Nucleic acid aptamer screening method
A screening method and nucleic acid aptamer technology, which can be used in biochemical equipment and methods, and the determination/inspection of microorganisms, and can solve problems such as no candidate nucleic acid aptamer screening methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
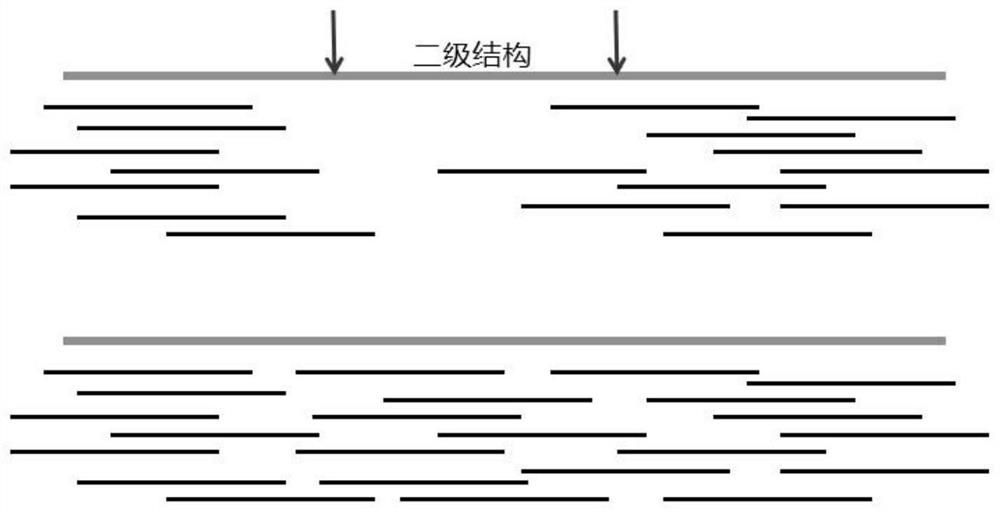
[0032] To the nucleic acid sample to promote nucleic acid samples to form a secondary structure, amplification and sequencing of nucleic acid samples, including the following steps:
[0033] (1) The genomic DNA was extracted from phenol-chloroform from the cultured human K562 cell line and dissolved in TE buffer. The nucleic acid sample to be tested is divided into two groups, each containing 10 μl of a total of 100 ng of genome nucleic acid.
[0034] (2) Add a final concentration of 1 μm MnCl to the above-mentioned nucleic acid sample 2 The solution enables both to mix; another group of isometric water.
[0035] (3) The MDA total genome is added to the MDA total genomic, 4 mmDNTP, 1U / μl29 polymerase, and corresponding buffer, respectively, the reaction conditions for the MDA total genome, and the reaction conditions were carried out on a 50 μm random primer, 4 mmdNTP, 1 U / μL29 polymerase and corresponding buffer.
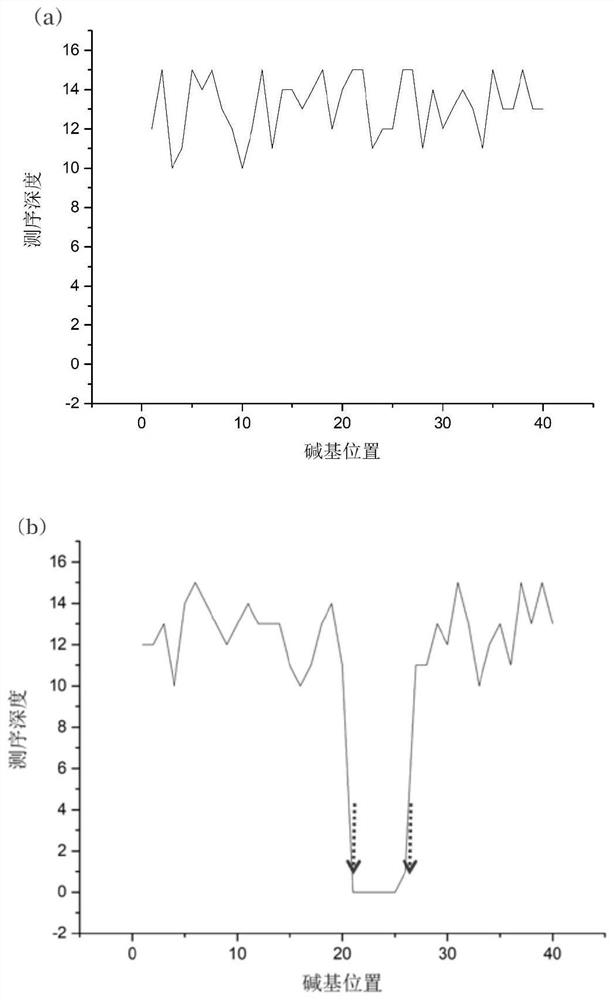
[0036] (4) After the amplification, the two sets of samples wer...
Embodiment 2
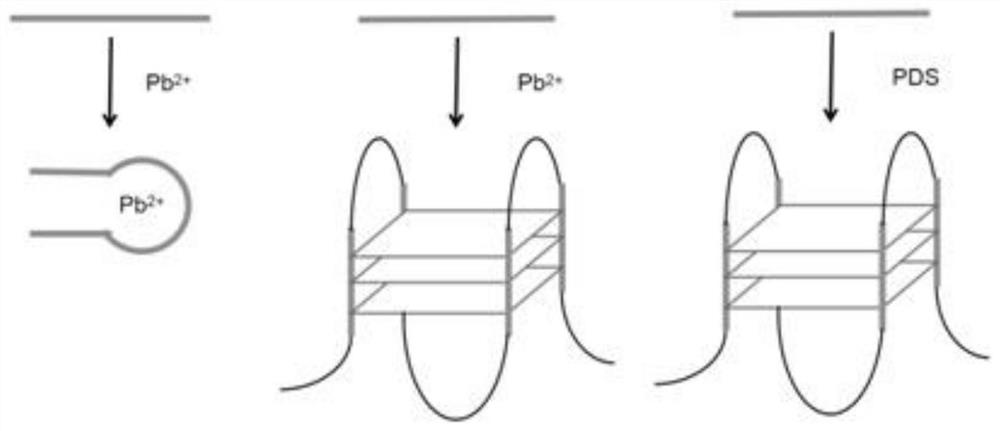
[0040] According to the method of Example 1, a sequence of artificially synthetic nucleic acids were screened by a sequence of nucleic acids.
[0041]
[0042] 2 μl of concentration of 100 μm Pb (NO) was added to a nucleic acid sample of 198 μL of concentration of 20 μm (NO 3 ) 2 The solution allows it to fully react. Another group of sample nucleic acid concentrations are maintained, but add the same molar NANO 3 Solution.
[0043] The amplification of the primary ionic nucleic acid sample set and the non-lead ion-free nucleic acid sample group was amplified, and the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) was amplified. The PCR reaction system contains 400 μm DNTPs, 2 μm primers, 0.025 unit / μl RTAQ and 1 μL of the template in 50 μl of 1 × PCR buffer. The process of PCR is denaturation (92 ° C, 15S), annealing (58 ° C, 30S), extending (72 ° C, 20S), a total of 14 cycles, and finally extends at 72 ° C for 5 min.
[0044] After amplification, the two groups of samples were subjected to...
Embodiment 3
[0047] According to the method of Example 1, a PDS nucleic acid aptamer was performed on a natural nucleic acid sequence from human lymphocytes. The final concentration of 1 μm PDS was added to a nucleic acid sample having a concentration of 20 μm to sufficiently reacted. Another group of sample nucleic acid concentrations is maintained, but is added to the same amount of water.
[0048] The amplification of the PDS-containing nucleic acid sample group and the Nucleic acid sample group containing the PDS were amplified by PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The PCR reaction system contains 400 μm DNTPs, 2 μm primers, 0.025 unit / μl RTAQ and 1 μL of the template in 50 μl of 1 × PCR buffer. The process of PCR is denaturation (98 ° C, 15S), annealing (58 ° C, 30S), extending (72 ° C, 90S), a total of 14 cycles, and finally extends at 72 ° C for 5 min.
[0049] After amplification, the two groups of samples were subjected to ultrasound interruption and ligation enzyme connection sequenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com