Method for improving power transmission capability of grid-connected inverter under extremely weak power grid
A power transmission and inverter technology, applied in reactive power compensation, photovoltaic power generation, AC network voltage adjustment, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient power transmission capacity of grid-connected inverters, improve power transmission capacity, and expand output current The effect of the cap
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
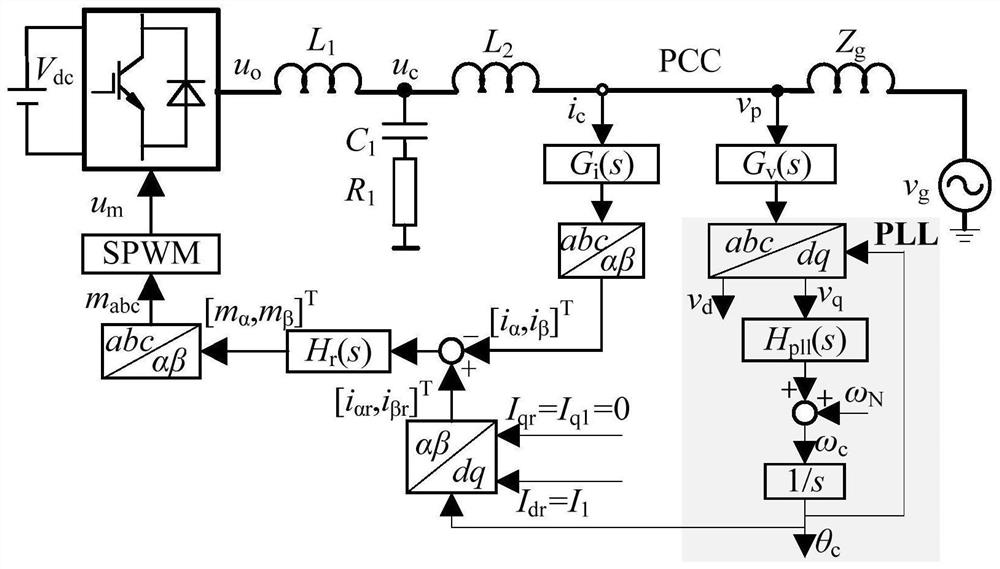
[0027] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 with figure 2 Describe this implementation mode, a method for improving the power transmission capacity of a grid-connected inverter under an extremely weak grid described in this implementation mode, the method includes the following content:
[0028] Step 1. Collect the common coupling point voltage v p Input the voltage sampling function, the output value is transformed by the Parker converter, and the d-axis component v of the common coupling point voltage is obtained d and the common coupling point voltage q-axis component v q ;
[0029] Step 2. Common coupling point voltage q-axis component v d After the proportional-integral controller, the obtained value is consistent with the given angular frequency ω N The sum is obtained to obtain the output angular frequency ω of the phase-locked loop c Send it to the integration link to get the output phase θ of the phase-locked loop c , the output phase θ of the PL...
specific Embodiment approach 2
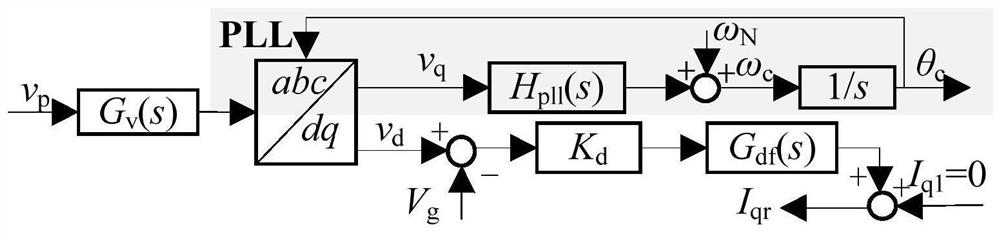
[0039] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is to further limit the method for improving the power transmission capacity of grid-connected inverters under extremely weak power grids described in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, it is characterized in that the reactive power compensation coefficient K d Expressed as:
[0040]
[0041] In the formula, V g is the grid voltage amplitude, I 1 is the given value of inverter d-axis current, X g is the grid impedance.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0042] Specific Embodiment 3: This embodiment further limits the method for improving the power transmission capacity of grid-connected inverters under extremely weak power grids described in Specific Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, the inverter output current q-axis refers to Value I qr Expressed as:
[0043] I qr =(v d -V g )K d G df (s) Formula 2,
[0044] In the formula, I qr is the inverter output current q-axis reference value, v d is the q-axis component of the common coupling point voltage, K d is the reactive power compensation coefficient, G df (s) is a low-pass filter.
[0045] In this embodiment, the PCC voltage amplitude information is introduced into the q-axis current reference quantity of the inverter current loop to realize feedforward control, and the reference quantity is changed from 0 to: I qr =(v d -V g )K d G df (s); I qr is the inverter output current q-axis reference value, v d is the d-axis component of the PCC voltage, that is, i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com