Lumbar vertebra posterior zero-incisura fusion cage, driving-in system and driving-in method
A cage, zero-notch technology, used in spinal implants, joint implants, joint implants, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty, large trauma, affecting sight, and achieve the effect of stable position
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
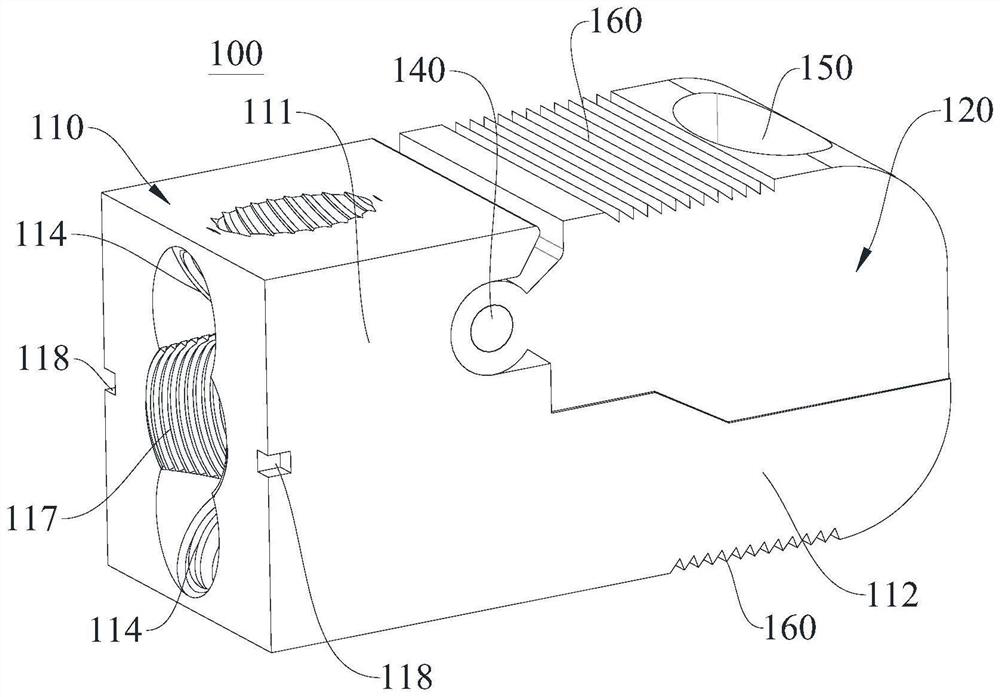
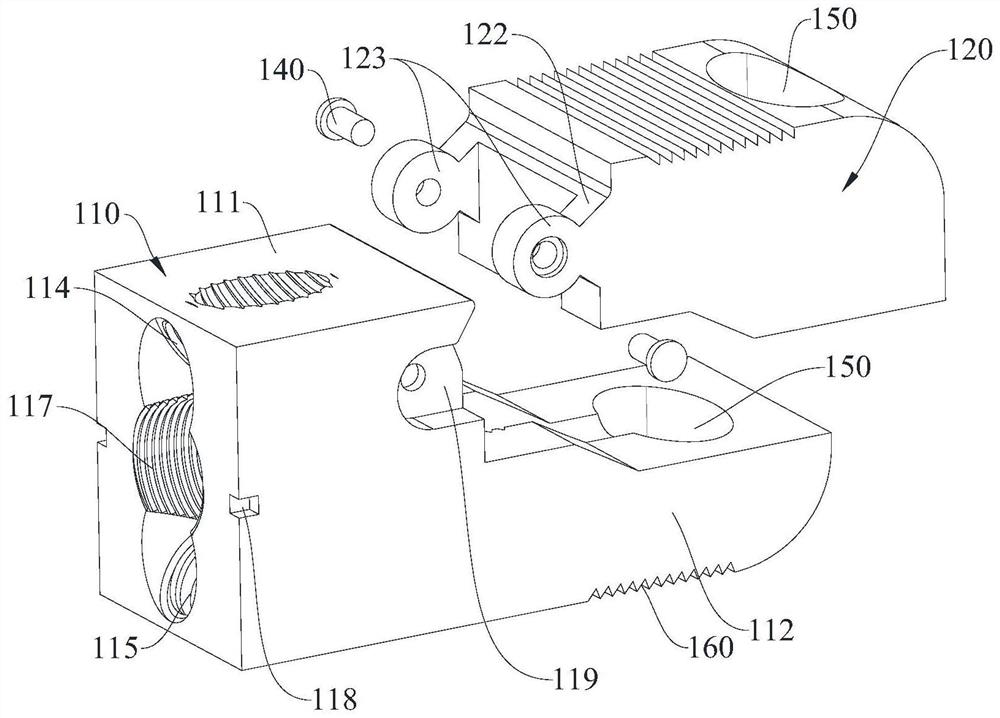
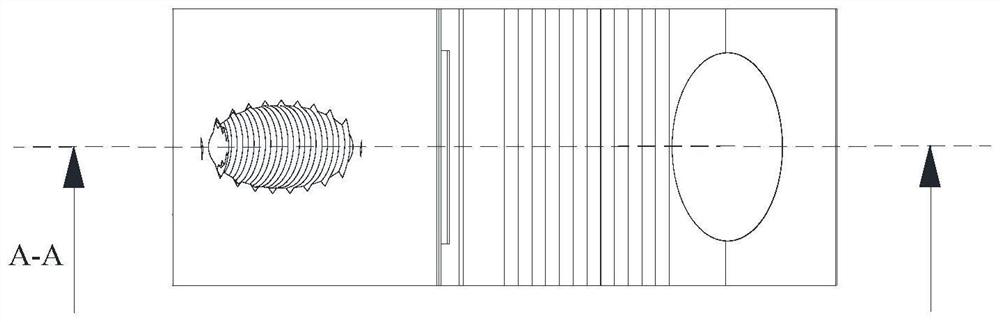
[0054] Please refer to Figure 1-9 , Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a posterior lumbar spine zero-notch fusion cage, which includes a fixed part 110 and a spreader part 120, the spreader part 120 is rotatably connected to the upper part of the side of the fixed part 110, so as to be relatively The fixing portion 110 rotates. The fixing part 110 is used for locking on the upper vertebral body and the lower vertebral body of the lumbar vertebrae, and the spreading part 120 is used for upwardly spreading so that the upper side of the cage 100 has an upward slope, that is, when the cage 100 is opened, After entering between the upper vertebral body and the lower vertebral body of the lumbar vertebrae, the stretching portion 120 is propped up by opening the screw to rotate relative to the fixing portion 110, so that the upper vertebral body is stretched and abutted upward and the upper vertebral body is pushed up. the front column, and the fixing part 110 is locked...
Embodiment 2
[0072] like Figure 12-17 As shown, Embodiment 2 of the present invention provides a system for driving a posterior lumbar vertebrae with zero-notch fusion device, which includes a driving device and the fusion device shown in Embodiment 1.
[0073] like Figure 12-16 As shown, the driver 200 includes a sleeve 230 , a head 210 and a hollow screw 220 with a tail cap 240 . The head 210 is detachably connected to the cage 100, so as to connect the cage 100 through the head 210, and then drive it between the upper vertebral body and the lower vertebral body. A through hole 211 is formed in the middle of the head 210 . The head is connected with the sleeve 230, and a through hole 211 is opened in the middle of the head, which communicates with the sleeve 230 and is coaxially arranged; the hollow screw is sleeved on the sleeve 230 and passes through In the hole 211, one end of the hollow screw close to the end cap 240 is threadedly connected to the sleeve 230, and the end of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] like Figure 18-22 As shown, Embodiment 3 of the present invention provides an application method of the fusion device 100, that is, an insertion method, which includes the following steps:
[0082] After the decompression of the spinal canal in the posterior lumbar vertebrae and the resection of the intervertebral disc are completed, the cage and the driver are detachably connected into one body, and then the cage is driven into the upper vertebral body and the lower vertebral body from the posterior lumbar vertebra. The opening part of the cage faces the side of the upper vertebral body; the opening pin is passed through the driver into the cage, and abuts the opening part to make it open upward Abutting and pushing up the anterior column of the upper vertebral body, the spreading portion is stretched to a preset height and then stops screwing in the spreading pin; the fixing portion of the cage is locked by the locking pin 170 Within the upper and lower vertebral bo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com