Controlling plant flowering
A plant and sequence technology, applied in angiosperms/flowering plants, plant peptides, plant products, etc., can solve the problems of unknown and ununderstood genetic control of development
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0414] Example 1: Materials and methods
[0415] Microvine Plant Lines
[0416] At the CSIRO Urrbrae base in Adelaide, Australia, microvine plants are grown in a greenhouse or growth chamber at 25-30°C during the day and 20-25°C at night for 16 hours. Keep plants in pots, water daily and give slow-release fertilizers at regular intervals. The microvine genotypes studied had male flowers (FSL / fsl), female flowers (fsl / fsl) or hermaphroditic flowers (FSL / FSL or FSL / fsl). Many microvine lines with different flower types were studied, examples include 03C003V0060 (L1 Pinot Meunier progeny x Richter 110) (male flowers, M / f), 04C023V0003 (female flowers, f / f ), 04C023V0006 (hermaphrodite flowers, H / H). A microvine line with male flowers was obtained by crossing the vine rhizome Richter110 (M / f) with the female microvine line 0C001V0008 (f / f).
[0417] Phenotyping of flower sex by morphological scoring using OIV descriptor No 151 (http: / / www.oiv.int / ).
[0418] Genomic DNA w...
Embodiment 2
[0432] Example 2: Cloning of androgynous sex loci by gene mapping and cloning and sequencing of males, females and hermaphrodites body allele
[0433] Through gene mapping, the inventors have identified genes believed to be responsible for flower sex in grapevines. The inventors named it the flower sex (FSL) gene. Sequencing of this locus identified single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between the male (M), female (f) and hermaphrodite (H) alleles of FSL. SNP markers from this gene have been used for genotyping of plant H and F alleles with 100% match between genotype and phenotype. Full length H cDNA from Cabernet Sauvignon was sequenced from a floral cDNA library generated at CSIRO using standard molecular methods. A cDNA library was prepared from immature inflorescences at stage 12 of the modified E-L system. Tissues were collected from field grown plants. A description of the modified E-L system can be found in the paper by B.G. Coombe (1995) Aust. J. Grape and W...
Embodiment 3
[0435] Example 3: Protein Sequence and BLAST Analysis
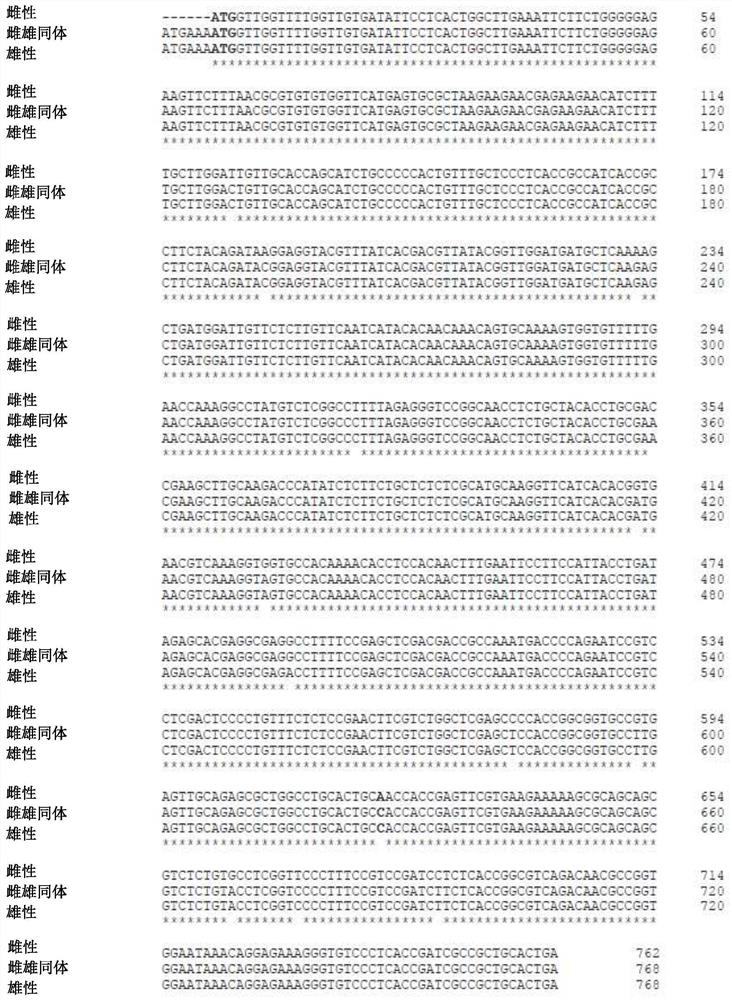
[0436] The protein sequence was obtained from the cDNA sequence, and blast analysis was performed on the protein and cDNA sequences. The protein sequence is shown in image 3 A-C and SEQ ID NO: 5-7. These alignments predict the presence of a PLATZ (Plant AT Rich and Zinc Binding) domain (Nagano et al. (2001) Nucleic Acids Res. 29(20):4097-4105).
[0437] For cDNA sequences ( figure 1 A-D) and amino acid sequence ( image 3 A-C), The predicted region of the PLATZ domain (zinc finger box) is highlighted in yellow. The region in each case was identified using the online tool PROSITE (Sigrist, C.J.A., (2009) Nucleic Acids Research, 38:161-166.). It is evident from the sequences that there are no differences in the amino acid sequence between the different alleles, however there is a C to T substitution in the cDNA sequence of the female allele (bold), which yields a homozygous asparagus Amino acid sense mutation GAC→...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com