide dispersion compensator controlled by two-section erverse electrode oriented coupler
InactiveCN1588149AFull range coupling adjustableCoupling adjustableCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionClosed loopParallel I/O
The invention discloses a regulatable optical waveguide dispersion compensator controlled by binodal reverse-electrode orientation coupler, arranging parallel I / O optical waveguides in a part of the closed-loop optical waveguide microring to compose an orientation coupler, where the effective length of the orientation coupler is once to thrice as long as its coupled length and is a length influencing the coupling in the graded separation, two driving electrodes of the same length are arranged on the orientation coupler and reversely arranged on two waveguides composing the orientation coupler, thus composing the binodal reverse-electrode structural 2x2 input controllable orientation coupler. This structural regulable coupling mechanism can realize regulable coupling in the whole range and can have a bending shape, and even for a circular optical microring, it need not adopt special structure processing, thus unable to enlarge the circumference of the optical microring. This brings about extreme flexibility to the design and besides, it has extreme flexibility in designing and realizing multiple-stage cascade.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
On-line dispersion compensation device for a wavelength division optical transmission system
InactiveUS7221872B2Low insertion lossLow costWavelength-division multiplex systemsDistortion/dispersion eliminationGratingBroadband
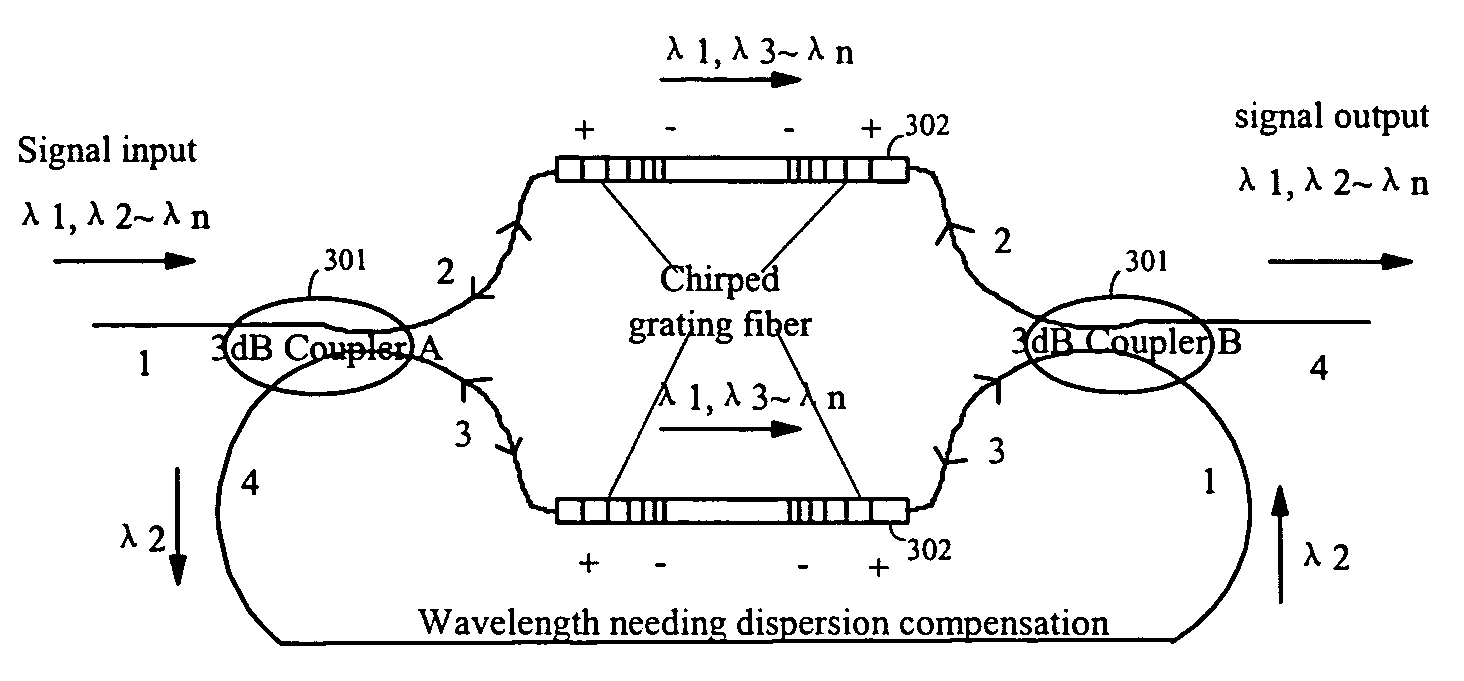
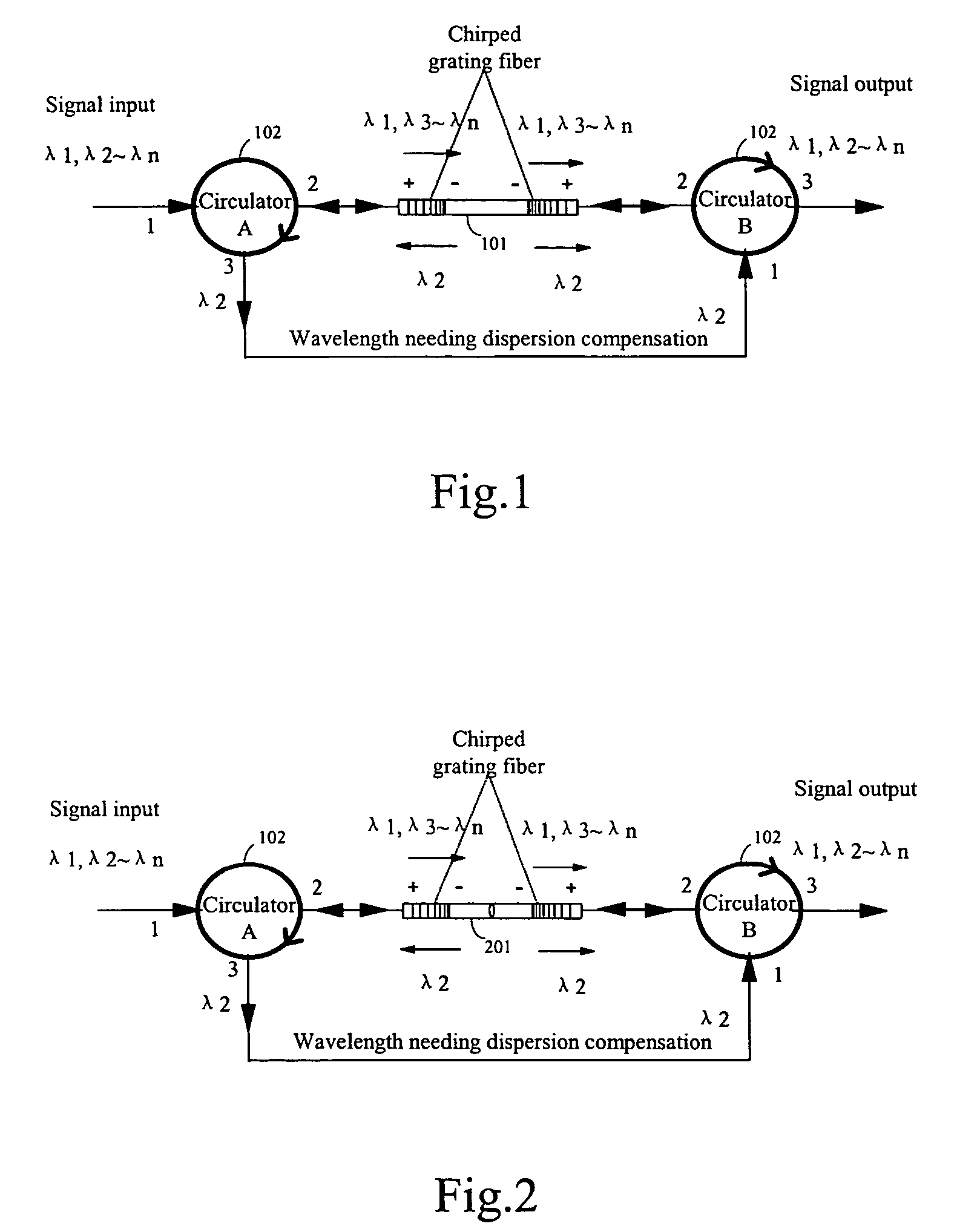
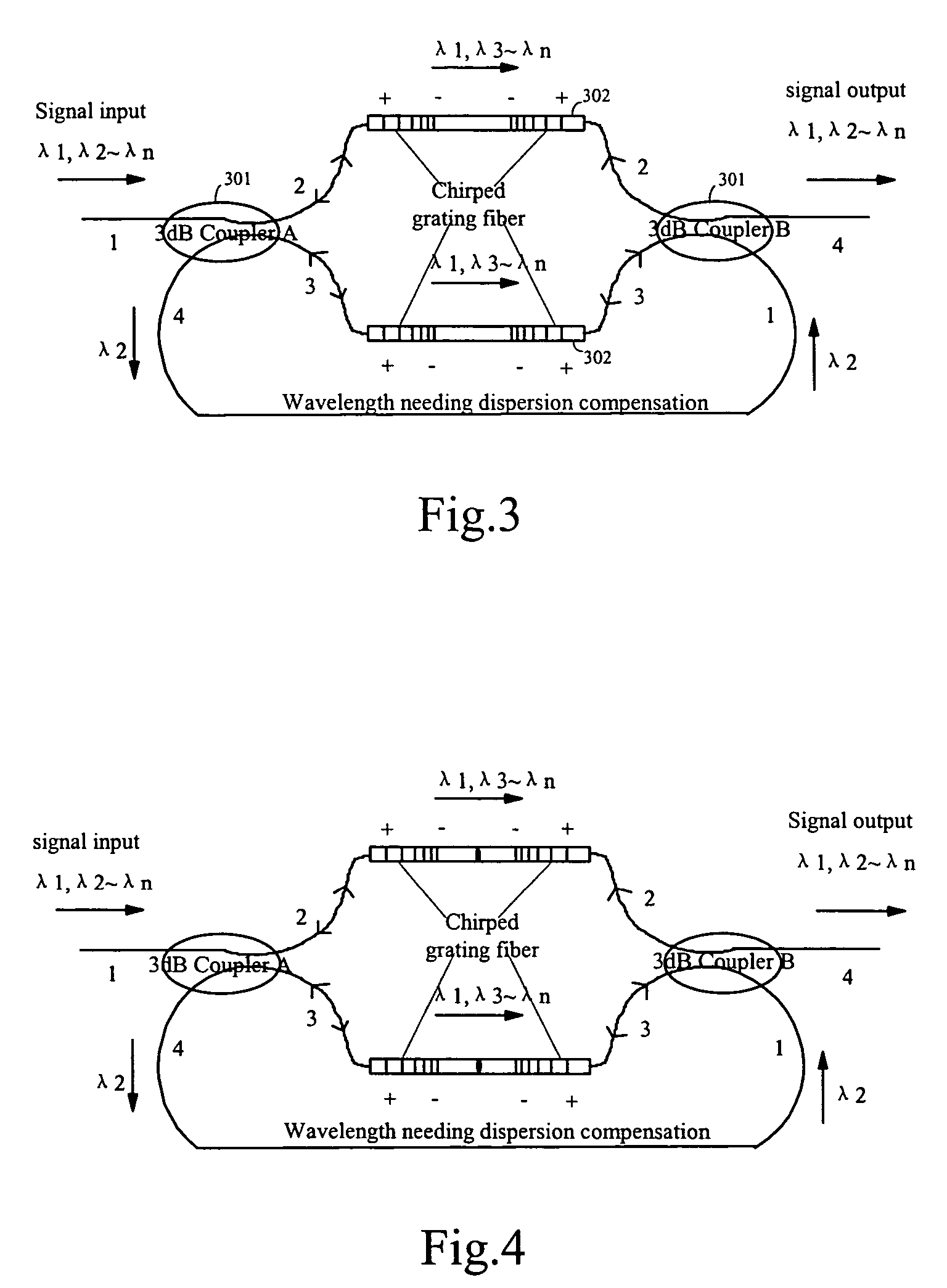
The invention discloses an on-line dispersion compensation device for a wavelength division optical transmission system. The device is consisted of two optical path selectors and at least one chirped grating fiber unit. The chirped grating fiber unit is consisted of two chirped grating fibers with same wavelength band and connected oppositely. In addition, the chirped grating fiber unit is serially connected between the appropriate ports of the two optical path selectors. The invention applies a structure that combines a chirped grating fiber unit with two optical path selectors. The structure is suitable to on-line dispersion compensation in a DWDM system and has low insertion loss. When only a few wavelengths need to be compensated, the structure makes dispersion compensation with low cost, low insertion loss and compensating a large dispersion value. For single channel or broadband compensation, the invention provides dispersion compensation without through OADM or MUX / DEMUX filtering. For an urban area network system with rare high-speed service, the invention provides a low cost solution for dispersion compensation, and the structure of the device is suitable for structure design of the integrated waveguide dispersion compensation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source
ActiveCN105762626ABreak through the loss limitIncrease spectral bandwidthActive medium shape and constructionMiddle infraredMicro imaging
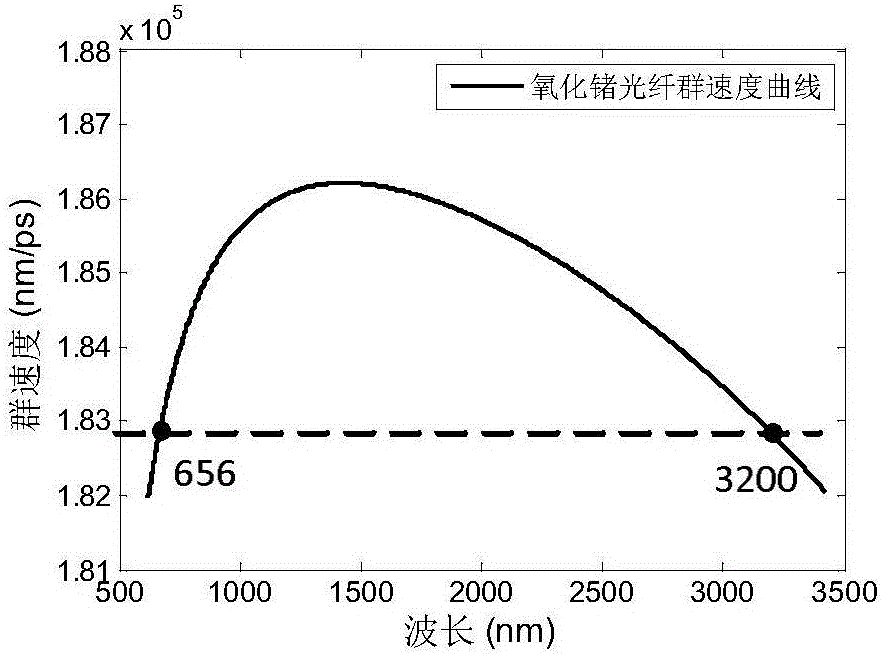
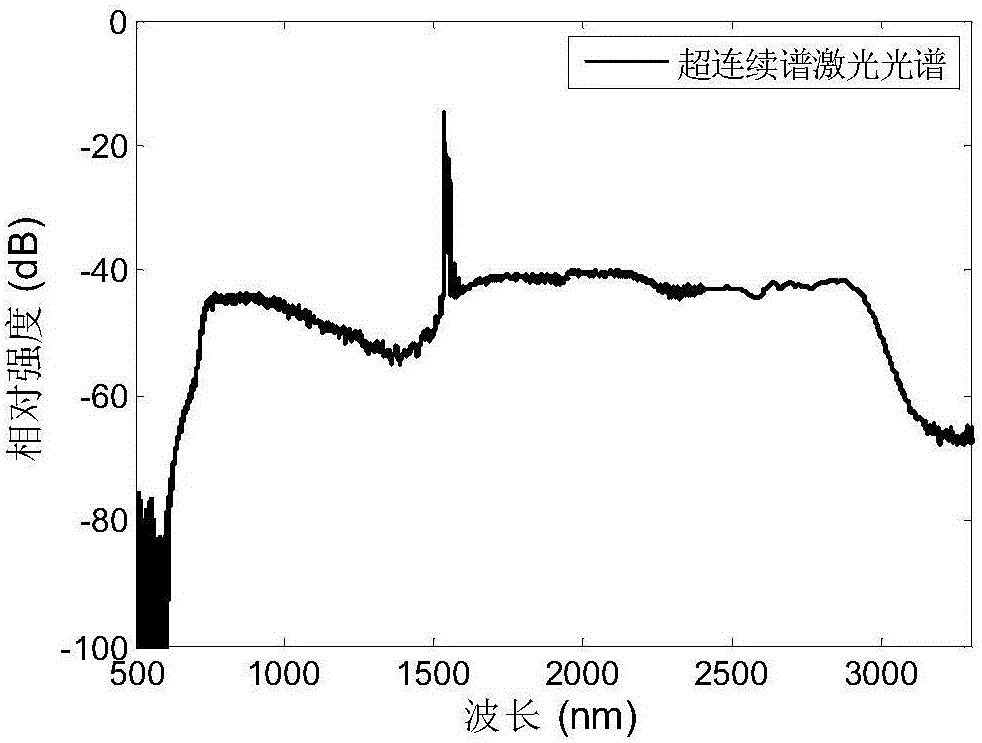
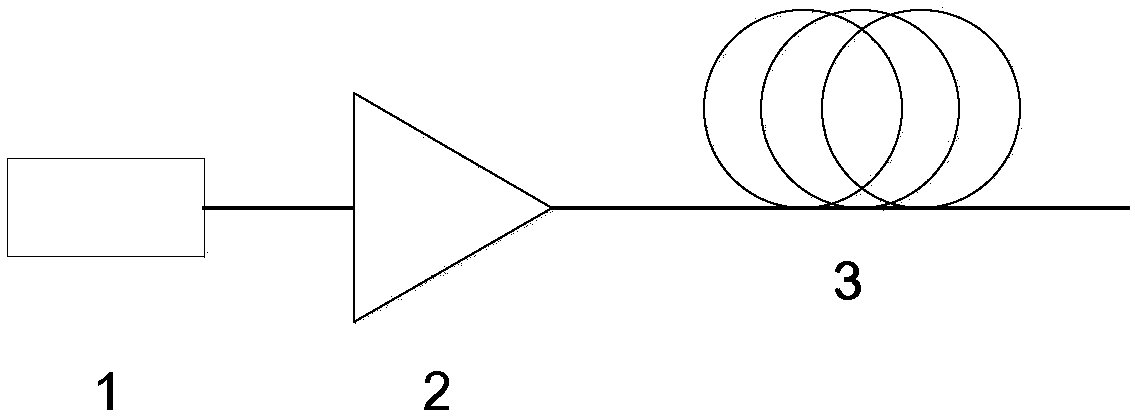
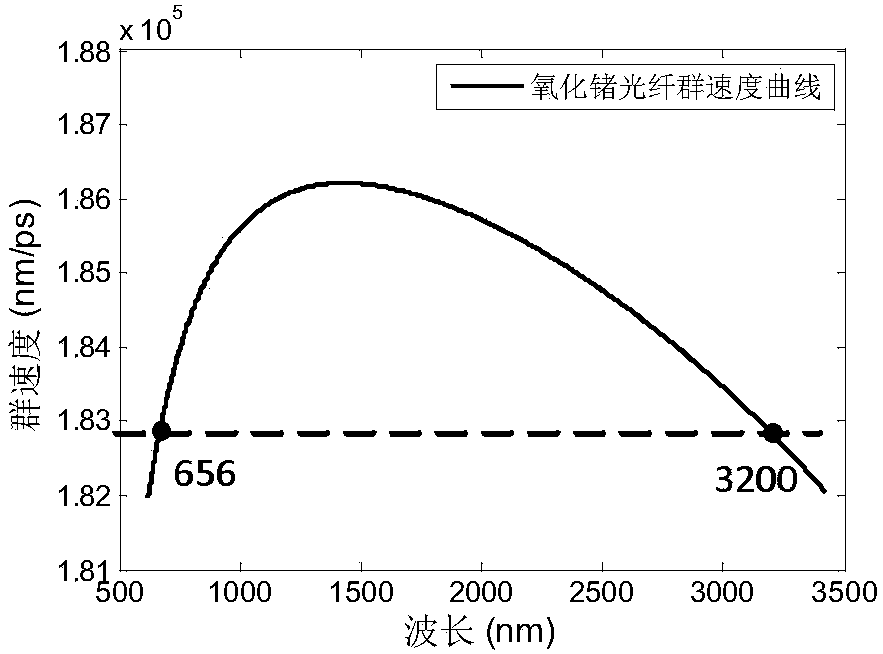
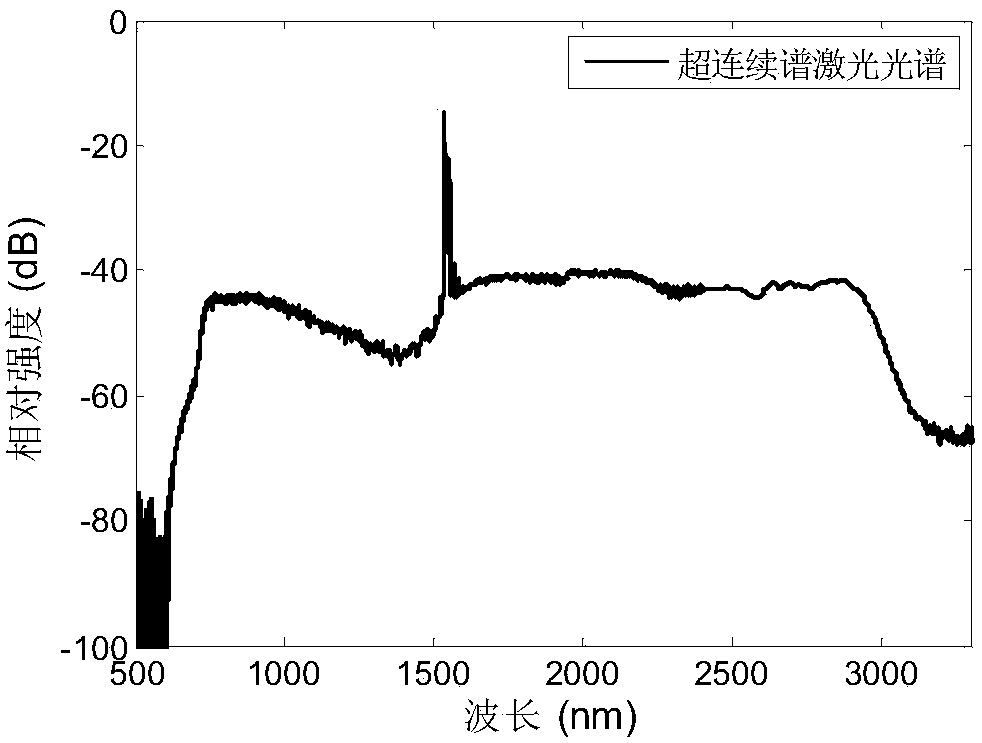
The invention provides an ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source. The ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source mainly comprises a pulse optical-fiber laser device, an optical fiber amplifier and a germanium oxide optical fiber, wherein the germanium oxide optical fiber is a step-index type optical fiber with a refractive structure, an optical fiber with a photonic crystal structure or a micro-structural optical fiber. The ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source introduces positive waveguide dispersion through the germanium oxide optical fiber, can move zero dispersion points of the germanium oxide optical fiber from a 1.7-micron waveband to a nearby 1.5-micron waveband in the short waveguide direction, makes the zero dispersion points be close to the wave length of the pulse optical-fiber laser device and forms a group velocity dispersion curve of frequencies symmetrically distributed about the zero dispersion points. An output spectrum of the laser source can cover a middle-infrared waveband of visible light, the ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source has the advantages of being of an all-fiber structure, low in cost, good in stability and the like and is easily popularized and used in the lots of fields of optical element performance testing, micro-imaging, biomedicines, broad-spectrum sensing, spectroscopy and the like in a wide-range mode.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Helical welded pipe torsion-bending guided wave testing method and device using a helical transducer
ActiveCN104880510BOvercoming the disadvantages of echoImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWave detectionFinite element method
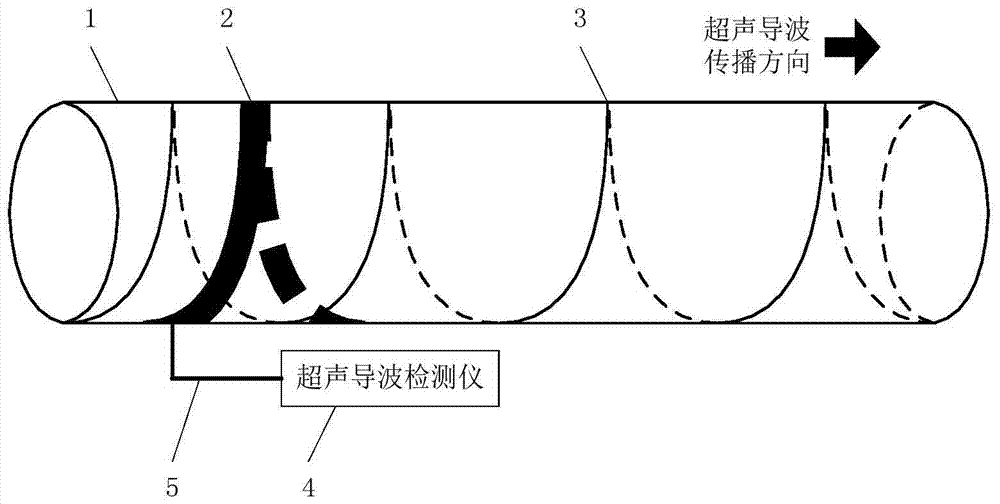
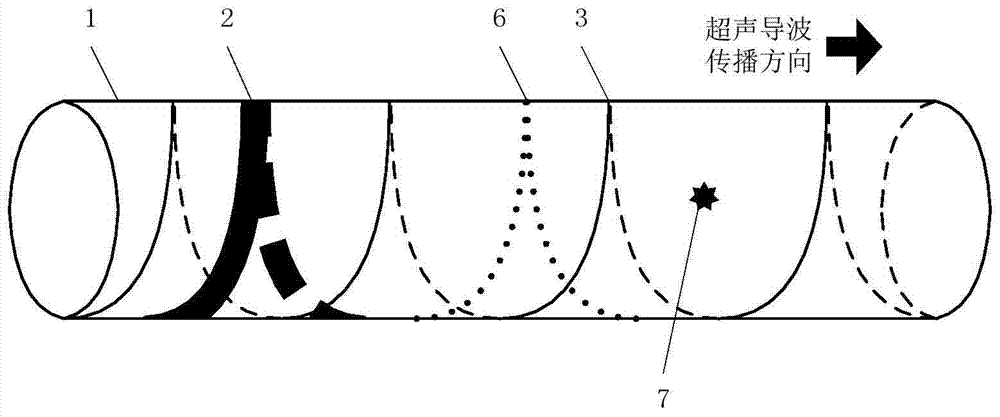
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting a torsion-bending guided wave of a spiral welded pipe using a spiral transducer. The guided wave dispersion characteristics of the spiral welded pipe are calculated by the semi-analytical finite element method, and then the frequency and wave velocity of the torsion-bending guided wave of the parallel spiral weld are calculated; the spiral transducer is arranged in a circle along the spiral direction, and is controlled by a guided wave detector The twisted guided wave is excited, propagates along the axial direction of the spiral welded pipe and receives the echo after encountering the reflection of the defect; the position of the defect is determined according to the wave packet of the defect, and the distance of the defect is calculated. The invention eliminates the phenomenon that the spiral weld signal continues to appear in the echo when the traditional ring-shaped integrated magnetostrictive transducer performs guided wave detection, improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the echo, makes the defect signal easy to extract, and improves the spiral seam signal. Reliability of guided wave testing for welded pipes.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZHEJIANG UNIV JINGYI ELECTROMECHANICAL TECH ENG
Uplink and downlink filters based on single anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity
InactiveCN109254351AImplement the download functionImplement the insert functionOptical waveguide light guideCouplingResonance
The invention discloses uplink and downlink filters based on single anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity, wherein the bus waveguide and the uplink and downlink waveguides are laterally coupled with the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity in the coupling region; the periodic waveguide of the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity at the coupling region supports not less than two working modes and the propagation constants of two modes are different from each other, there is inverse crossover in the energy band of the two working modes in the periodic waveguide dispersion relation of the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity in the coupling region, and there is reflection coupling between the two modes. The invention can enable the light wave propagating in the bus waveguide and located at the resonance frequency of the anti-symmetric multi-mode periodic waveguide micro-cavity to be downloaded to the downlink output end of the uplink and downlink waveguides through the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity, or enable the light wave at the resonant frequency input from the uplink end of the uplink and downlink waveguides to be inserted into the bus waveguide, thereby obtaining an on-chip filter with a simple structure, high upload and download efficiency, and ultra-compact size.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Dispersion control method suitable for integrated optical waveguide and integrated optical waveguide
The embodiment of the invention discloses a chromatic dispersion control method for an integrated optical waveguide and an integrated optical waveguide. According to the control method, respective width values of a first waveguide and a second waveguide are controlled according to an operating waveband, so that effective refractive indexes of a fundamental mode of the first waveguide and a second-order mode of the second waveguide are equal at the operating waveband; and a coupled chromatic dispersion value reaches a target chromatic dispersion value based on control of the spacing distance between the first waveguide and the second waveguide. On the basis of a mode coupling principle, chromatic dispersion value controlling is realized by adjusting the width space between waveguide cores. Compared with the traditional method for optical waveguide dispersion control based on the waveguide cross section shape and dimension, the chromatic dispersion control method disclosed by the invention has no special requirement on the process and has high compatibility because only the parameters of the integrated optical waveguide at the width dimension need to be adjusted. The chromatic dispersion control method can be applied to most of application occasions including the technical field of fables design.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
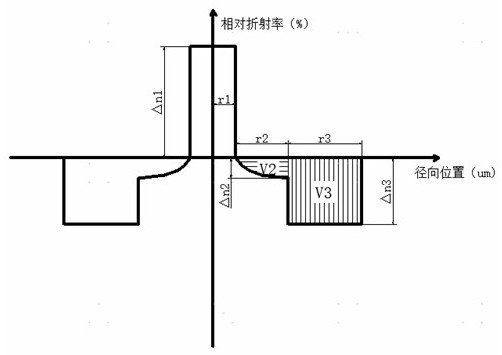
A dispersion-optimized bend-insensitive optical fiber
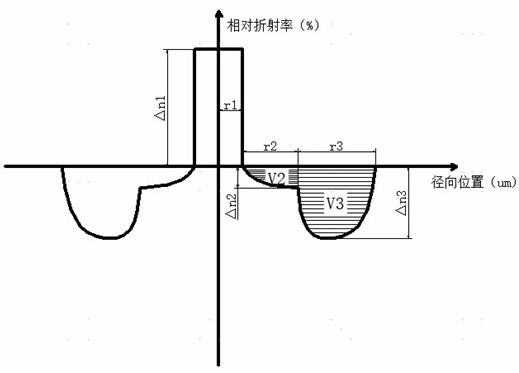
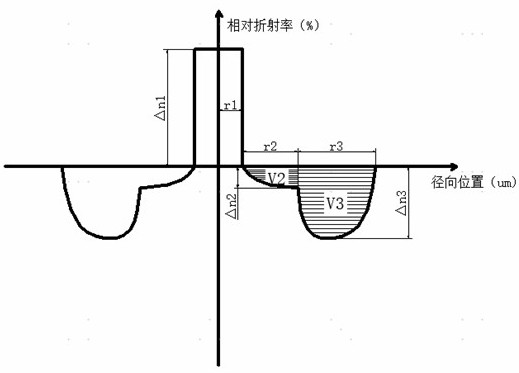
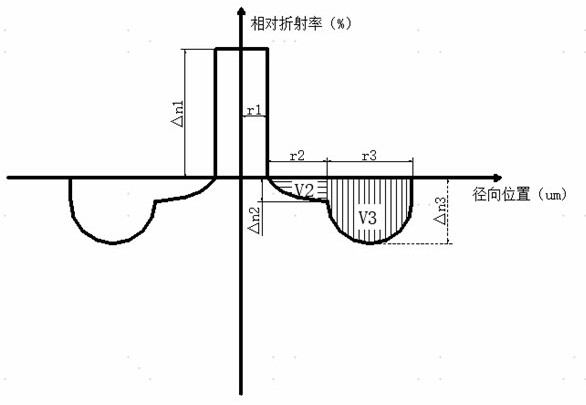
ActiveCN113625390BFlexibility is not affectedAvoid the problem of excessive bending lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexMaterials science
The invention discloses a dispersion-optimized bend-insensitive optical fiber, which is provided with a transitional sunken cladding between the core layer and the sunken cladding, and the relative refractive index difference of the transitional sunken cladding is continuous from the inside to the outside from 0%. Changes to the relative refractive index difference at the junction point of the depressed cladding. The present invention adopts double sunken cladding to balance and optimize waveguide dispersion and macrobending performance, and reduce its dispersion coefficient without affecting the bending performance of the optical fiber; wherein the transitional sunken cladding between the core layer and the sunken cladding, its The refractive index changes continuously to reduce the waveguide dispersion caused by the difference in refractive index between the core layer and the cladding layer in the waveguide structure, limit the refractive index distribution and width of the transitional depressed cladding layer, optimize the dispersion coefficient, and avoid the problem caused by the convex cladding layer. The problem of excessive bending loss at small bending radii.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
An Add-Drop Filter Based on a Single Antisymmetric Multimode Periodic Waveguide Microcavity
InactiveCN109254351BSmall sizeHigh upload and download efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses uplink and downlink filters based on single anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity, wherein the bus waveguide and the uplink and downlink waveguides are laterally coupled with the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity in the coupling region; the periodic waveguide of the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity at the coupling region supports not less than two working modes and the propagation constants of two modes are different from each other, there is inverse crossover in the energy band of the two working modes in the periodic waveguide dispersion relation of the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity in the coupling region, and there is reflection coupling between the two modes. The invention can enable the light wave propagating in the bus waveguide and located at the resonance frequency of the anti-symmetric multi-mode periodic waveguide micro-cavity to be downloaded to the downlink output end of the uplink and downlink waveguides through the anti-symmetric multimode periodic waveguide micro-cavity, or enable the light wave at the resonant frequency input from the uplink end of the uplink and downlink waveguides to be inserted into the bus waveguide, thereby obtaining an on-chip filter with a simple structure, high upload and download efficiency, and ultra-compact size.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
A Broadband Dielectric Loaded Gyro TWT High Frequency System
ActiveCN107591306BChanging waveguide dispersion characteristicsIncrease output powerTransit-tube coupling devicesDielectricLinear amplification
The invention discloses a novel wideband dielectric loaded gyro traveling wave tube high frequency system, and belongs to the technical field of microwave, millimeter wave and terahertz devices. The system comprises pre-bunching section, a linear amplification section, a nonlinear amplification section and an output gradual change section which are sequentially connected, and is characterized in that the pre-bunching section, the linear amplification section, the nonlinear amplification section and the output gradual change section comprise a metal circular waveguide shell and an annular lossless dielectric loading waveguide which is loaded in a mode of attaching to the circular waveguide inner wall, the linear amplification section is uniformly provided with rectangular lossy dielectric pieces in the angular direction, and the lossy dielectric pieces are distributed in a periodic manner along the axial direction. Dispersion characteristics of the whole high frequency structure are changed through loading the lossless dielectric waveguide, an electron beam curve and a waveguide dispersion curve are enabled to meet resonance conditions within a wide frequency band range, and wideband operating characteristics are ensured; and meanwhile, a gradually changing output structure is adopted, so that a problem of low output power brought about by low gain of a high frequency point is solved. The system disclosed by the invention not only can meet wideband operating requirements, but also can provide high microwave power output within the frequency band range.
Owner:四川杰诺创科技有限公司
Tunable light wave guide dispersion compensator controlled by two-section erverse electrode oriented coupler
InactiveCN1255693CFull range coupling adjustableCoupling adjustableCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionClosed loopParallel I/O
The invention discloses a regulatable optical waveguide dispersion compensator controlled by binodal reverse-electrode orientation coupler, arranging parallel I / O optical waveguides in a part of the closed-loop optical waveguide microring to compose an orientation coupler, where the effective length of the orientation coupler is once to thrice as long as its coupled length and is a length influencing the coupling in the graded separation, two driving electrodes of the same length are arranged on the orientation coupler and reversely arranged on two waveguides composing the orientation coupler, thus composing the binodal reverse-electrode structural 2x2 input controllable orientation coupler. This structural regulable coupling mechanism can realize regulable coupling in the whole range and can have a bending shape, and even for a circular optical microring, it need not adopt special structure processing, thus unable to enlarge the circumference of the optical microring. This brings about extreme flexibility to the design and besides, it has extreme flexibility in designing and realizing multiple-stage cascade.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical waveguide dispersion control device for nonlinear process and its design method
ActiveCN110908215BSuitable for nonlinear applicationsRealize second-order nonlinear effectsNon-linear opticsOptical elementsFrequency spectrumPhase difference
The invention proposes an optical waveguide dispersion regulating device and a design method thereof for nonlinear processes. By dividing the optical waveguide into several waveguides whose widths vary periodically, broadband phase matching under the control of multiple degrees of freedom can be realized. First, the relationship between the wave vector mismatch of light participating in the second-order nonlinear process and the waveguide width is obtained through numerical simulation. According to the overall planning, the width and length of each waveguide can be optimized through an optimization algorithm. Calculate the amount of phase mismatch brought by each section, and make the phase difference introduced by each section of the waveguide cancel each other within an optimized nonlinear period, obtain a flat phase difference spectrum, and finally make the average of the nonlinear process in the wavelength range of interest The wave vector difference is close to 0, thereby realizing nonlinear phase matching with large bandwidth. The invention can further improve the bandwidth of the phase matching while ensuring the existence of the phase matching working point in the integrated optical waveguide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Supercontinuum Laser Source with Ultra-wide Bandwidth
ActiveCN105762626BBreak through the loss limitIncrease spectral bandwidthActive medium shape and constructionMiddle infraredMicro imaging
The invention provides an ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source. The ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source mainly comprises a pulse optical-fiber laser device, an optical fiber amplifier and a germanium oxide optical fiber, wherein the germanium oxide optical fiber is a step-index type optical fiber with a refractive structure, an optical fiber with a photonic crystal structure or a micro-structural optical fiber. The ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source introduces positive waveguide dispersion through the germanium oxide optical fiber, can move zero dispersion points of the germanium oxide optical fiber from a 1.7-micron waveband to a nearby 1.5-micron waveband in the short waveguide direction, makes the zero dispersion points be close to the wave length of the pulse optical-fiber laser device and forms a group velocity dispersion curve of frequencies symmetrically distributed about the zero dispersion points. An output spectrum of the laser source can cover a middle-infrared waveband of visible light, the ultra-large bandwidth super-continuum spectrum laser source has the advantages of being of an all-fiber structure, low in cost, good in stability and the like and is easily popularized and used in the lots of fields of optical element performance testing, micro-imaging, biomedicines, broad-spectrum sensing, spectroscopy and the like in a wide-range mode.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Cascade silicon-based waveguide optical isolator
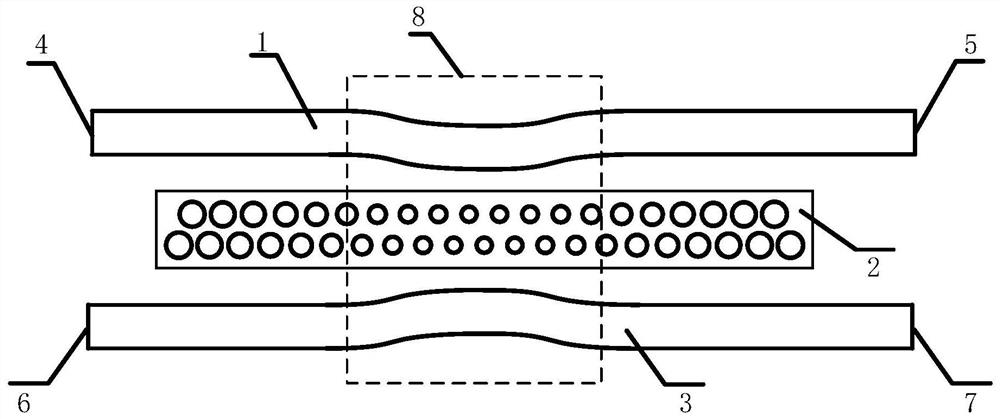
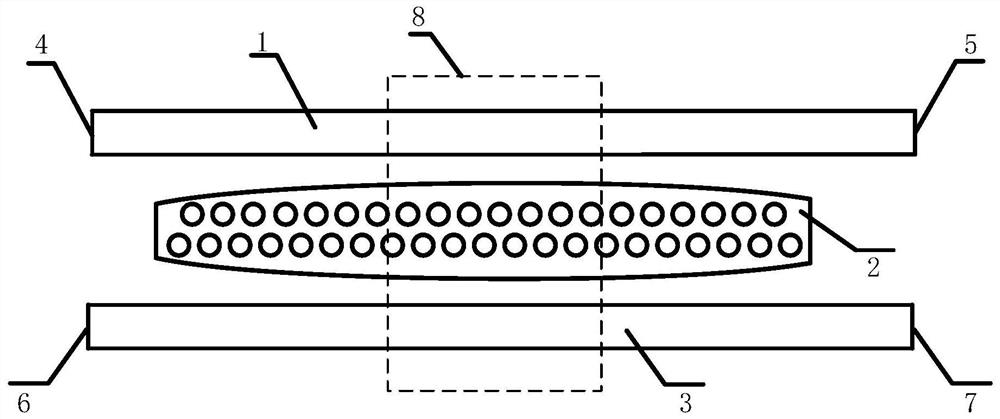
InactiveCN105629388ASuitable for large-scale integrationCoupling light guidesPhysicsWaveguide dispersion
The invention provides a cascade silicon-based waveguide optical isolator. The two-stage time-dependent perturbation structure and the two-stage filtering structure can realize the optical signal isolation of the two frequencies. The dual-frequency independent isolation is realized through utilizing the selection frequency of the unparallel portion of two different energy bands in the waveguide dispersion relation in order to realize the dual-frequency independent isolation, and the mutual interaction does not happen in the signal isolation process. The time-dependent perturbation structure is used for coupling the two optical signals of two specific frequencies which is in the forward propagation along the waveguide as the two optical signal of the target frequency which is in the forward propagation along the waveguide; and the specific frequency filtering structure which is in successive series is used for absorbing two target frequency optical signal which is in the forward propagation along the waveguide. The perturbed structure and the filtering structure do not produce effect on the two optical signal with specific frequencies which are propagated in the opposite directions. The scale of the optical isolator is in the micron dimension and is applicable to the mass integration and has no requirement for the signal strength.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Dispersion-optimized bend-insensitive optical fiber
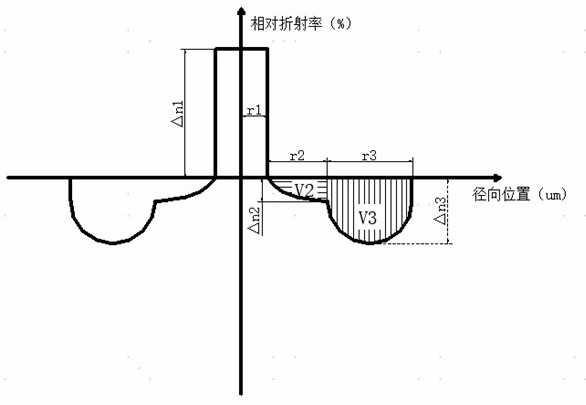
ActiveCN113625390AFlexibility is not affectedAvoid the problem of excessive bending lossOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexMaterials science
The invention discloses a dispersion-optimized bending-insensitive optical fiber. A transition sunken cladding is arranged between a core layer and a sunken cladding, and the relative refractive index difference of the transition sunken cladding continuously changes from 0% to the relative refractive index difference of a junction point of the sunken cladding from inside to outside. According to the invention, the waveguide dispersion and macro-bending performance are balanced and optimized by adopting the double sunken claddings, so that the dispersion coefficient of the optical fiber is reduced on the premise that the bending performance of the optical fiber is not influenced; wherein the refractive index of the transition sunken cladding between the core layer and the sunken cladding changes continuously, so that waveguide dispersion caused by the refractive index difference between the core layer and the cladding in the waveguide structure is reduced, the refractive index distribution and width of the transition sunken cladding are limited, the dispersion coefficient is optimized, and the problem that the bending loss is too large under the small bending radius due to the convex cladding is avoided.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com