Method for co-processing and utilization of arsenic-containing materials in non-ferrous smelting
A technology of collaborative processing and materials, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of secondary resource utilization of unfavorable tailings, serious environmental pollution, poor arsenic removal effect, etc., to increase processing costs, prevent environmental pollution, The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
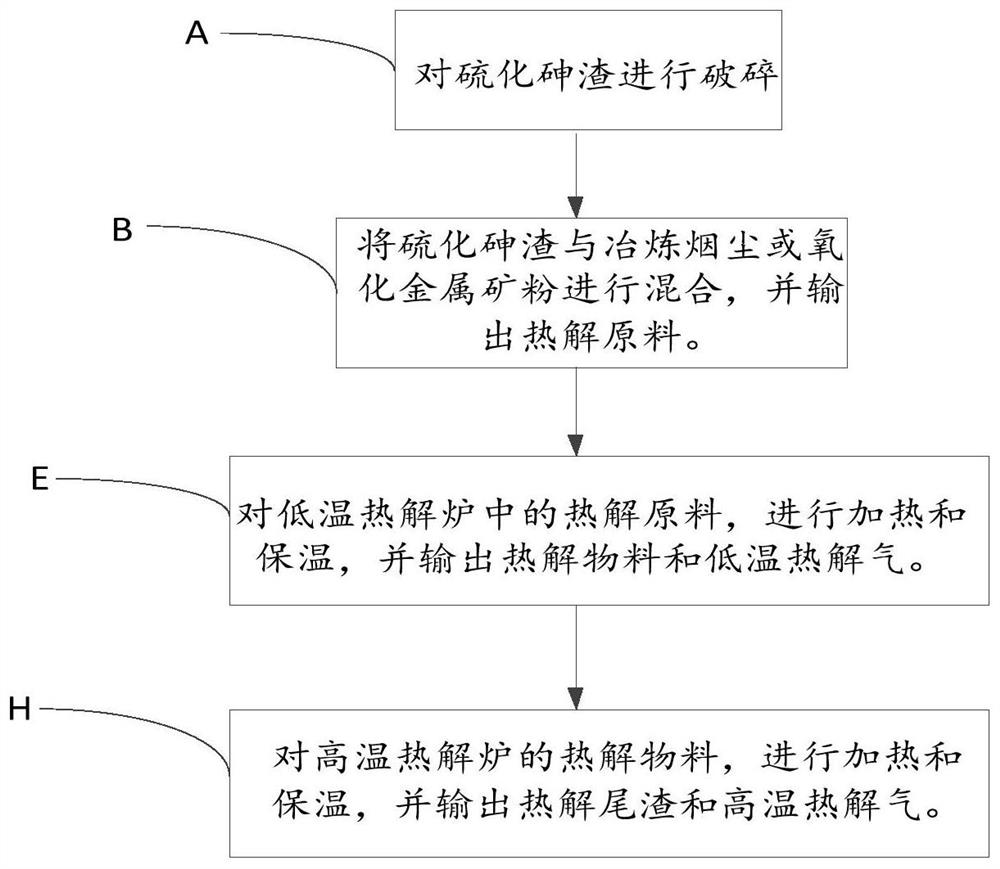
[0089] A method for co-processing and utilization of arsenic-containing materials in non-ferrous smelting. The arsenic sulfide slag and smelting smoke come from a smelting company in Yunnan. The arsenic sulfide slag contains 25% of S and 38% of As in the arsenic sulfide slag.
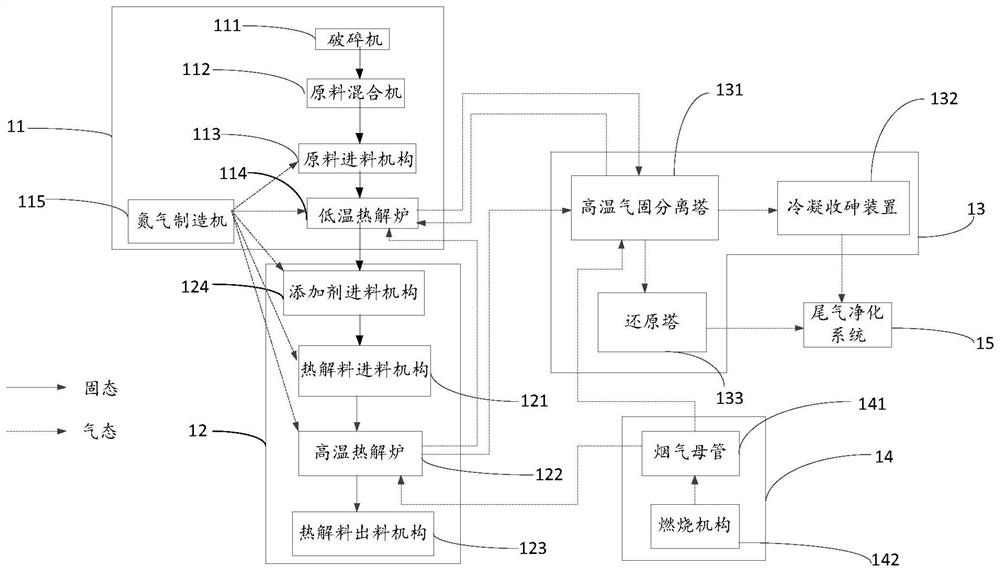
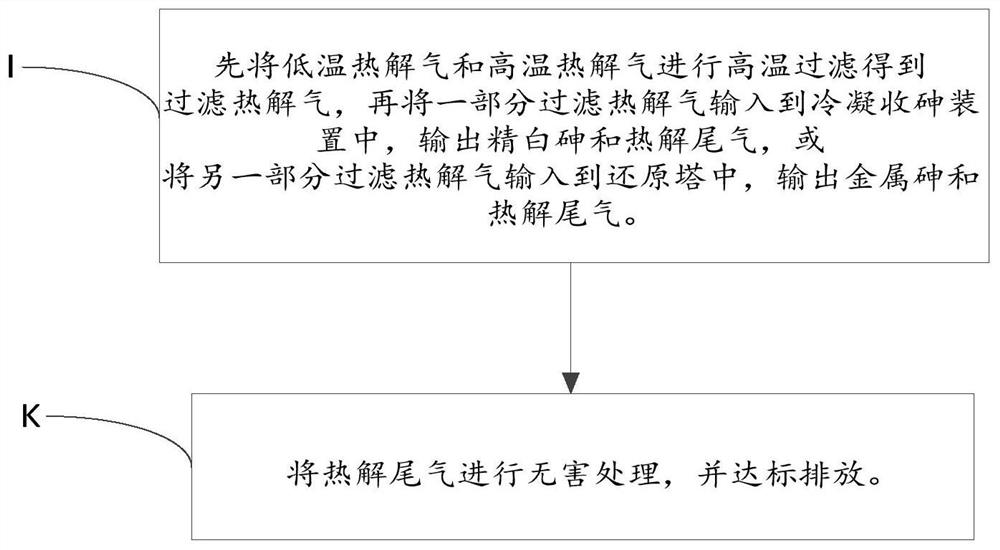
[0090] The raw materials are put into the preheated low-temperature pyrolysis furnace 114 through the closed raw material feeding mechanism, heated to 400° C., and kept for 90 minutes, and nitrogen gas is introduced into the low-temperature pyrolysis furnace 114 at the same time, and the sulfur in the material is in the form of metal sulfides. The form remains in the material, and arsenic enters the high temperature gas-solid separation tower 131 in the form of gaseous arsenic trioxide;
[0091] The solid sulfur material is directly sent to the preheated external heat type high temperature pyrolysis furnace 122, heated to 600 ° C, and kept for 90 minutes. , feeding nitrogen gas and adding carbon powder ...
example 2
[0096] A method for co-processing and utilization of arsenic-containing materials in non-ferrous smelting. Arsenic sulfide slag and smelting smoke come from a smelting company in Yunnan. The arsenic sulfide slag contains 20% of S and 33% of As in the arsenic sulfide slag.
[0097] The raw material is put into the preheated low-temperature pyrolysis furnace 114 through the closed raw material feeding mechanism, heated to 300 ° C, and kept for 60 minutes, and nitrogen is introduced into the low-temperature pyrolysis furnace 114 at the same time, and the sulfur in the material is in the form of metal sulfide. The form remains in the material, and arsenic enters the high temperature gas-solid separation tower 131 in the form of gaseous arsenic trioxide;
[0098] The solid sulfur material is directly sent to the preheated external heat type high temperature pyrolysis furnace 122, heated to 700 ° C, and kept for 60 minutes, and the original solid arsenic trioxide in the material is h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com