Isogeometric particle fluid dynamics method
A particle fluid, isogeometric technology, applied in the field of numerical analysis of complex physical systems, to achieve the effects of reducing calculation errors, improving calculation accuracy, and improving calculation efficiency and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
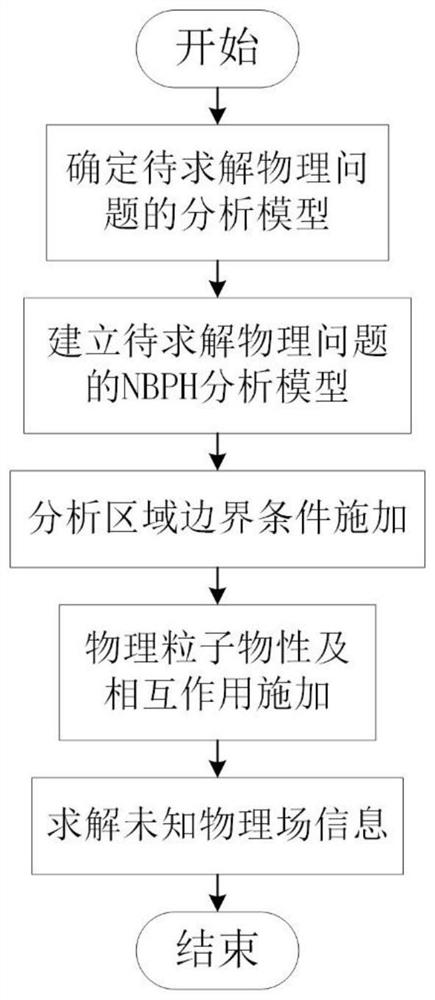
[0052] Embodiment 1, with reference to figure 2 , an equigeometric particle hydrodynamics method comprising the following steps:
[0053] 1) Determine the analytical model of the flow field to be solved:
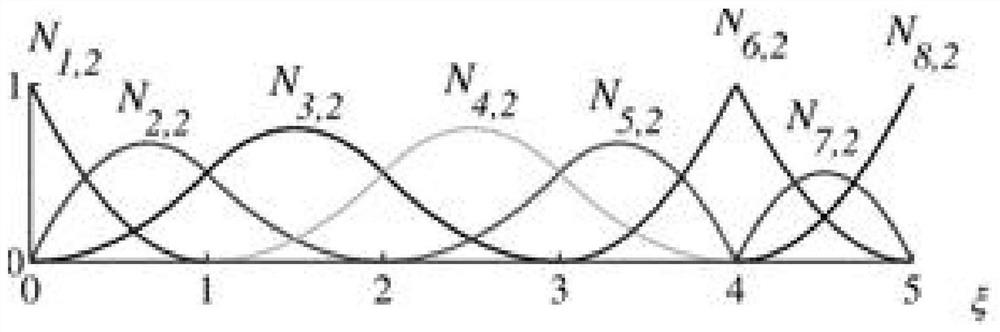
[0054] 1.1) According to the real geometric configuration of embodiment 1, the calculation and analysis area is extracted, and based on the non-uniform rational B-spline curve (NURBS), the geometric coefficients used to characterize the analysis area are defined, that is, the control points for solving the shape of the area are defined. According to the geometric configuration accuracy Requirements, establish a complete spline curve node vector in the parameter coordinate system and a NURBS-based shape interpolation basis function, take 4 control points to construct a secondary B-spline curve, and its control vector is a non-decreasing sequence ξ between 0 and 1 ={ξ 1 , ξ 2 ,…,ξ m+p+1}, the recursive formula of the B-spline basis function is as follows:
[0055]
[...
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2 takes the heat conduction problem of the third type of boundary condition as an example, such as Figure 7 As shown, the power density of the heat source around the rectangle in the figure is 300W / cm 2 , heat transfer fluid temperature 300K, internal cooling power density 300W / cm 2 .
[0087] Embodiment 2, with reference to figure 2 , an equigeometric particle hydrodynamics method comprising the following steps:
[0088] 1) Determine the analytical model of the temperature field to be solved:
[0089] 1.1) According to the real geometric configuration of embodiment 2, the calculation and analysis area is extracted, and based on the non-uniform rational B-spline curve (NURBS), the geometric coefficients used to characterize the analysis area are defined, that is, the control points for solving the shape of the area are defined. According to the geometric configuration accuracy Requirements, establish a complete spline curve node vector in the parameter ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com