Forest stand radiation flux calculation method based on point cloud data and computer graphics
A technology of computer graphics and point cloud data, applied in the field of stand radiation flux research, can solve the problems of reducing the universality of results, time-consuming experimental work, unstable results, etc., and achieve the effect of strong practicability and scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0137] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below according to the accompanying drawings:
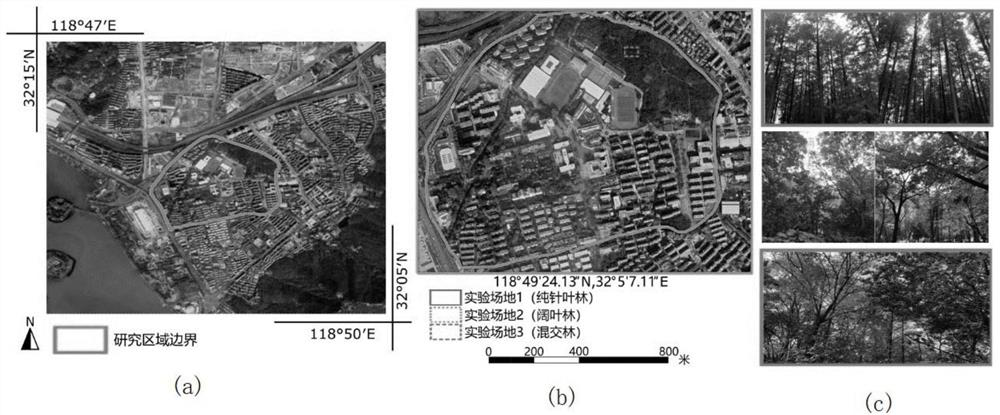
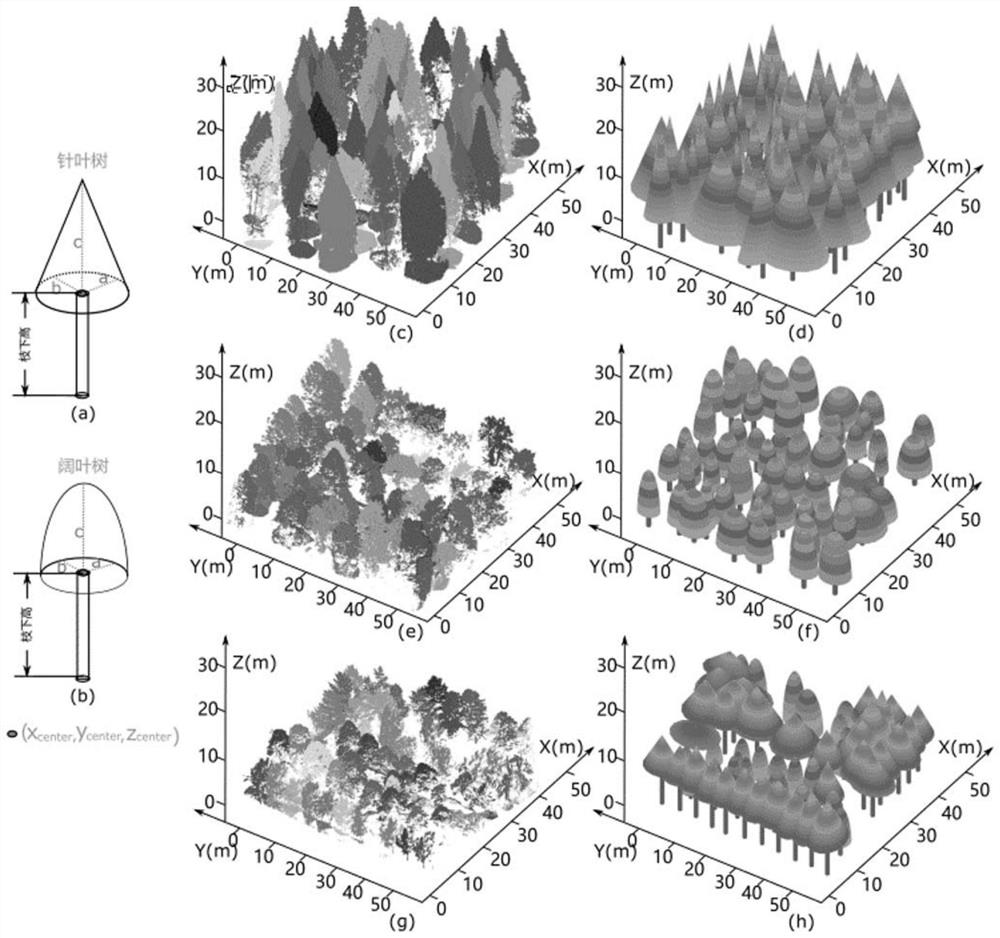
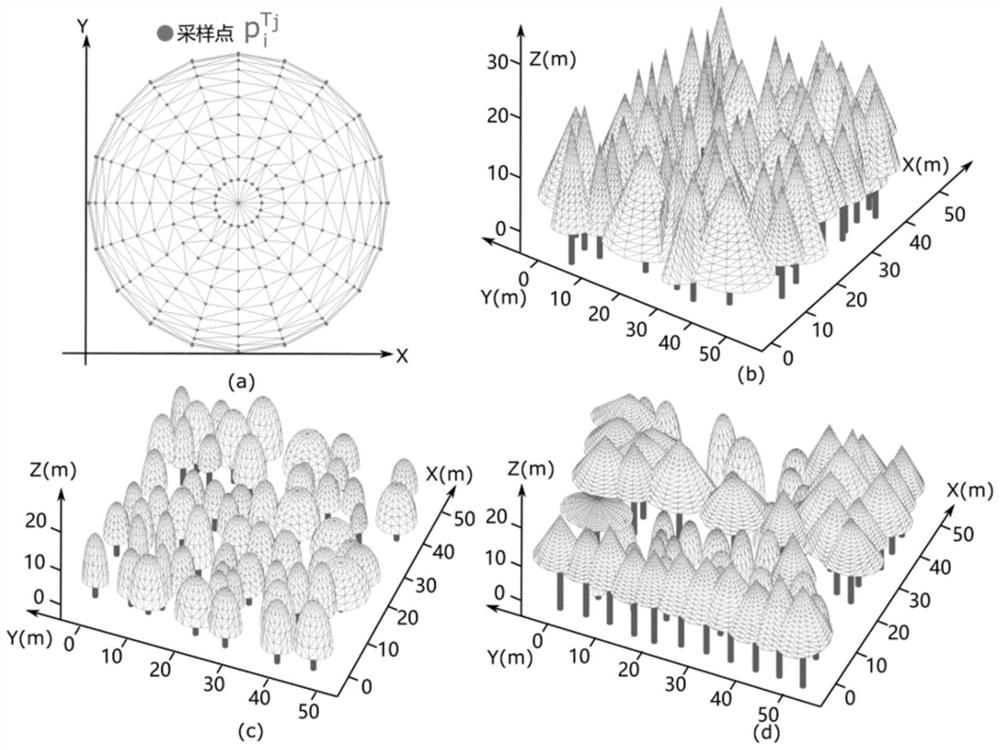
[0138] Forest environments have a highly complex radiation regime, and the 3D canopy structure prevents solar radiation from entering the forest; therefore, canopy radiation varies with time, season, and meteorology, making both measurement and modeling of radiative flux challenging. Here, this embodiment provides a synergistic approach, namely, a stand radiant flux calculation method based on point cloud data and computer graphics, using airborne LiDAR data and computer graphics to simulate the forest canopy and calculate three Radiative fluxes of individual forest stands (coniferous, broad-leaved and mixed forests). The forest canopy surface is decomposed into triangular elements by emitting a directional incident solar beam according to the solar elevation and azimuth. A ray tracing algorithm is used to simulate the propagation of reflected and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com