Track vibration reduction fastener with high transverse stability and rigidity changing method thereof
A lateral stability and vibration damping fastener technology, applied in the field of rail vibration damping, can solve the problems of reduced service life of rails, poor lateral stability, limited lateral stiffness, etc. Effect of low dynamic-static stiffness ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
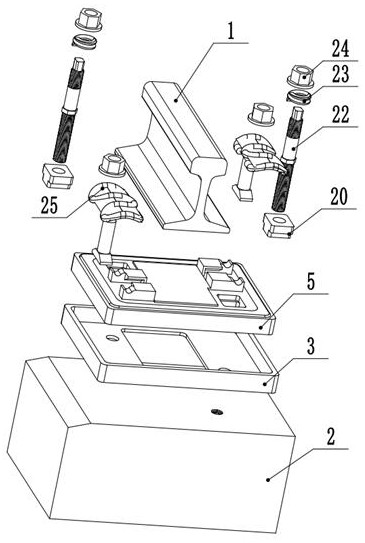
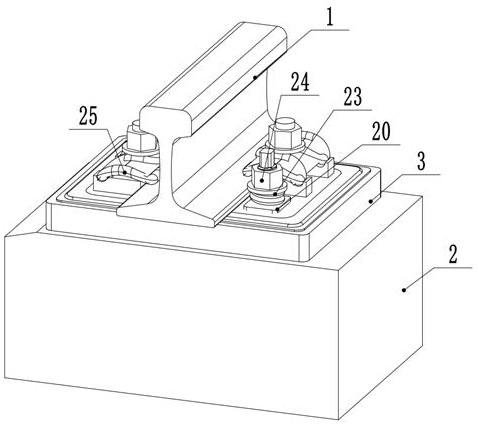
[0042] A rail damping fastener with high lateral stability, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a rail damper 5 located at the lower end of the rail 1 and a sleeper 2 located below the rail damper 5. A base support 3 is provided between the rail damper 5 and the sleeper 2, and the base support 3 is fixed on the On the upper end of the sleeper 2, the bottom support 3 includes a accommodating groove 4 with an upward opening; such as figure 2 As shown, the rail damper 5 is limited to the accommodating groove 4 of the bottom support 3, and the bottom support 3 can prevent the rail damper 5 from moving and swaying in the horizontal direction, improving the lateral stability of the damping fastener, preventing Rail 1 is worn. The base support 3 in this embodiment is a rectangular parallelepiped that matches the shape of the rail damper 5 . Those skilled in the art can also set the base support 3 according to the shape requirements of the rail damper 5 in actual working conditio...
Embodiment 2
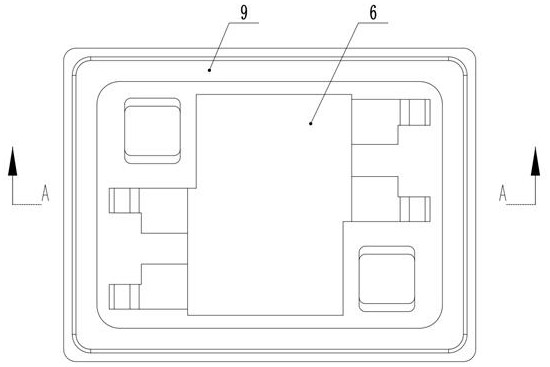
[0049] The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that, as Figure 7 As shown, the arrangement and quantity of the large bosses 17 and the small bosses 18 are different from those in the first embodiment. Specifically, the large bosses 17 and the small bosses 18 are evenly spaced on the horizontal row. This embodiment includes three A horizontal row of large bosses 17 and three horizontal rows of small bosses 18 . The non-linear variable stiffness and protection stiffness are formed by the large boss 17 and the small boss 18 .
Embodiment 3
[0051] The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is that, if Figure 8 As shown, the shapes of the large bosses 17 and the small bosses 18 are different from those in the second embodiment, and the large bosses 17 and the small bosses 18 in this embodiment are inverted trapezoidal structures.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com