Polarity-variable bus connector for transmitting pulse large current into vacuum chamber
A technology for transmitting pulses and converging polarities, applied in electromagnetic terminals/connectors, climate sustainability, transformers/inductor coils/windings/connections, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
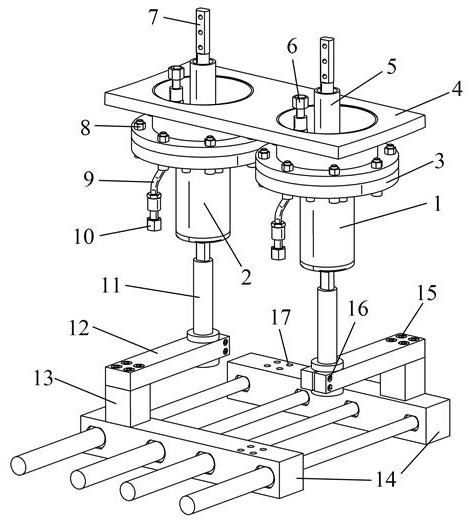
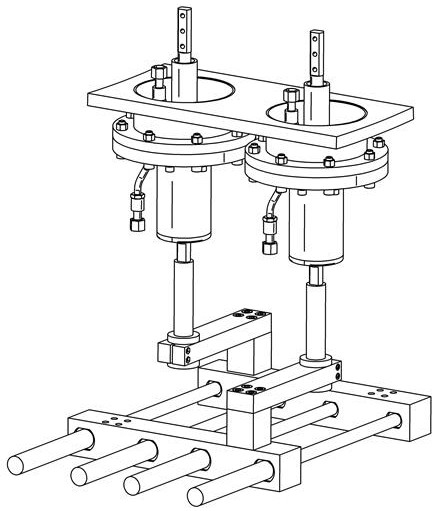
[0032] Specific implementation mode 1, refer to Figures 1 to 3 Describe this embodiment in detail. A variable polarity bus connector for transmitting pulsed large currents to the vacuum chamber described in this embodiment, the bus connector includes a positive terminal 1 and a negative terminal 2 with the same structure and function. , connecting terminal fixing flange 3, ceramic insulating sleeve 5, cabin water pipe ferrule 6, metal conductor 7, terminal fixing flange screw 8, metal water pipe 9, outer water pipe ferrule 10, terminal connecting rod 11, Variable connecting rod 12, transition module 13, bus bar 14, transition module fixing screw 15, clamping screw 16, bus bar fixing screw hole 17.
[0033] The positive terminal 1 and the negative terminal 2 have the same structure and function, and are bridges connecting the load coil in the cabin and the pulse current device outside the cabin.
[0034] The connecting terminal fixing flange 3 is connected with the flange of ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
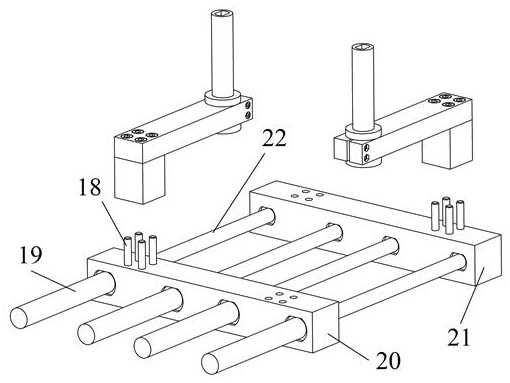
[0044] Specific Embodiment 2. This embodiment is a further description of the variable polarity bus connector that transmits pulsed large currents to the vacuum chamber described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the bus bar 14 includes The outer core bus bar 20, the inner core bus bar 21, and the connecting screw 18. The outer core bus bar 20 and the inner core bus bar 21 are both metal conductors, which are respectively connected to the coaxial cable outer core 19 and the coaxial cable inner core 22, and are used to gather output pulse currents of several discharge modules of the pulse high current device. The number of discharge modules busbar can be extended to access different numbers of coaxial cables.
[0045] The transition module 13 is connected to the outer core bus bar 20 and the inner core bus bar 21 through connecting screws 18, and there are 2 groups in total, 4 pieces in each group. When it is necessary to change the position of the variable connecting rod 1...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0047] Specific Embodiment 3. This embodiment is a further description of the variable polarity bus connector that transmits pulsed large currents to the vacuum chamber described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the polarity conversion function described It is realized by changing the positions of the variable connecting rod 12 and the transition module 13 . When a group of variable connecting rods 12 and transition modules 13 are connected to the positive terminal 1 and the inner bus bar 21, and another group of variable connecting rods 12 and the transition module 13 are connected to the negative terminal 2 and the outer core bus bar 20, When it is necessary to change the direction of the excitation current provided by the pulse high current device to the load coil, after removing the connecting screw 18, rotate the variable connecting rod 12 connected to the inner core bus bar 21 and the transition module 13 with the terminal connecting rod 11 as the axis 180 degrees, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com