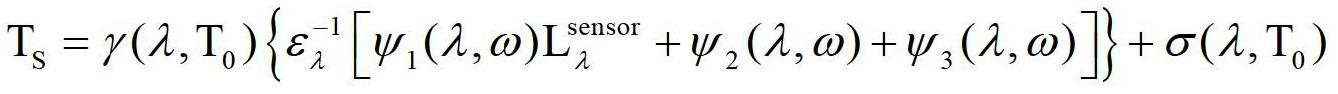Patents
Literature
95 results about "Radiative flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radiative flux, also known as radiative flux density or radiation flux (or sometimes power flux density), is the amount of power radiated through a given area, in the form of photons or other elementary particles, typically measured in W/m². It is used in astronomy to determine the magnitude and spectral class of a star and in meteorology to determine the intensity of the convection in the planetary boundary layer. Radiative flux also acts as a generalization of heat flux, which is equal to the radiative flux when restricted to the infrared spectrum.
Sequential UV induced chemical vapor deposition
Ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes are disclosed where an ion flux, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or an electron flux, respectively, is used to induce the chemical reaction in the process. The process for depositing a thin film on a substrate includes introducing a flow of a first reactant gas in vapor phase into a process chamber where the gas forms an adsorbed saturated layer on the substrate and exposing the substrate to a flux of ions, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or a flux of electrons for inducing a chemical reaction of the adsorbed layer of the first reactant gas to form the thin film. A second reactant gas can be used to form a compound thin film. The ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential CVD process of the present invention can be repeated to form a thin film of the desired thickness.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
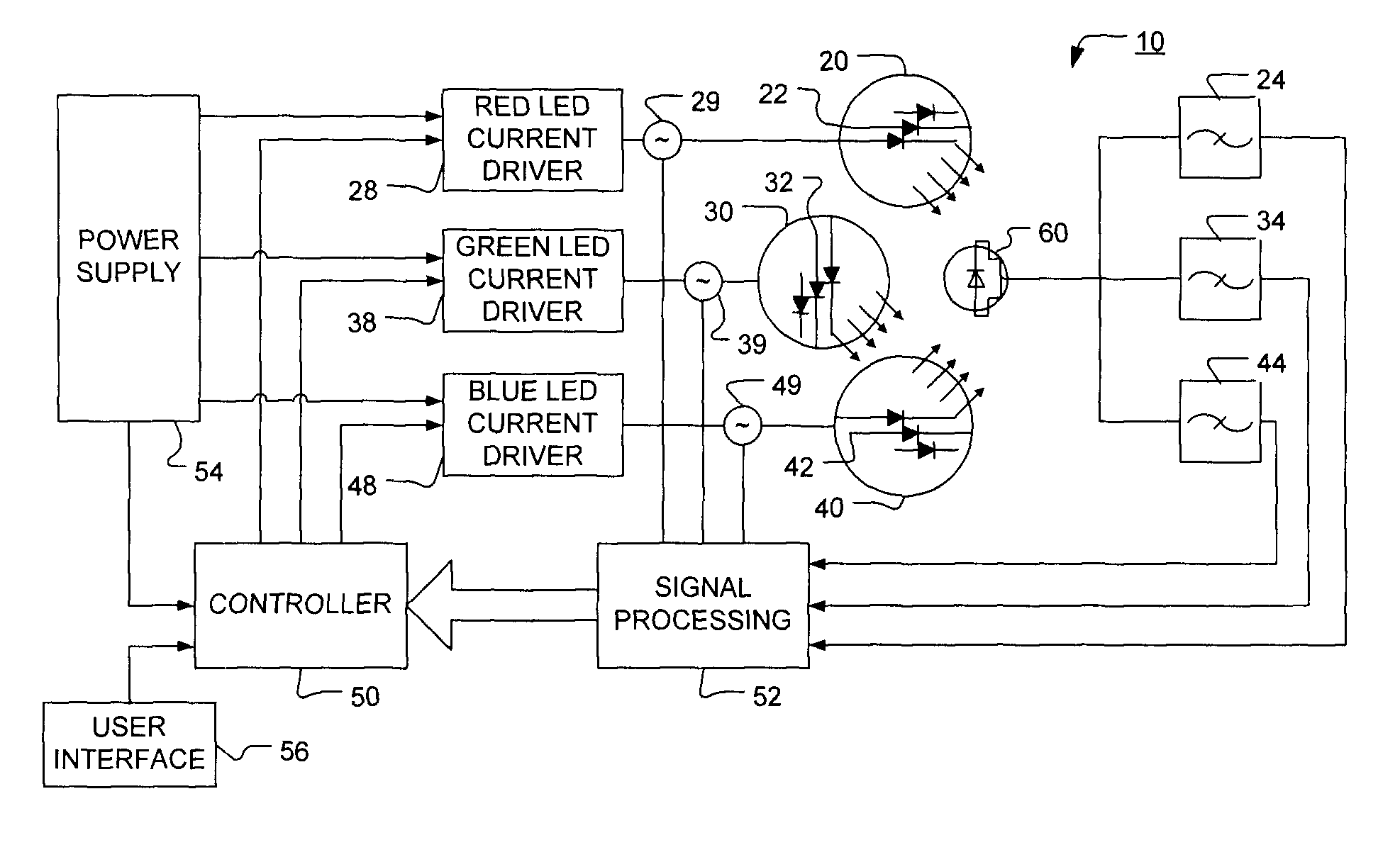
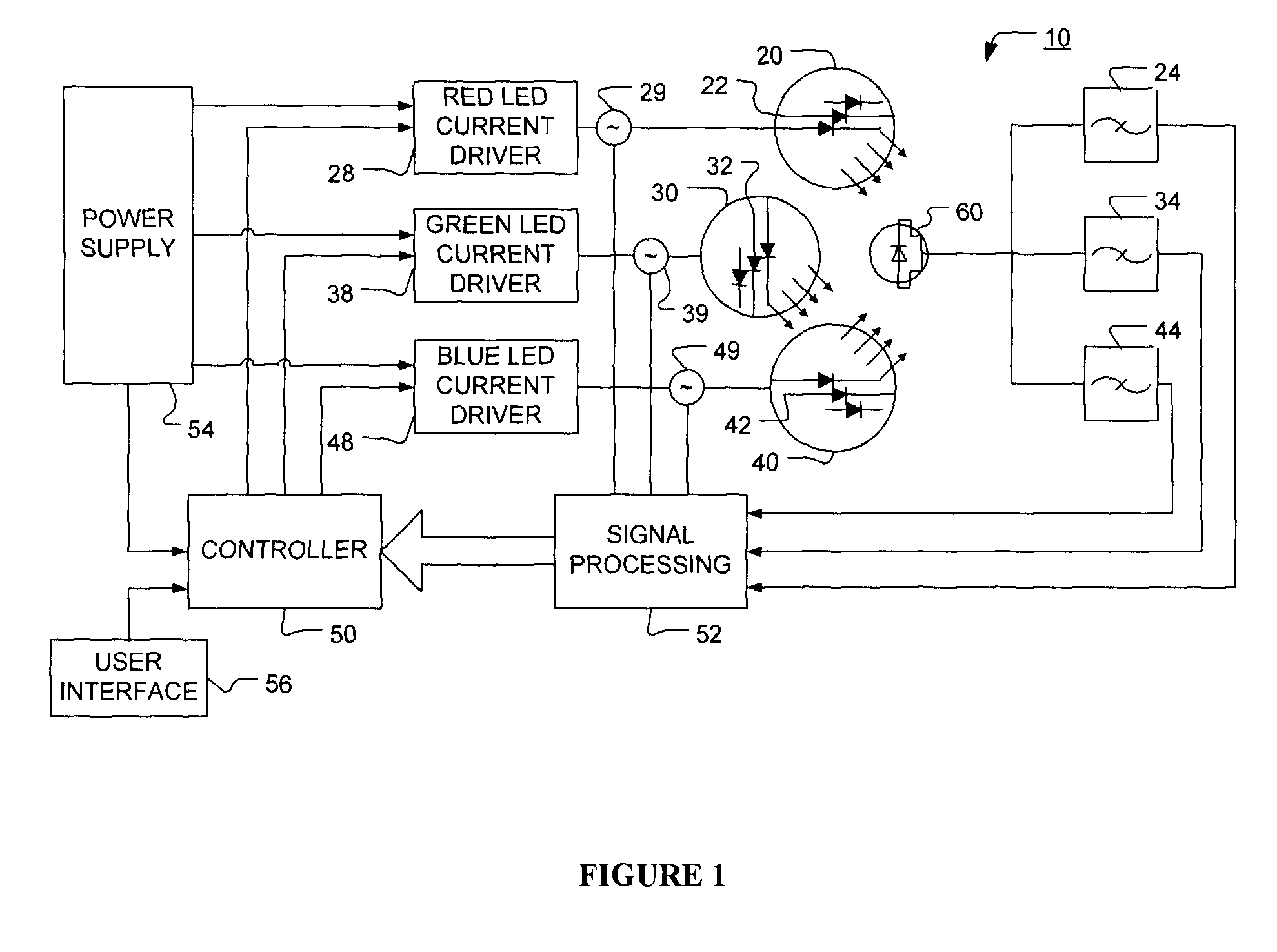
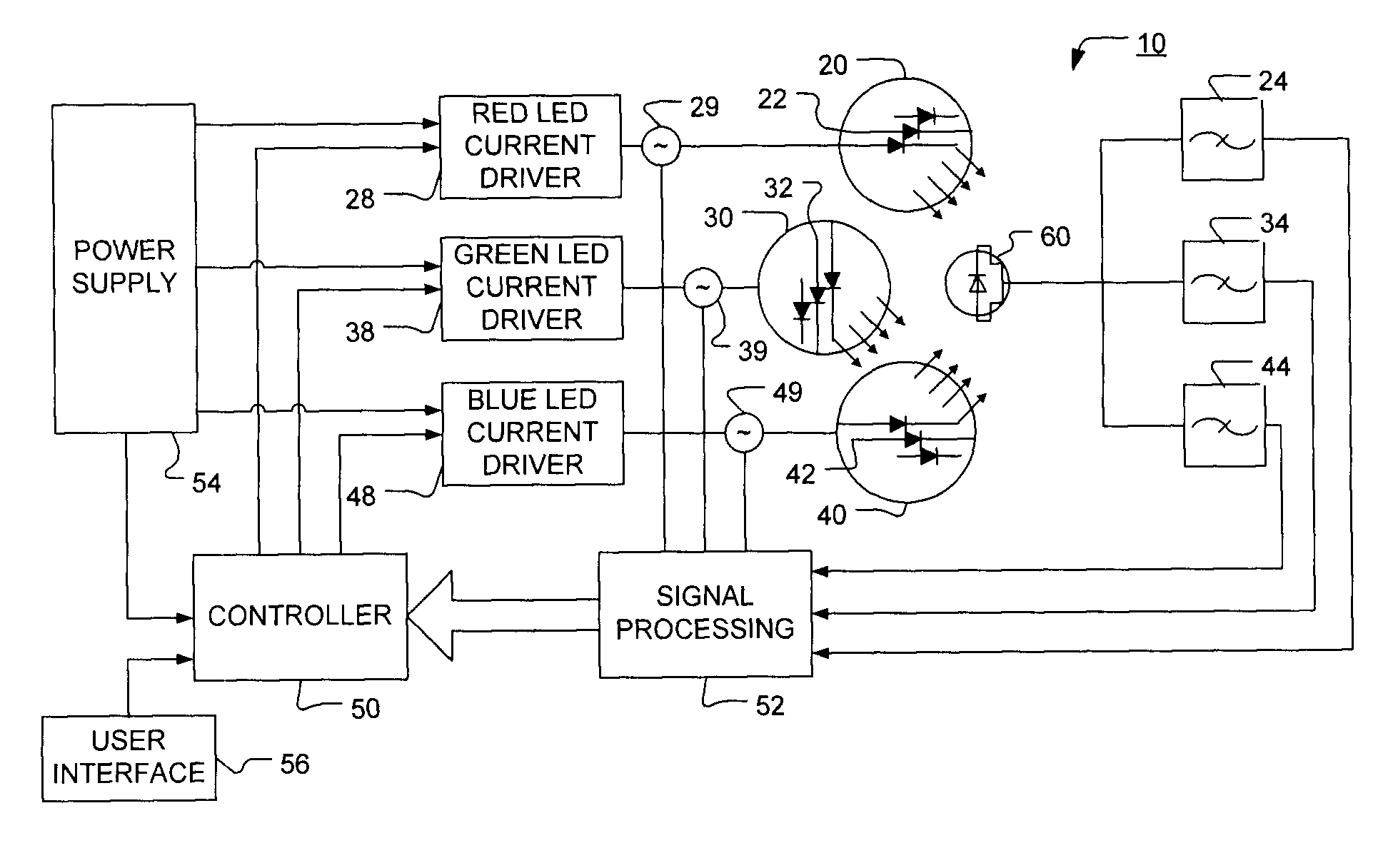
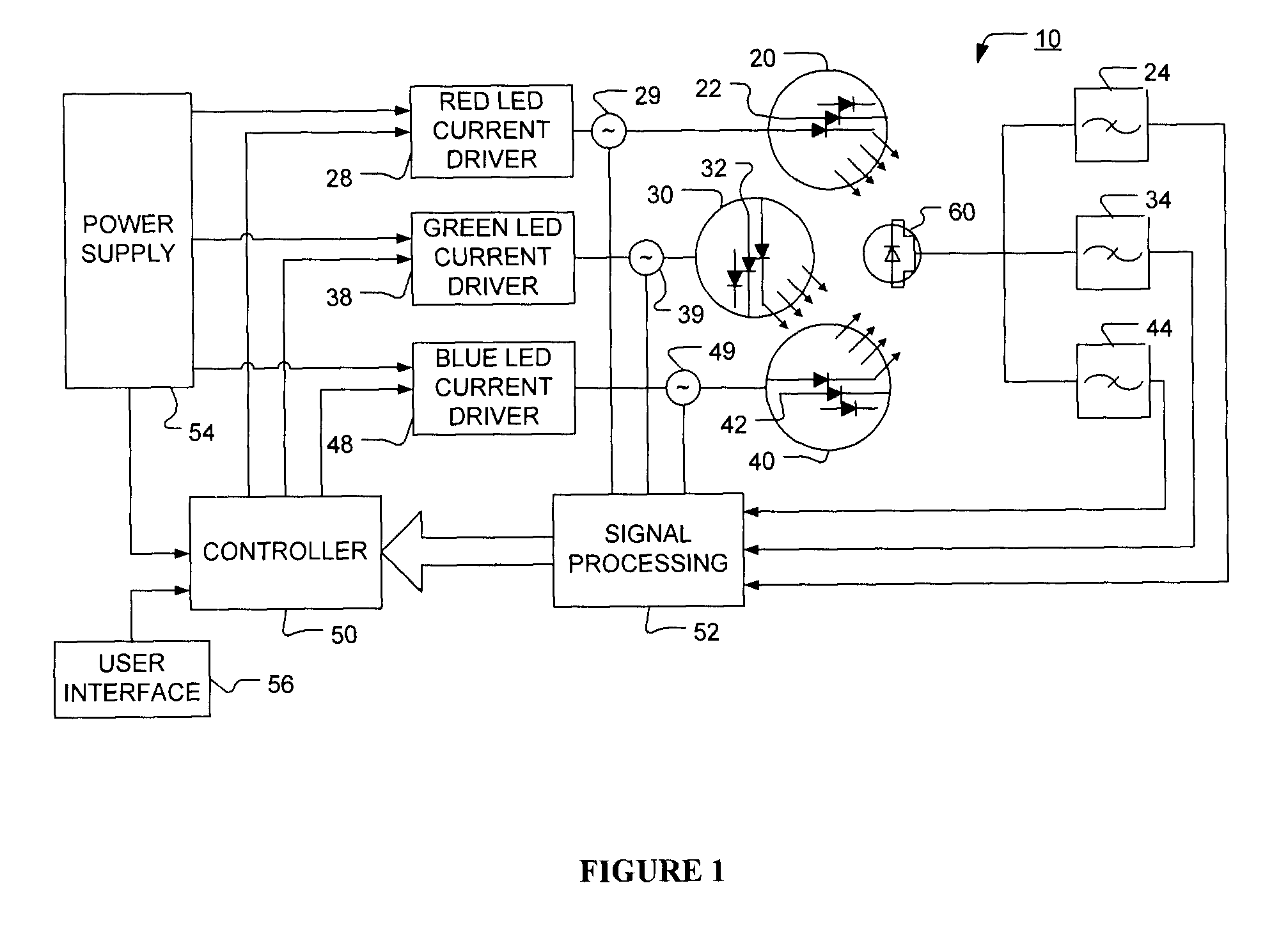
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
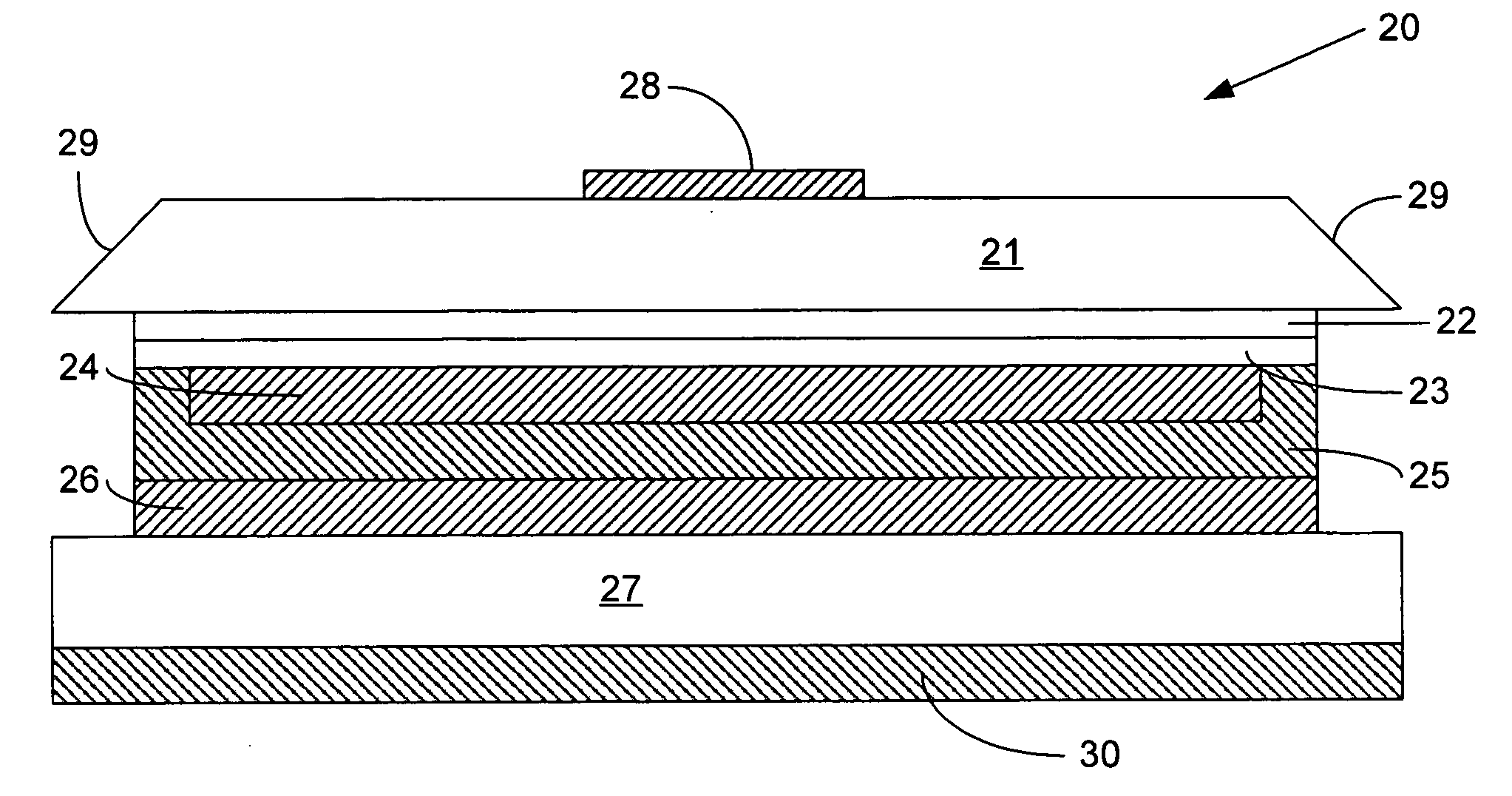
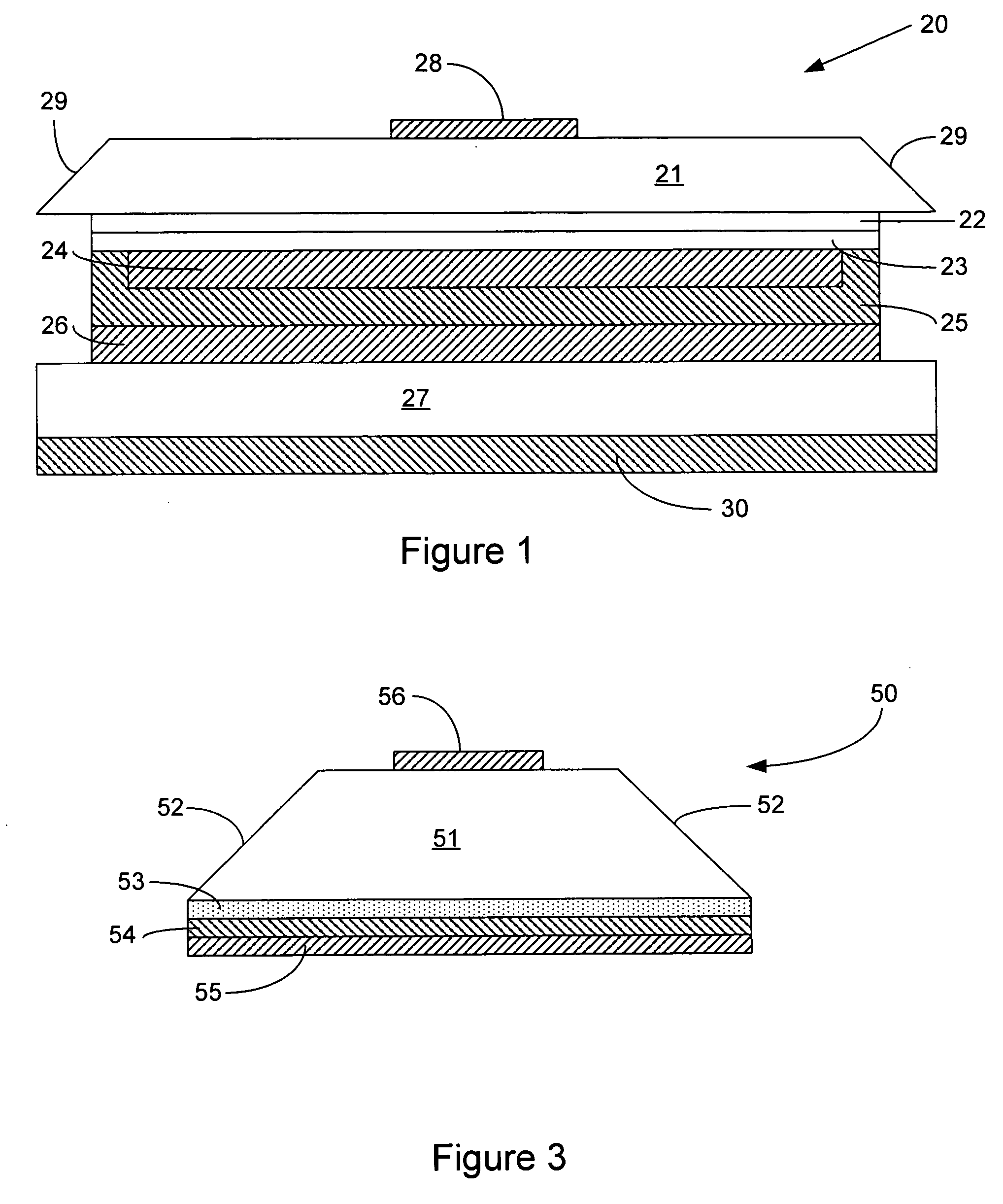
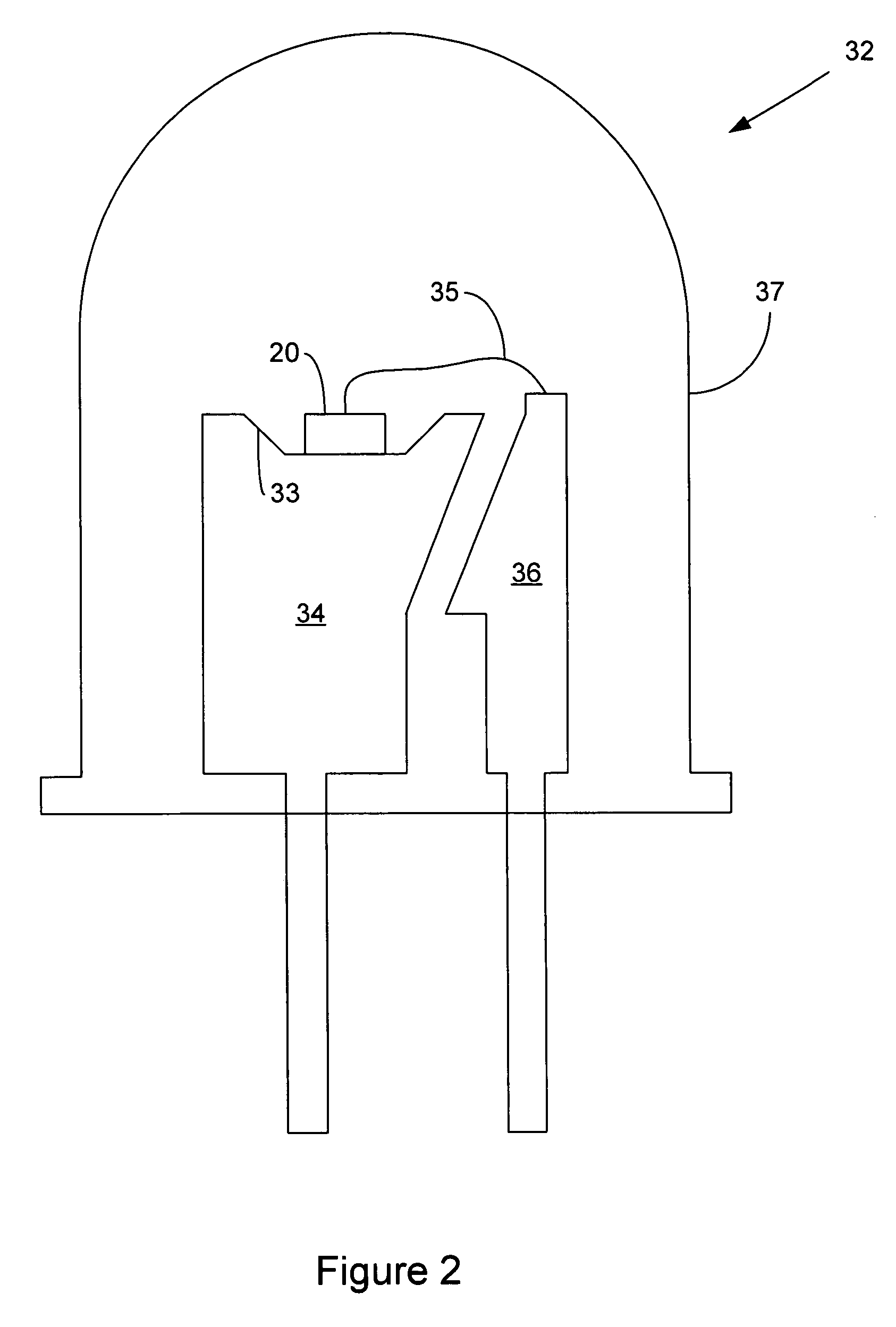
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular color, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each color. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colors of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated color, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for light intensity control
InactiveUS20090189530A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentControl signal
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for optical feedback control for an illumination device, wherein the control signal for each array of one or more light-emitting elements corresponding to a particular colour, is independently configured using a modification signal whose frequency is different for each colour. Electronic filters whose center frequencies are substantially equal to the modification signal frequencies of the drive currents for the light-emitting elements are used to discriminate between the radiant flux corresponding to each of the different colours of light-emitting elements, from a sample of the mixed radiant flux output collected by one or more optical sensors. The output of an individual electronic filter is substantially directly proportional to the radiant flux output of the light-emitting elements of the associated colour, which together with the desired luminous flux and chromaticity of the output light, the controller can use to adjust the control signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
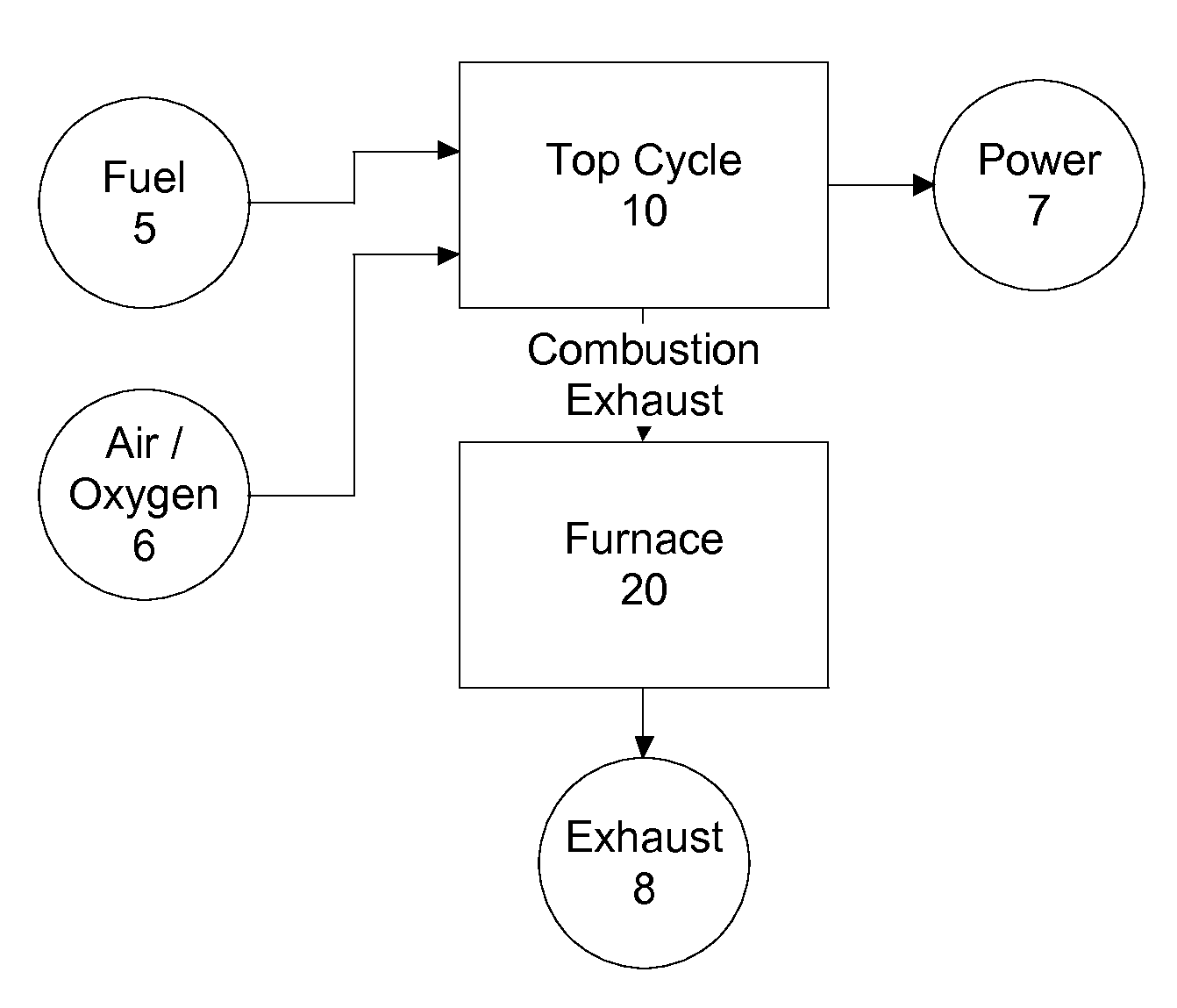
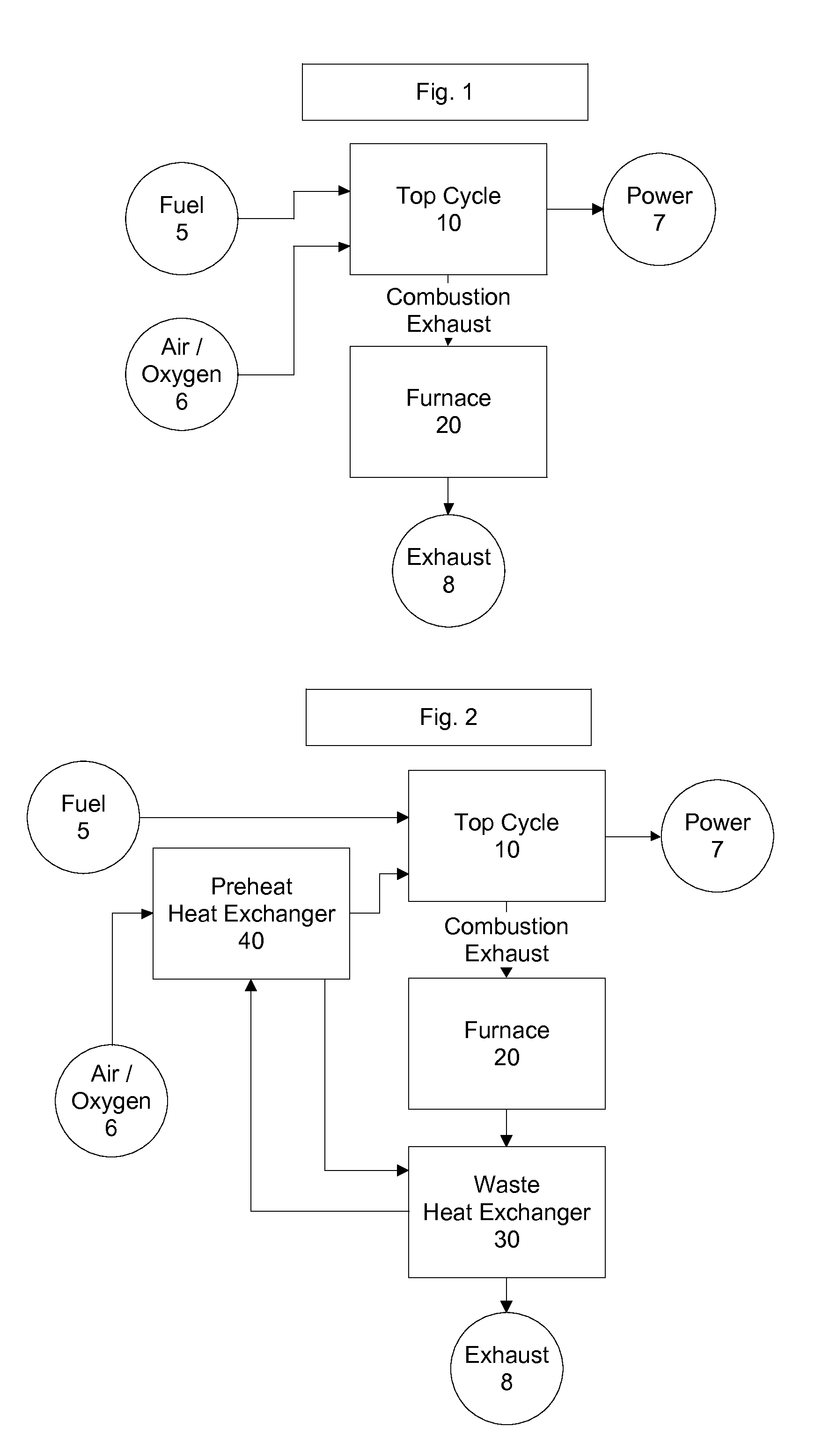
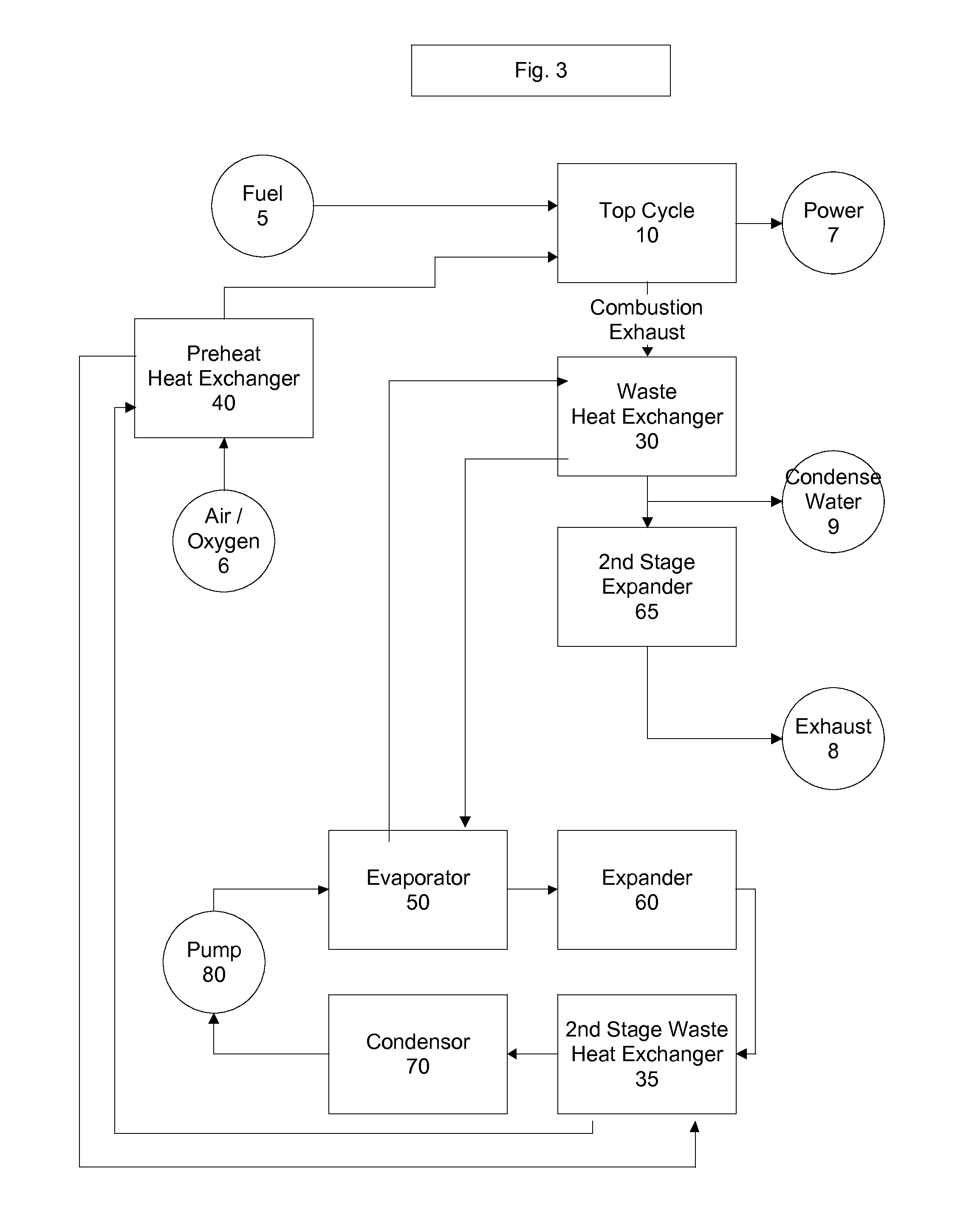
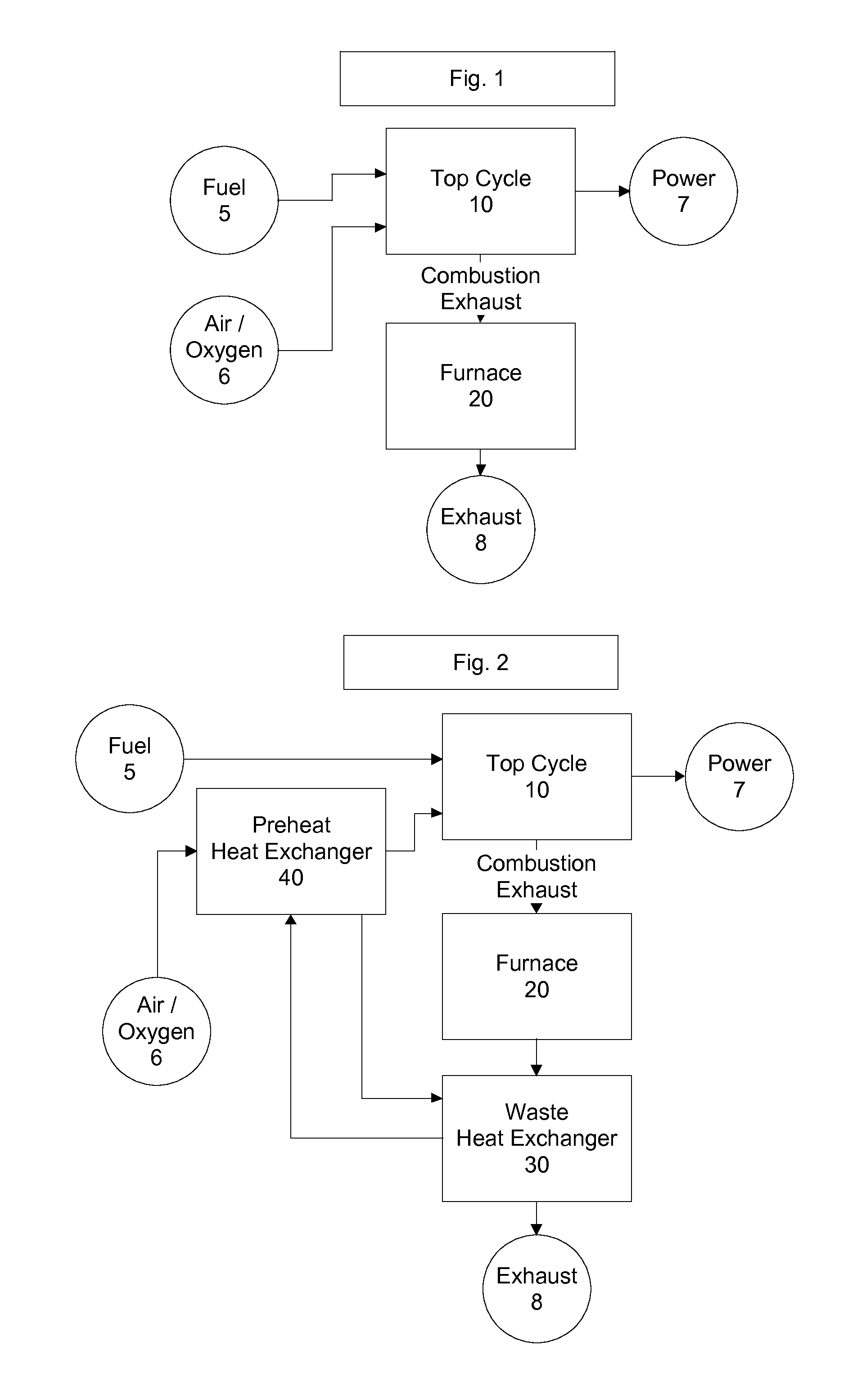
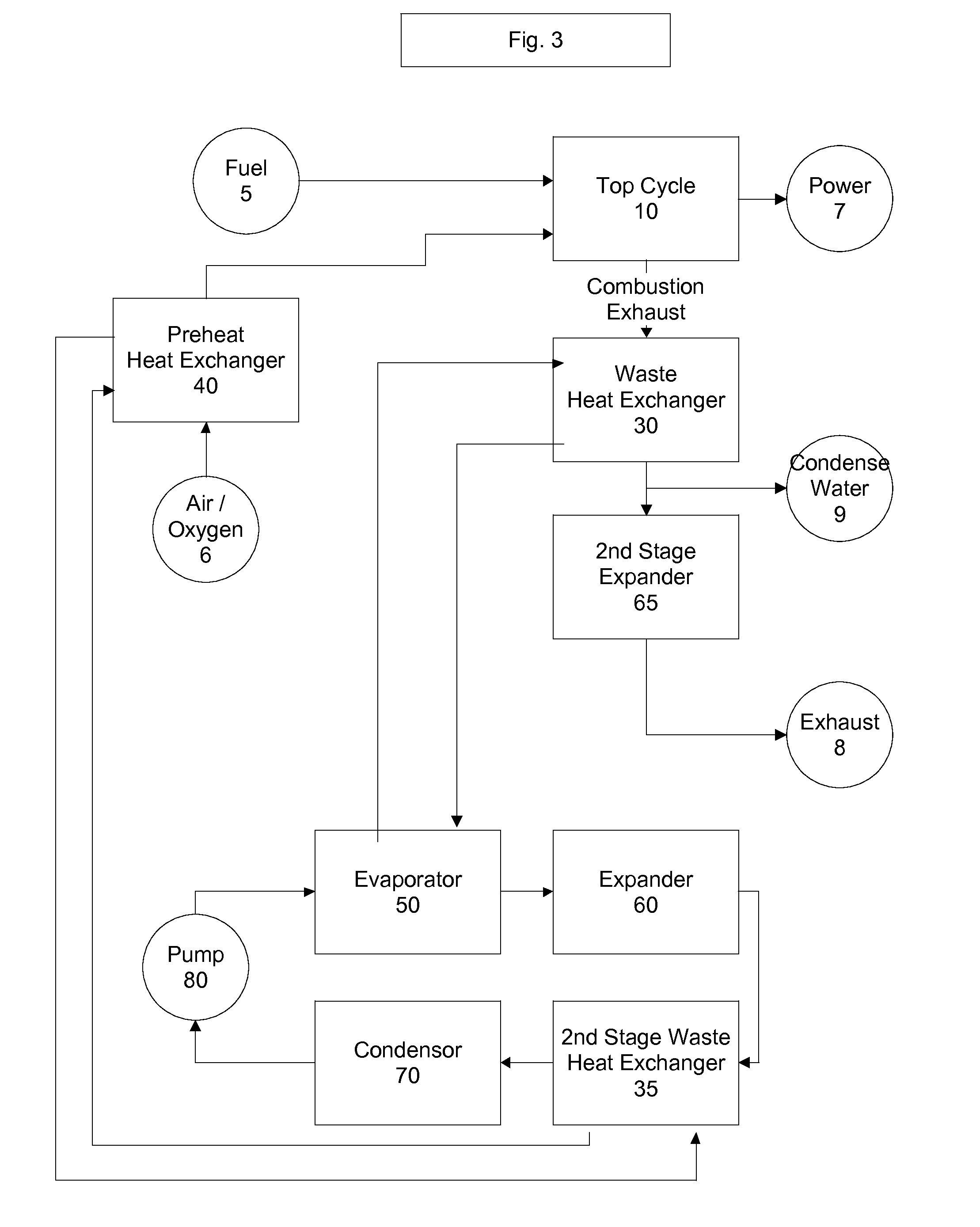
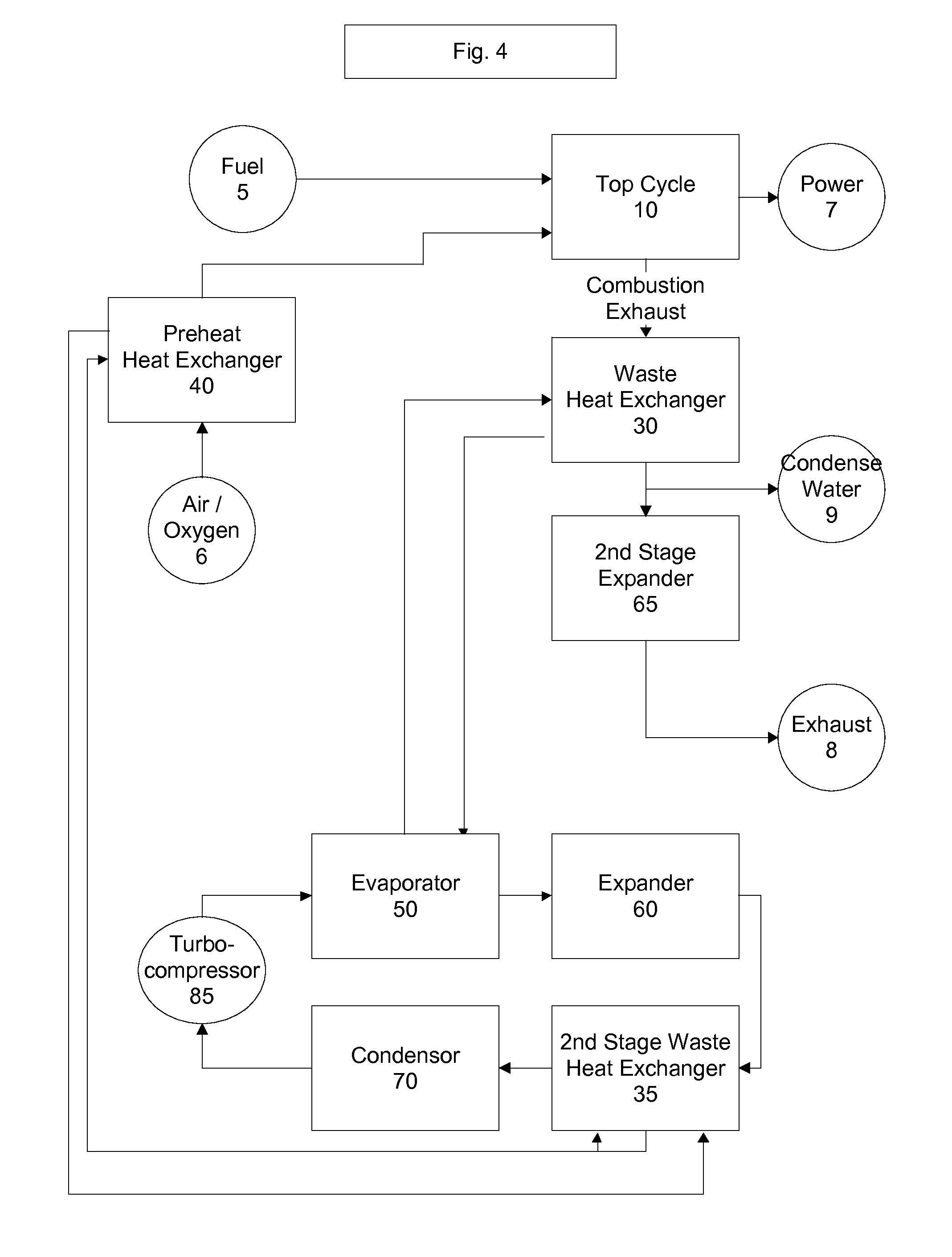
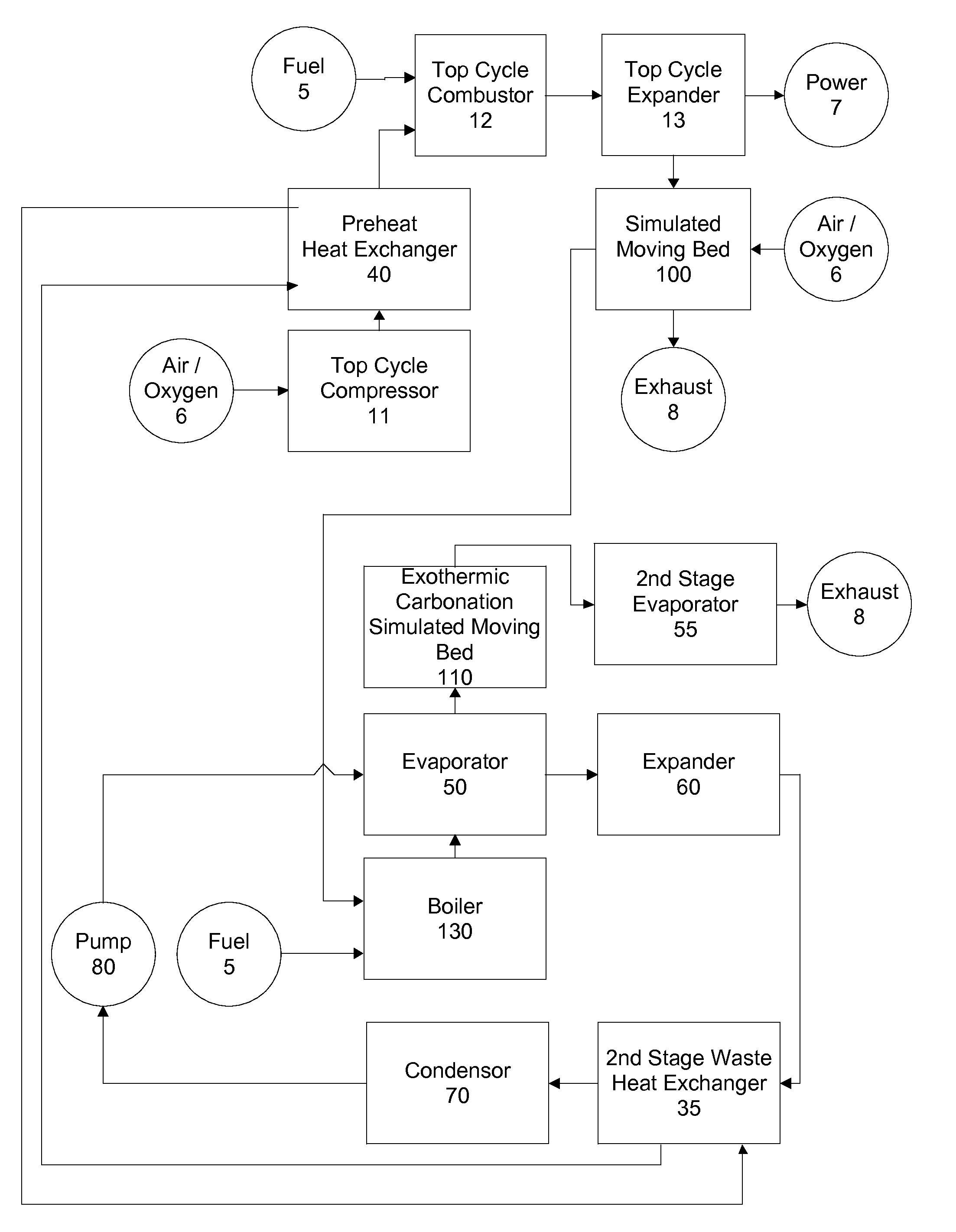
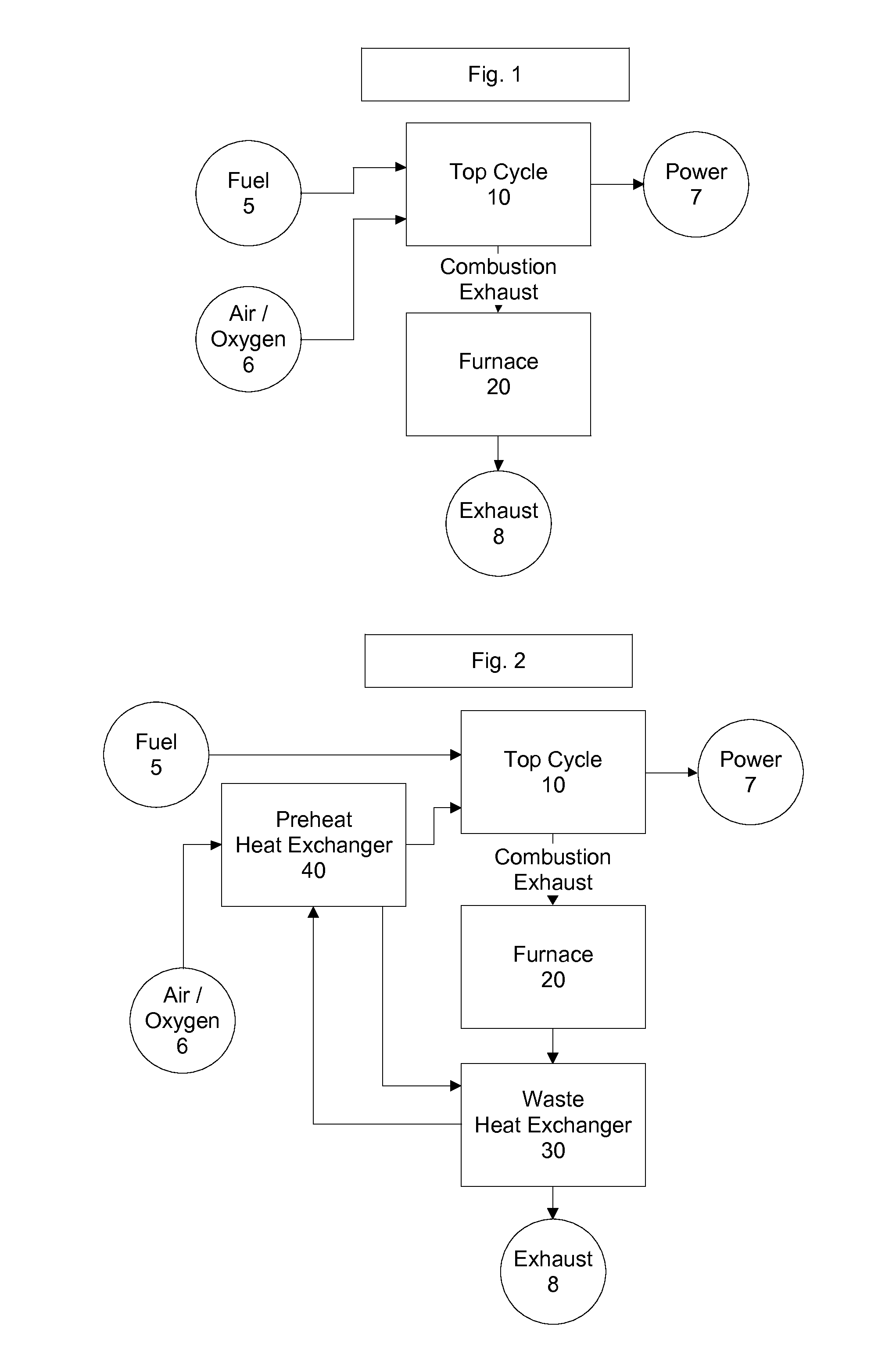
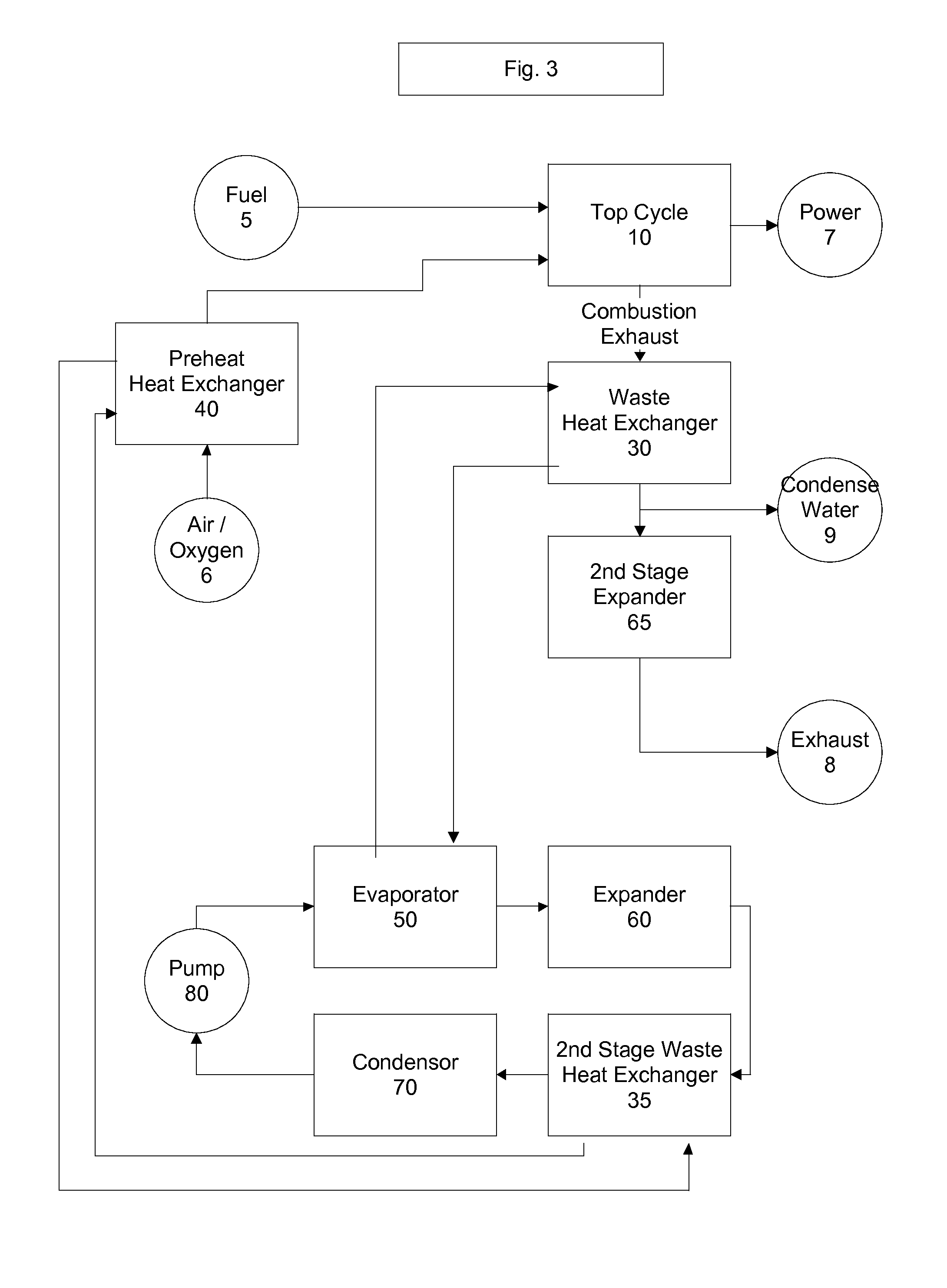
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize exergy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
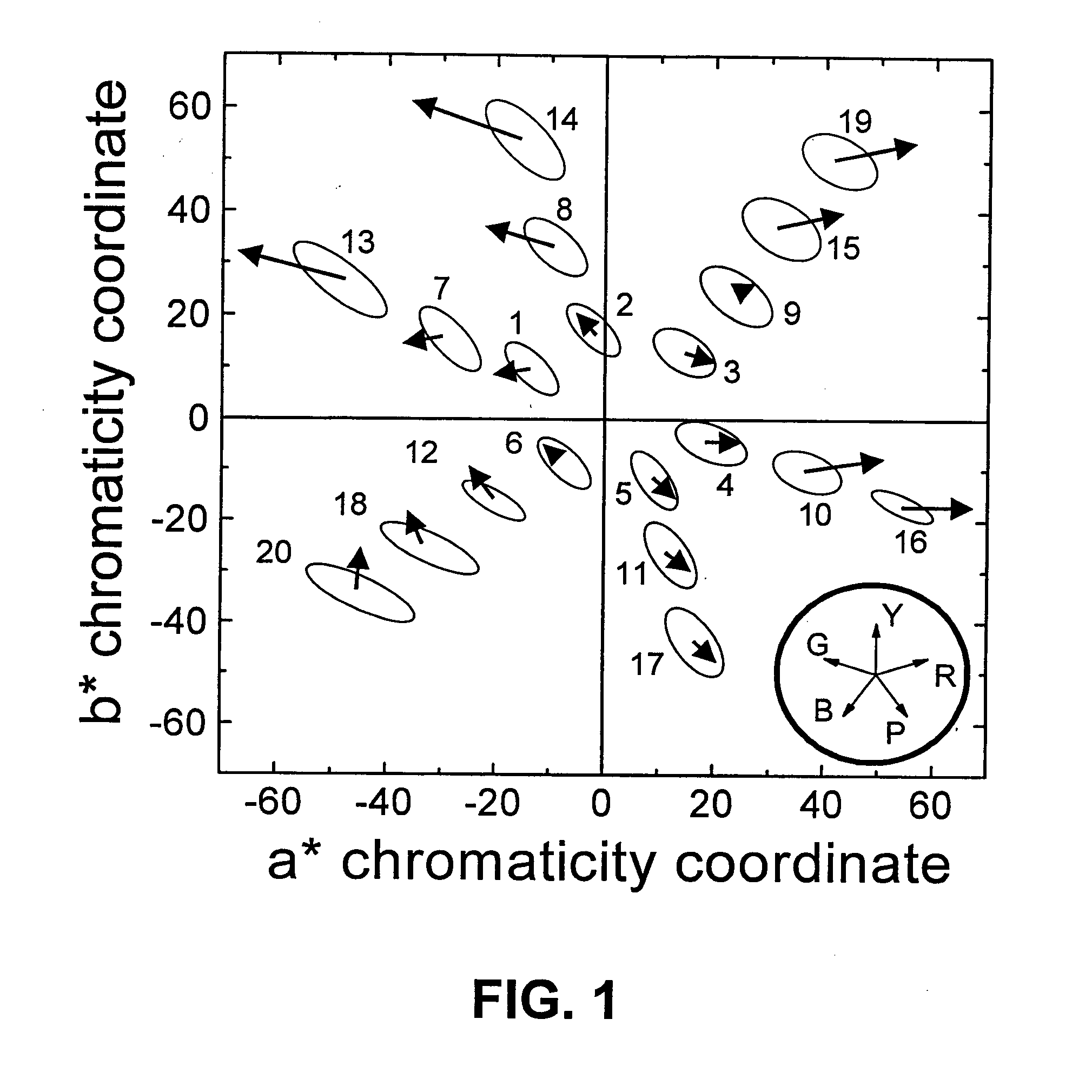
Polychromatic solid-state light sources for the control of colour saturation of illuminated surfaces
InactiveUS20140167646A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminophoreLight-emitting diode
Polychromatic light sources of white light are composed of at least two different coloured emitters, such as groups of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Disclosed are the spectral power distributions and relative partial radiant fluxes of the coloured emitters that allow controlling the colour saturating ability of the generated light, namely, the ability to render colours with increased saturation and the ability to render colours with decreased saturation. Also disclosed is a method for dynamical tailoring the colour saturating ability of the generated light.
Owner:VILNIUS UNIV
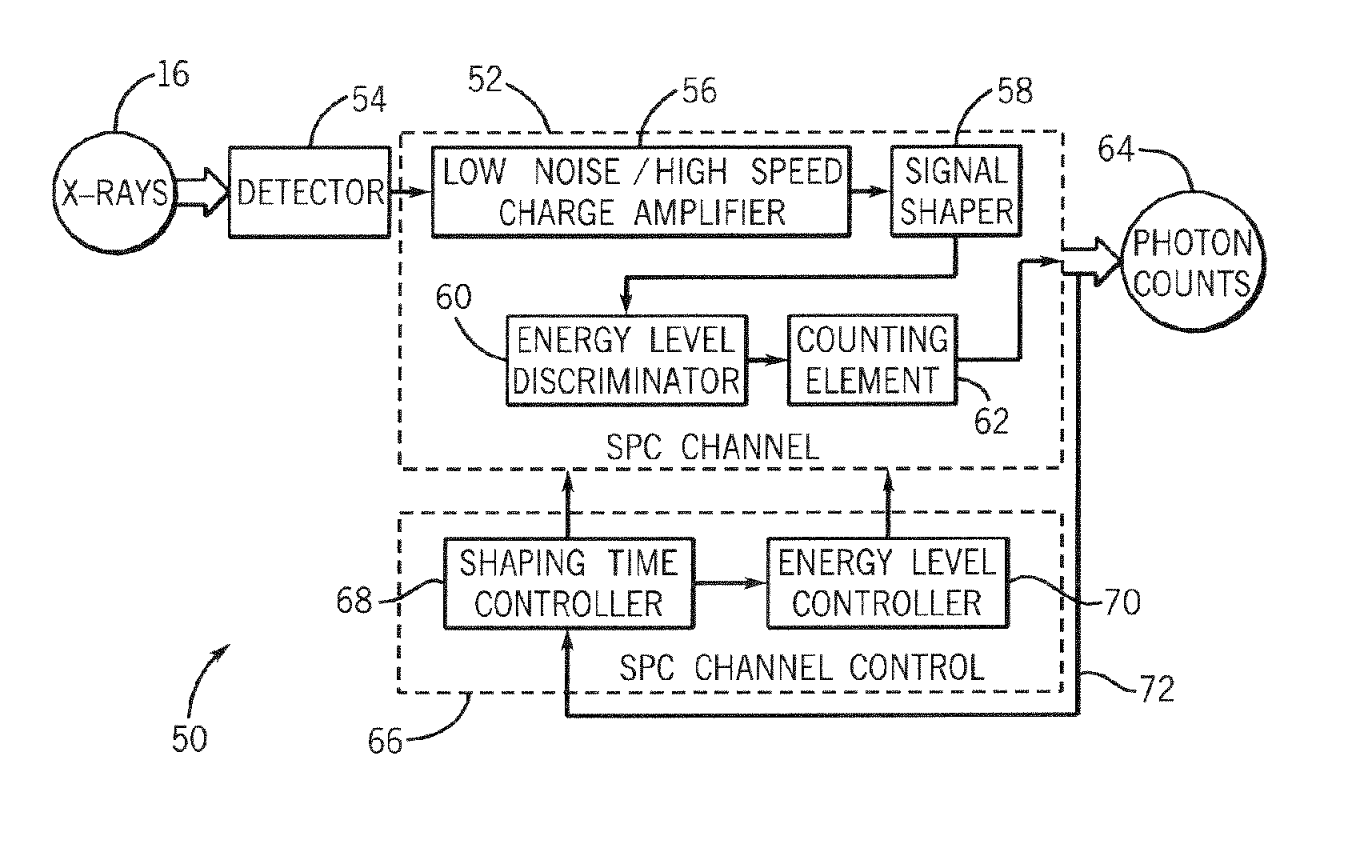
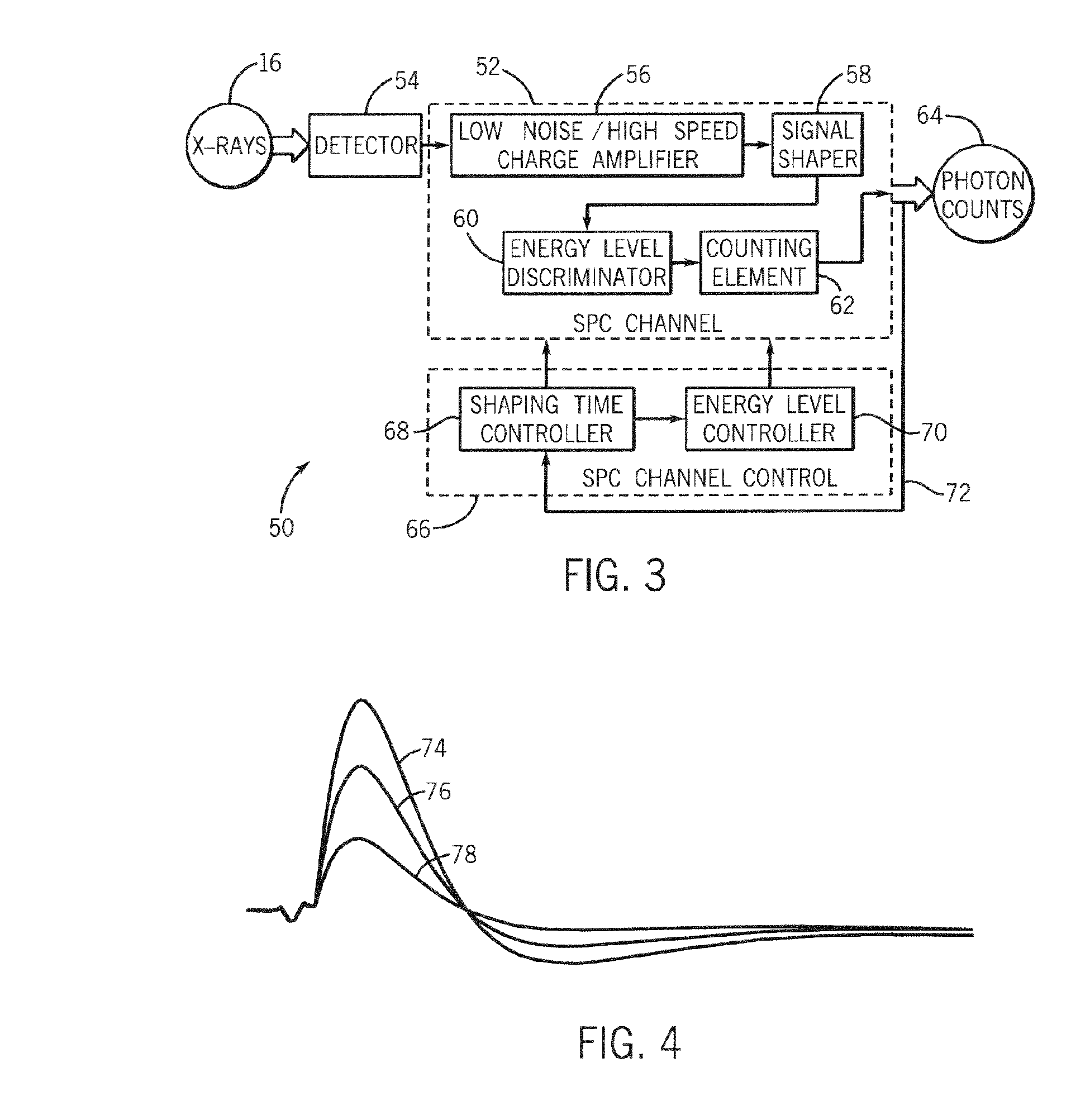
Method and system of dynamically controlling shaping time of a photon counting energy-sensitive radiation detector to accommodate variations in incident radiation flux levels
ActiveUS20060056576A1Avoid saturationDetection efficiency sacrificedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorHigh flux
A method and system of counting and tagging radiation energy received by a radiation detector is presented. The method and system are designed to dynamically control the sampling window or shaping time characteristics of a photon counting detector to accommodate variations of flux experienced by the detector so as to preserve optimum detector performance and prevent saturation during high flux conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Direct conversion of nanoscale thermal radiation to electrical energy using pyroelectric materials
InactiveUS20110298333A1Minimize thermal contact resistanceEnhance radiative heat fluxThermoelectric device with dielectric constant thermal changeThermal electric motorComposite filmPower cycle
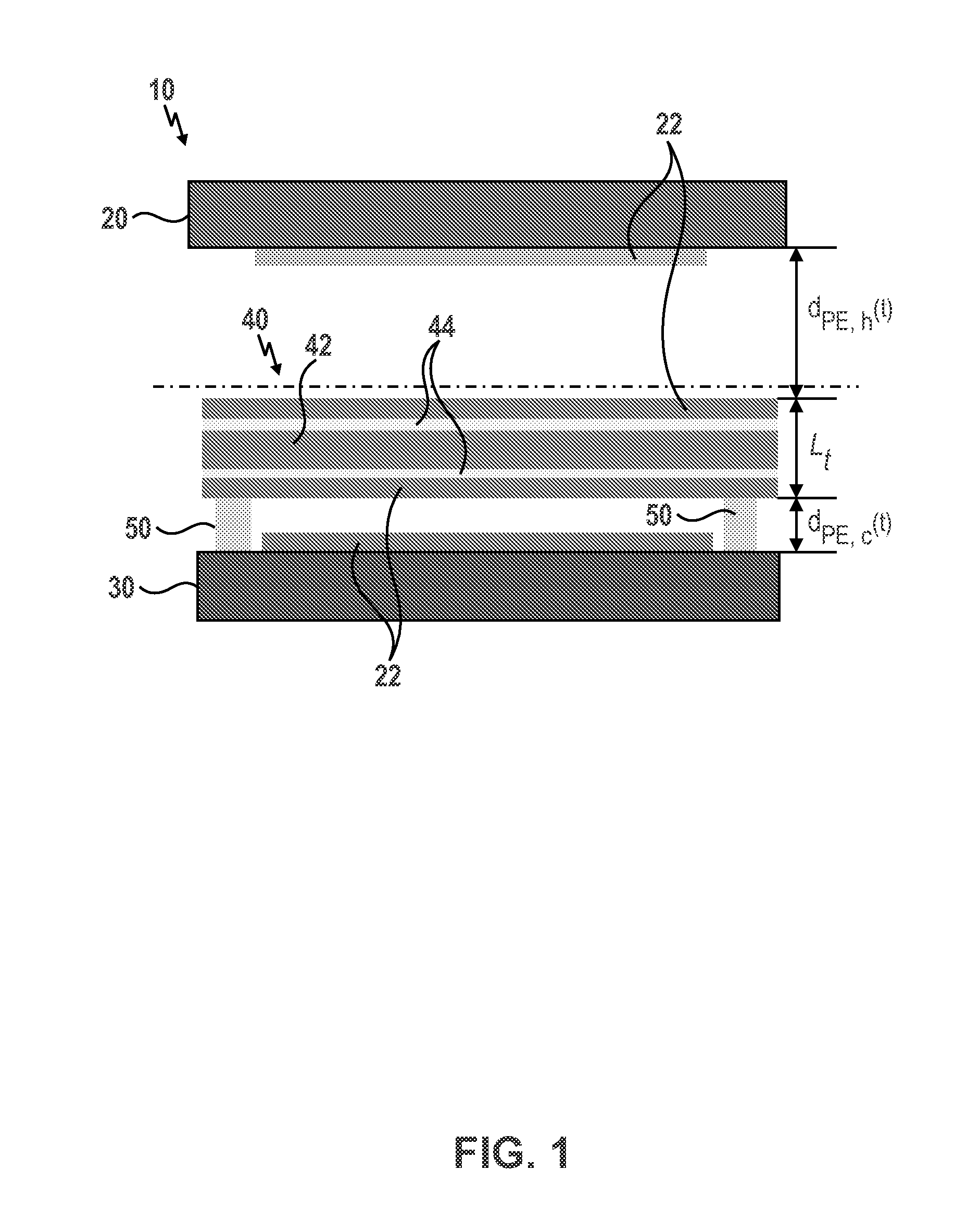
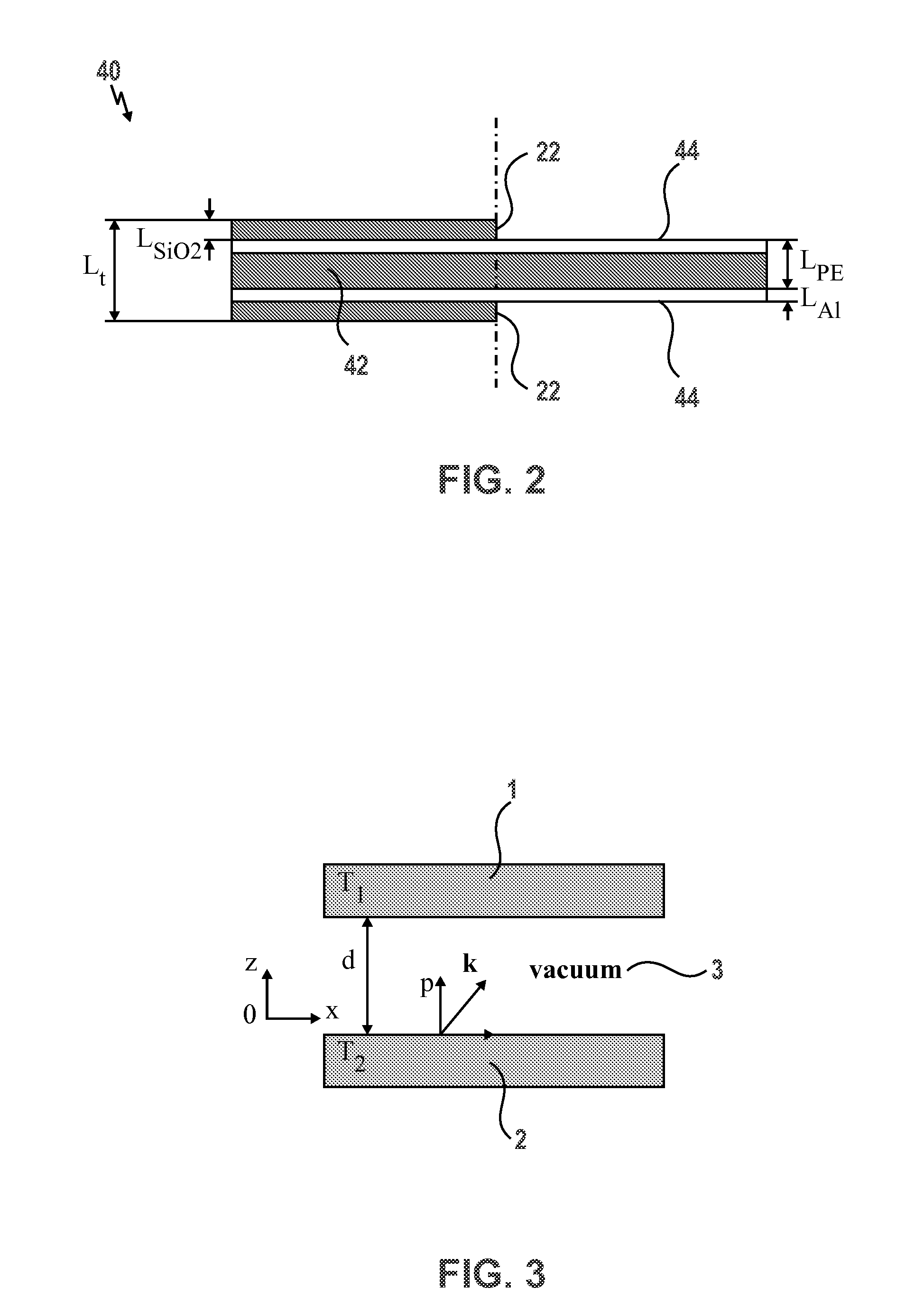
The embodiment provided herein are directed to a pyroelectric (PE) energy converter which is capable of combining nanoscale thermal radiation and pyroelectric energy conversion for harvesting low grade waste heat. The converter advantageously makes use of the enhanced radiative heat transfer across a nanosize gap to achieve high operating frequencies or large temperature oscillations in a composite PE plate. The PE energy converter generally comprises a hot source, a cold source, and a PE plate, wherein the PE plate oscillates between the hot and cold source and the PE plate can be subjected to a power cycle in the displacement-electric field diagram. The hot and cold sources of the converter can be coated with SiO2 absorbing layer to further enhance the radiative heat fluxes. The converter comprising a PE plate made of 60 / 40 P(VDF-TrFE) operated between 273 K and 388 K experiences a maximum efficiency of 0.2% and a power density of 0.84 mW / cm2. The converter comprising a PE plate made of 0.9PMN-PT composite thin films achieve a higher efficiency and a larger power output namely 1.3% and 6.5 mW / cm2, respectively, for a temperature oscillation amplitude of 10 K around 343 K at 5 Hz.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize energy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
Top cycle power generation with high radiant and emissivity exhaust
The present invention generally relates to power generation methods and secondary processes requiring high radiant and emissivity homogeneous combustion to maximize production output. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a top cycle power generator with combustion exhaust modified to have radiant flux in excess of 500 kW per square meter and emissivity greater than 0.90, and supercritical CO2 power generating cycle to maximize exergy efficiency.
Owner:GURIN MICHAEL
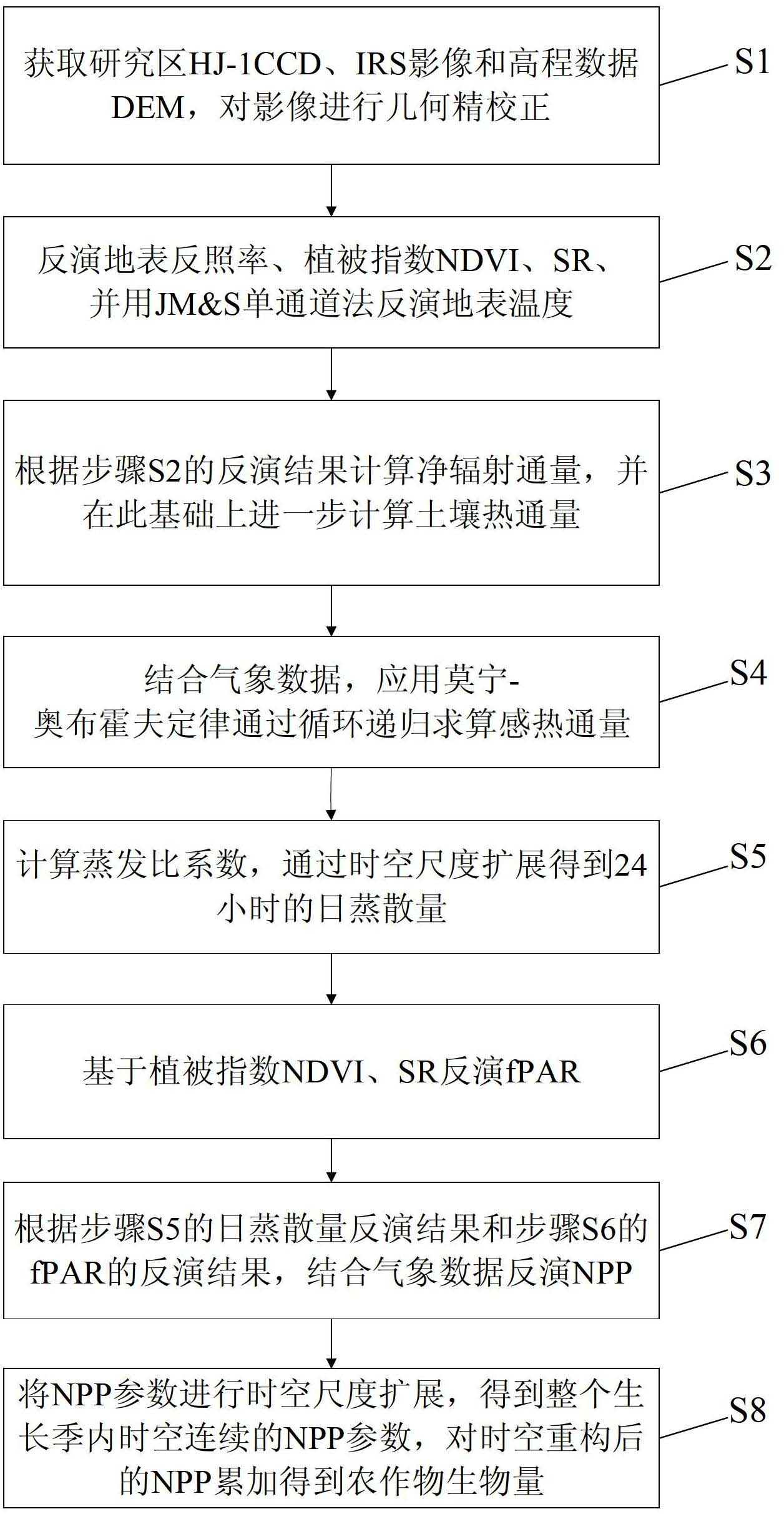
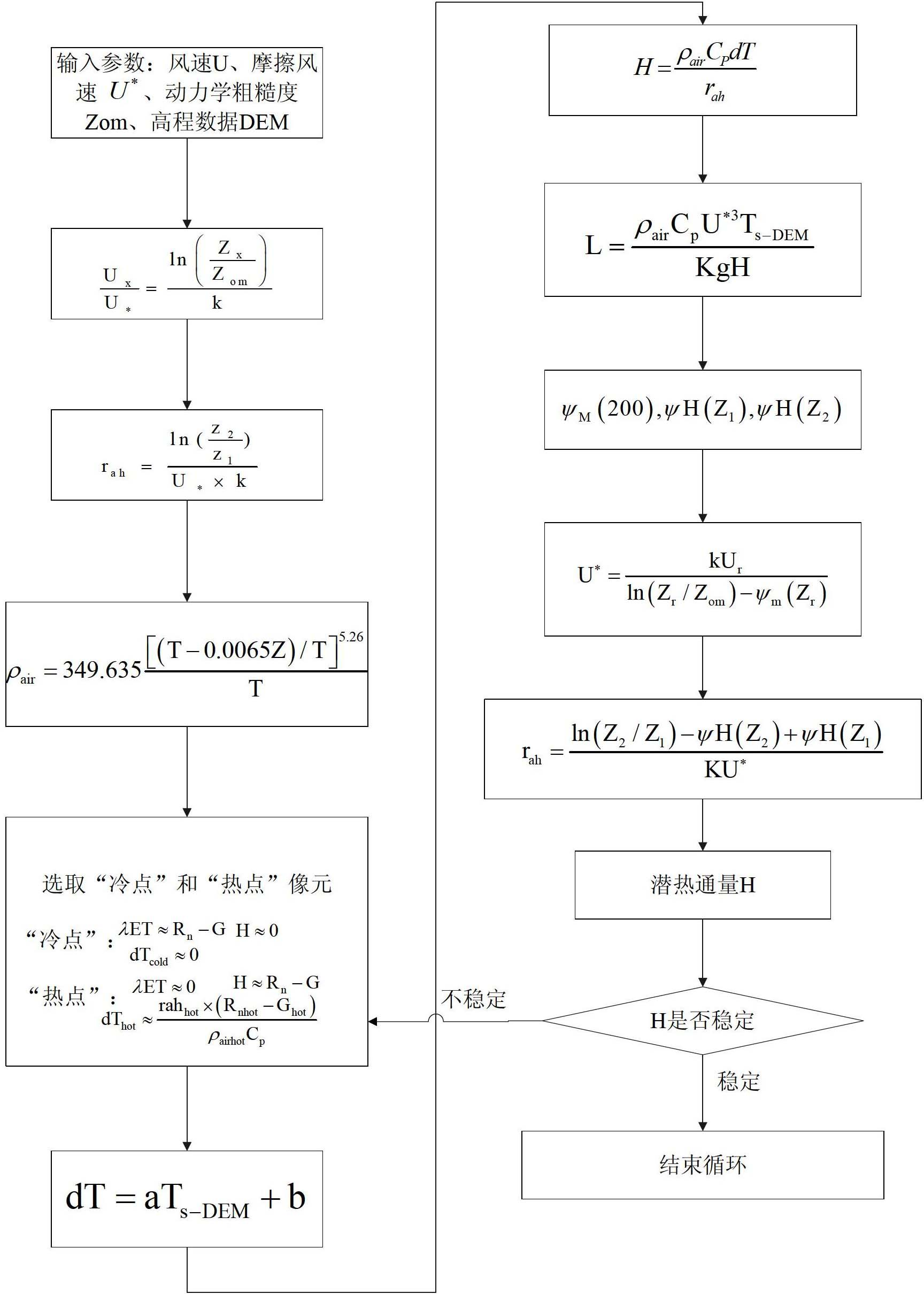
Crop biomass inversion method based on SEBAL-HJ model
ActiveCN102650587AImprove inversion accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCyclic reductionEvaporation
The invention discloses a crop biomass inversion method based on a SEBAL-HJ model. The crop biomass inversion method is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, acquiring HJ-1 CCD, IRS images and elevation data DEM in a research plot, and carrying out geometric fine revision to the images; S2, inversing a land surface albedo, NDVI, SR, land surface emissivity and inversing land surface temperature; S3, calculating net radiation flux according to inversion results in the S2, and further calculating soil heat flux on the basis; S4, calculating sensible heat flux through cyclic reduction; S5, calculating the coefficient of evaporation ratio and obtaining evapotranspiration per day through space-time dimension expansion; S6, inversing fPAR on the basis of vegetative cover indexes NDVI and SR; S7, inversing NPP according to the inversion results of evapotranspiration per day in the step S5 and the inversion results of fPAR in the step S6; and S8, obtaining crop biomass through the accumulation of NPP after space-time reconstruction. According to the invention, the high-precision inversion of crop biomass is achieved, and the amount of calculation is relatively smaller.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
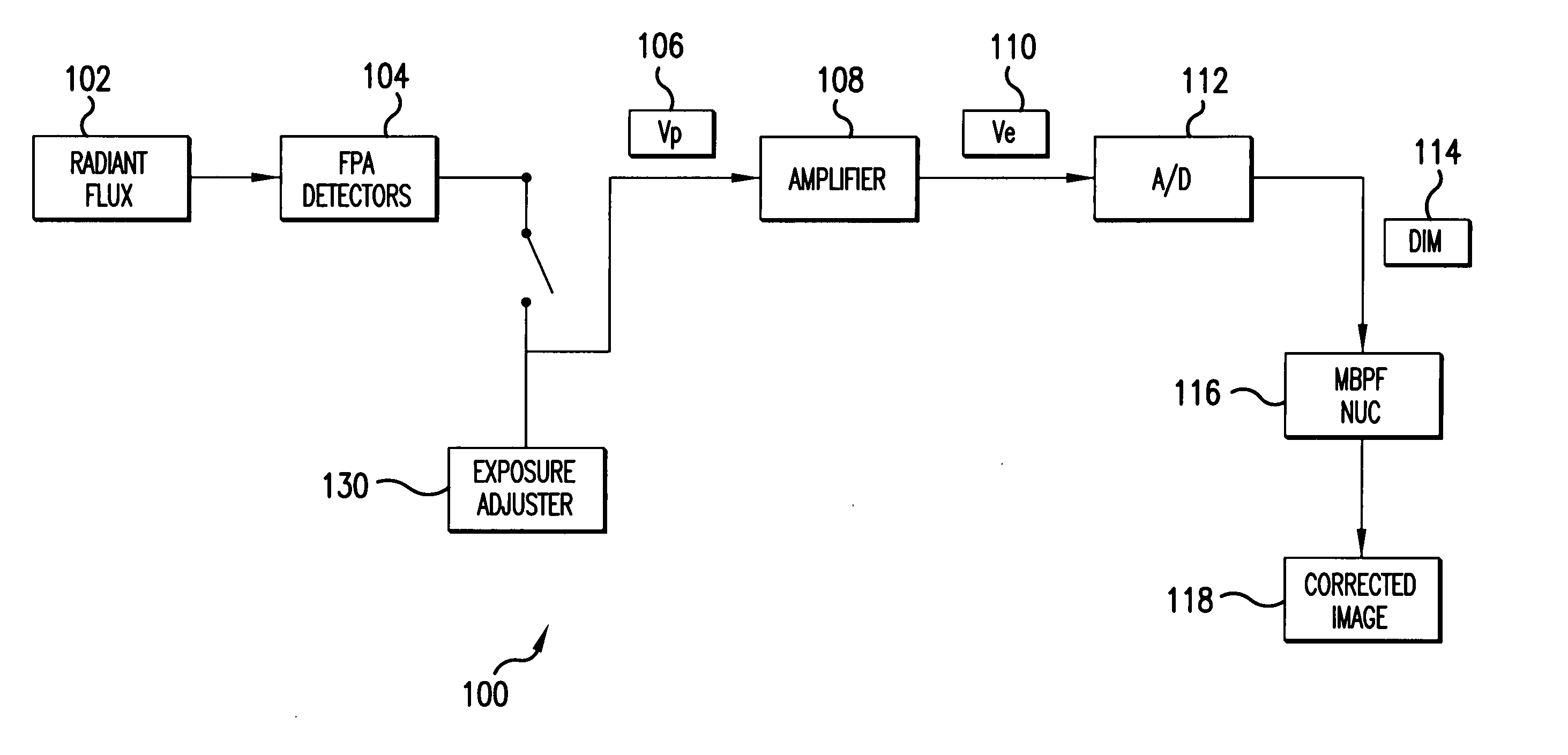
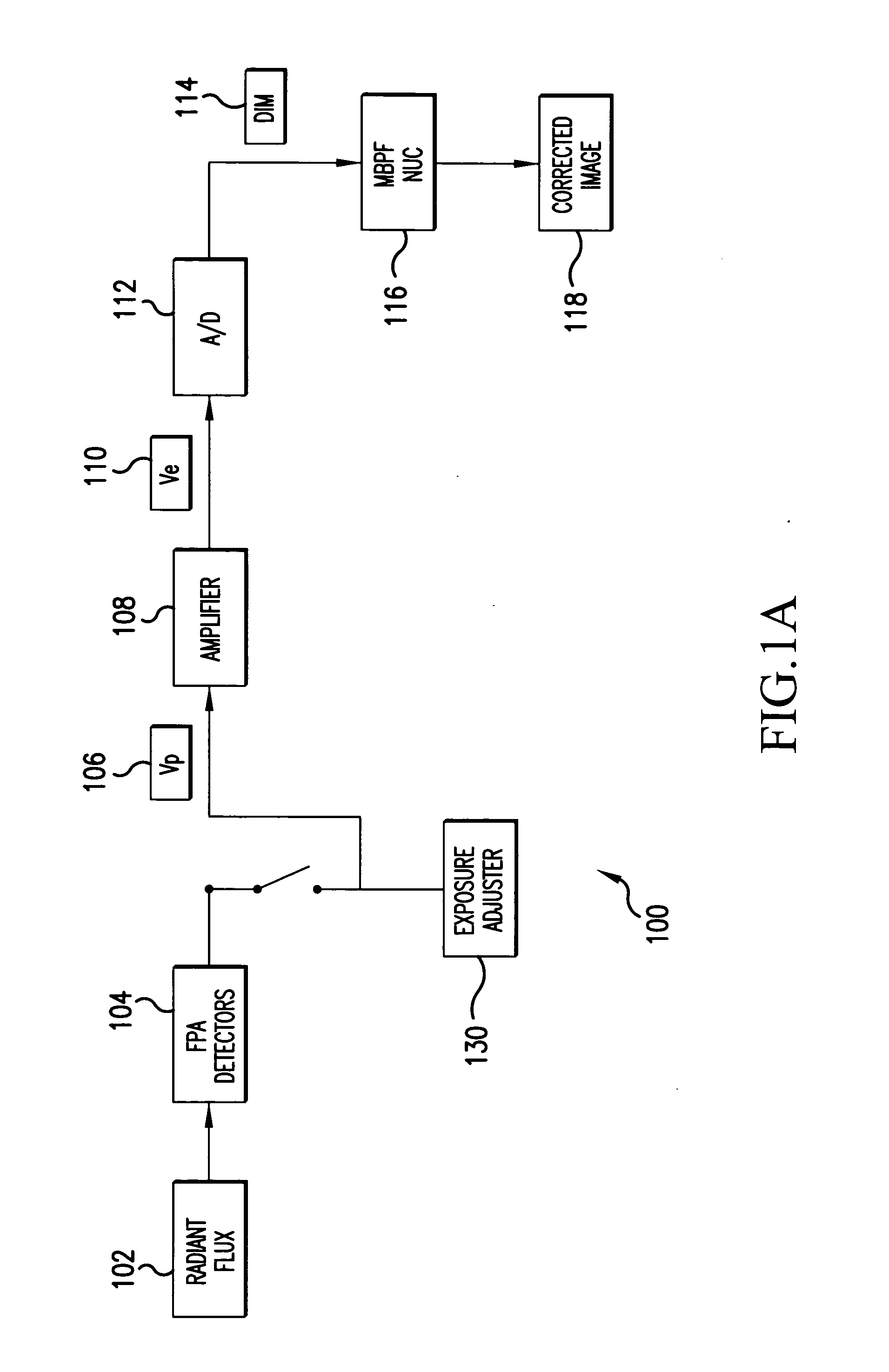
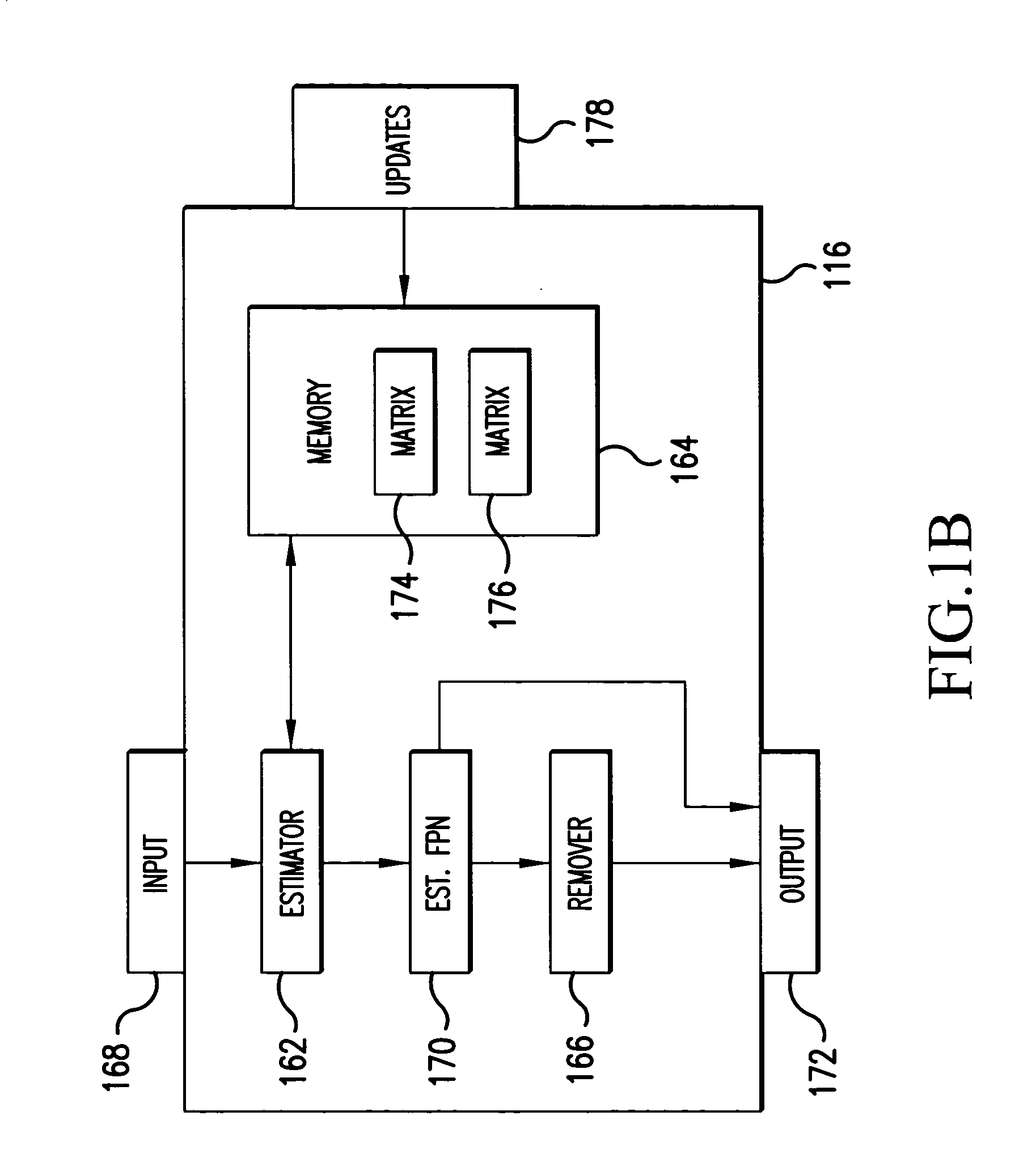
System and method for estimating noise using measurement based parametric fitting non-uniformity correction
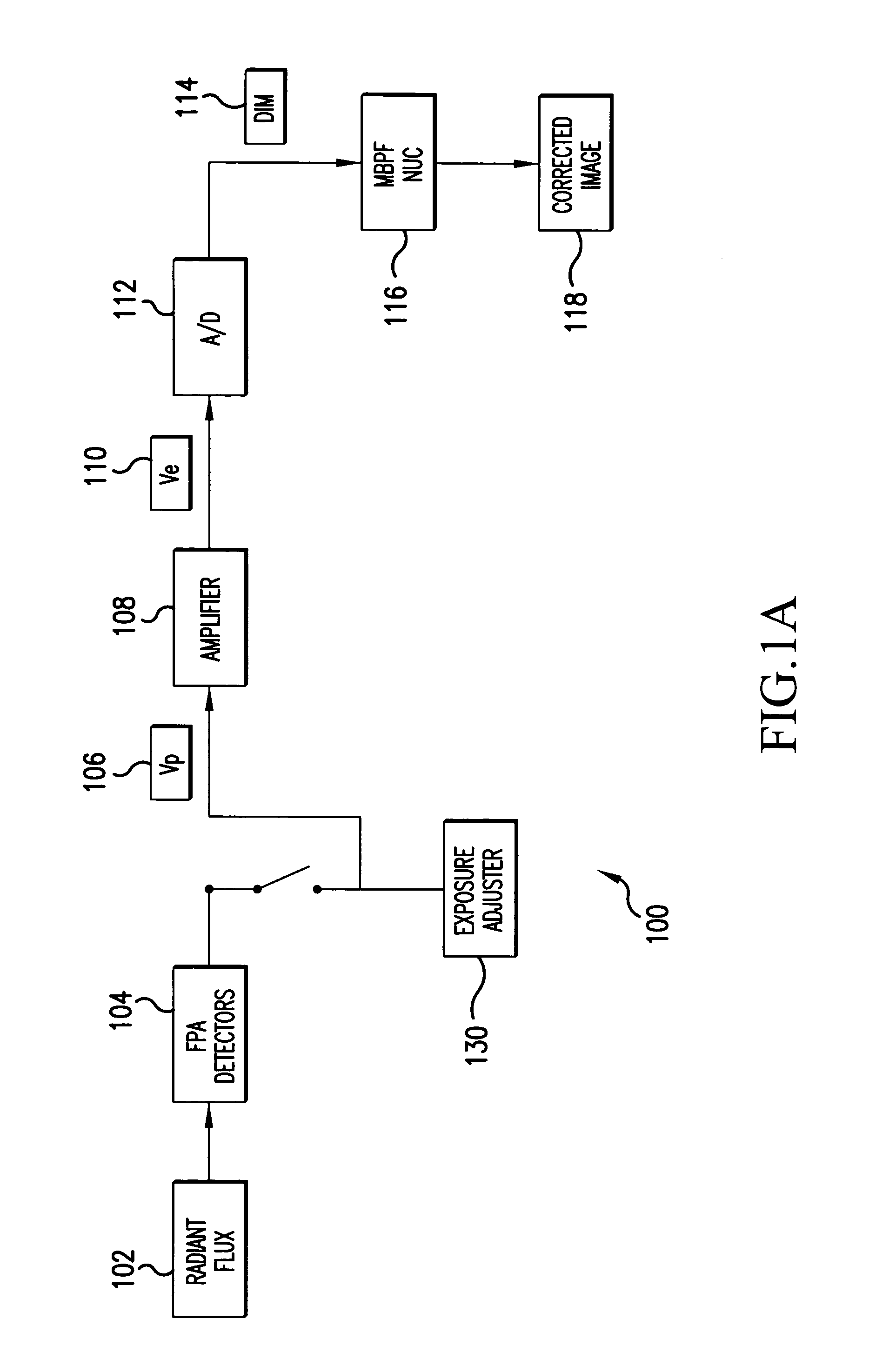
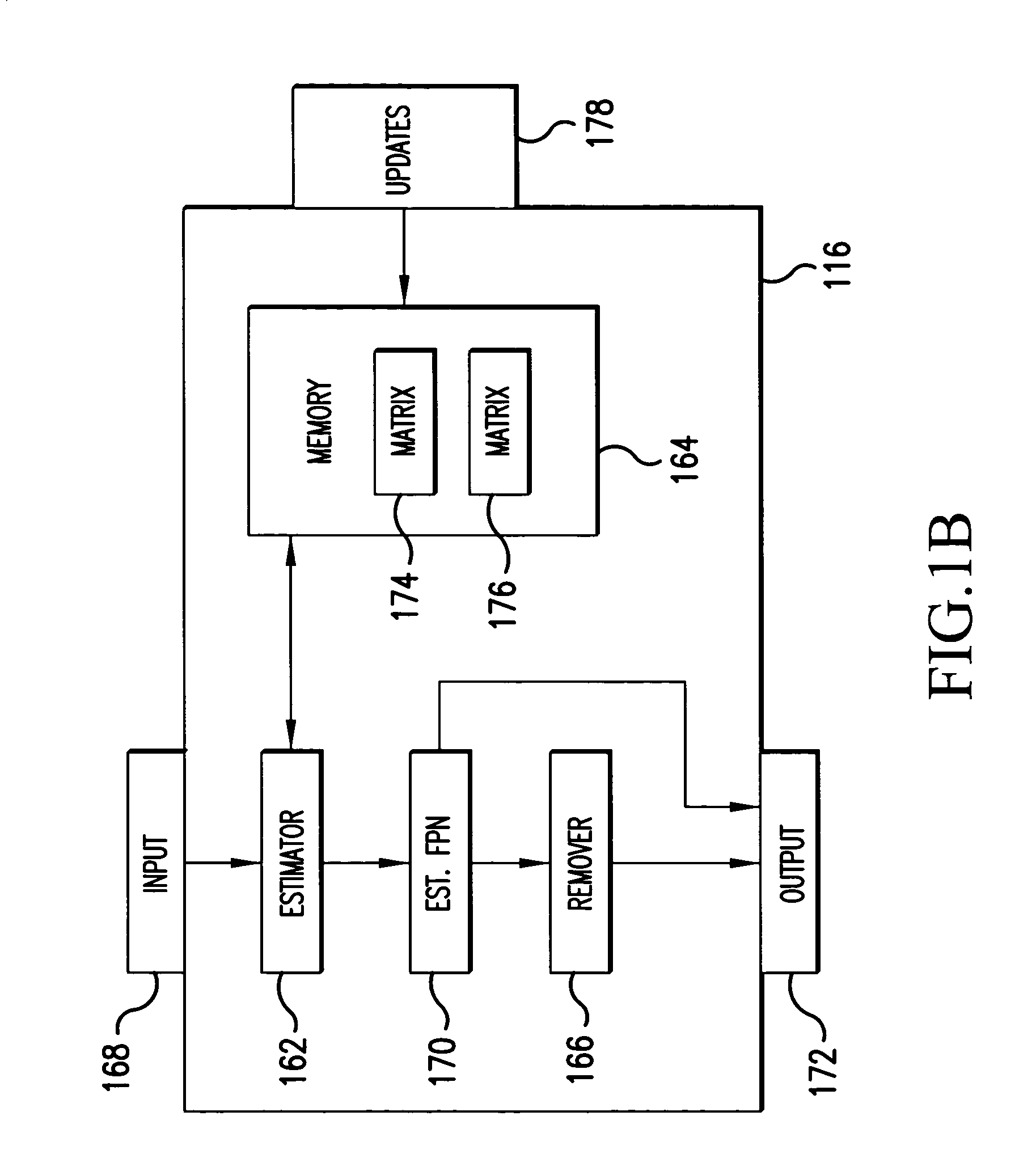
InactiveUS20050157942A1Solve the deficienciesSolves shortcomingImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDigital imageComputer science
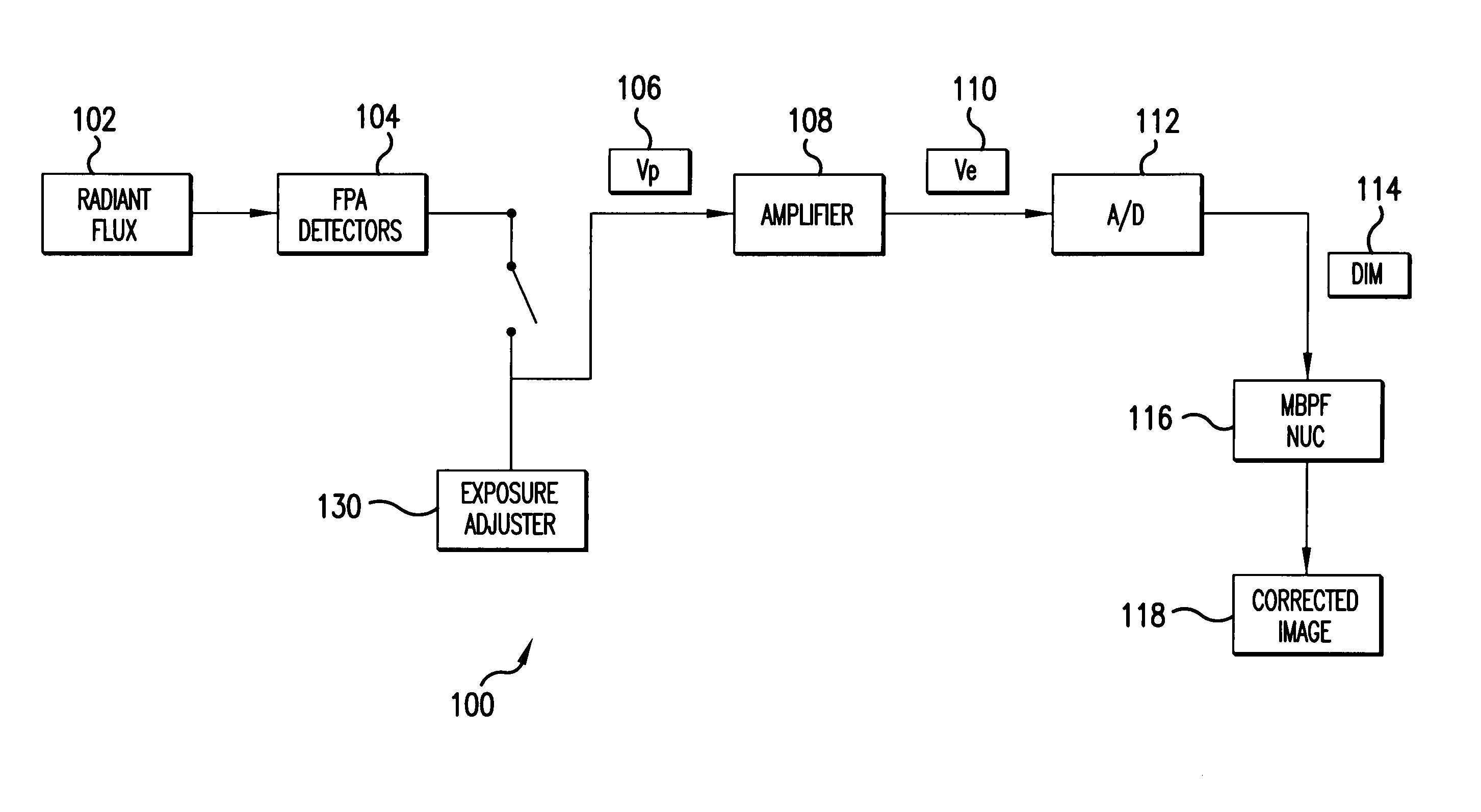
A system and method for estimating noise using measurement based parametric fitting non-uniformity correction is disclosed. Fixed pattern noise (“FPN”) is estimating from an overall noise component within a detection system to enhance candidate target detection and tracking. A sensor in the detection system receives energy, such as radiant flux, that is converted to a digital image. A non-uniformity correction device generates an estimated FPN according to an applicable temperate range and integration time. A memory storing an array of coefficients is accessed to determine the estimated FPN. The valves within the array of coefficients are based on actual FPN measurements that are parametrically fitted.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN MISSILES & FIRE CONTROL
Compact radiation source
InactiveUS20070189459A1Efficient source of X-rayImprove directionX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingUV curingX-ray
A radiation source which can emit X-ray flux, UV-C flux and other forms of radiation uses electron beam current from a cathode array formed on the window through which the radiation will exit the source. The source can be made in formats which are compact or flat compared with prior art radiation sources. X-ray, UV-C and other radiative flux produced by the source can be used for such purposes as radiation imaging, sterilization, decontamination of biohazards, UV curing or photolithography.
Owner:STELLAR MICRO DEVICES
Multiple Aperture Hand-Held Laser Therapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20130317571A1Easy to changeIncrease the areaLaser detailsControlling energy of instrumentHigh energyHand held
A hand-held therapeutic laser apparatus with a special opto-mechanical construction, which enables changeability of a front collimating lens to create different effective laser apertures. A smaller effective aperture has a comparatively higher radiant flux density for treatment of a small area that requires a higher energy dose, while a larger effective aperture facilitates treatment of a large area at a relatively reduced radiant intensity.
Owner:MEDICAL COHERENCE
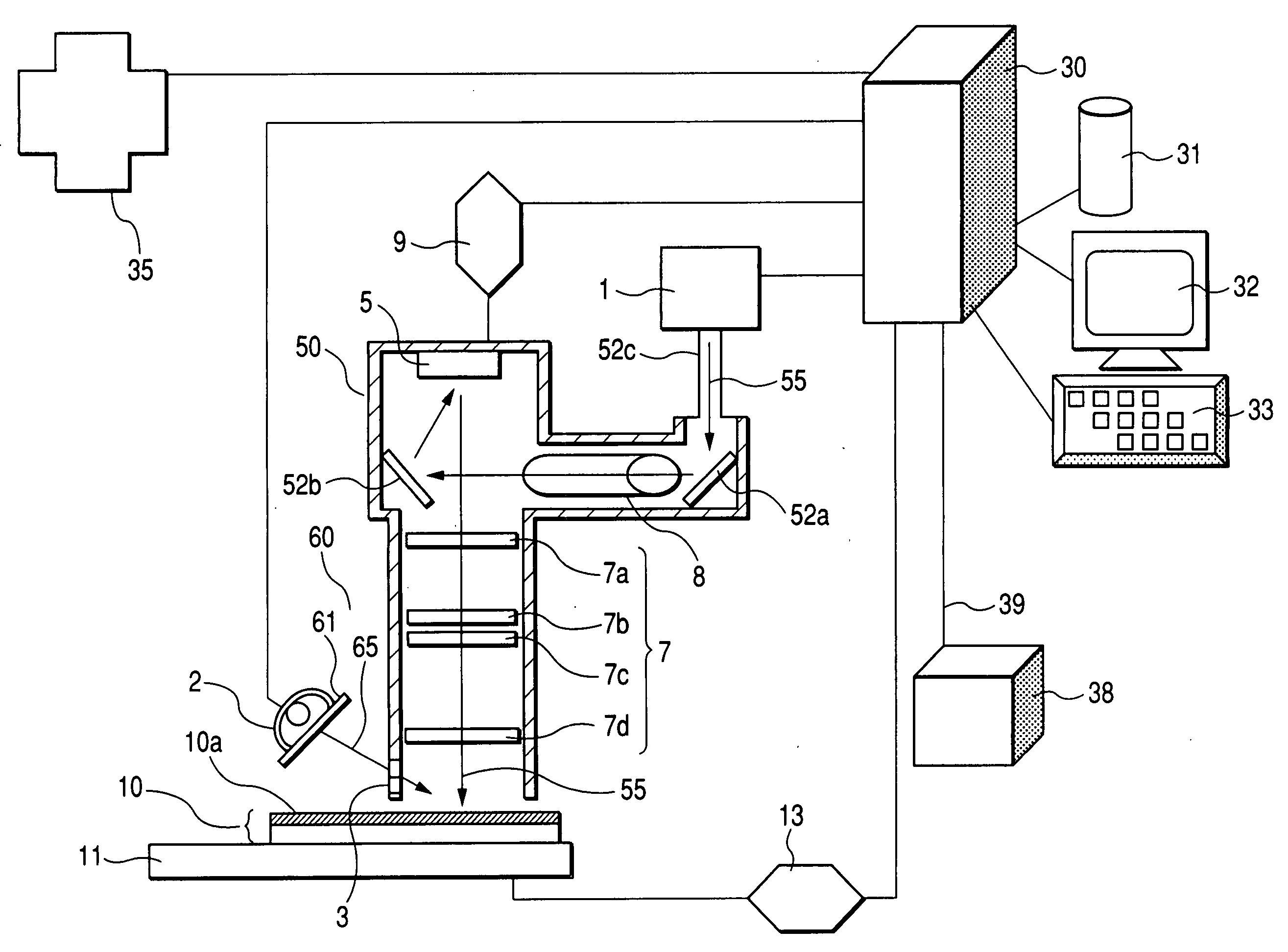
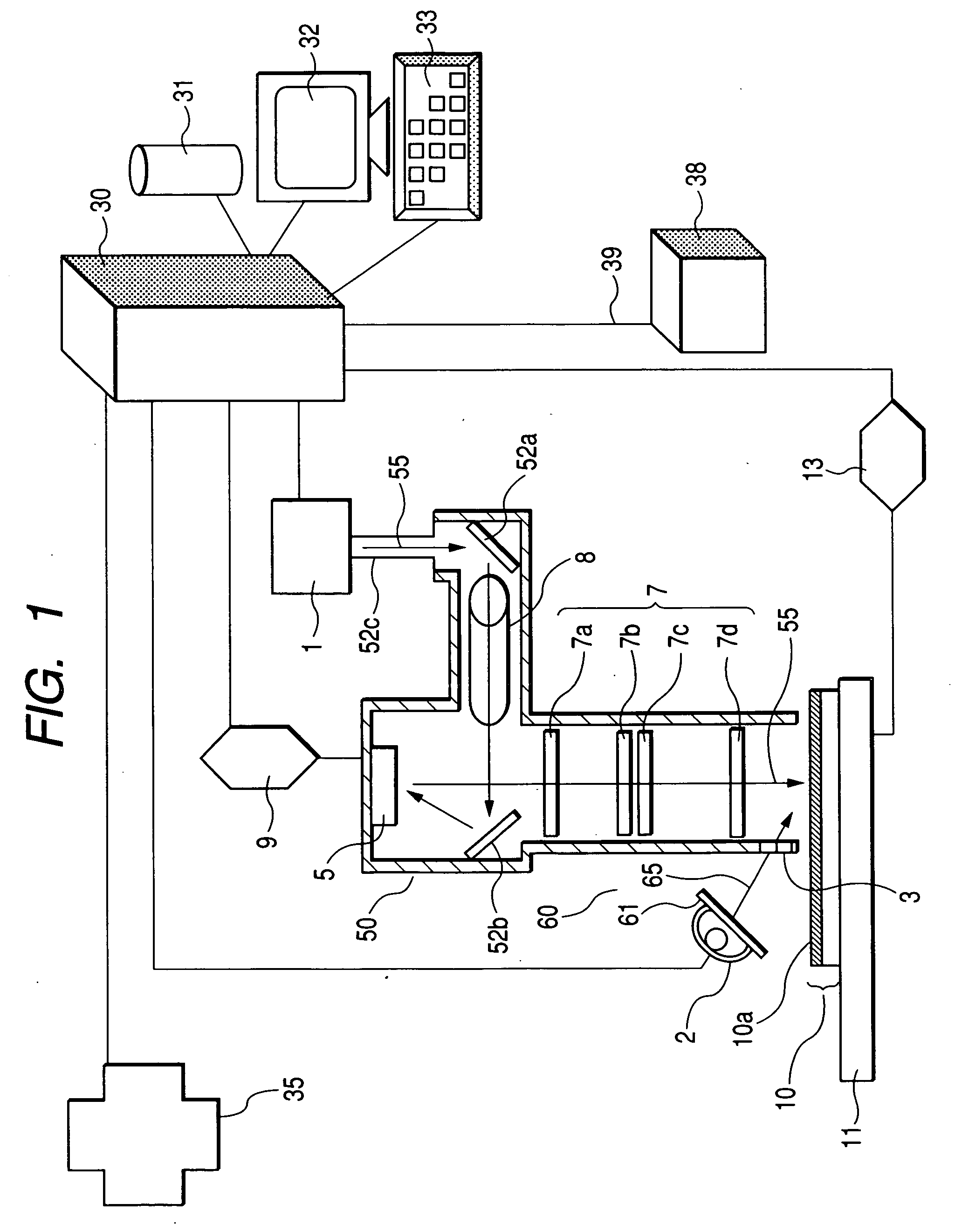
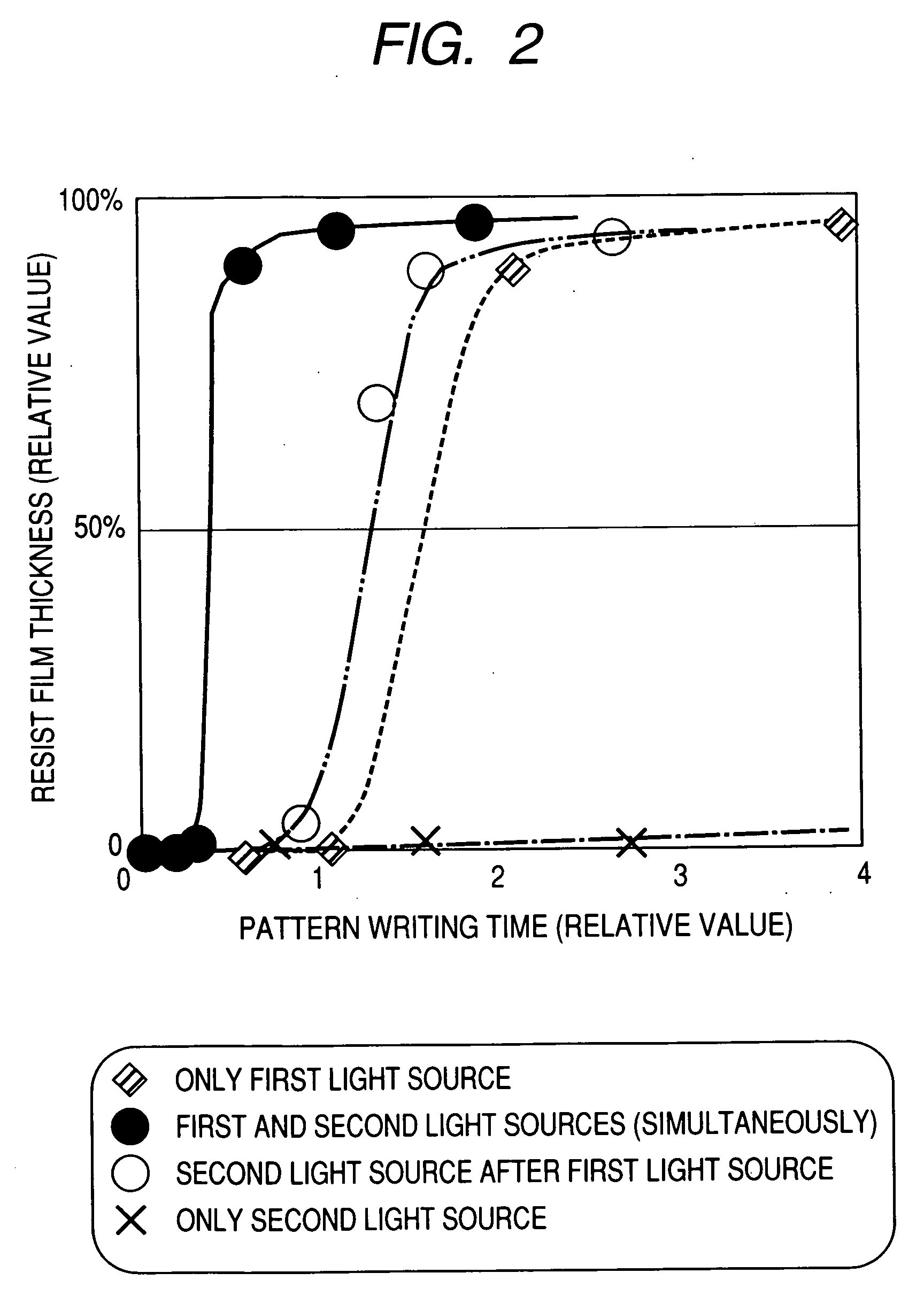
Exposure apparatus and exposing method and method of manufacturing a printed wiring board
ActiveUS20060215143A1Low costImprove stabilityPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingLight irradiationUltraviolet
The mask-less exposure apparatus includes: a stage which moves with the substrate having a photosensitive resin layer with sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation formed thereon; a first light source for emitting light containing a wavelength component in the wavelength range of 300 to 410 nm; a first light irradiation optical system for modulating a radiant flux emitted from the first light source based on data of a desired exposure pattern to image a pattern on the photosensitive resin layer; a second light source for emitting light containing a wavelength component in the wavelength range of 450 to 2500 nm; and a second light irradiation optical system for guiding a radiant flux emitted from the second light source to a second light irradiation area that is set so as to include at least a first light irradiation area.
Owner:ADTEC ENG
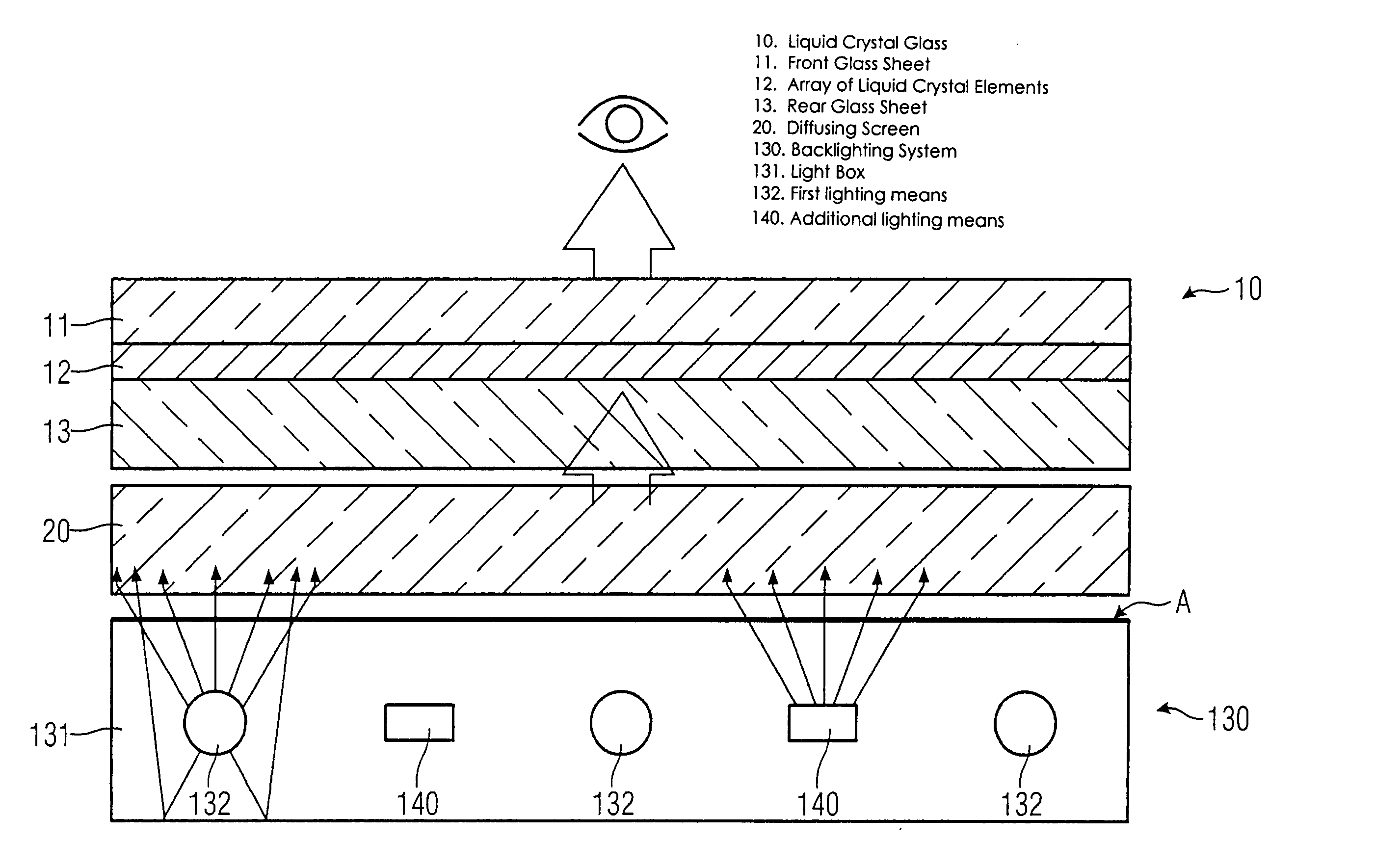
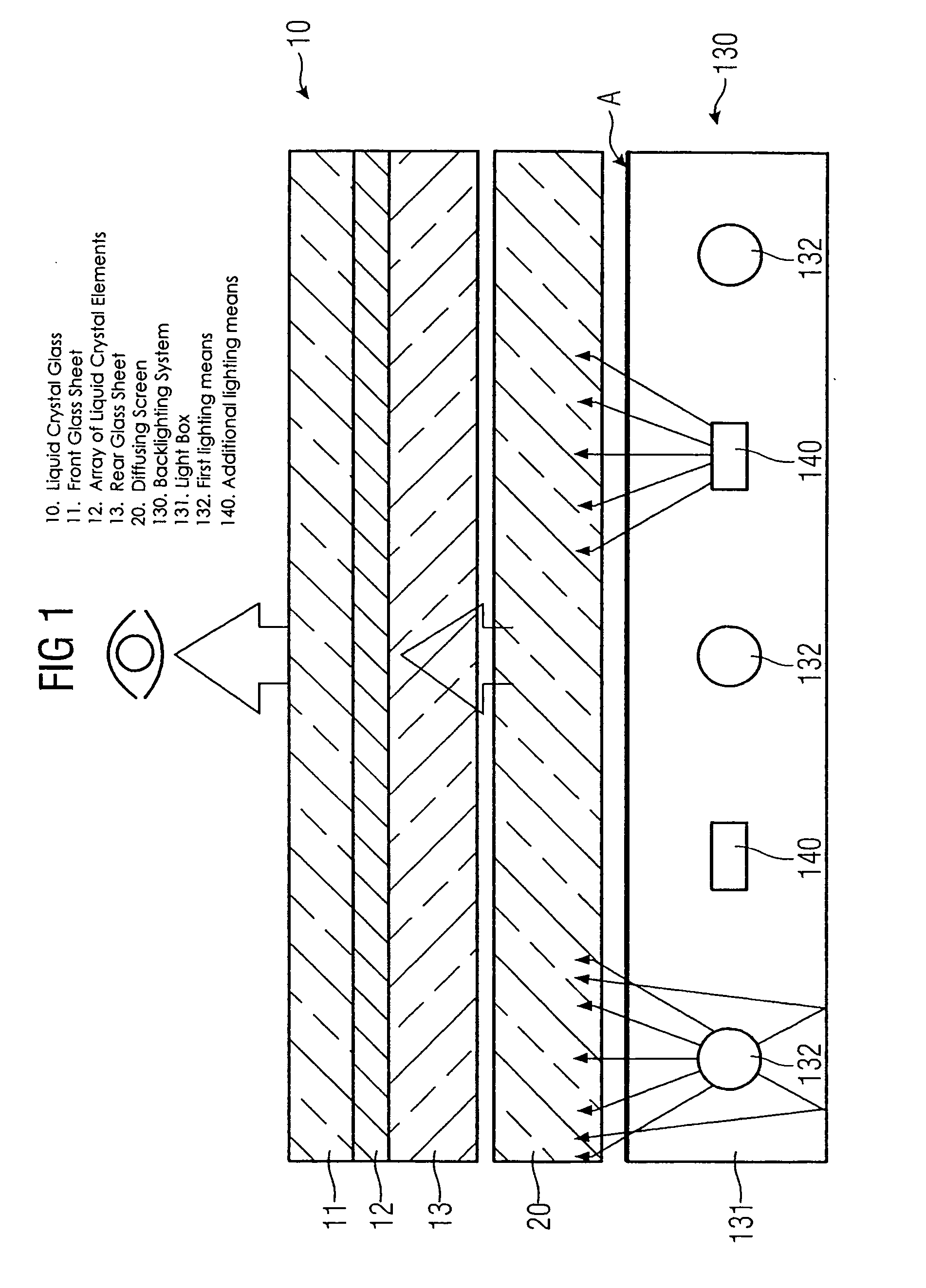
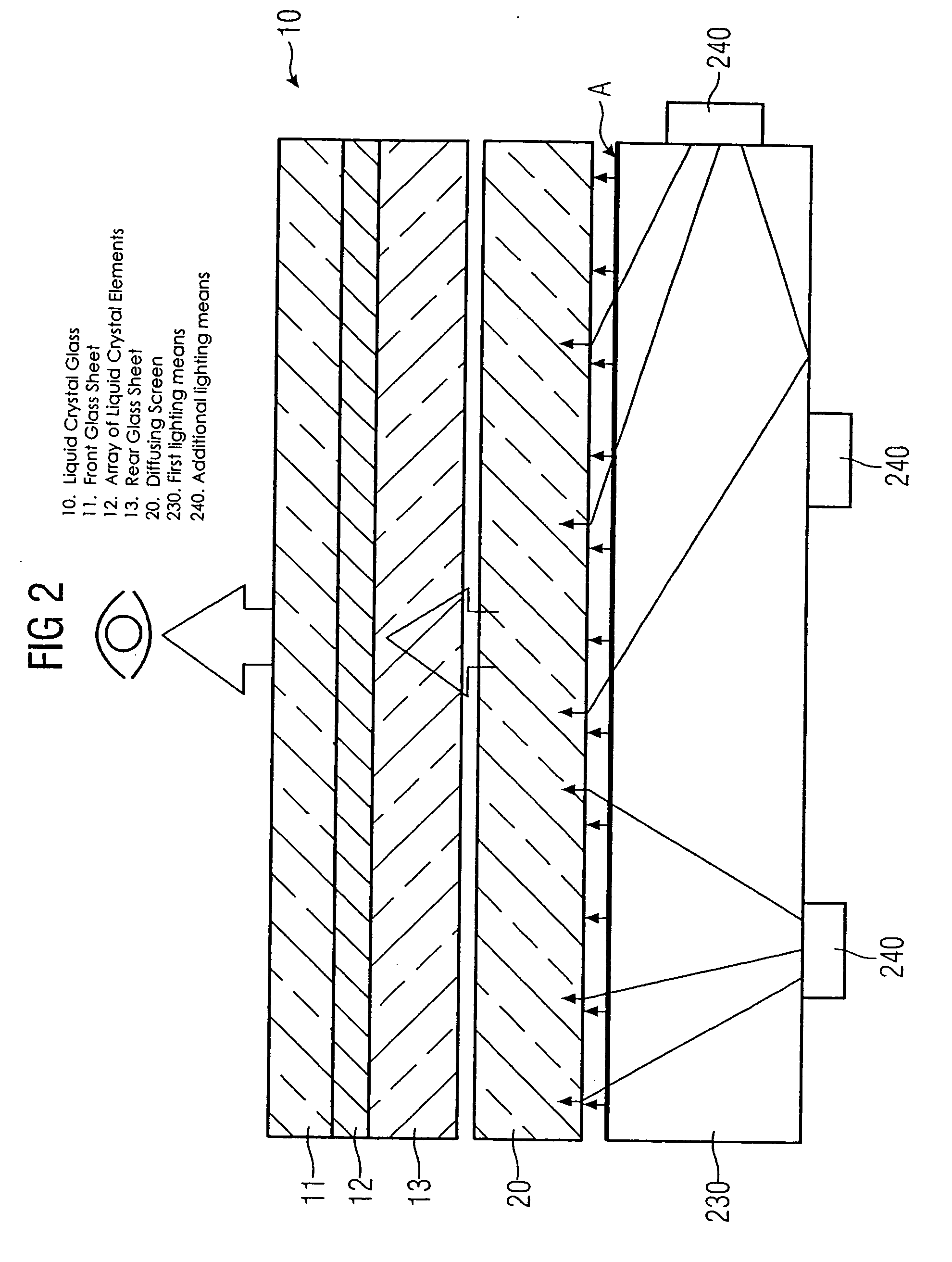
Backlighting system for liquid crystal displays
InactiveUS20050099791A1The process is simple and effectiveSimple methodIlluminated signsNon-linear opticsOperating pointLiquid-crystal display
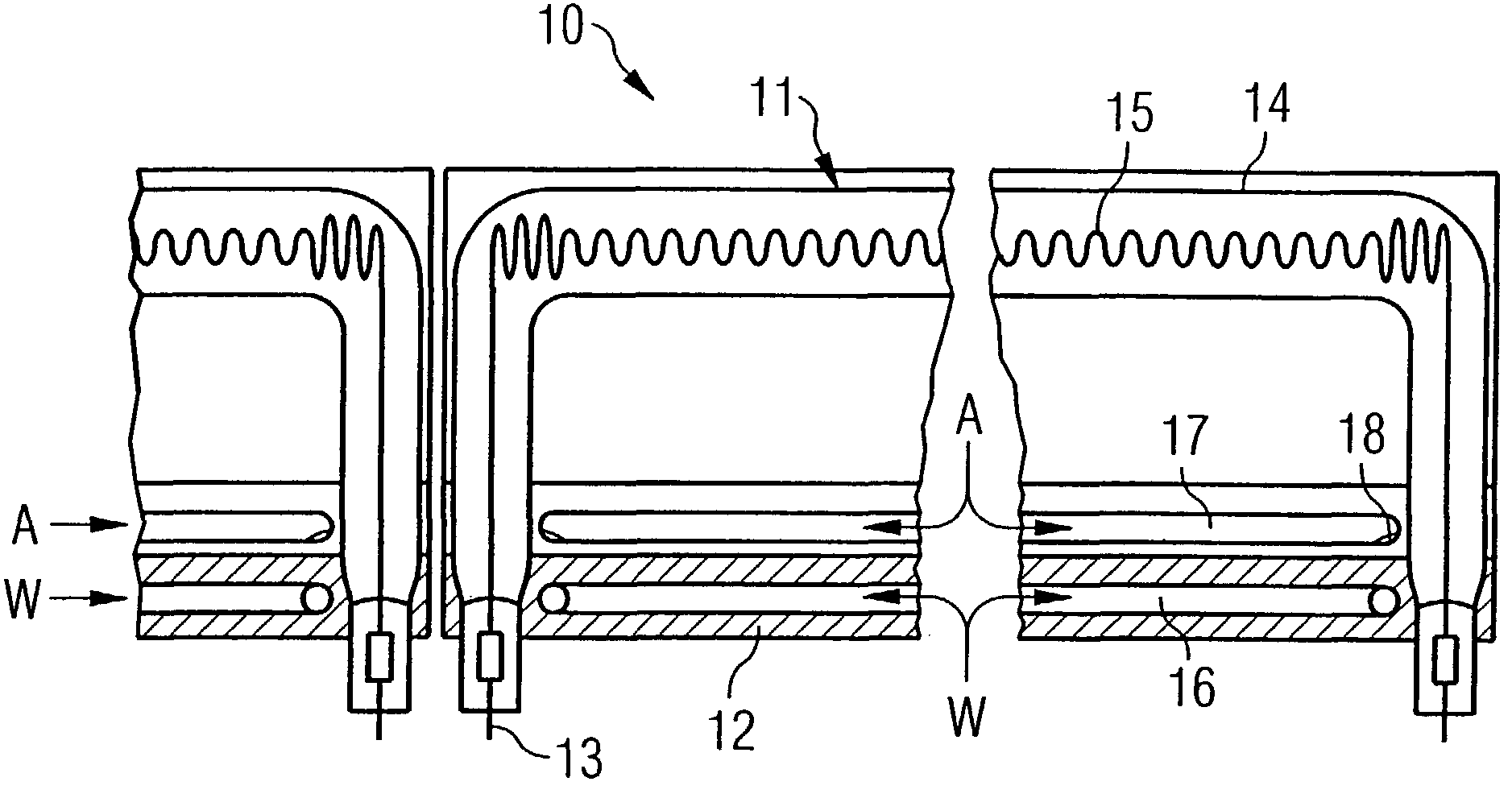
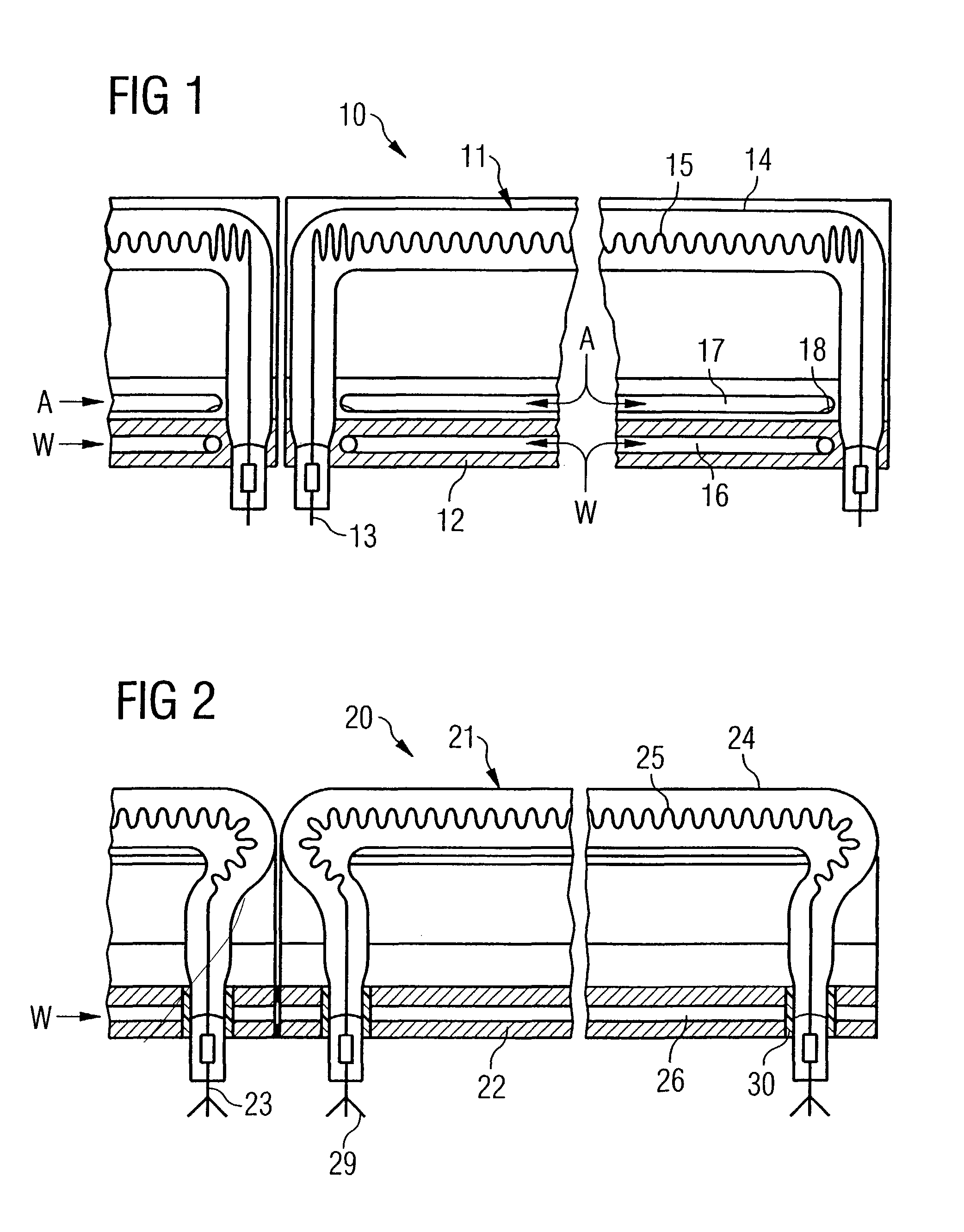
A backlighting system for liquid crystal displays includes one or more first lighting structure (130, 230), which has a defined radiant flux with spectral color components at one operating point. The radiant flux output from the first lighting structure (130, 230) exits across a radiant surface (A) of the backlighting system and thus provides a defined luminous flux with spectral color components on a liquid crystal glass (10) that can be arranged in front of this radiant surface (A). Also, the backlighting system has one or more additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340). The radiant flux of the additional lighting structure varies. This additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340) is arranged such that the spectral color components of the luminous flux change when the radiant flux of the additional lighting structure (140, 240, 340) is changed. The liquid crystal display is used for controlling and monitoring in an automation system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
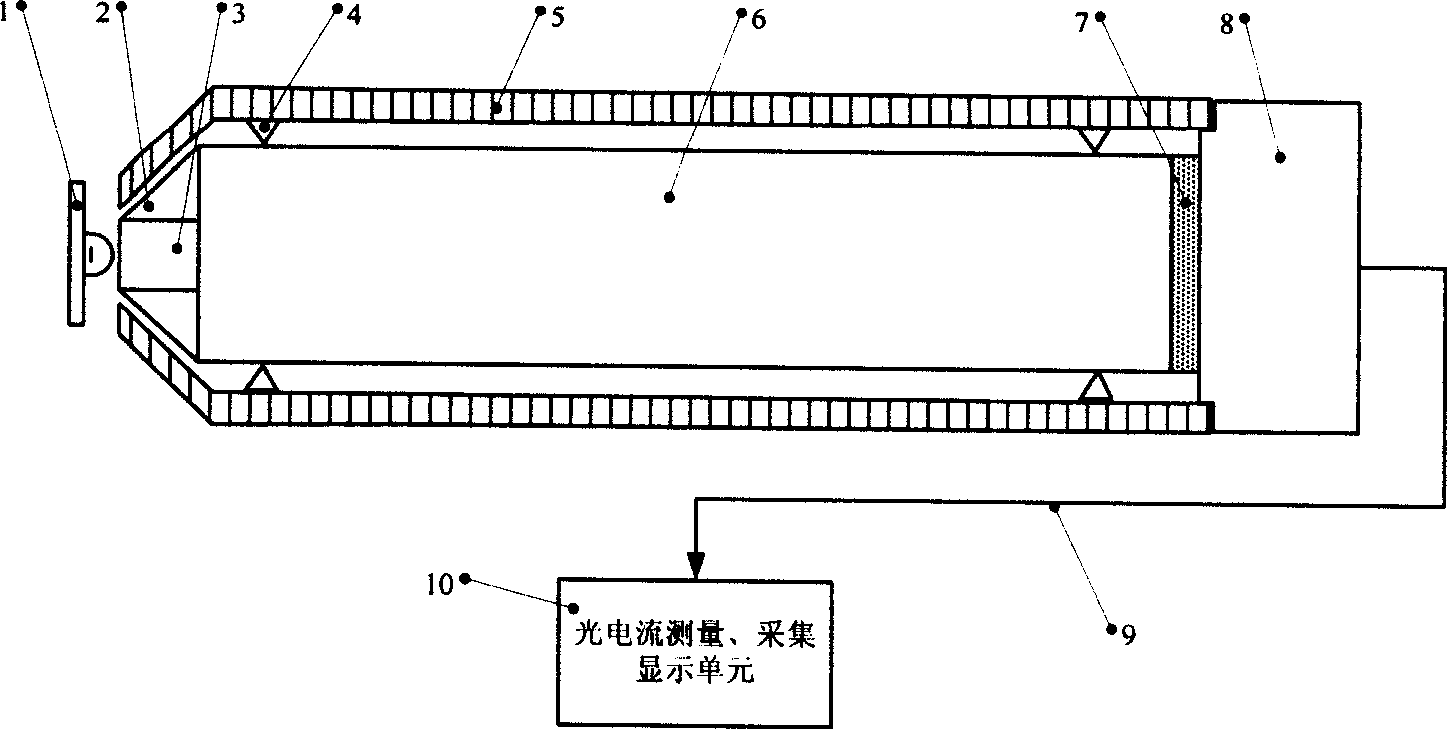
LED luminous flux measurement apparatus and method
InactiveCN101368872AAchieving Absolute MeasurementsReduce volumePhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLamps testingUltravioletLuminous flux
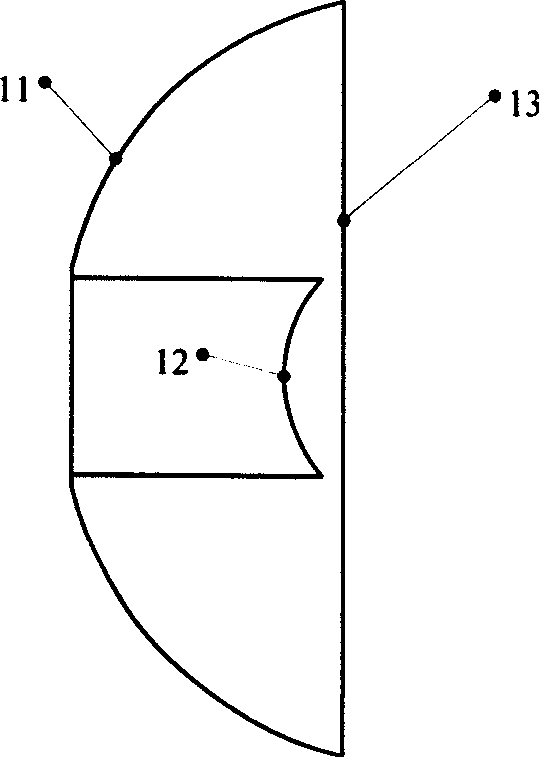
The invention relates to a measuring device and a measuring method using optoelectronic devices to measure the luminous flux, radiant flux or radiant power of light-emitting diodes and other solid light sources so as to solve the problems that the existing device and method are of low accuracy and can not achieve on-line measurement. The measuring device mainly comprises an illumination or irradiance measurement probe (8), a photocurrent measurement display unit (10), a reflector (2), an integral rod lens (6), a support ring (4) and an outer shell (5). The measuring method comprises the following steps: the reflector (2) is used to collimate the light emitted by a light-emitting diode (1) in a hemisphere, and then the light is sent to the integral rod lens (6) and homogenized; the illumination or irradiance of the exit end (15) of the integral rod lens (6) is measured; and the measured result is multiplied by the area of the exit end (15) of the integral rod lens (6) so as to obtain the luminous flux or radiant power of the light-emitting diode (1). The measuring device and the measuring method can realize absolute measurement and has the advantages of small size, low cost and good long-term stability; the invention can be used for fast, real-time and online measurement of various light-emitting diodes from the ultraviolet to the near infrared full band.
Owner:HANGZHOU REALOPTIX
Photometry apparatus of luminophor
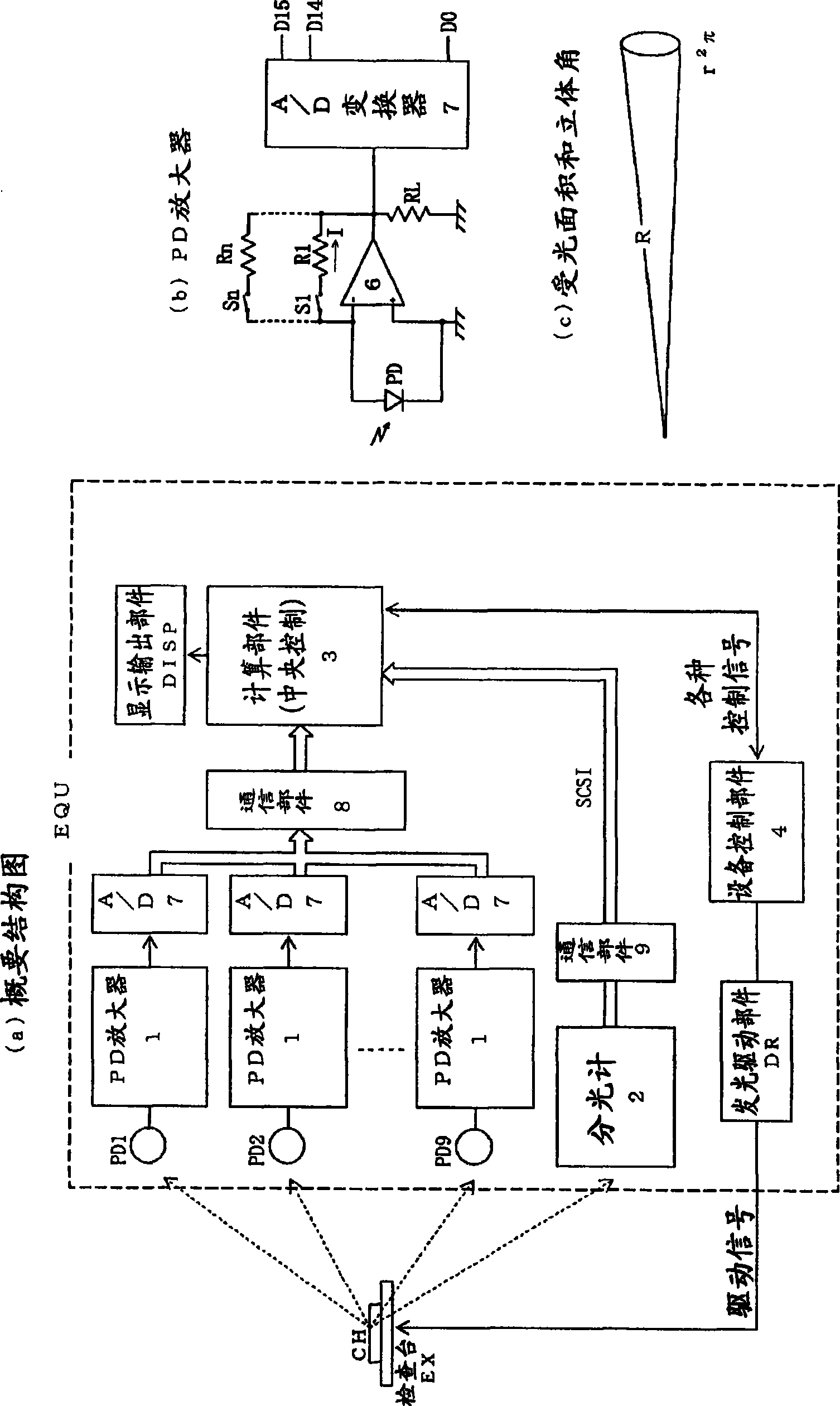
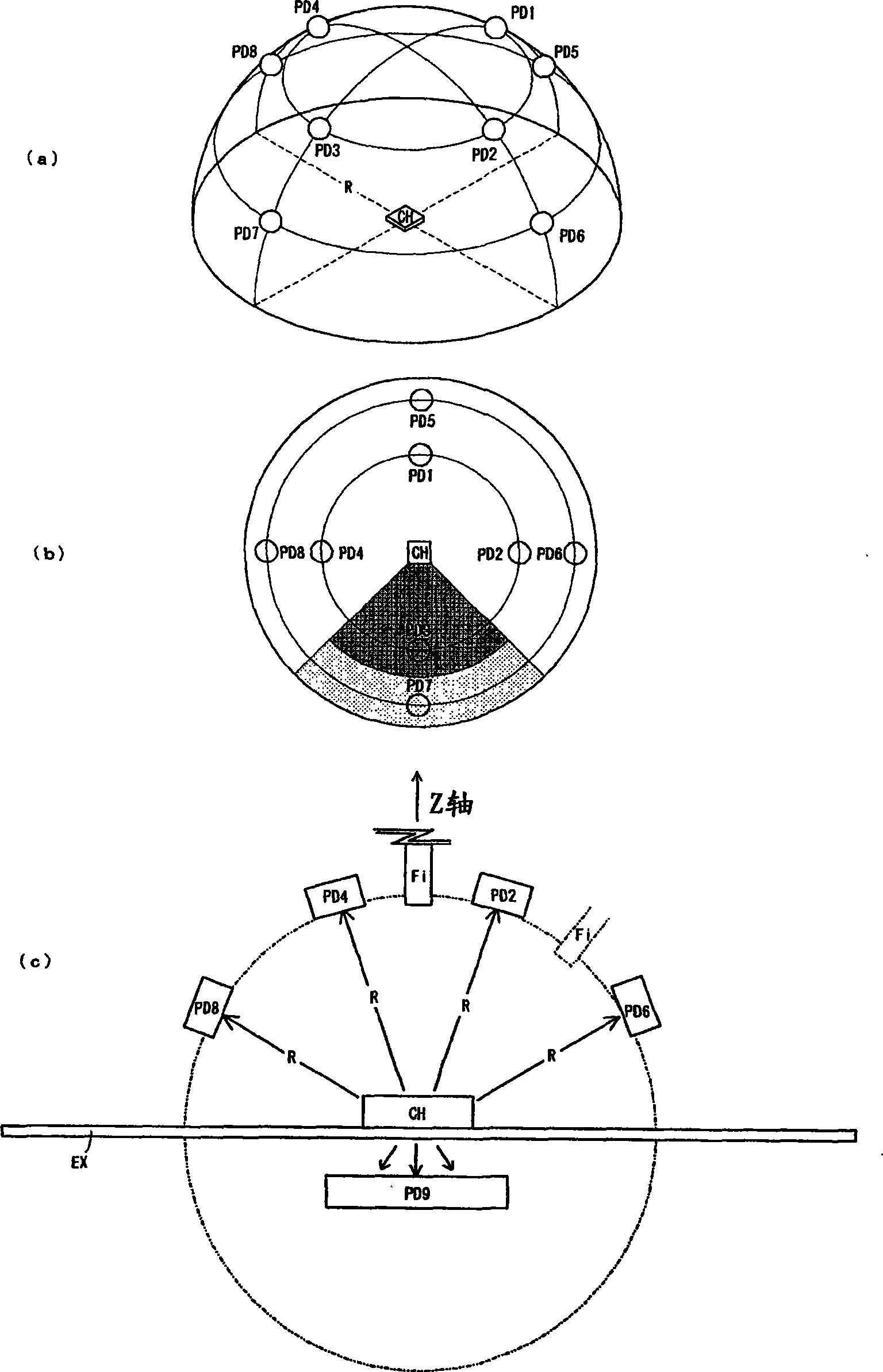
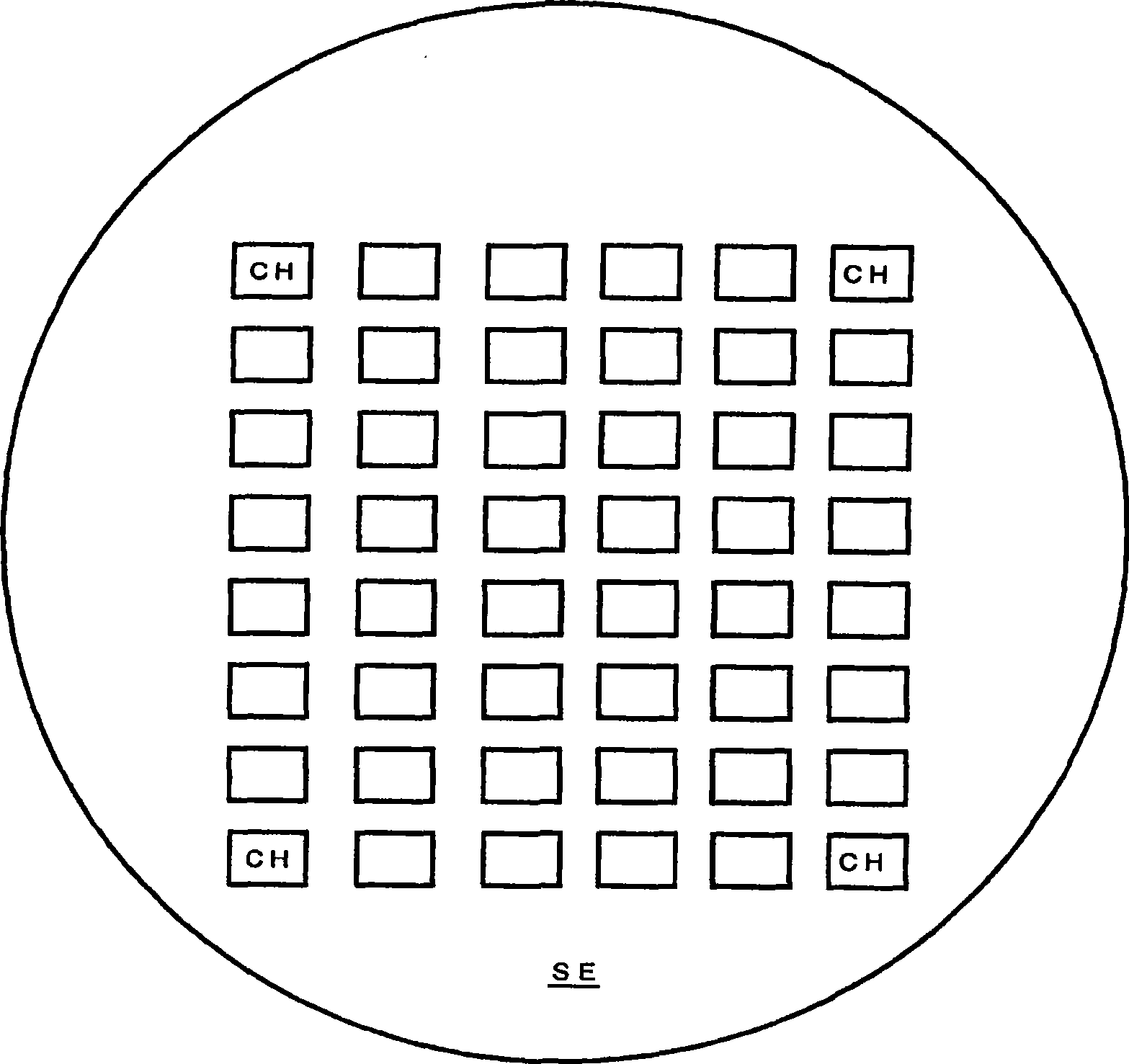
InactiveCN101464186ARapid determinationHigh precision measurementSpectrum investigationPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLight fluxTransmitted power
The invention discloses a light measuring device of a luminophor comprising: n light interception members for outputting and receiving detection data (Ii) corresponding to a light reception strength; a spectral analysis member for outputting spectral distribution data (P(lambada)) of the receiving light; a storage member corresponding to n interception members for respectively storing spectral sensitivity data (PDi(lambada)) of a light interception member sensitivity; and a control member executing an operation action. The control member comprises: a first treatment for calculating the spectral distribution (EGi(lambada)) of the lumiophor transmit power according to n detection data (Ii), n spectral sensitivity data (PDI(lambada)) and the spectral distribution data (P(lambada)); a second treatment for calculating a radiant flux (EGi) according to the spectral distribution (EGi(lambada)); and a third treatment for calculating a light flux (theta i) according to the spectral distribution (EGi(lambada)) and a spectral visible efficiency (V(lambada)). The light measuring device of the invention can fast and high precisely measure the light quantity for the luminophor with uneven lighting distribution.
Owner:オプトシステム
High output small area group III nitride LEDs
ActiveUS8513686B2Small sizeLower forward voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDriving currentLength wave
Owner:CREELED INC
RF shielding for acoustic devices
InactiveUS20130064406A1Electrical transducersMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringConductive materials
A receiver includes a housing and a sleeve. The housing forms a chamber, and the coil is disposed in the chamber and radiates a flux. The sleeve at least partially surrounds the coil such that a majority of flux radiated from the coil is blocked by the sleeve. The sleeve is constructed of a highly conductive material and is insulated from the housing
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
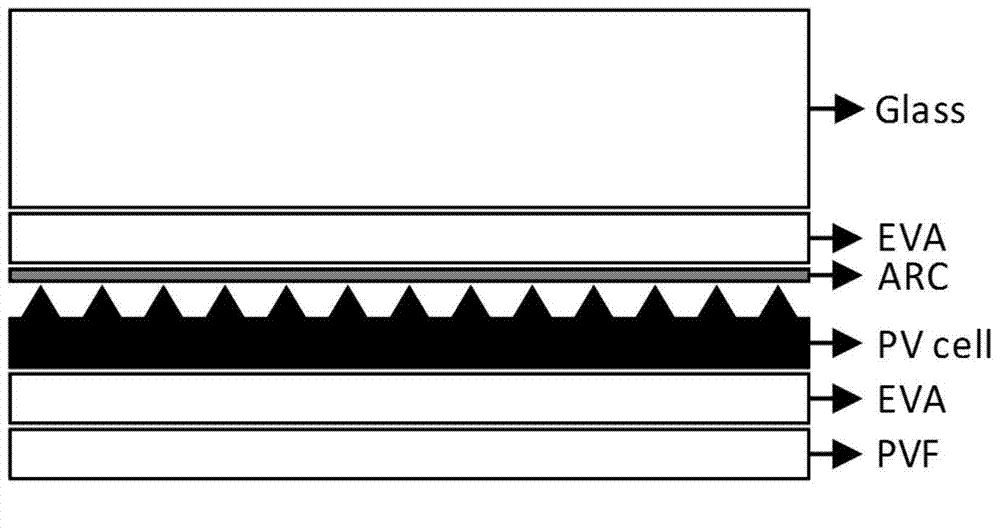
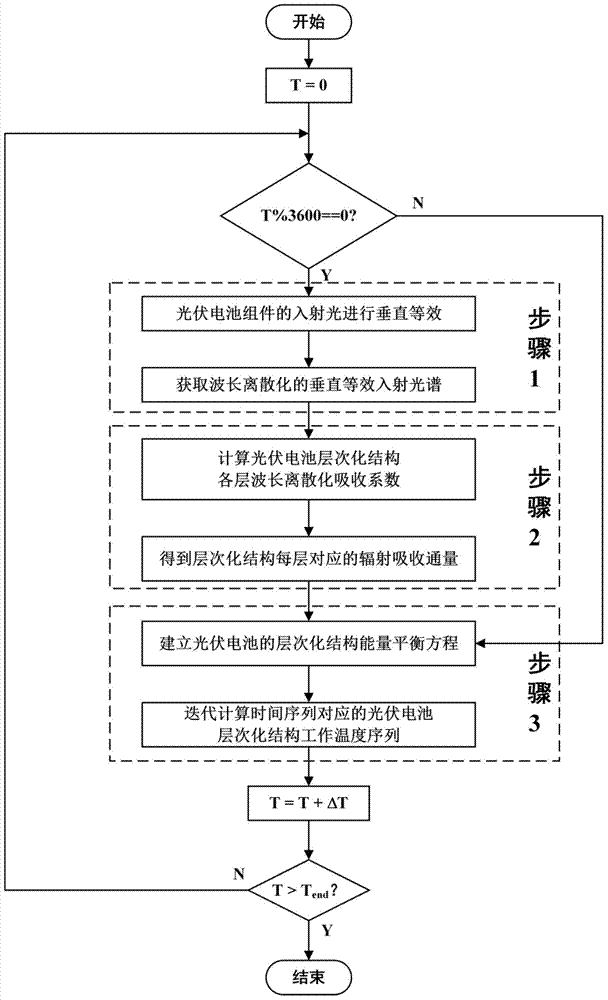
Method for predicating temperature of photovoltaic cell through photo-thermal property coupling
ActiveCN104767483AImprove forecast accuracyAccurate predictionPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationCell layerEnergy balance equation
The invention discloses a method for predicating the temperature of a photovoltaic cell through photo-thermal property coupling. The method includes the following steps that in combination with actual time and irradiance information provided by TMY data obtained through standard measurement, vertical equivalence is performed on incident light of the photovoltaic cell module, and based on an atmospheric dispersion longitudinal transmission model method, a vertical equivalence incident spectrum of a disperse wavelength is obtained; in combination with a crystal silicon layer texture structure and photo-thermal coupling properties of the anti-reflection process of an ARC layer, the wavelength dispersion absorption coefficient of each layer of the layered structure of the photovoltaic cell is calculated to obtained the flux of radiation absorbed by each layer of the structure; a layered structure energy balance equation of the photovoltaic cell is established, and a photovoltaic cell layered structure working temperature sequence corresponding to a time sequence is obtained through iterative calculation. On the basis of the existing function of predicating the output power of the photovoltaic cell, the function of predicating the working temperature of the photovoltaic cell module is further achieved, so that the precision of predicating the output power of the photovoltaic cell module is easily improved, and accordingly the output power of the photovoltaic cell module is accurately predicated.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
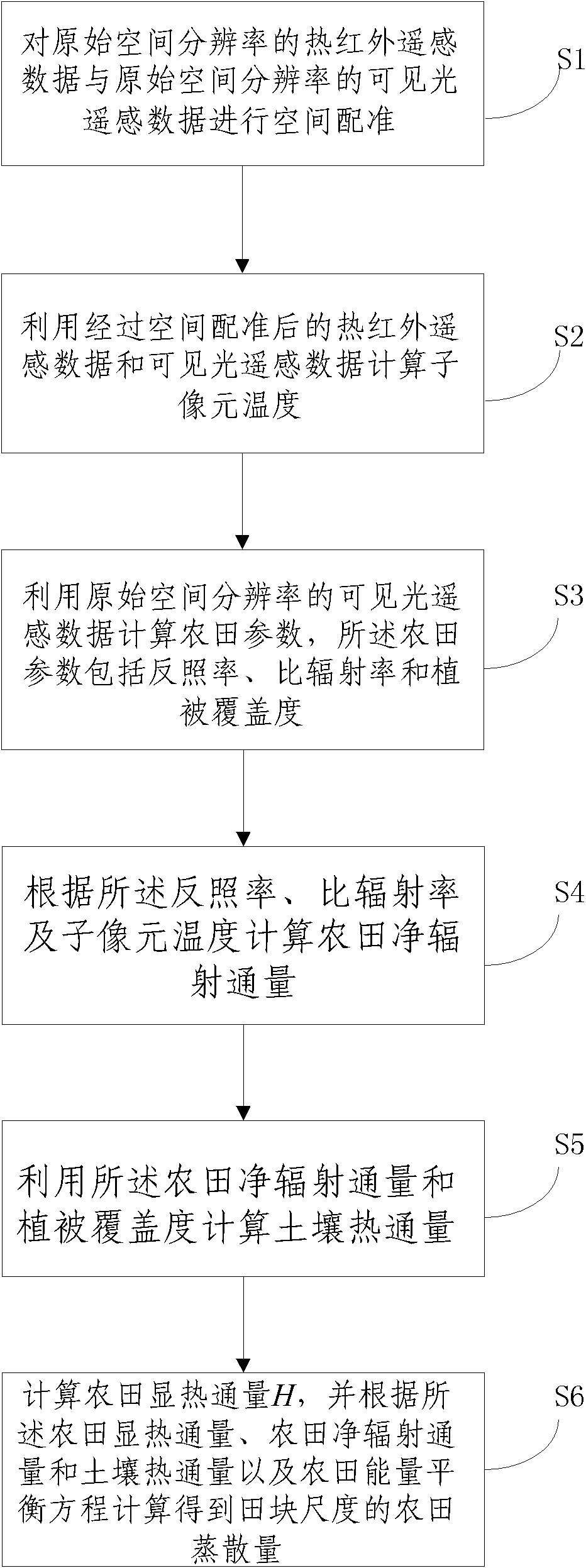
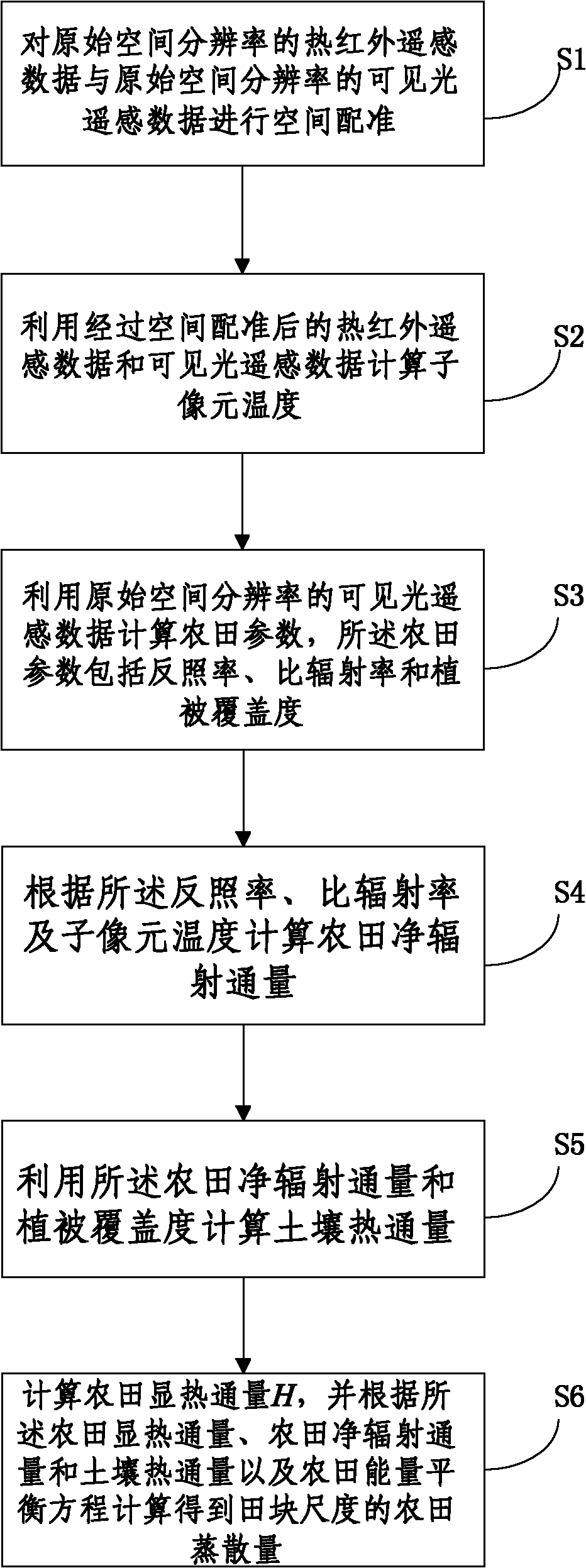
Method for obtaining field evapotranspiration of field scale
ActiveCN102136035AAccurately express the continuous change of spaceReduce spatial resolutionMaterial heat developmentSpecial data processing applicationsSensing dataHeat flux
The invention discloses a method for obtaining field evapotranspiration of field scale, comprising the following steps: S1. space registration is carried out to thermal infrared remote sensing data of original spatial resolution and visible light remote sensing data of the original spatial resolution; S2. sub-pixel temperature is calculated by utilizing the thermal infrared remote sensing data and the visible light remote sensing data whichare treated with space registration; S3. field parameters including albedo, specific emittance and vegetation coverage are calculated by utilizing the visible light remote sensing data of the original spatial resolution; S4. the field net radiation flux is calculated according to the albedo, the specific emittance and the sub-pixel temperature; S5. soil heat flux is calculated by utilizing the field net radiation flux and the vegetation coverage; and S6. the field sensible heat flux H is calculated, and the field evapotranspiration of the field scale can be calculated according to the field sensible heat flux, the field net radiation flux, the soil heat flux and field energy equilibrium equation. By adopting the method in the invention, the field evapotranspiration of the field scale can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Radiation source and device
InactiveUS7820991B2Reliable coolingIncrease heating capacityDischarge tube luminescnet screensLayered product treatmentElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
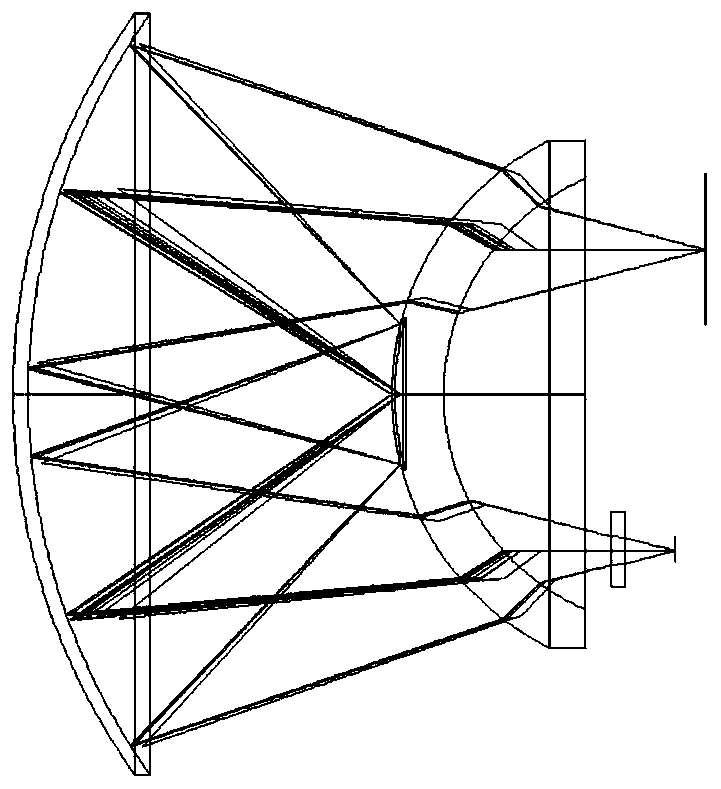
Radiation source for electromagnetic radiation the major effective component of which is in the near-infrared region, in particular in the wavelength region between 0.8 μm and 1.5 μm, to form an elongated irradiation zone, with an elongated halogen lamp comprising a glass body that has a tubular shape with bases at the ends and contains at least one spiral filament, and with an elongated reflector, such that the bases of the halogen lamp are disposed in the region of the reflector surface or behind it with reference to the position of the halogen lamp, wherein the ends of the halogen lamp are bent around toward the reflector and the spiral filaments or at least one of them is made thicker or is more densely wound in the bent region of the glass body, in such a way that the radiation flux density of the radiation source is substantially constant in the long direction of the source, between the outermost points of the bases.
Owner:ADPHOS INNOVATIVE TECH +1
System and method for estimating noise using measurement based parametric fitting non-uniformity correction
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN MISSILES & FIRE CONTROL
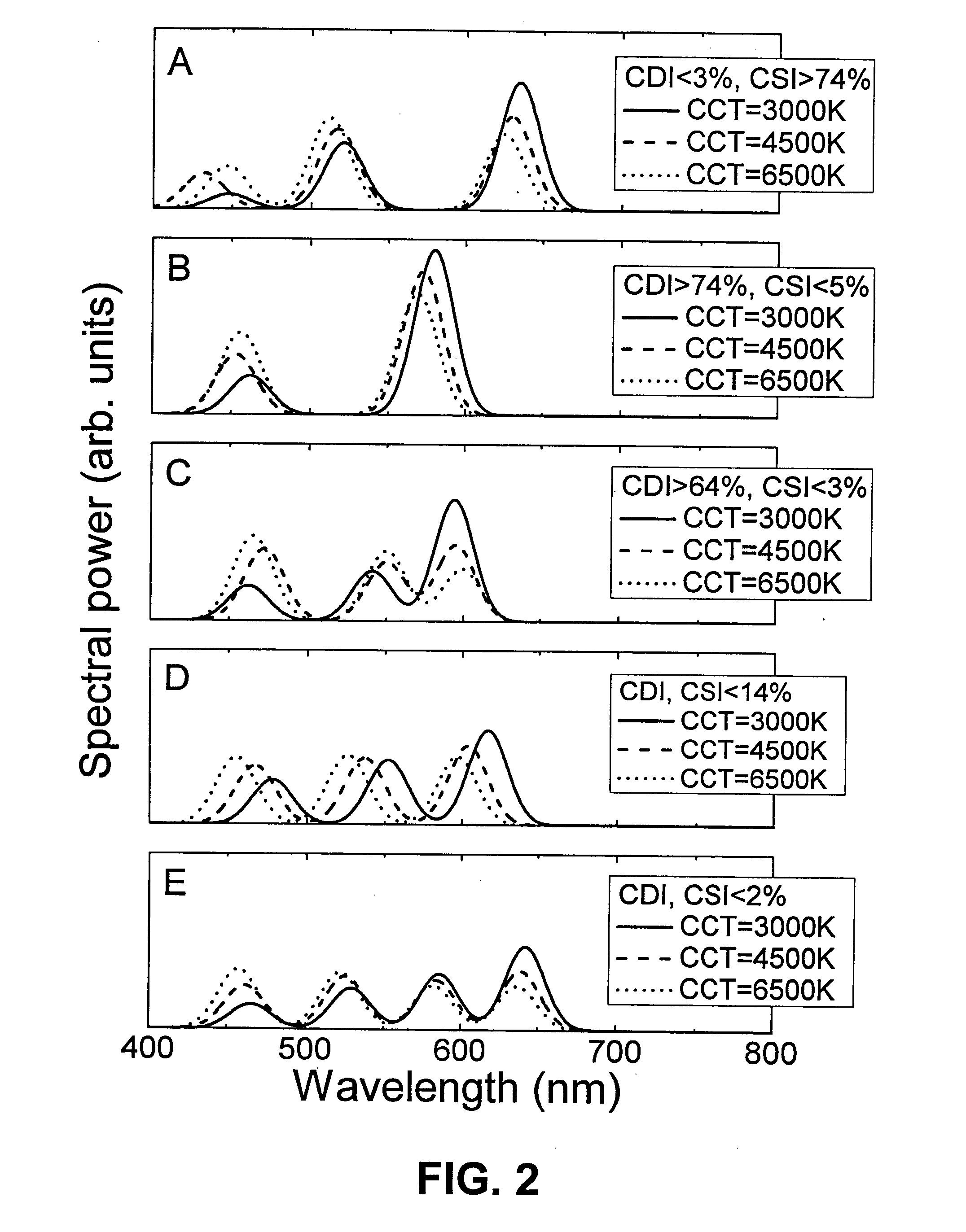
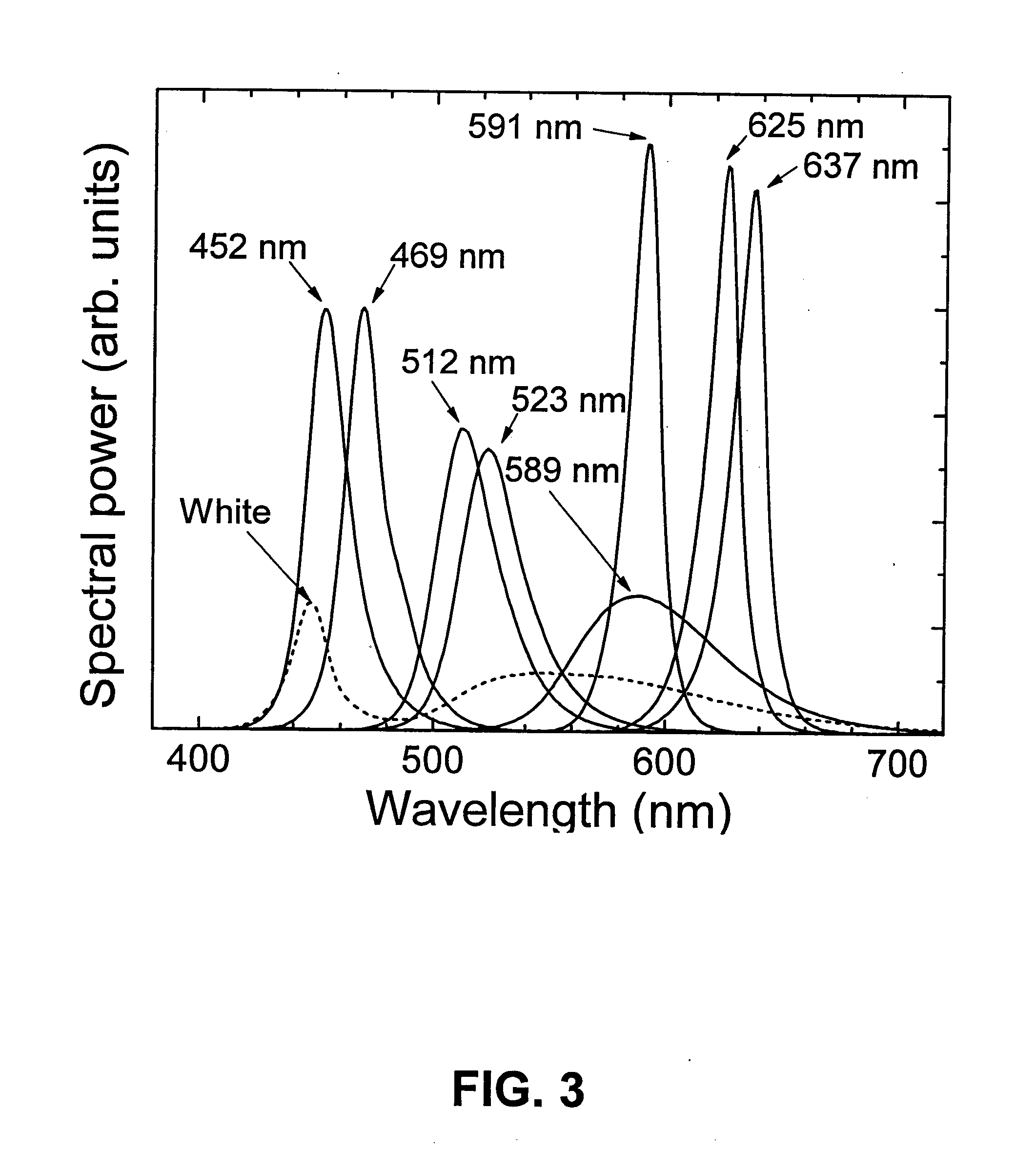
System and Method of Quantifying Color and Intensity of Light Sources
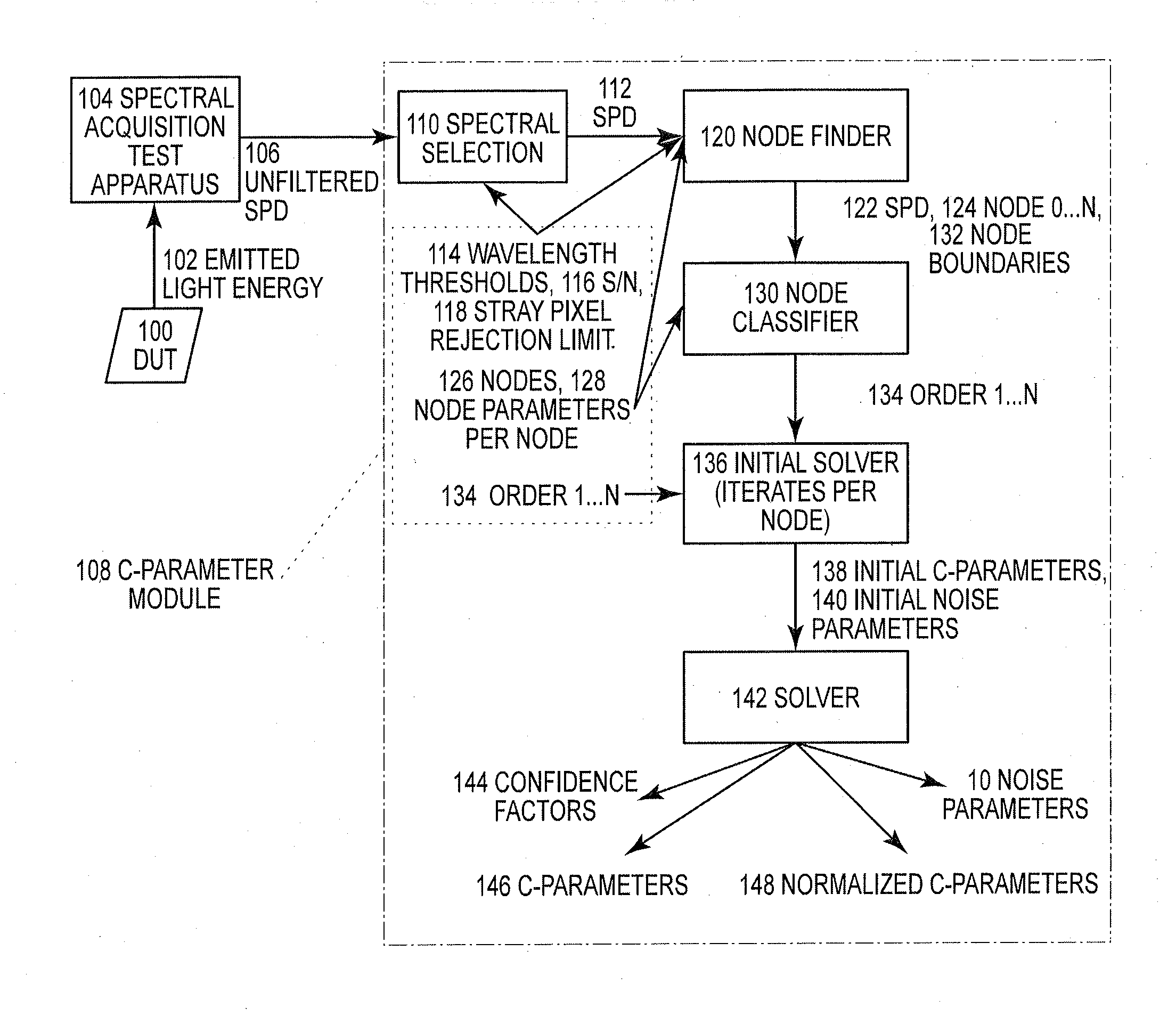
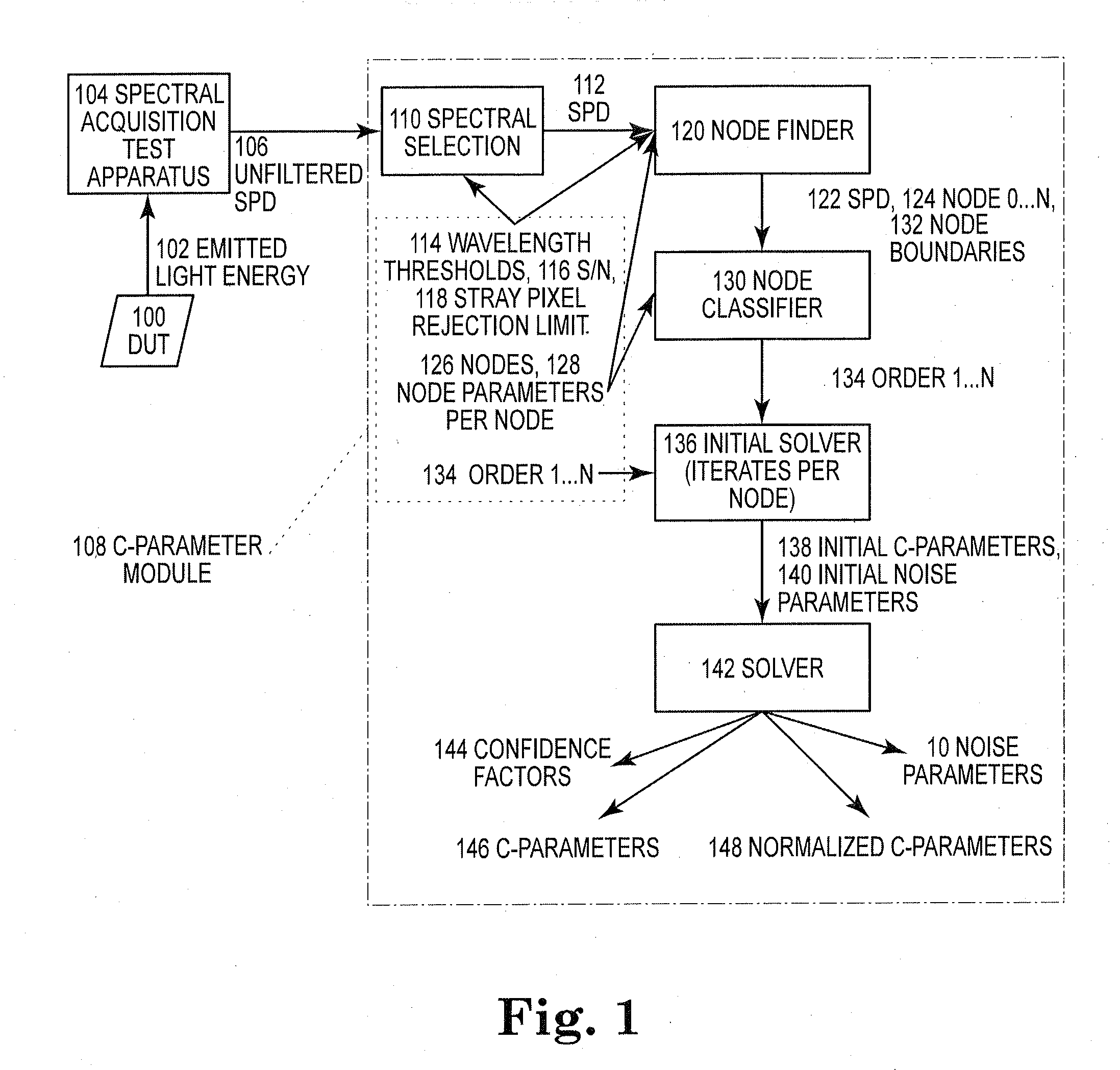
InactiveUS20120038363A1Improve precisionImprove accuracySpectrum investigationDiode testingCurve fittingProcedural approach
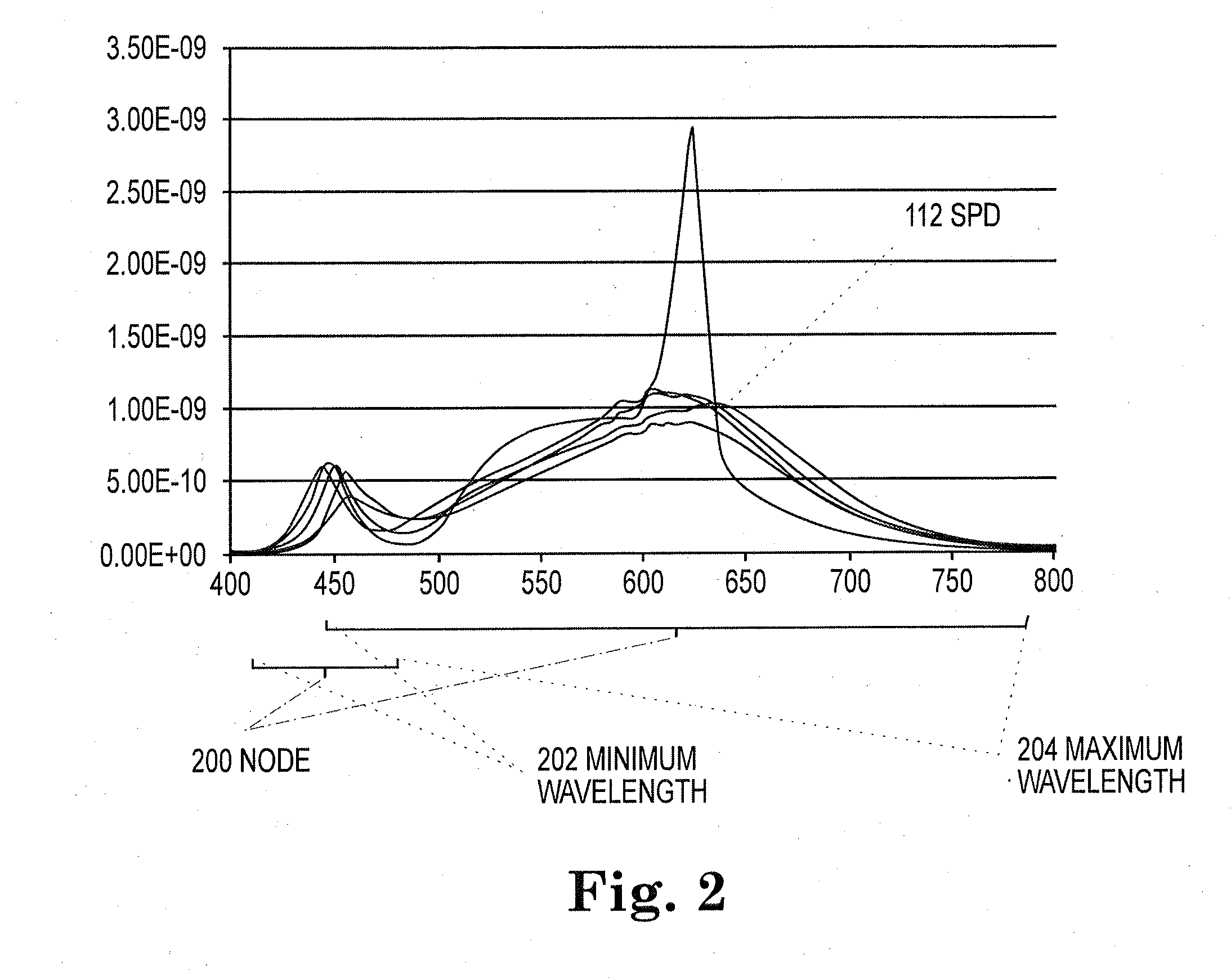
A system and method of quantifying color and intensity of light sources including LEDs, HBLEDs (High Brightness LEDs), and other Solid State Lights (SSLs) using C-parameters to model a Spectral Power Distribution (SPD) to improve precision, accuracy, repeatability and usefulness of measurement of optical properties of wavelength and radiant flux in manufacturing of an object, designing products and processes that use the object, and describing / defining the object, is provided. In one embodiment, a method of characterizing a Solid State Light (SSL) source includes a SSL source under test (DUT), a Spectral Power Distribution (SPD) of light emission of the SSL source, a curve-fitting function, a set of configuration data comprising the order of the curve-fitting function, the number of nodes, wavelength boundary limits, saturation threshold, and noise floor threshold, a computing device for curve-fitting, node detection, iteration and program control and inputting and outputting data; and a set of C-Parameters, noise parameters, and confidence values.
Owner:DODDS STANLEY CURTIS JR
Compact radiation source
ActiveUS20090080614A1Generation of X-rayHigh energyX-ray tube electrodesCathode ray concentrating/focusing/directingUV curingX-ray
A radiation source which can emit X-ray flux, UV-C flux and other forms of radiation uses electron beam current from a cathode array formed on the window through which the radiation will exit the source. The source can be made in formats which are compact or flat compared with prior art radiation sources. X-ray, UV-C and other radiative flux produced by the source can be used for such purposes as radiation imaging, sterilization, decontamination of biohazards, UV curing or photolithography.
Owner:STELLAR MICRO DEVICES
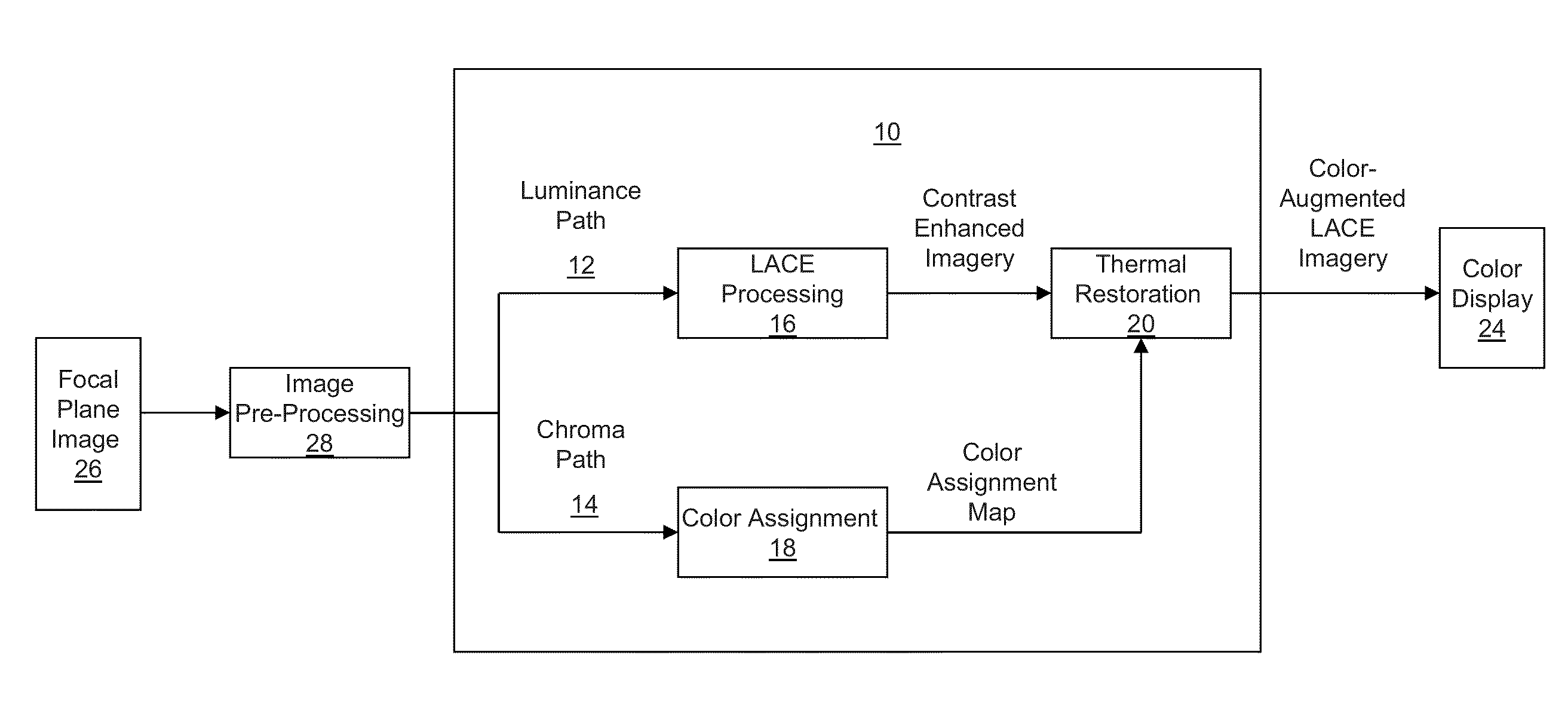
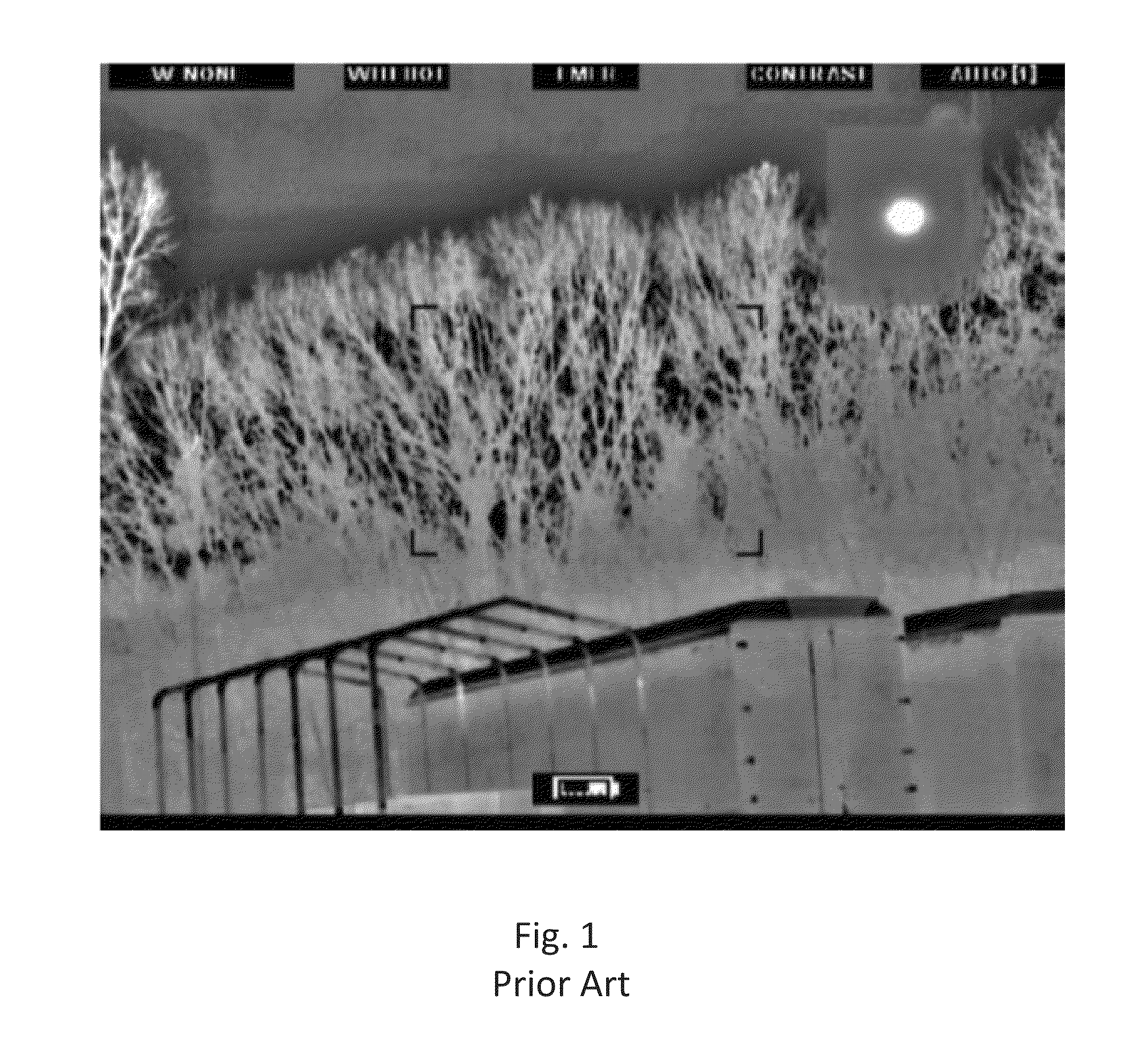
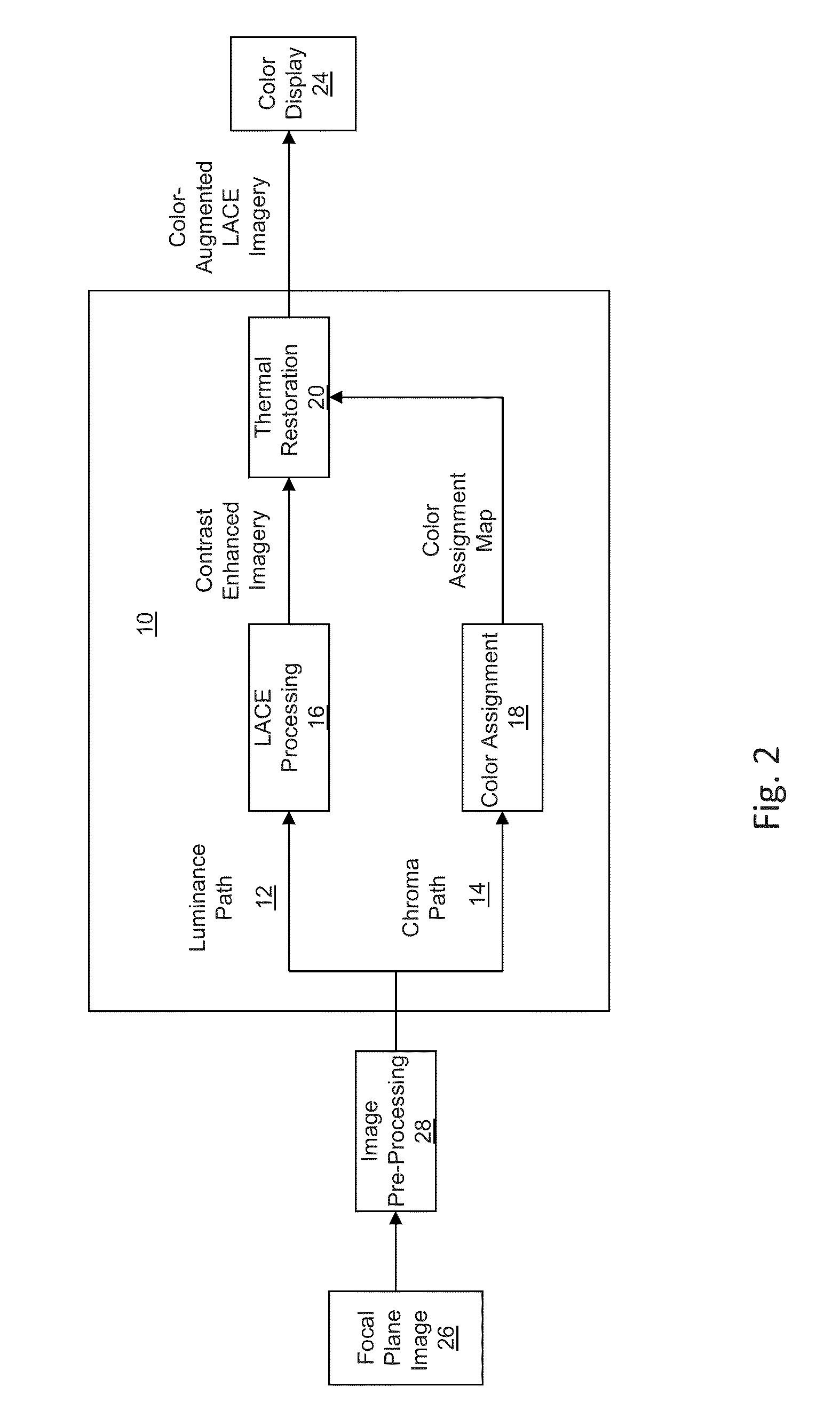
Color augmented local area contrast enhancement
ActiveUS20130038626A1Improve image contrastIncrease contrastImage enhancementTelevision system detailsContrast enhancementVisual perception
A method and system for color enabled local area contrast enhancement, are provided by generating a first copy of an image; processing the first copy to locally enhance visual contrast in the image; generating a second copy of the image; processing the second copy of the image to provide at least one visual cue to radiant flux within the image incident on the focal plane pixels; displaying a combined image formed from the combination of the locally enhanced first copy and flux mapped the second copy.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
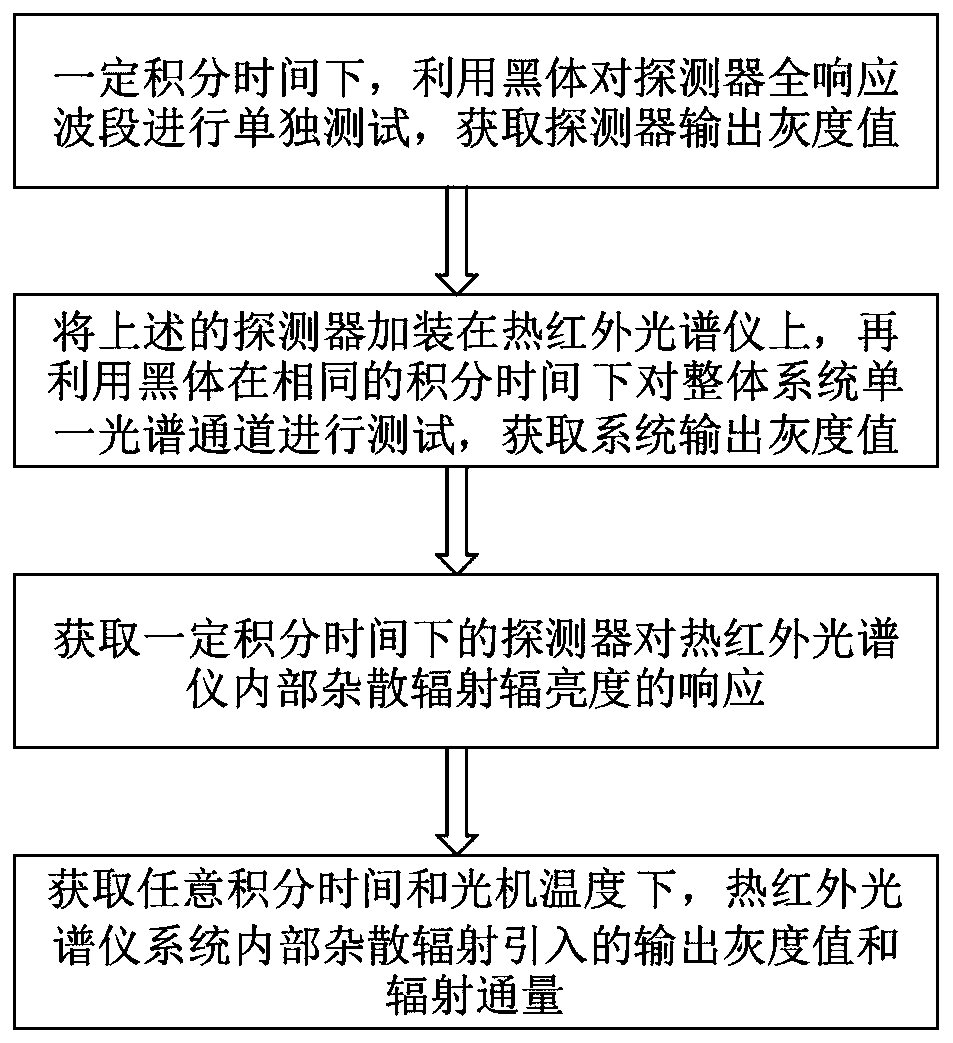
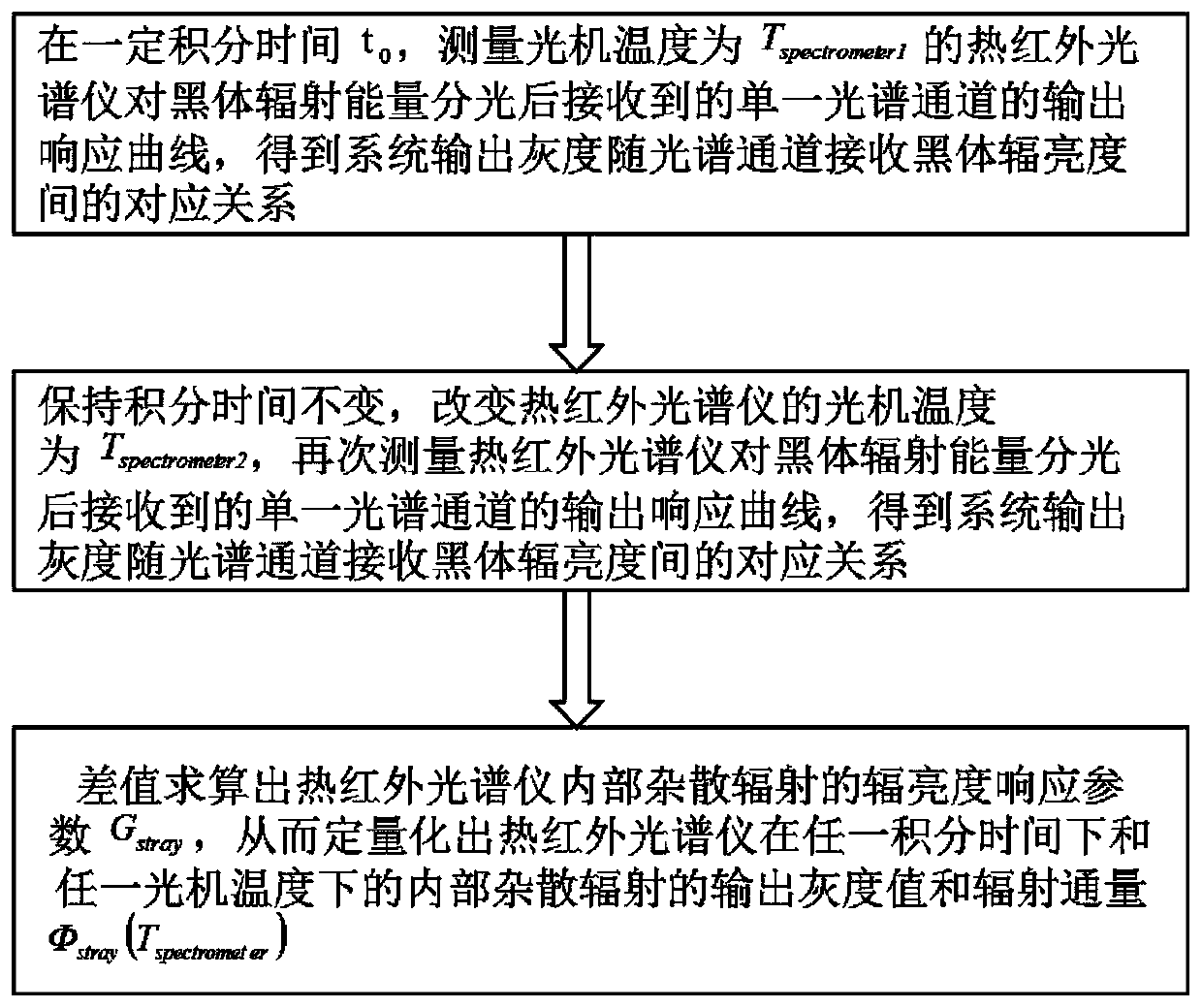
Method for testing internal stray radiation of thermal infrared spectrometer
InactiveCN110231090ASimple methodSolve the accuracy problemSpectrum investigationThermodynamicsBlack body
The invention discloses a method for testing internal stray radiation of a thermal infrared spectrometer. A radiation test is respectively performed on a full response band of a detector and a spectral channel of the thermal infrared spectrometer at an integration time by using a black body, an equivalent gray value and radiant flux of the internal stray radiation in the current state of the system can be measured by respectively performing a test on the detector and the spectrometer via the method, and the gray value and the radiant flux of the the internal stray radiation of the thermal infrared spectrometer at any integration time and any optical machine temperature can be obtained in combination with the optical machine temperature during the test. The method disclosed by the inventionis simple, can be used for effectively solving the problem that the internal stray radiation of the thermal infrared spectrometer seriously affects the system radiation precision and the system quantification, and is suitable for practical engineering applications.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ceramic composite for light conversion, process for production thereof, and light-emitting devices provided with same
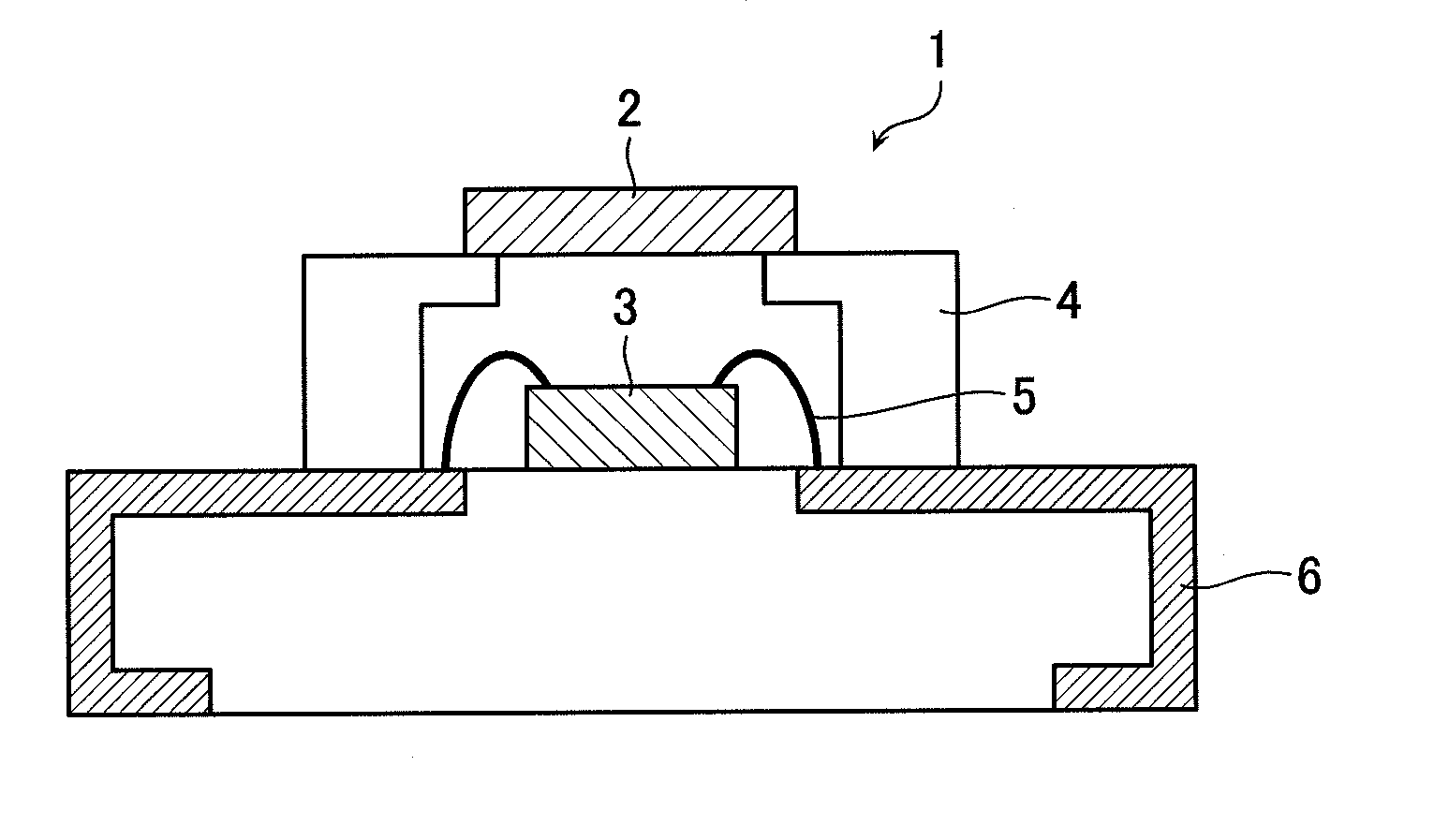
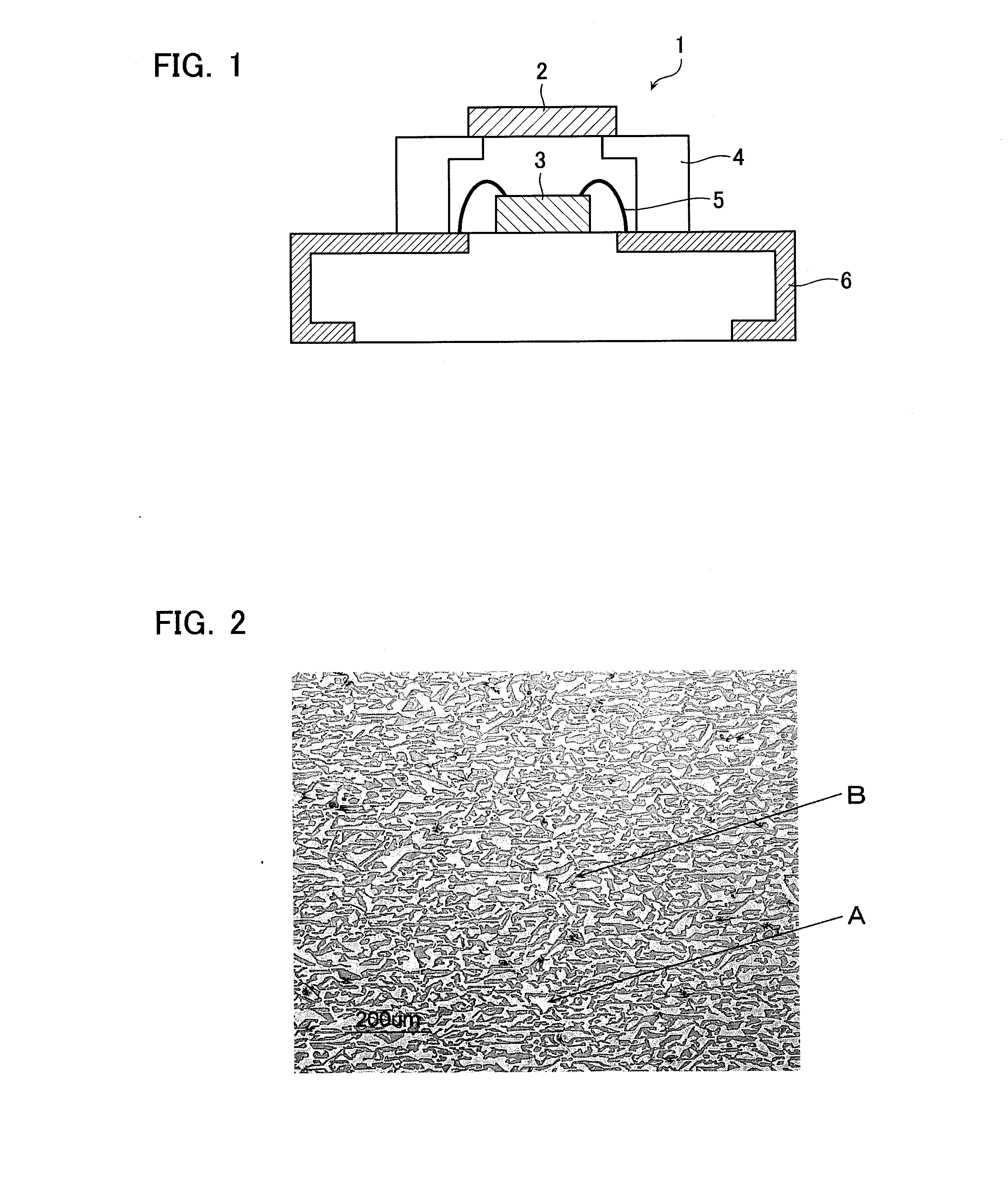
ActiveUS20130088143A1High radiant fluxDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesCeramic compositeFluorescence
Provided are a ceramic composite for light conversion, which is capable of maintaining a high radiant flux even when the proportion of Gd and Ce is increased to tune the fluorescence peak wavelength to the longer wavelength side, a process for producing the ceramic composite, and a light emitting device including the ceramic composite. The ceramic composite for light conversion is a solidification product including a composition that is represented by a specific formula, and has a texture of continuously and three-dimensionally mutually entangled oxide phases including at least two phases of a first phase and a second phase, characterized in that the first phase is a Y3Al5O12 fluorescent phase activated with Ce, and the second phase is an Al2O3 phase, and the first phase and second phase account for 97% by area or more of a cross section of the solidification product, or characterized in that the first phase is a Y3Al5O12 fluorescent phase activated with Gd and Ce, and the second phase is an Al2O3 phase, and the first phase and second phase account for 97% by area or more of a cross section of the solidification product.
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Fired heater
ActiveUS20080098967A1Minimize coke build up in tubesIncrease capacityBoiler water tubesFurnace-tube steam boilersCombustorHeat flux
Two improvements for heaters are disclosed which can be implemented as either apparatus or method. First is a novel flue gas injection system. Second is a novel burner configuration. The improvements can be used alone or together. In the flue gas injection system, flue gas is injected between the burners and the tubes to reduce heat flux on the tubes and shift part of the heat duty from the radiant to the convective section. These approaches work toward increasing the capacity of heaters where we can increase the firing rate in the heater and still keep the tube metal temperature and radiant fluxes within acceptable limits.
Owner:GARG ASHUTOSH
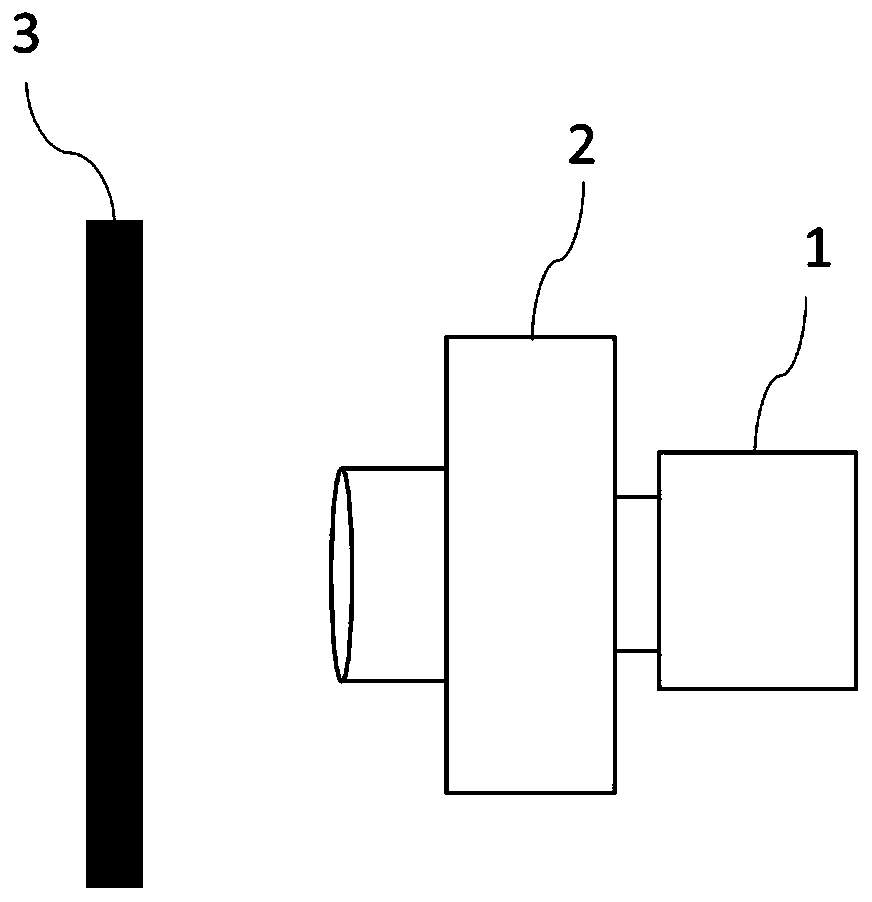
Method for measuring stray radiation of thermal infrared spectrometer
ActiveCN110470406ASolve the accuracy problemSolve the problem of system quantificationRadiation pyrometryBlack bodyMeasuring output
The invention discloses a method for measuring stray radiation of a thermal infrared spectrometer. The method comprises the steps of connecting a detector and a to-be-measured thermal infrared spectrometer; measuring output response curves, received after the thermal infrared spectrometer carries out light splitting on radiation energy of a black body, of single spectral channel at different spectrometer temperature separately at same integration time; and calculating a radiation luminance response parameter of internal stray radiation of the thermal infrared spectrometer through a differencevalue, thereby quantifying an output gray value and radiation flux of the internal stray radiation of the thermal infrared spectrometer at any integration time and any spectrometer temperature. The method disclosed by the invention has universality at different spectral channels and different integration time and has great engineering practical application value, and the problem that system radiation accuracy and system quantification are seriously affected by internal stray radiation of the thermal infrared spectrometer can be effectively solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com