Organic matter pore formation and evolution in-situ observation method and application
A technology of organic matter and pores, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, instruments, etc., can solve the in-depth study of the formation and evolution of shale organic matter type pores and affect the characteristics of marine shale reservoirs The evaluation of shale and the high degree of microscopic heterogeneity of shale can eliminate the influence of sample heterogeneity, visualize the characteristics of pore development, and save drilling core samples.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
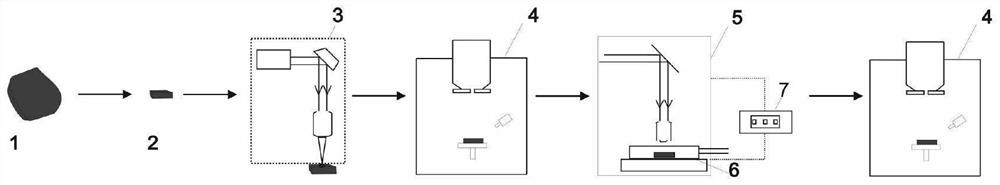
[0065] This example provides an in-situ observation method for the formation and evolution of organic pores. The schematic diagram of the in-situ observation process for the formation and evolution of organic pores is shown in figure 1 As shown, the Lower Silurian low-mature marine shale in the European Baltic Sea Basin was selected to carry out in-situ observation research on the formation and evolution of organic pores.
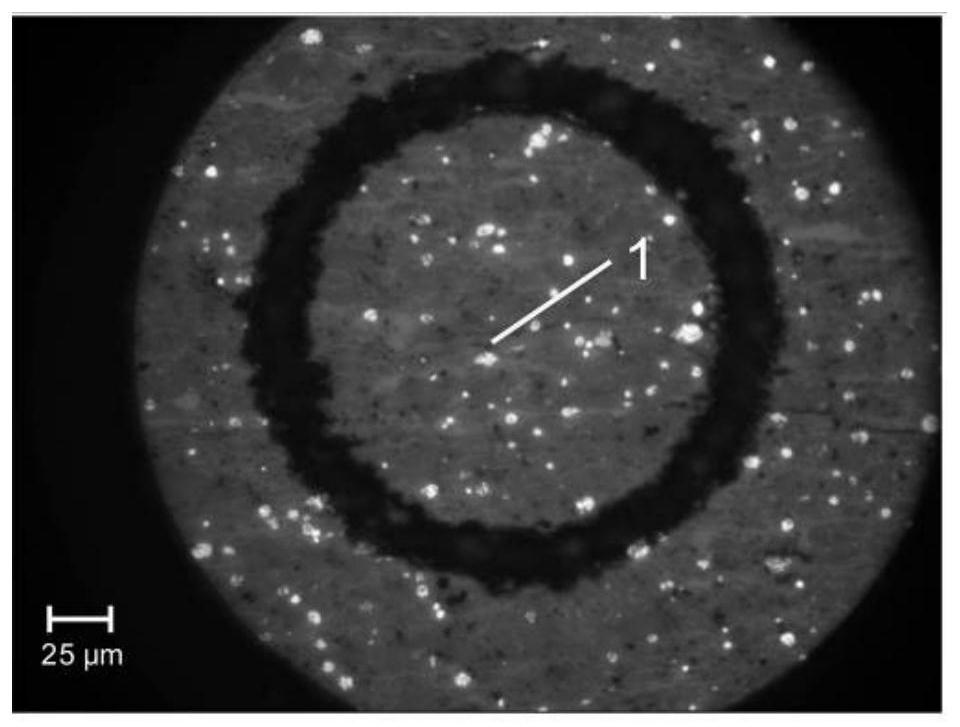
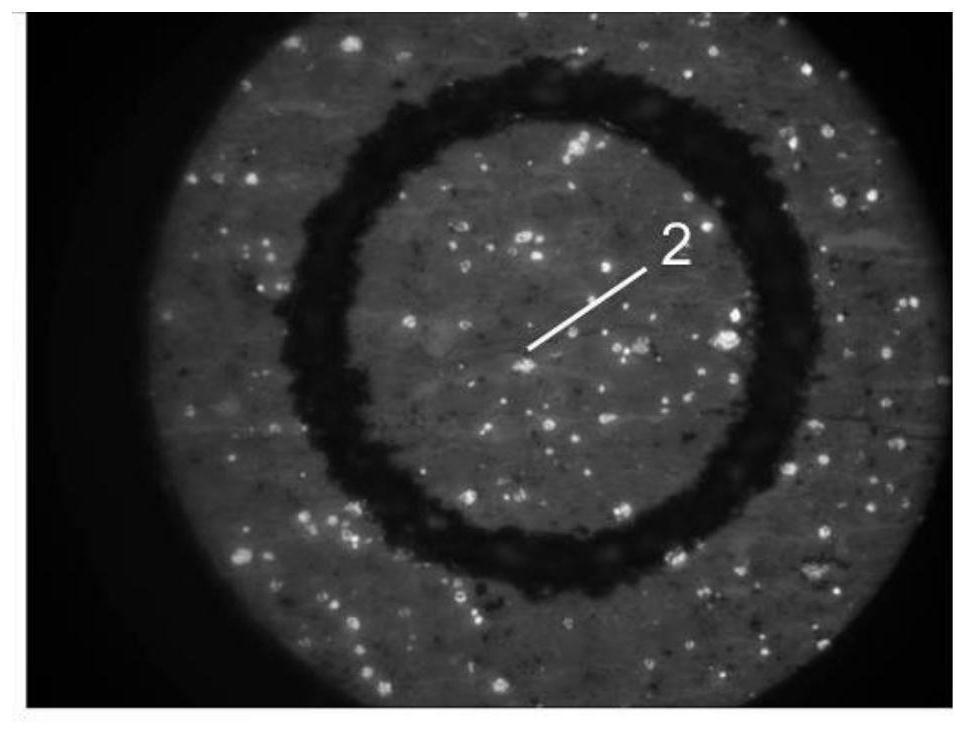
[0066] (1) For drilling core samples ( figure 1 Middle mark 1) Cut into a block sample of about 1cm square, fix the block sample on the base, and then fix the sample on the Leica lapping all-in-one machine, cut, grind and polish in sequence, and then transfer the sample to the Leica ion Ion beam polishing was used in the thinning instrument, and the samples after argon ion polishing ( figure 1 Mark 2) has a thickness of 0.8 mm.
[0067] (2) Select the target organic matter under the microscope. What this embodiment selects is the algae body, and use th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com