Patents
Literature
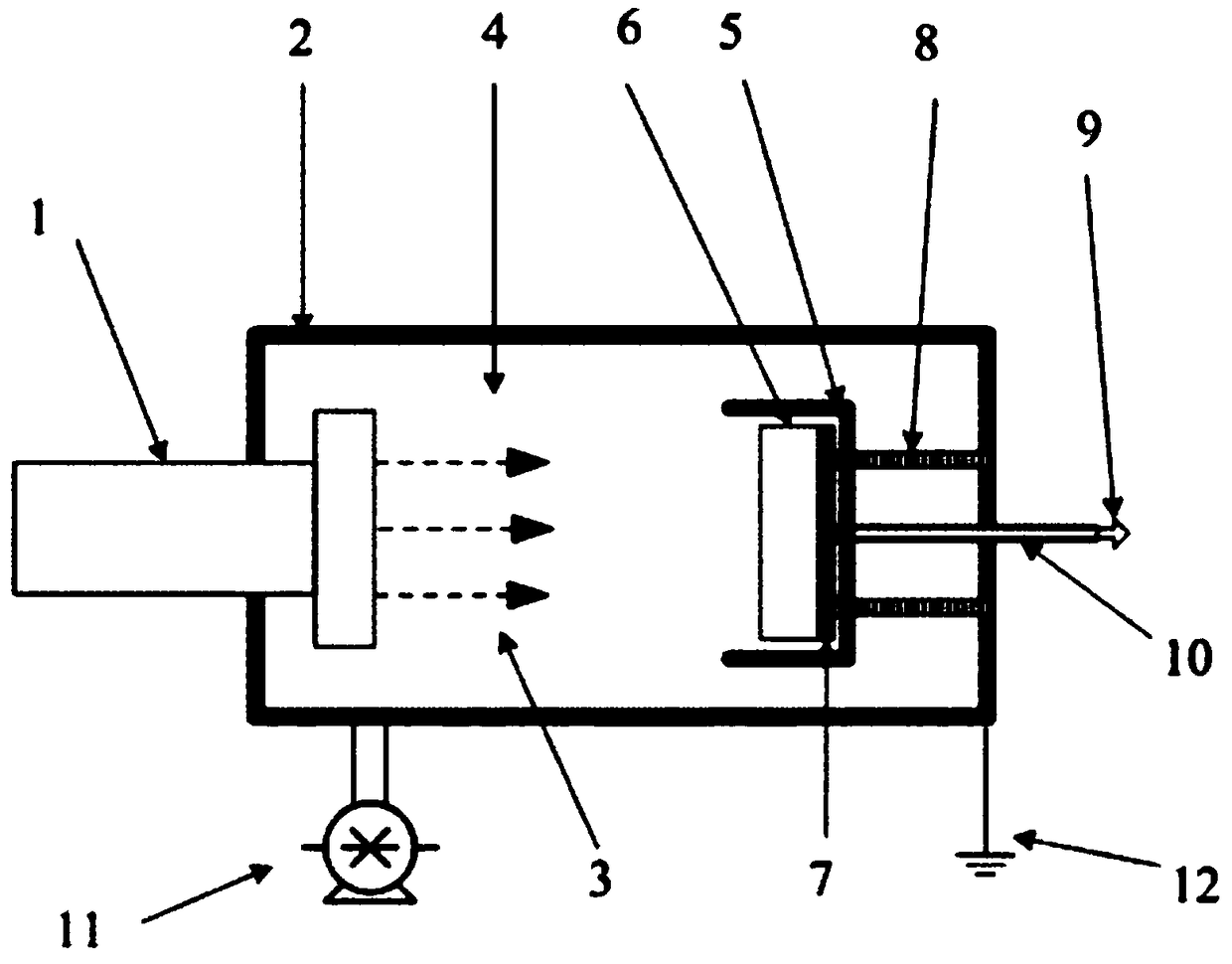
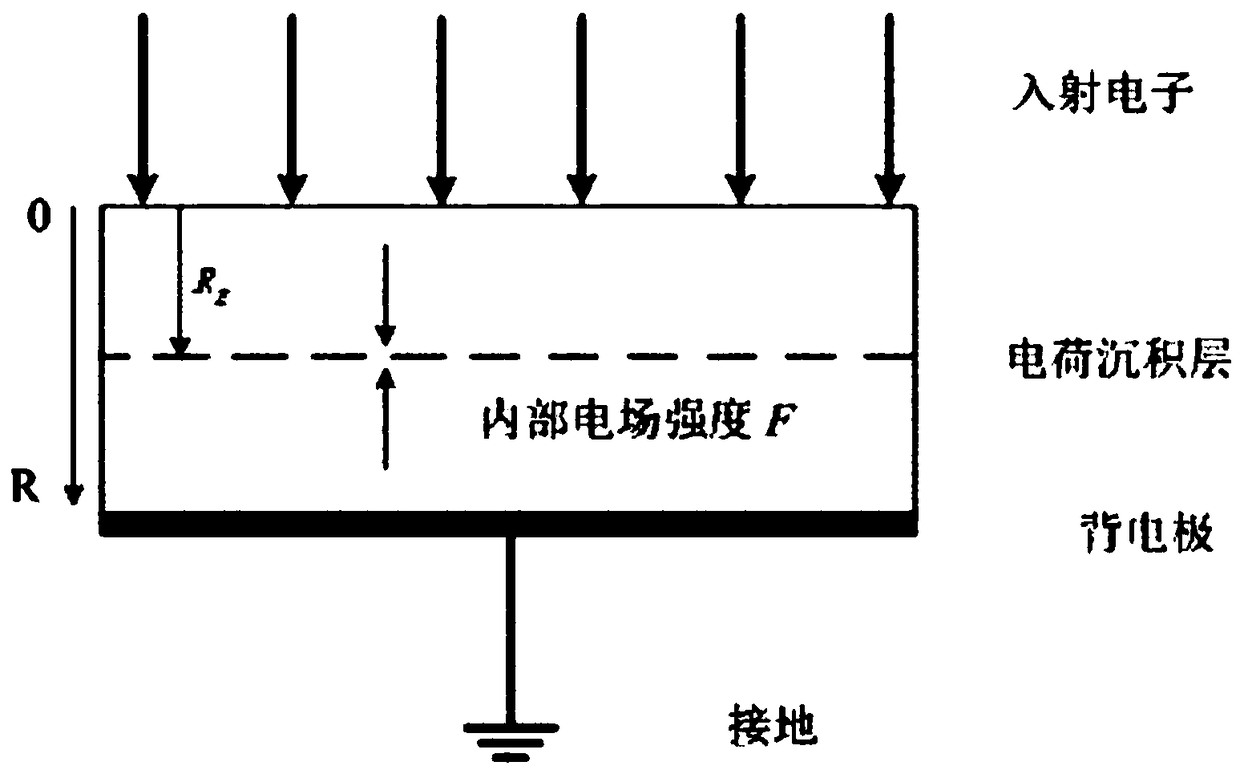
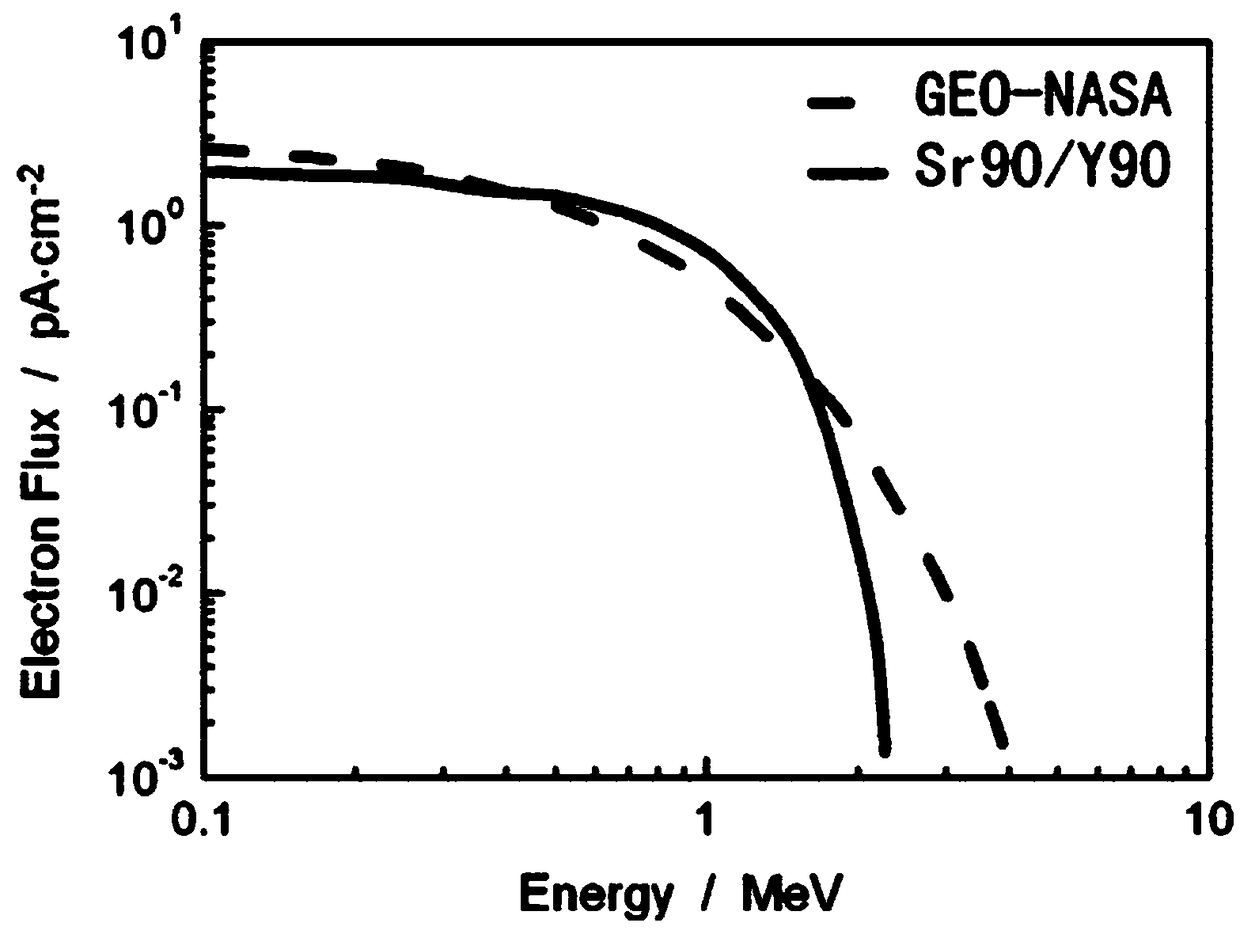
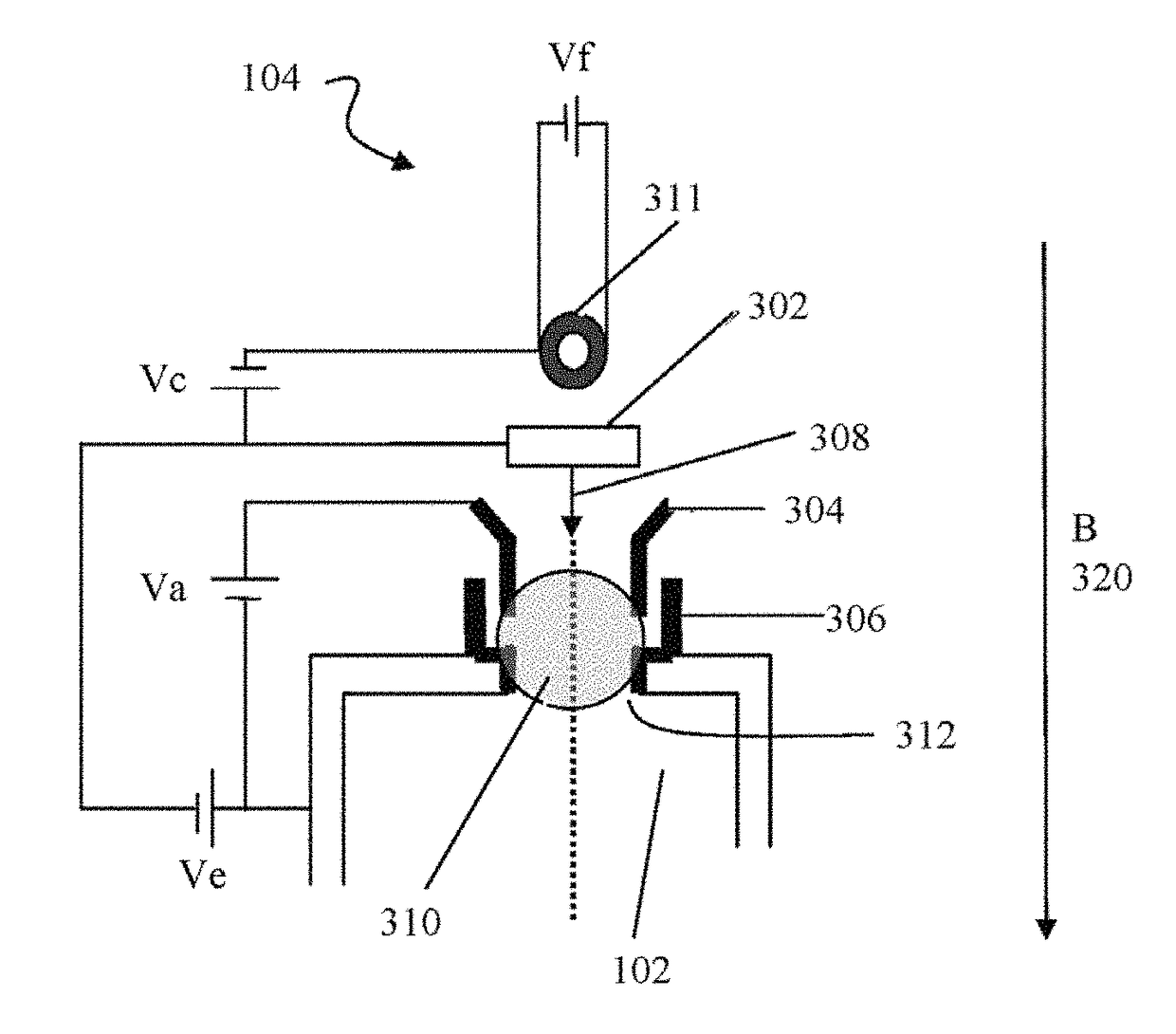
45 results about "Electron flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
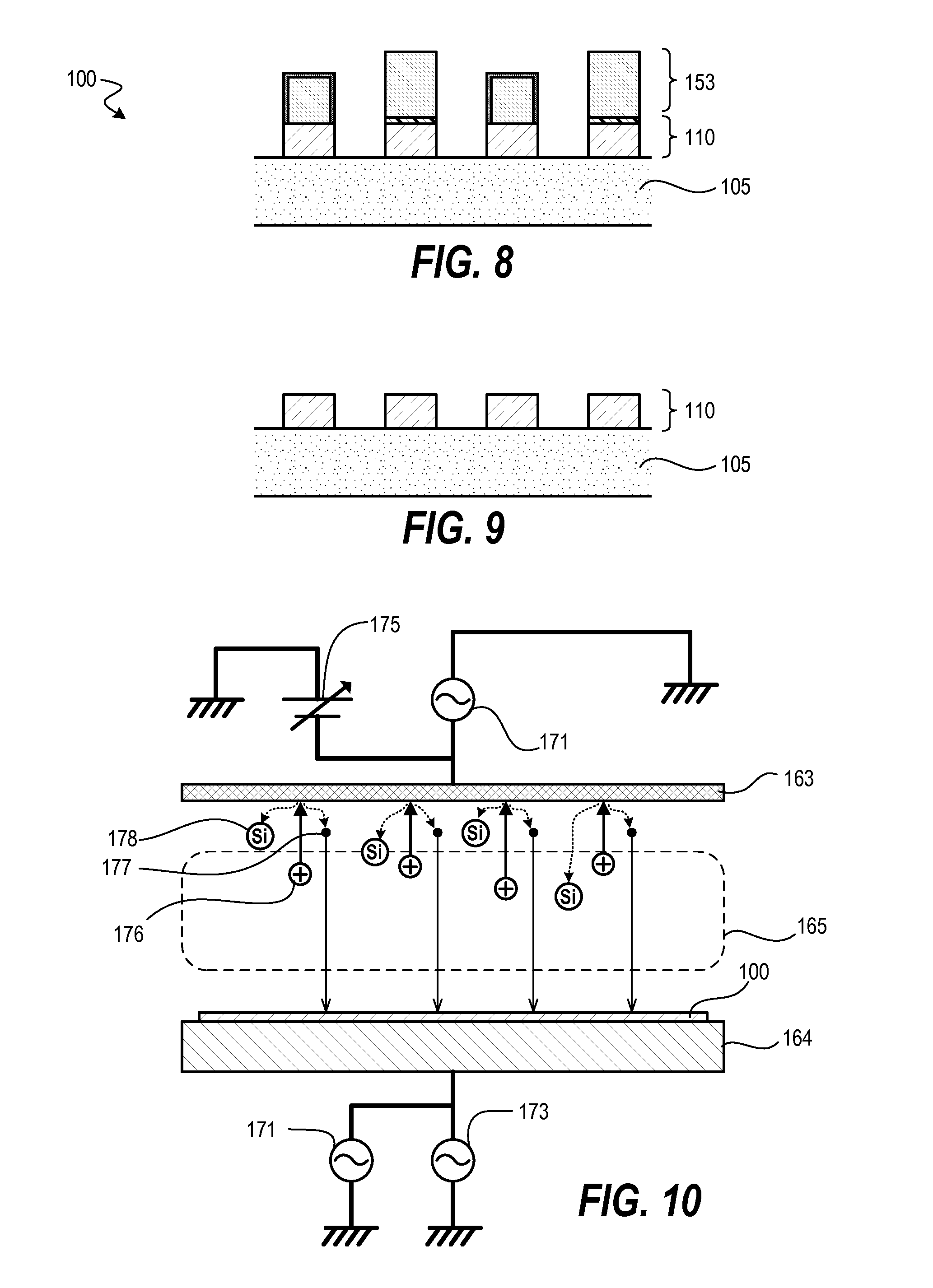
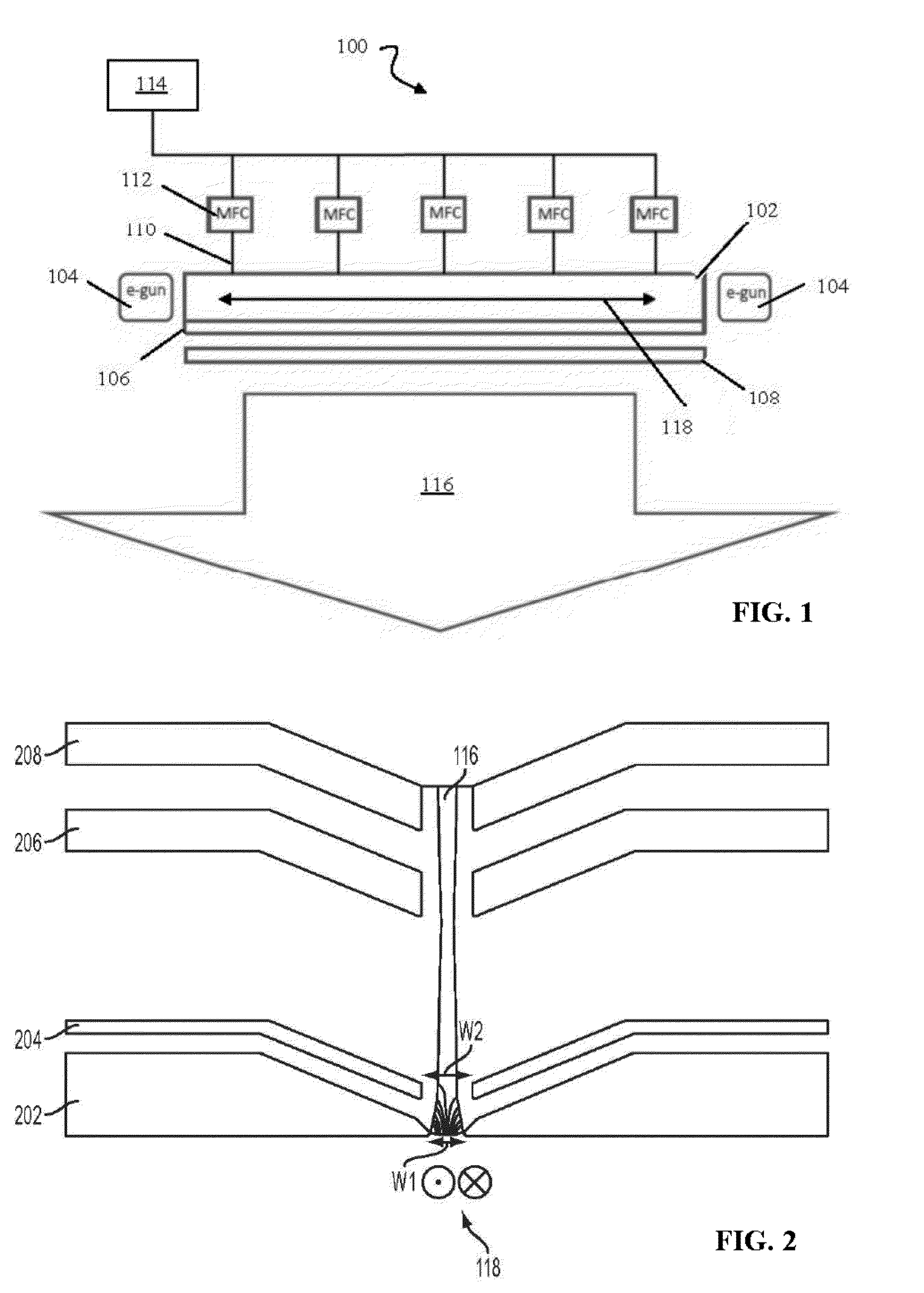
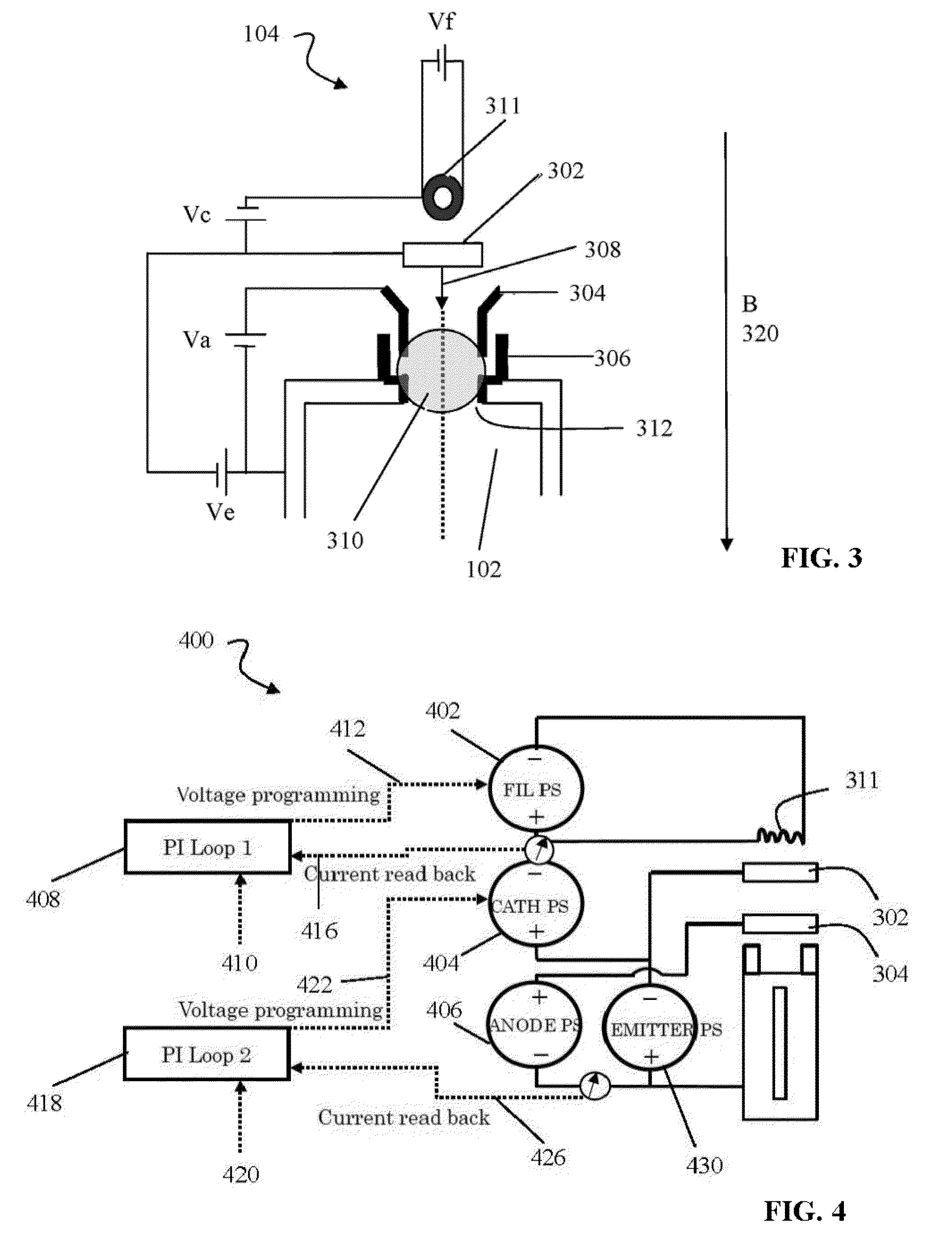
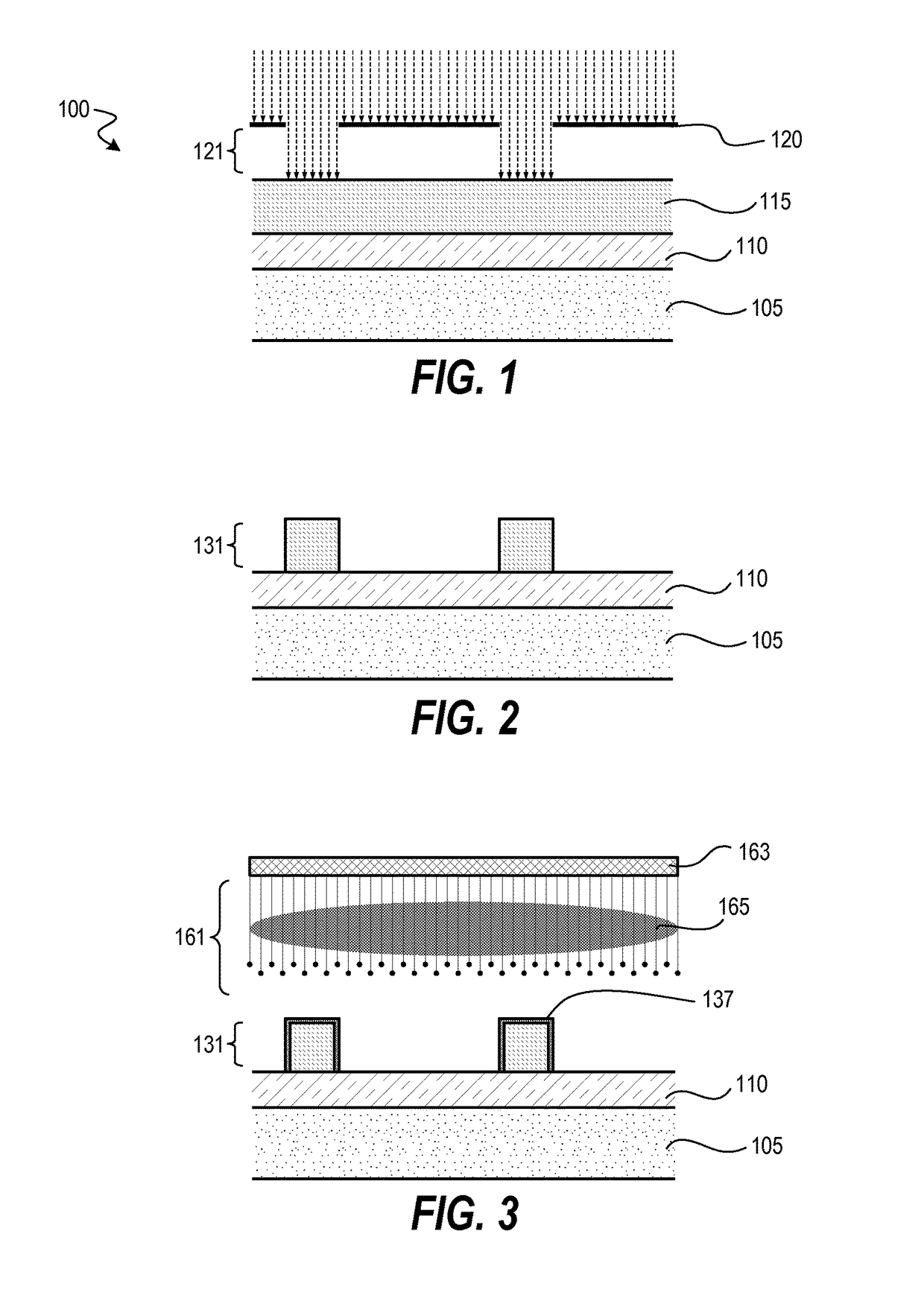
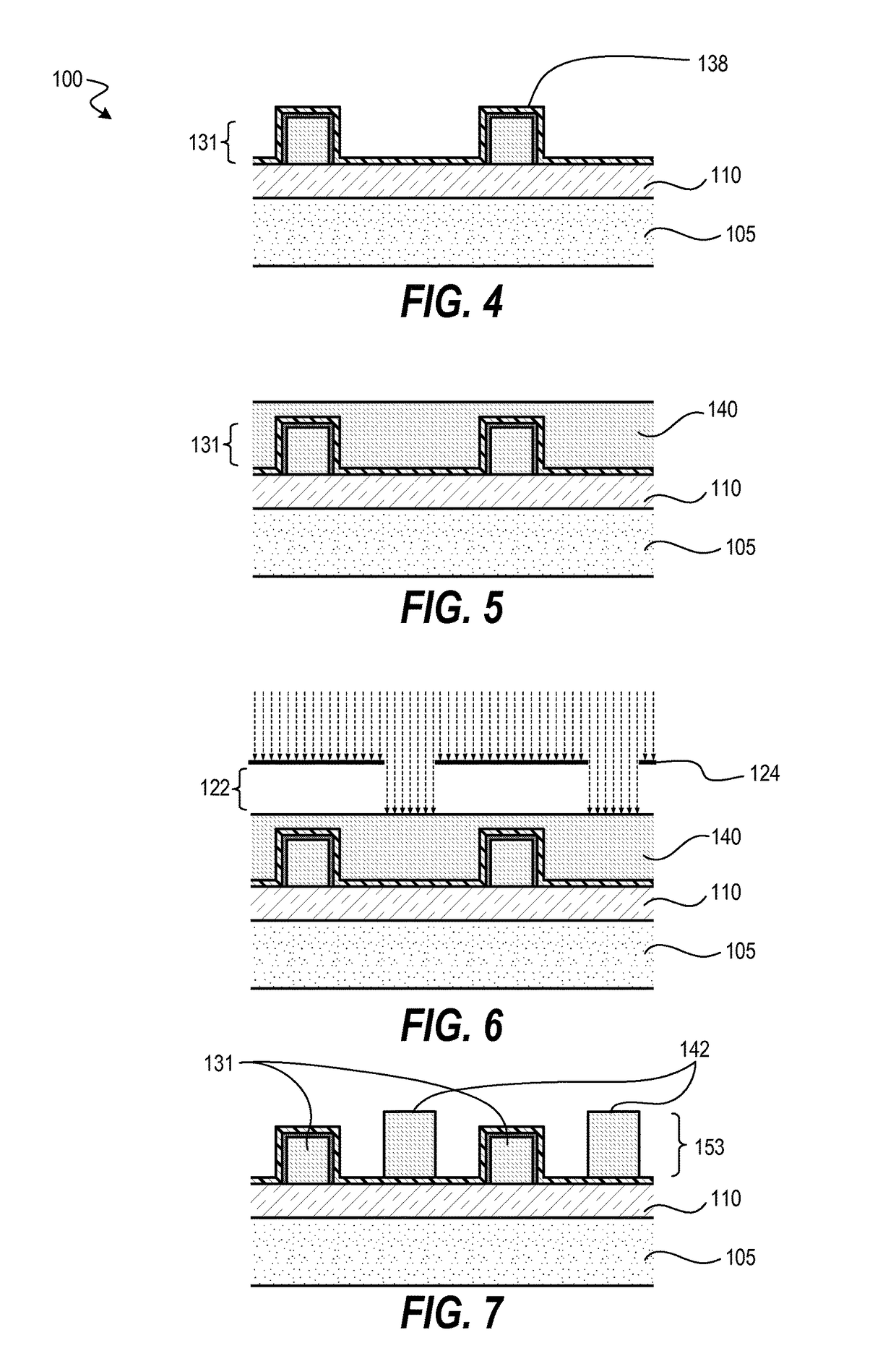
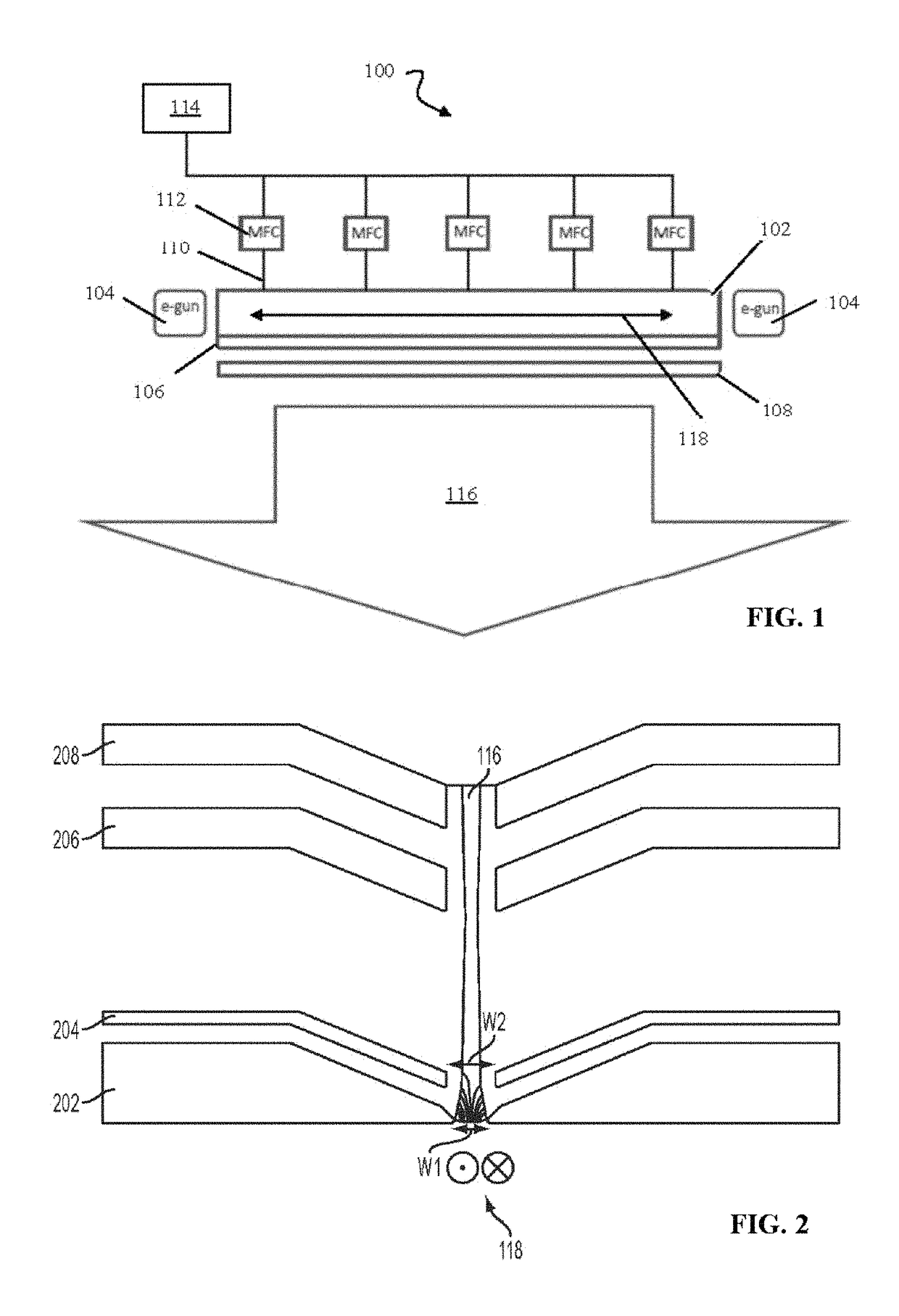
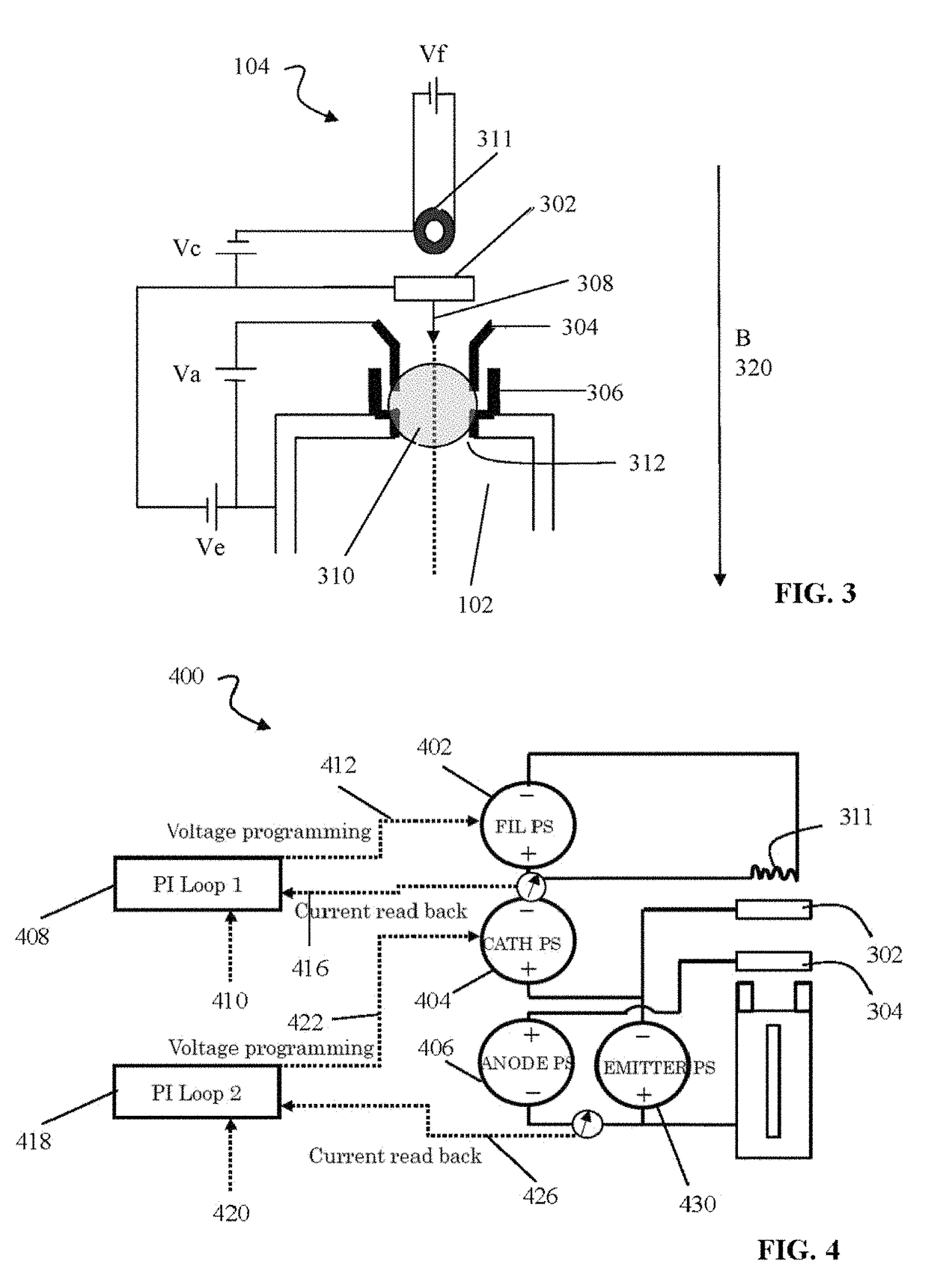
Sequential UV induced chemical vapor deposition
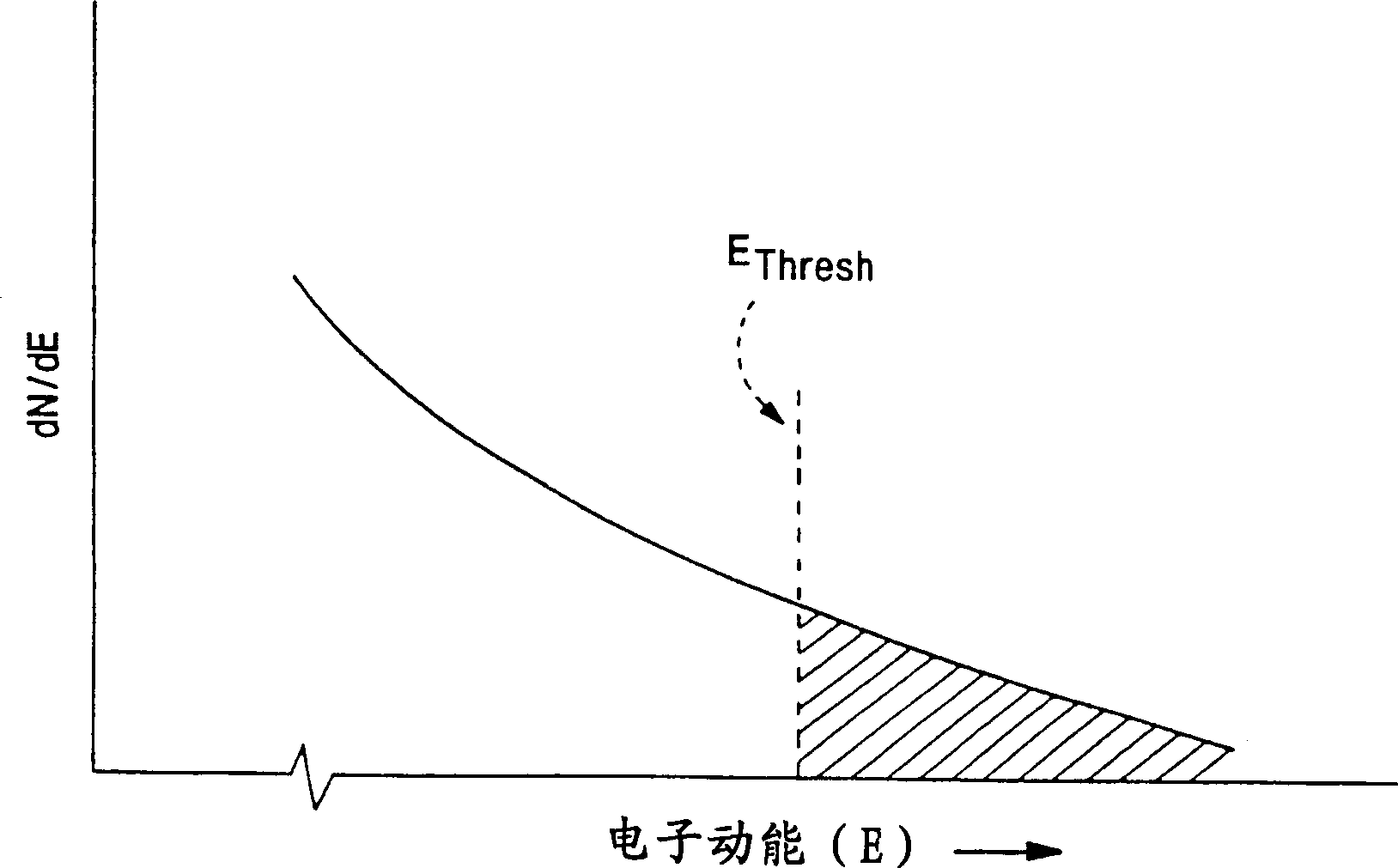
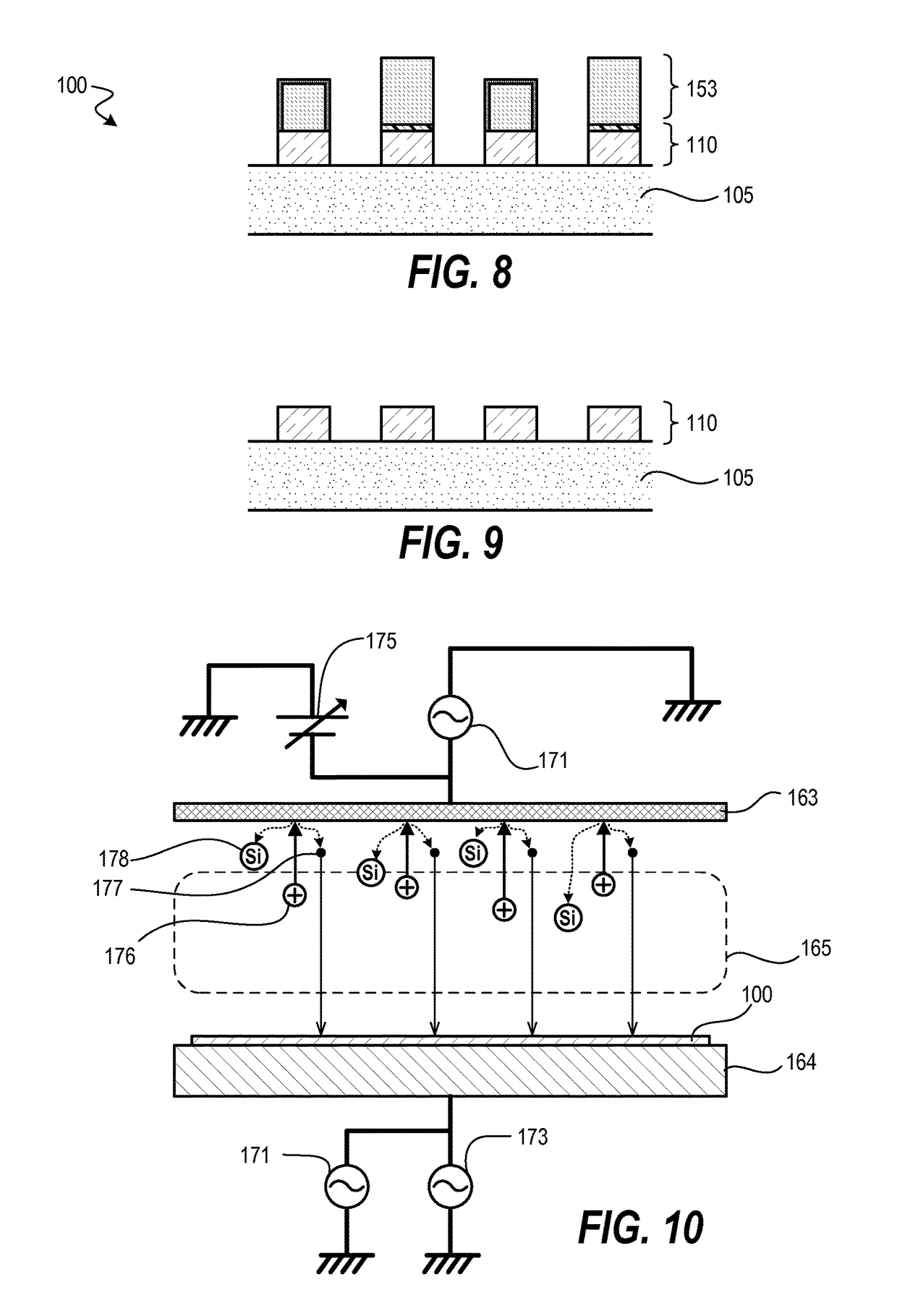
Ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes are disclosed where an ion flux, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or an electron flux, respectively, is used to induce the chemical reaction in the process. The process for depositing a thin film on a substrate includes introducing a flow of a first reactant gas in vapor phase into a process chamber where the gas forms an adsorbed saturated layer on the substrate and exposing the substrate to a flux of ions, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or a flux of electrons for inducing a chemical reaction of the adsorbed layer of the first reactant gas to form the thin film. A second reactant gas can be used to form a compound thin film. The ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential CVD process of the present invention can be repeated to form a thin film of the desired thickness.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Mono-energetic neutral beam activated chemical processing system and method of using
ActiveUS20090236314A1Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsChemical treatmentCompound (substance)
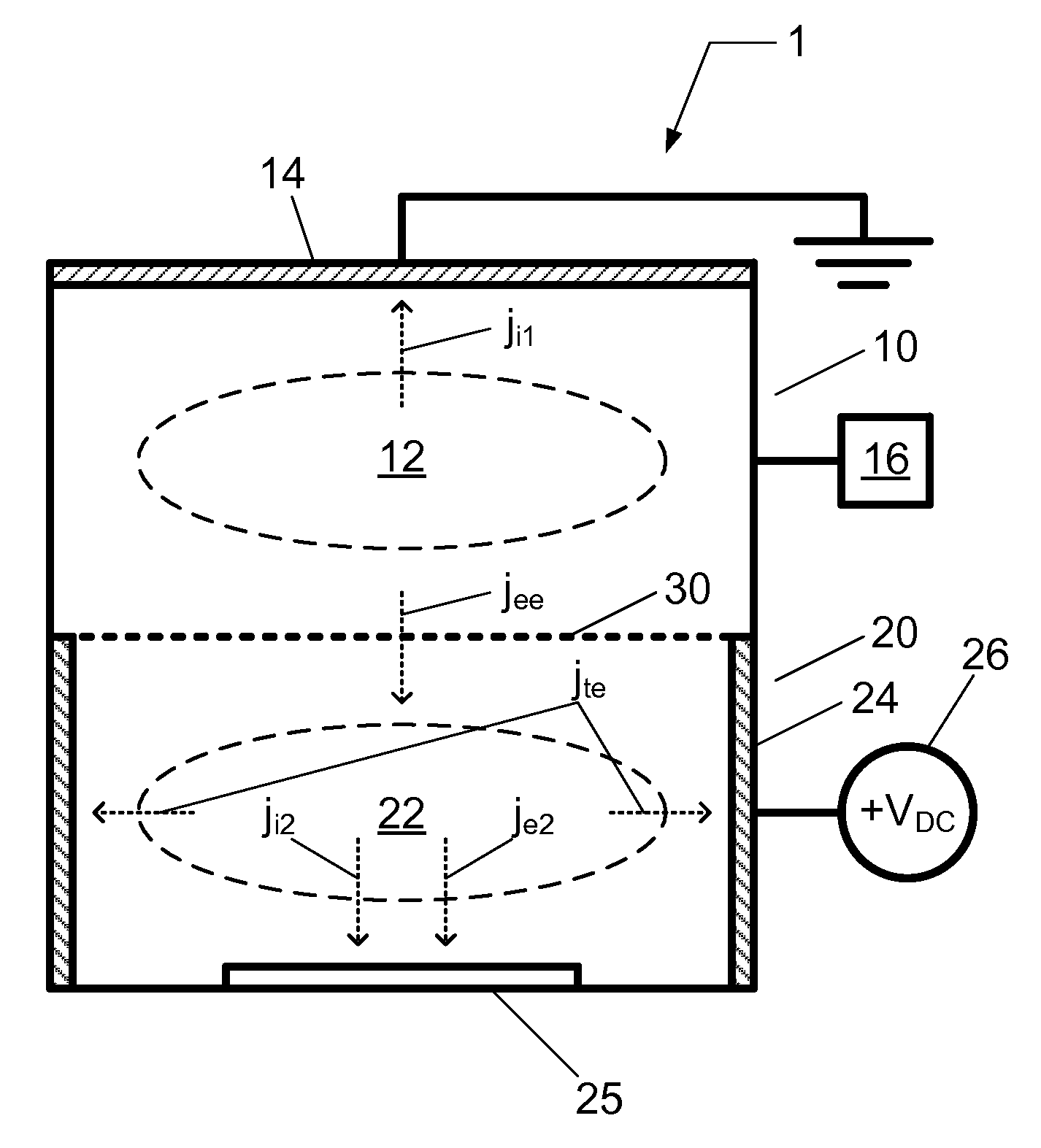
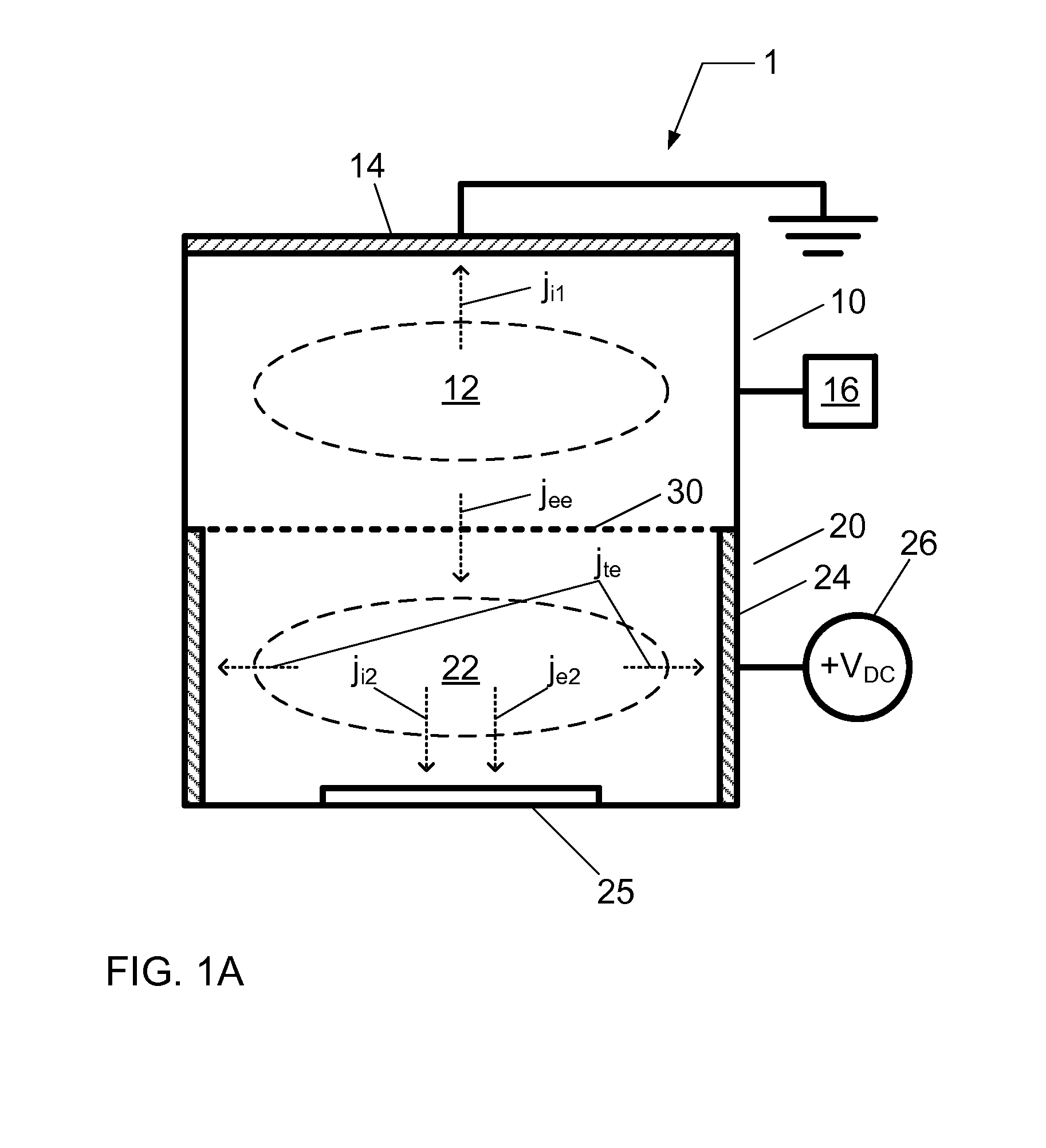
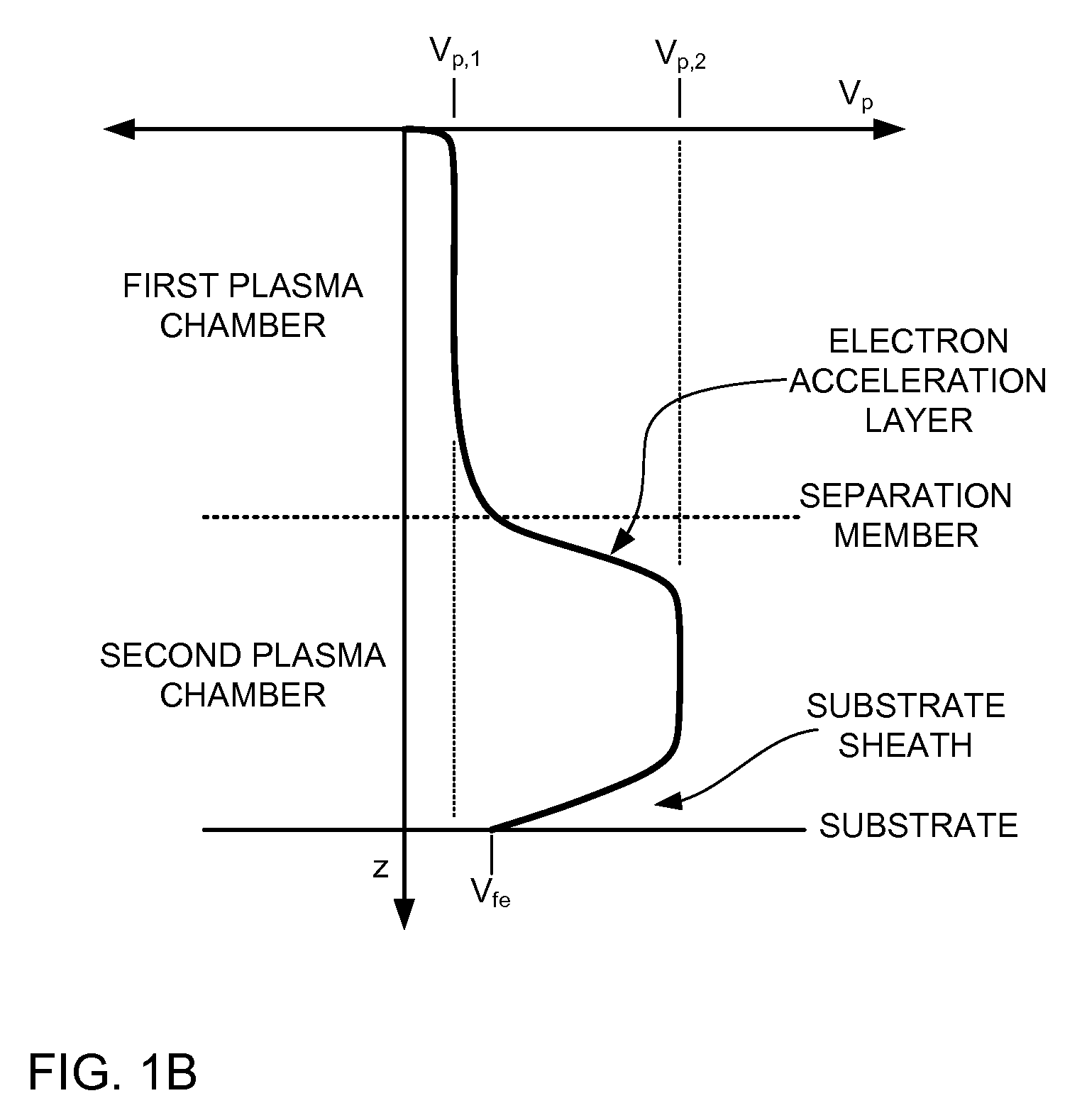
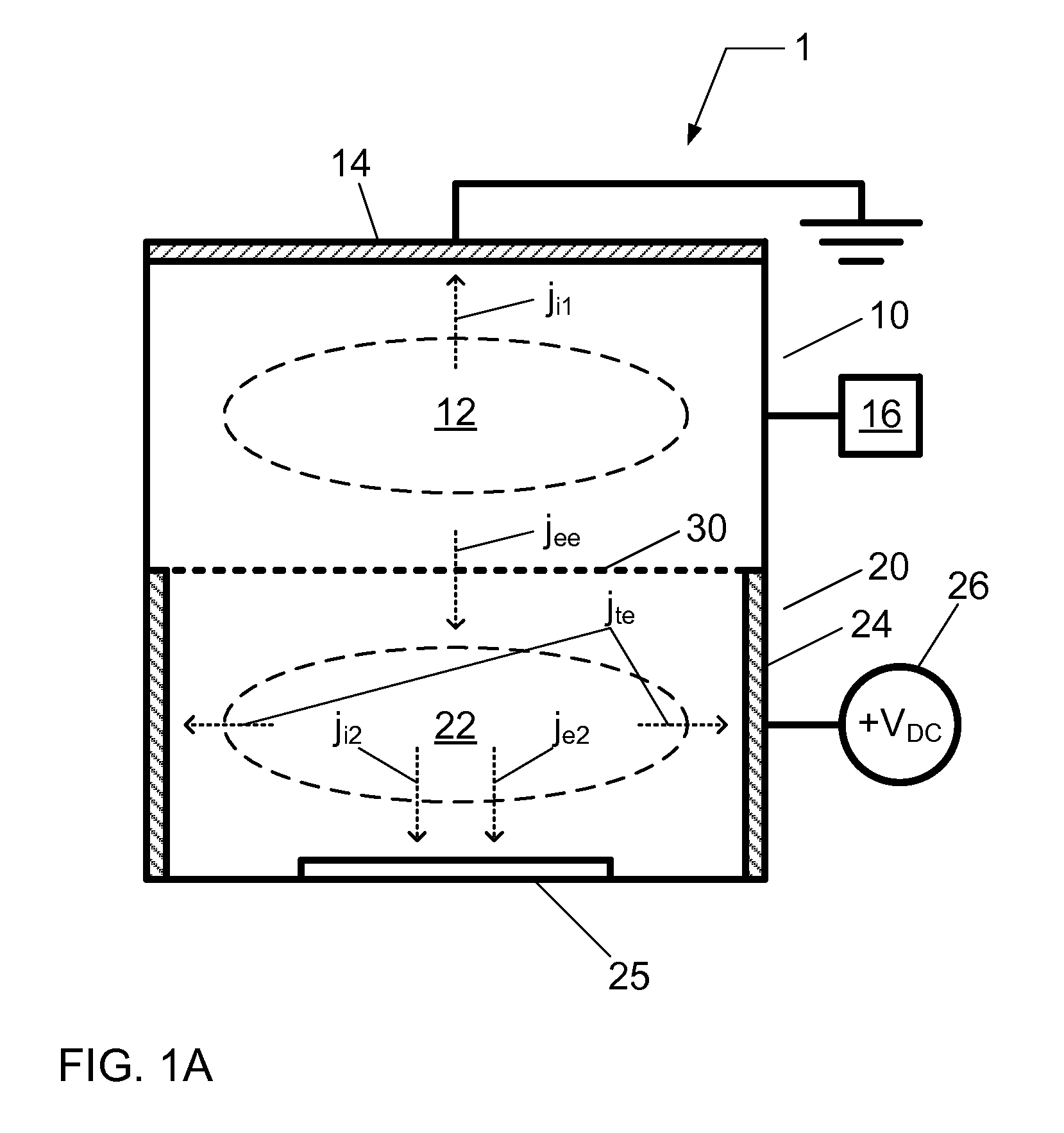
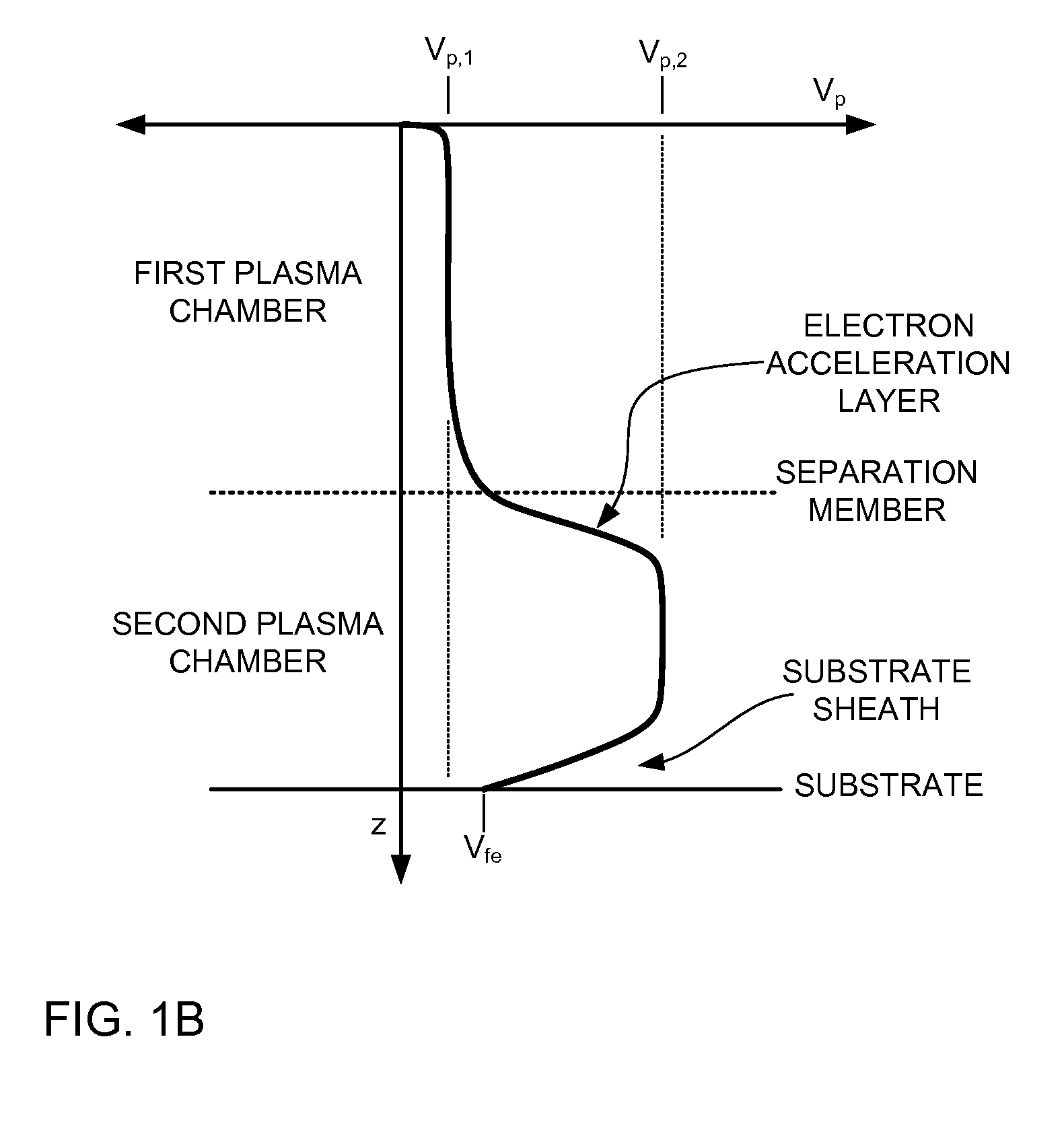
A chemical processing system and a method of using the chemical processing system to treat a substrate with a mono-energetic space-charge neutralized neutral beam-activated chemical process is described. The chemical processing system comprises a first plasma chamber for forming a first plasma at a first plasma potential, and a second plasma chamber for forming a second plasma at a second plasma potential greater than the first plasma potential, wherein the second plasma is formed using electron flux from the first plasma. Further, the chemical processing system comprises a substrate holder configured to position a substrate in the second plasma chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
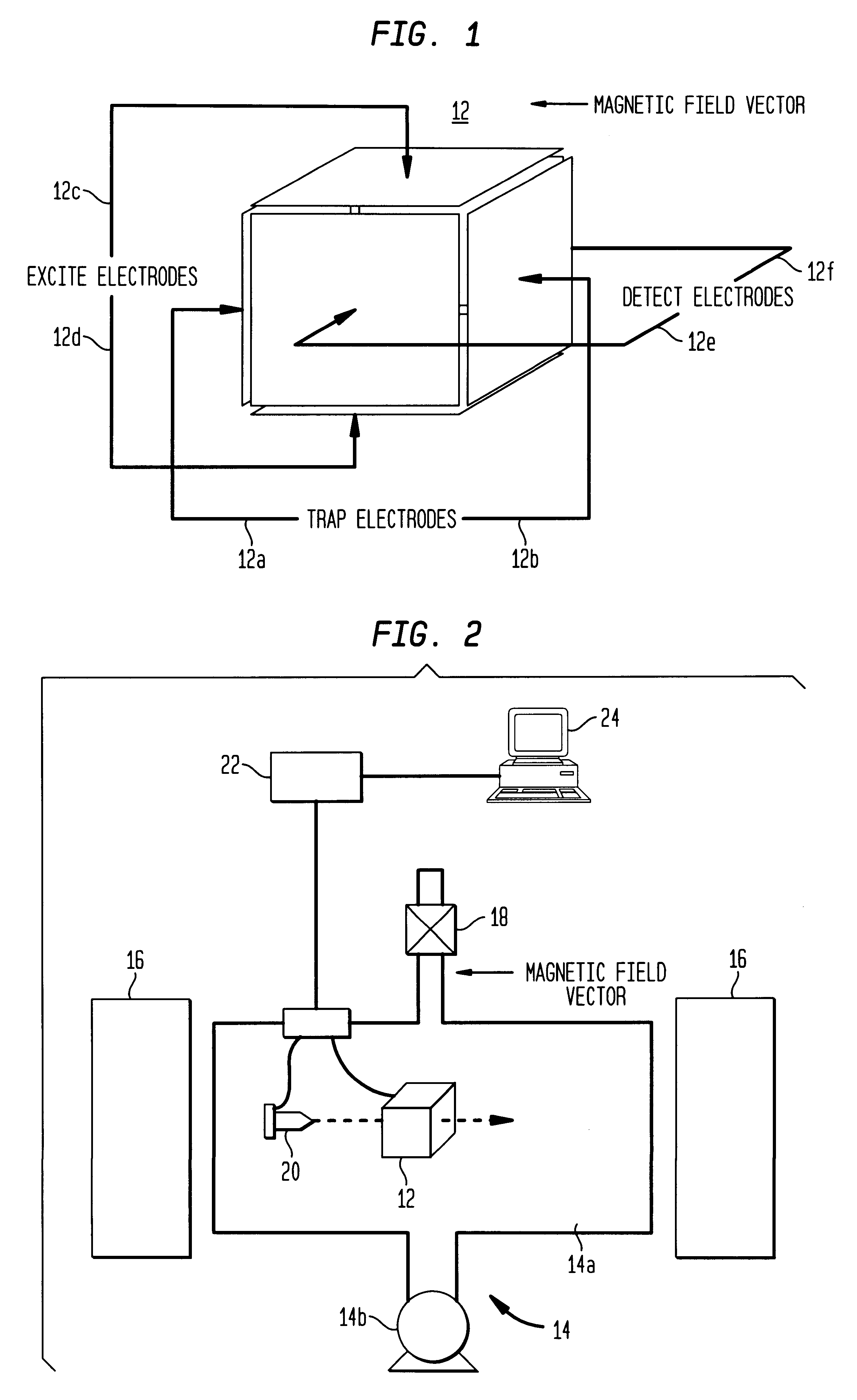
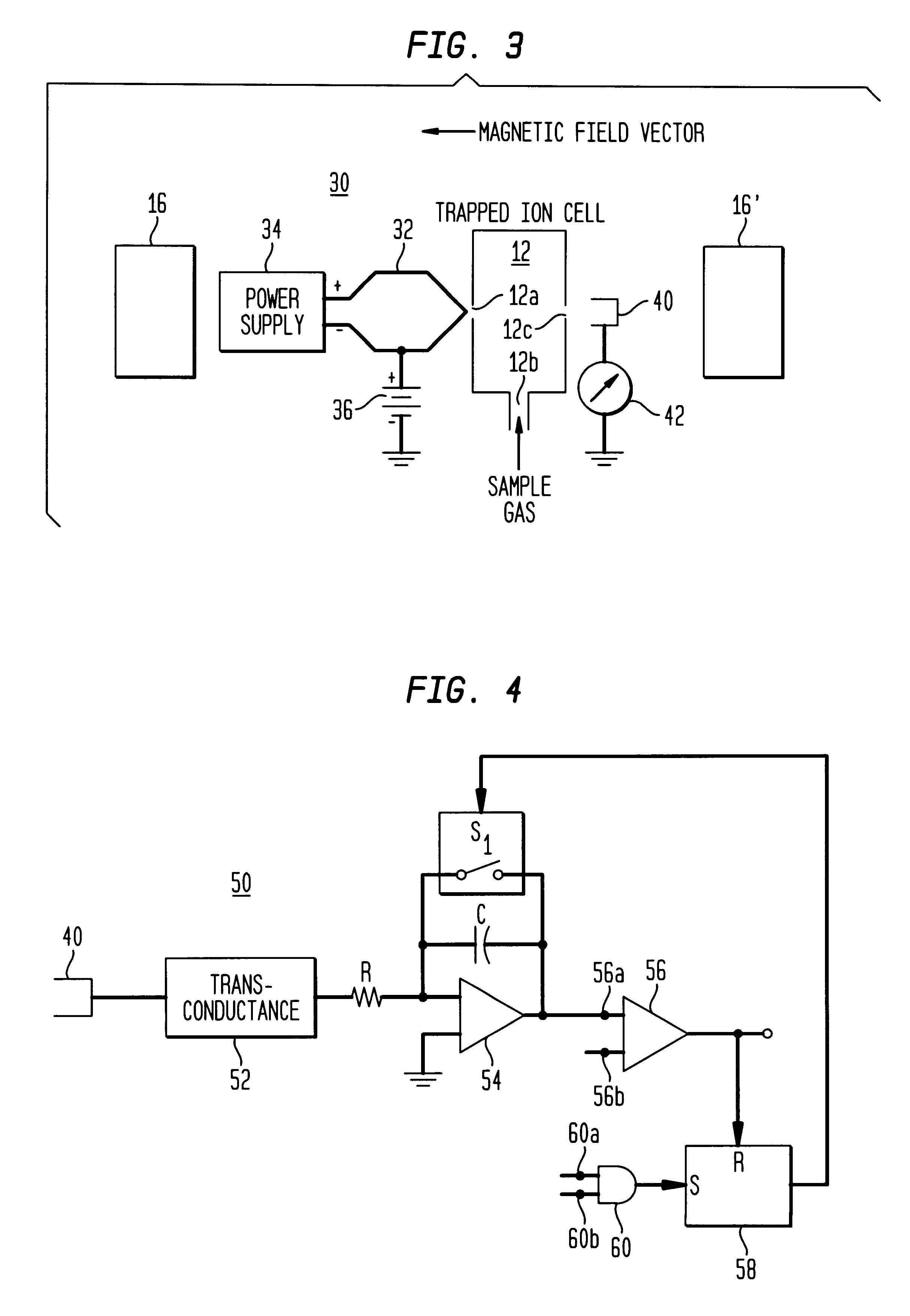
Programmed electron flux
InactiveUS6255648B1Spectrometer circuit arrangementsStability-of-path spectrometersElectron fluxIonization
A quantity of electrons that will be used in the ionization event in an FTICR MS is preprogrammed. When the number of electrons produced reaches that number, the electron beam is turned off. This approach assures that the same number of electrons are used for every measurement and eliminates the variations due to fundamental characteristics of the electron sourcere and the variations in temperature due to changing ambient conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Metabolic uncoupling therapy
InactiveUS20070160590A1Maximize synergyMinimizing undesired side effectHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideMedicineHigh energy
A combination of chemical agents reduces reductive stress by limiting the accumulation of high-energy electrons potentially available to the electron transport chain. A method of metabolic uncoupling therapy comprises: analyzing a specific physiologic process involving reductive stress; identifying a plurality of MUT agents that modulate metabolic pathways by influencing electron flux; and formulating a combination of MUT agents that limits the accumulation of high-energy electrons potentially available to the electron transport chain.
Owner:MCCLEARY EDWARD LARRY
Direct Current Superposition Freeze
ActiveUS20150160557A1Easy to operateReducing sidePhotomechanical exposure apparatusPhotosensitive material processingResistCross-link
Systems and methods include improved techniques for patterning substrates, including improvements to double patterning techniques. Direct current superposition plasma processing is combined with photolithographic patterning techniques. An electron flux or ballistic electron beam from a plasma processing system can induce cross linking in a given photoresist, which alters the photoresist to be resistant to subsequent light exposure and / or developer treatments. Plasma processing is also used to add a protective layer of oxide on exposed surfaces of a first relief pattern, thereby protecting the photoresist from a developing acid. By protecting an initial photoresist relief pattern from developing acid, a second pattern can be applied on and / or between the first photoresist relief pattern thereby doubling an initial pattern or otherwise increasing pattern density. This combined pattern can then be used for subsequent microfabrication such as transferring the combined pattern into one or more underlying layers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
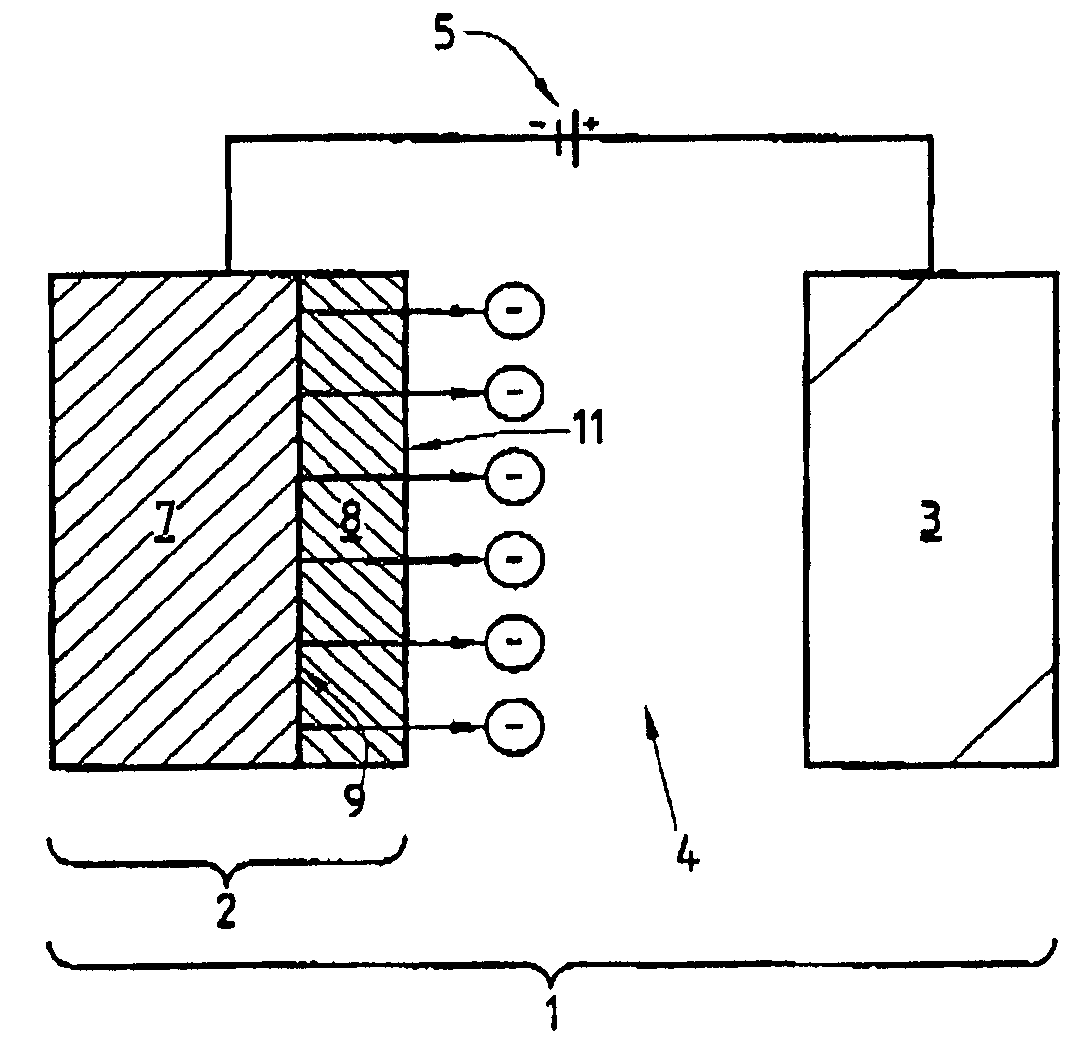
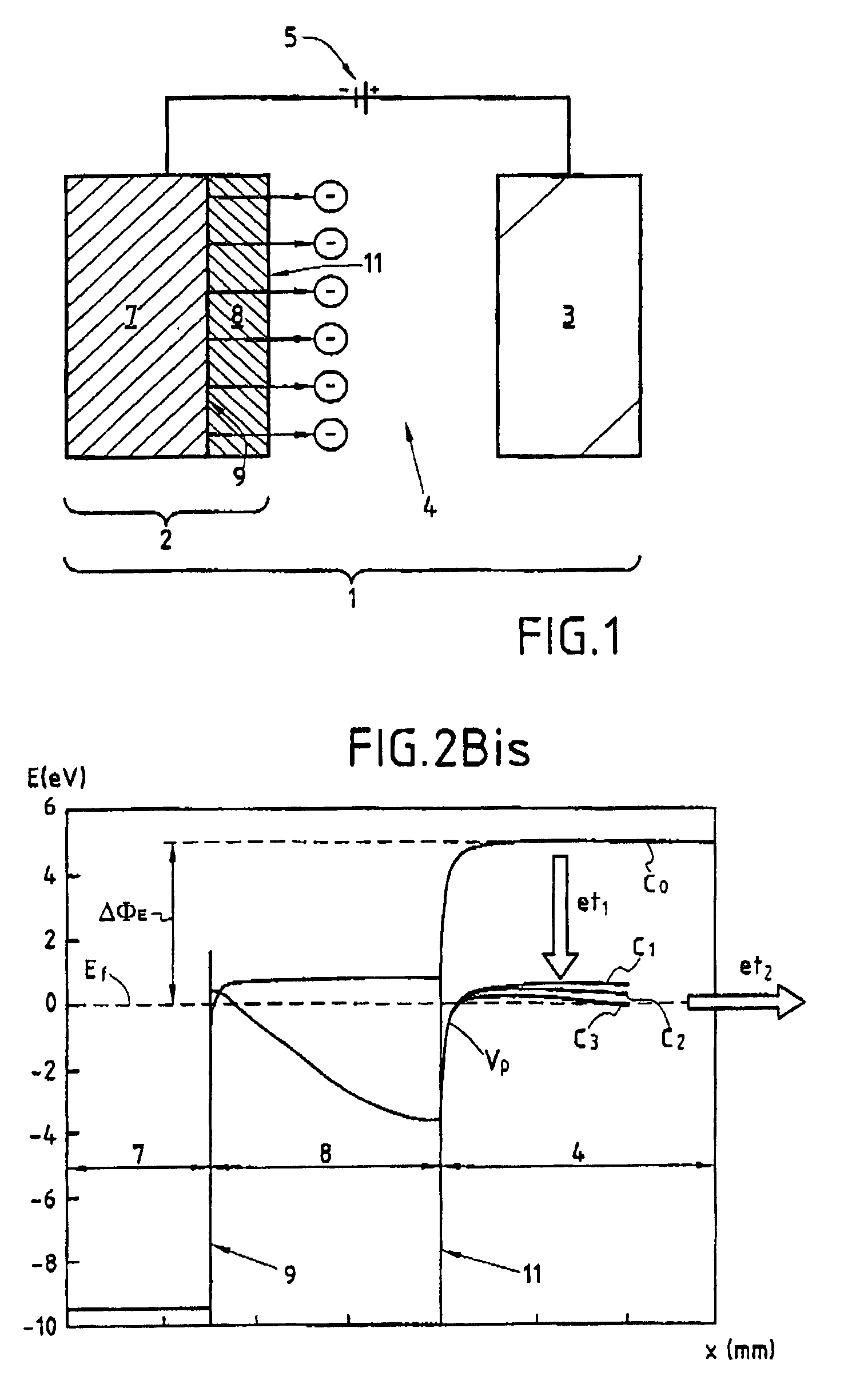
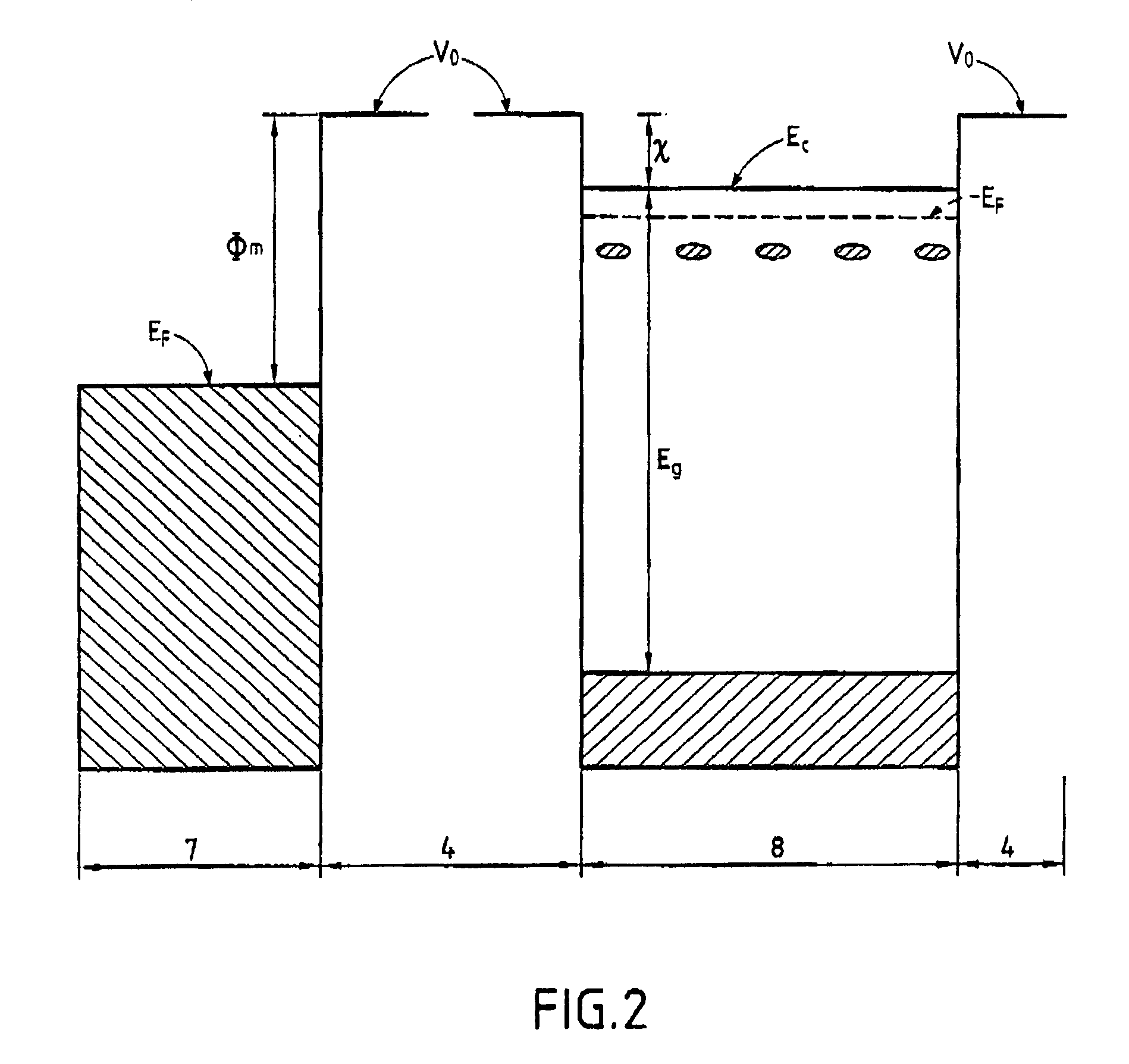
Method and device for extraction of electrons in a vacuum and emission cathodes for said device
InactiveUS7057333B1Discharge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectron fluxFermi level
The method of the invention for extracting electrons in a vacuum consists in:making a cathode presenting at least one junction (9) between a metal (7) acting as an electron reservoir and an n-type semiconductor (8) possessing a surface potential barrier with a height of a few tenths of an electron volt, and presenting thickness lying in the range 1 nm to 20 nm;injecting electrons through the metal / semiconductor junction (9) to create a space charge in the semiconductor (8) sufficient to lower the surface potential barrier of the semiconductor to a value that is less than or equal to 1 eV relative to the Fermi level of the metal (7); andusing the bias source creating an electric field in the vacuum to control the height of the surface potential barrier (Vp) of the n-type semiconductor in order to control the emission of the electron flux towards the anode.
Owner:UNIV CLAUDE BERNARD LYON 1
Plasma processing system and method
InactiveCN1397151AGood effectElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsElectron flux
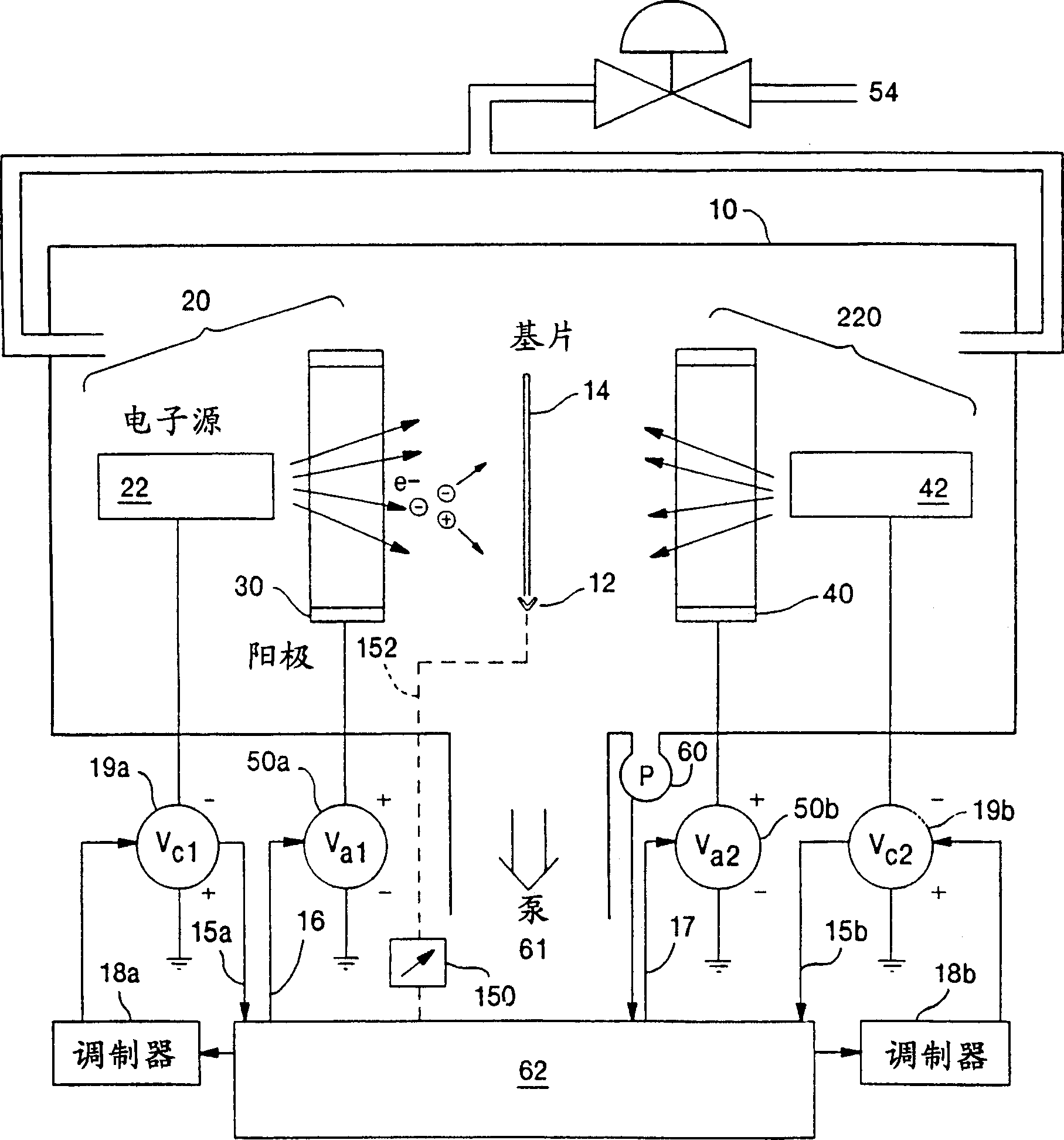
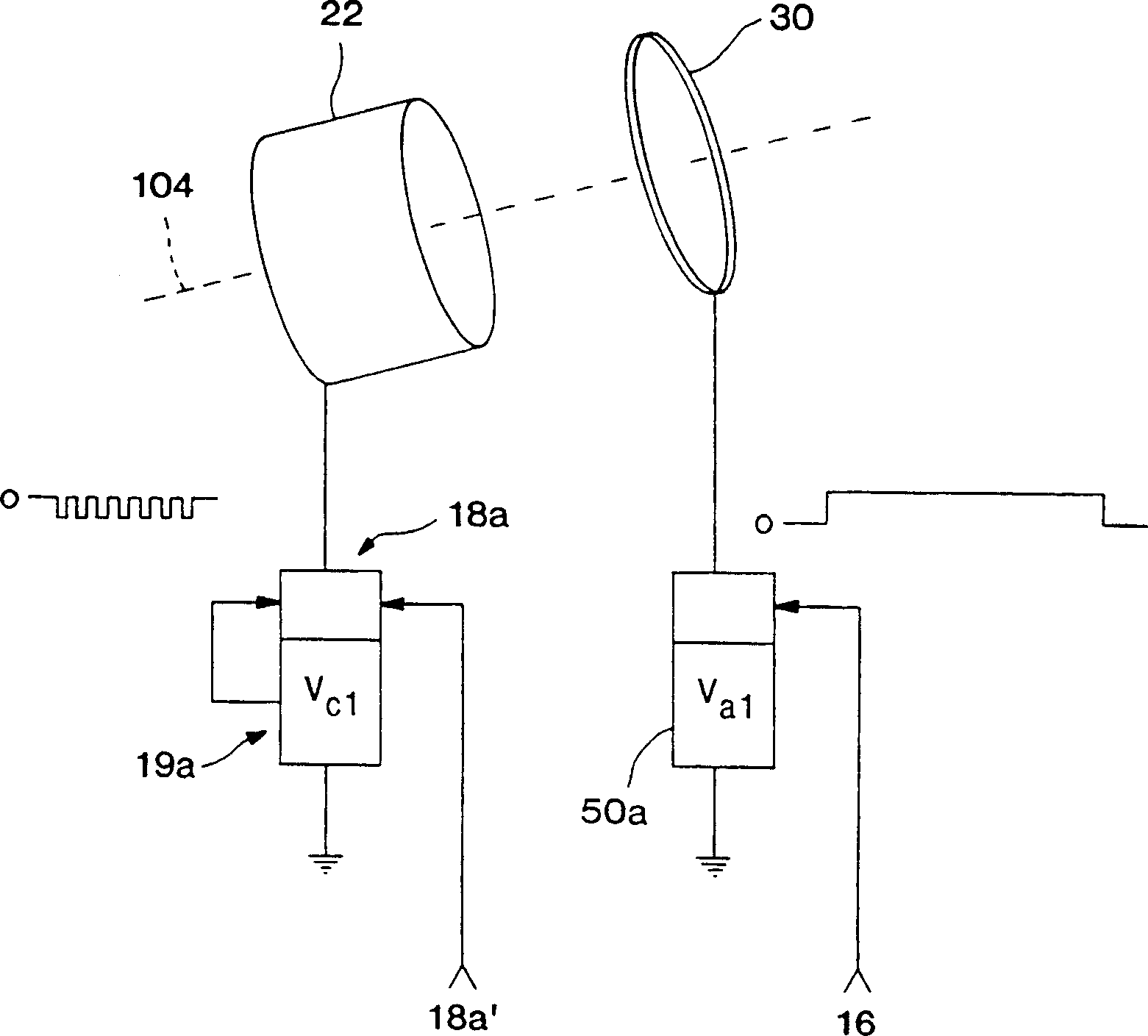
A substrate processing system includes a processing chamber (10), an electrically floating substrate holder (12) positioned in the chamber, a gas source (54) for supplying a process gas to the chamber, at least one ion source (20) located in the chamber, and a power source (19b) for energizing the ion source by positively biasing the anode (40) and negatively biasing the cathode (22) in a train of pulses of selectably variable duty cycle and magnitude to maintain a selected time averaged current, the bias in each instance being relative to the chamber. The ion source (20) ionizes the process gas producing ions for processing a substrate disposed on the floating substrate holder (12) in the chamber. The floating substrate is biased in accord with the net charge thereon as controlled by the energetic electron flux. One embodiment includes two such ion sources (22, 42). In this case, the power source energizes the first and second anodes (30, 40) and the cathodes (22, 42) in a time multiplexed manner, such that only one of the first or second ion sources is energized at any time and interactions between ion sources are eliminated.
Owner:INTEVAC
Plasma Generator With at Least One Non-Metallic Component
ActiveUS20160086759A1Little and no contaminantLower Level RequirementsVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingThermionic emissionMetallic materials
A plasma generator for an ion implanter is provided. The plasma generator includes an ionization chamber for forming a plasma that is adapted to generate a plurality of ions and a plurality of electrons. An interior surface of the ionization chamber is exposed to the plasma and constructed from a first non-metallic material. The plasma generator also includes a thermionic emitter including at least one surface exposed to the plasma. The thermionic emitter is constructed from a second non-metallic material. The plasma generator further includes an exit aperture for extracting at least one of the plurality of ions or the plurality of electrons from the ionization chamber to form at least one of an ion beam or an electron flux. The ion beam or the electron flux comprises substantially no metal. The first and second non-metallic materials can be the same or different from each other.
Owner:NISSIN ION EQUIP CO LTD
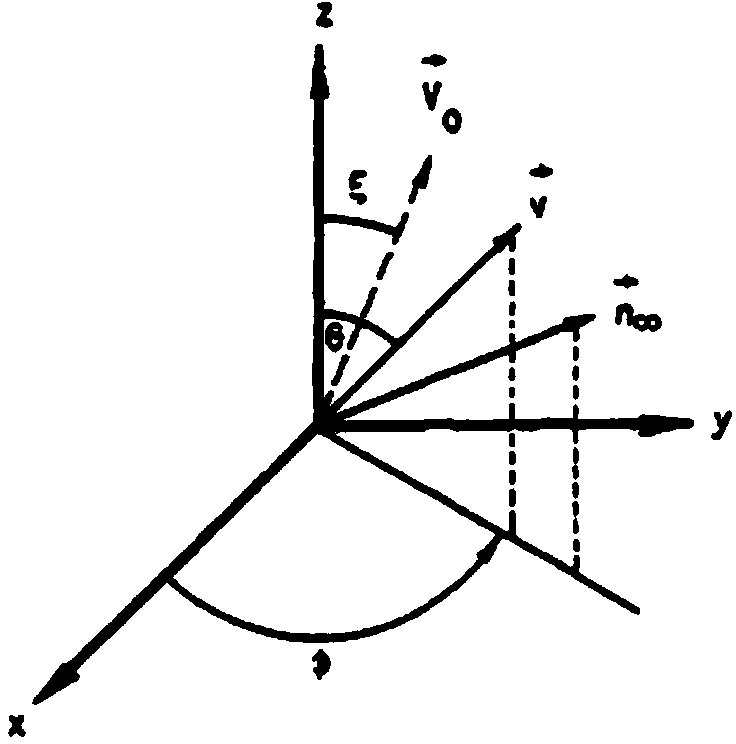
Charging effect simulation method at tail region of spacecraft
ActiveCN104239620AAchieve fitIn line with the actual charging processSpecial data processing applicationsIon distributionSecondary electrons
The invention provides a charging effect simulation method at a tail region of a spacecraft. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a fitting expression of a polar region precipitated electron spectrum, which is the relation for the variation of aurora electron flux phi with energy E, wherein the relation is expressed through superposition of power law distribution phip (E), maxwellian distribution phim (E) and Gaussian distribution phiG (E), and fitting the polar region precipitated electron spectrum; establishing an ion distribution characteristic spectrum in a background plasma environment; testing secondary electron emission spectrums of different surface materials of the spacecraft; performing process simulation of the charging effect at the tail region of the spacecraft by using a Particle-In-Cell (PIC) method based on the three-category spectrum. The method has the advantages that the simulation process is clear, the simulation result conforms to the actual monitored charging situation and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
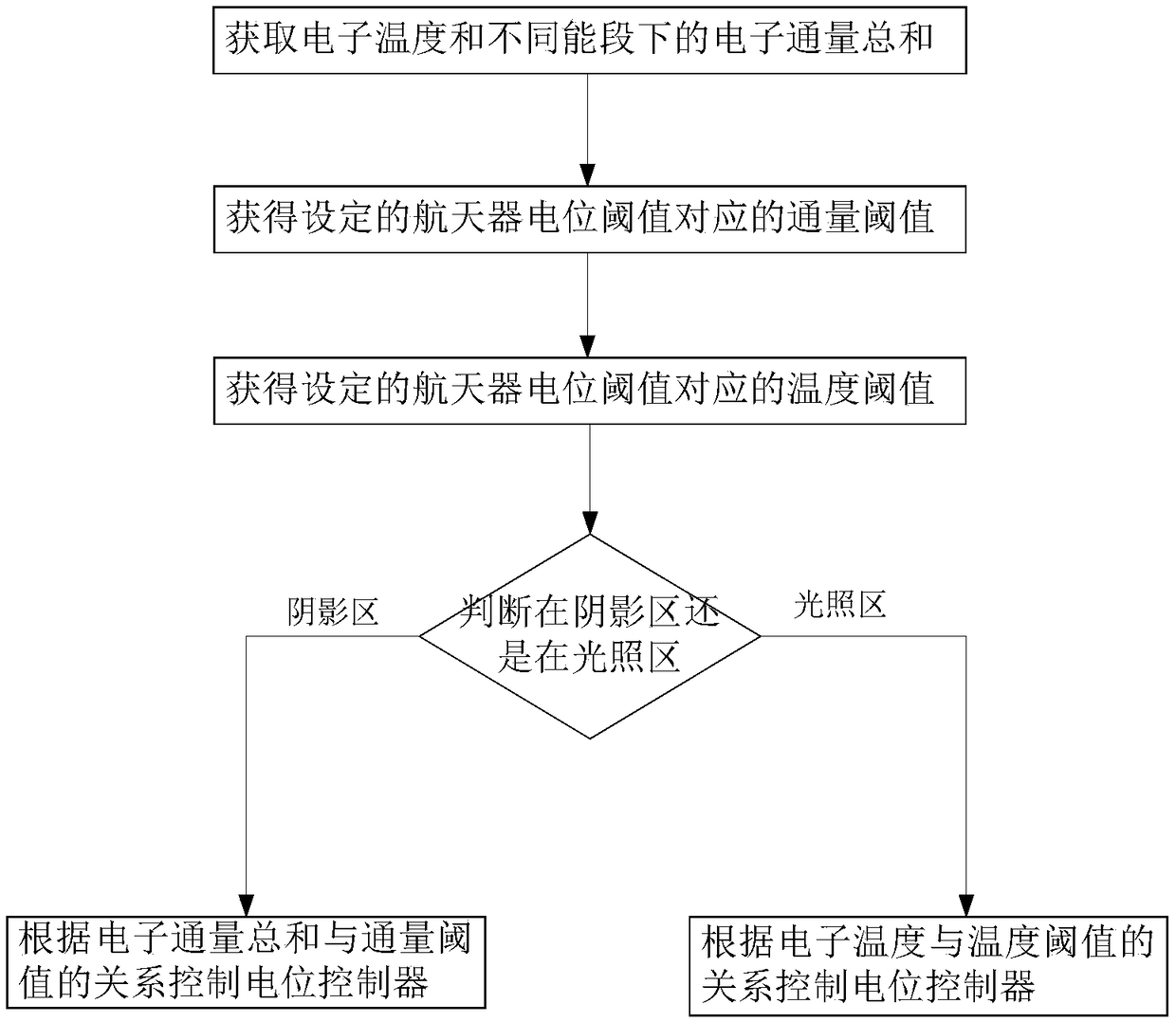
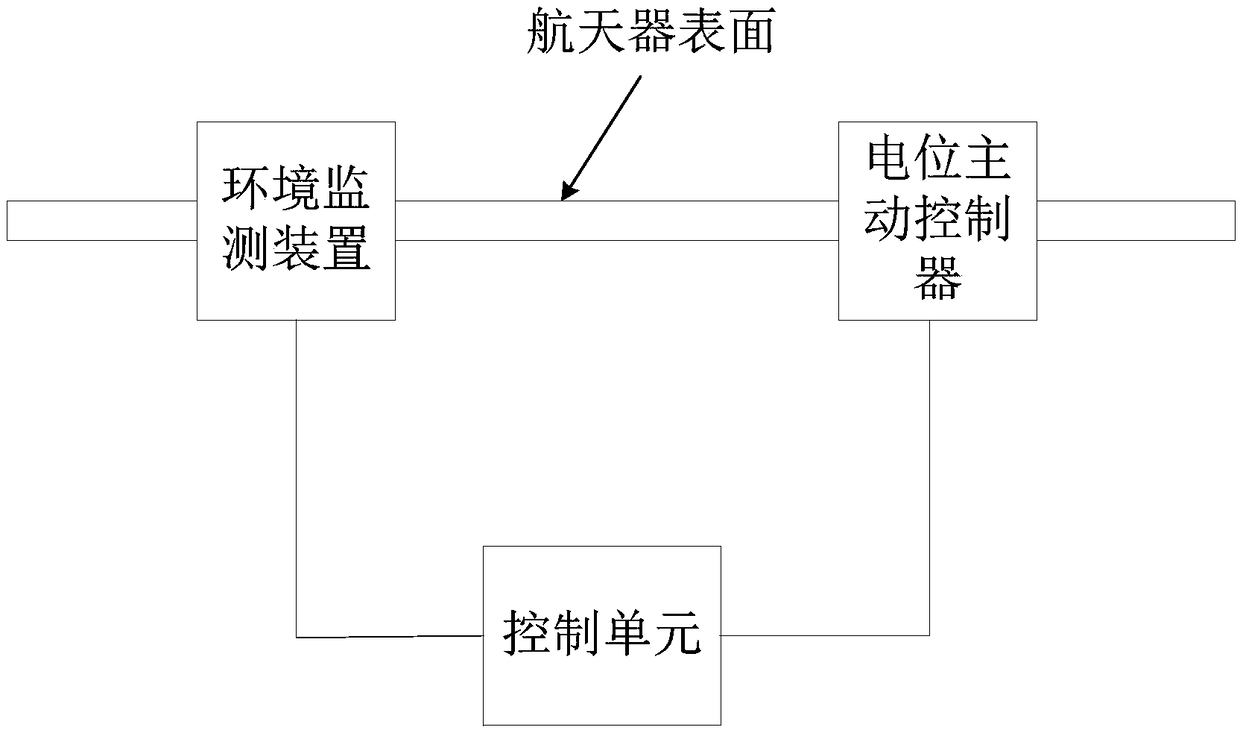
Method for controlling electrification effect on surface of spacecraft in orbit
ActiveCN109319172ATo achieve the purpose of surface potential controlQuick responseCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic radiation protectionElectron temperatureTime control
The invention discloses a method for controlling an electrification effect on the surface of a spacecraft in orbit. The method for controlling the electrification effect on the surface of the spacecraft in orbit comprises the steps that firstly, a flux threshold value and a temperature threshold value are obtained based on the relationship between an electron flux and a spacecraft surface potential and the relationship between a plasma temperature and the spacecraft surface potential and according to a potential threshold value borne by the spacecraft surface; and in real-time control, the electron flux and an electron temperature are monitored in real time so that a potential active controller switch can be controlled to achieve the purpose of surface potential control. Since the electronflux and the plasma temperature are observed, whether the spacecraft surface can reach the potential threshold value or not is predicted and the surface potential control is carried out instead of carrying out the surface potential control after electrons and plasmas accumulate on the spacecraft surface to reach the potential threshold value, so that the response speed can be improved, and stability and accuracy of active control over spacecraft surface electrification can be improved.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
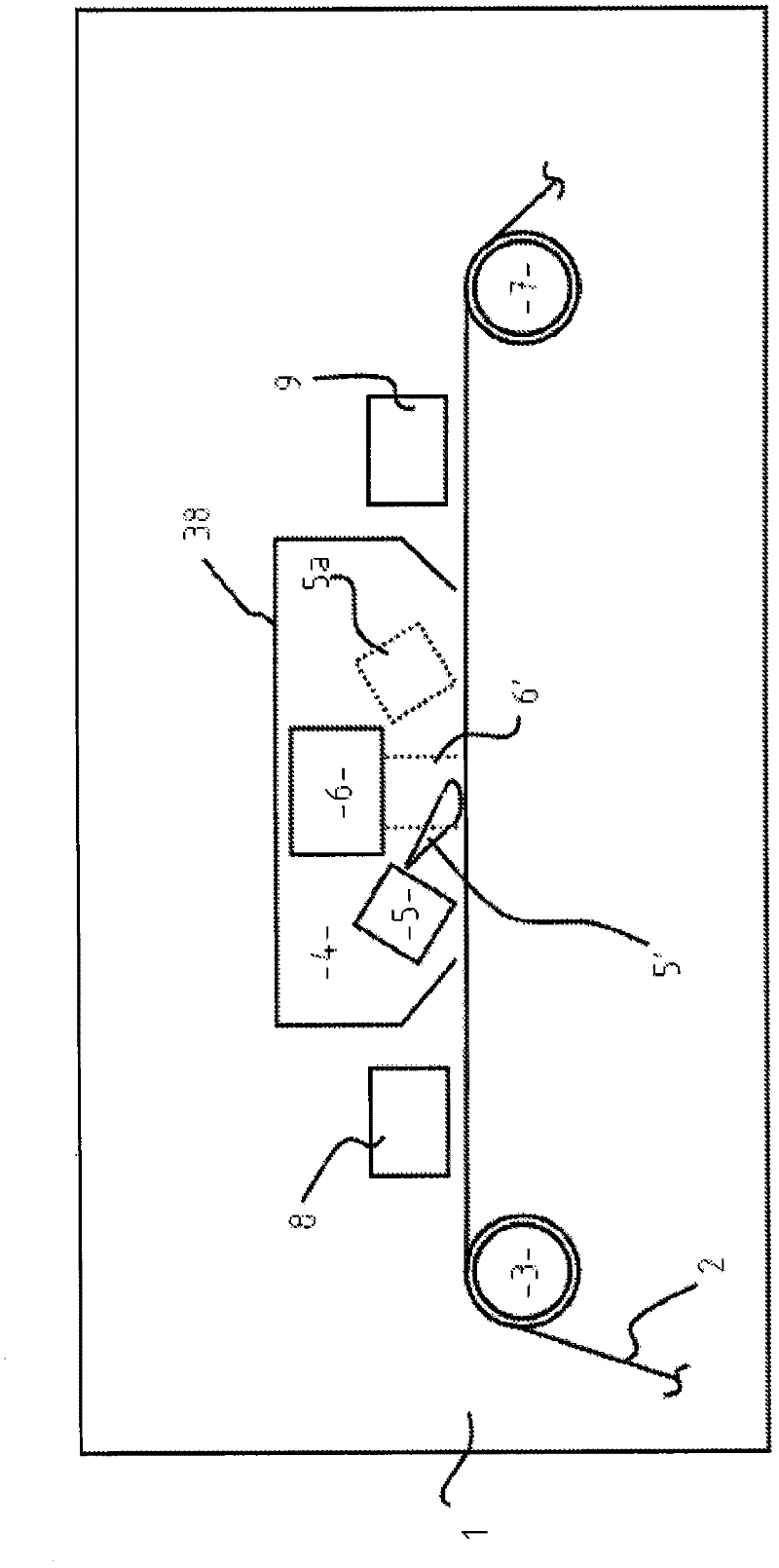
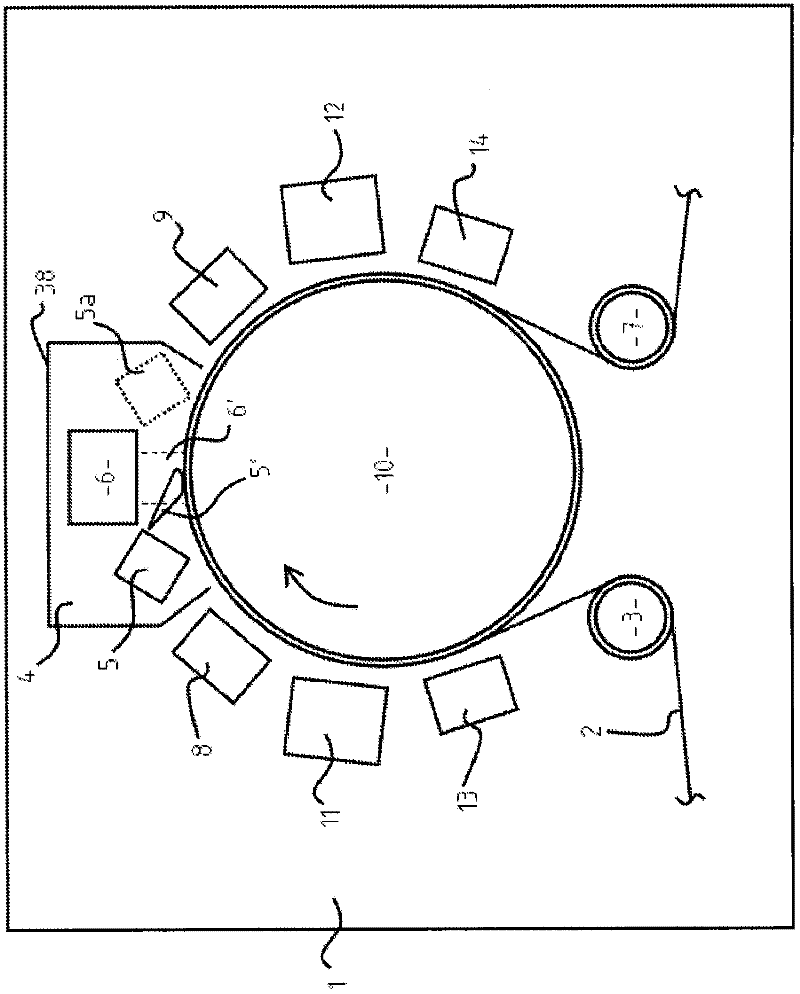
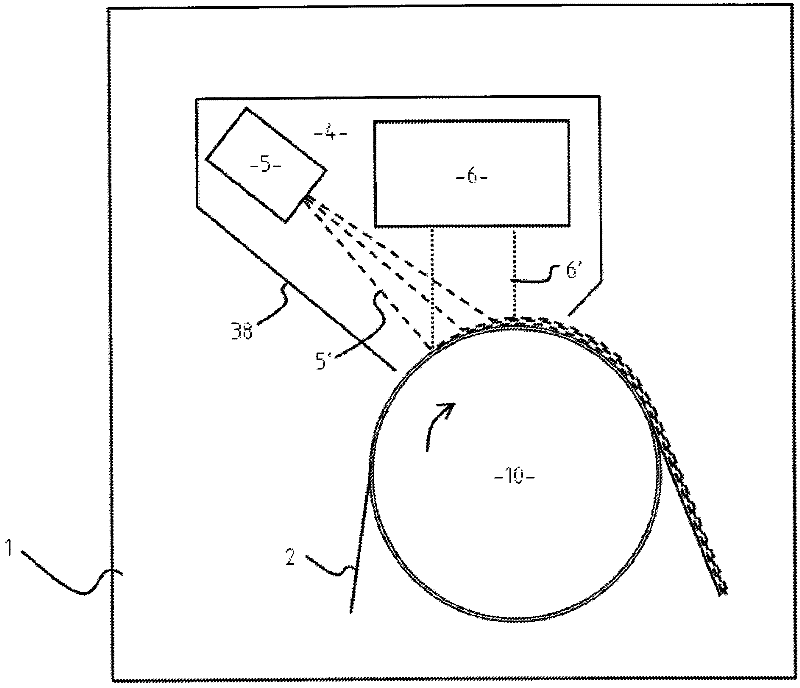
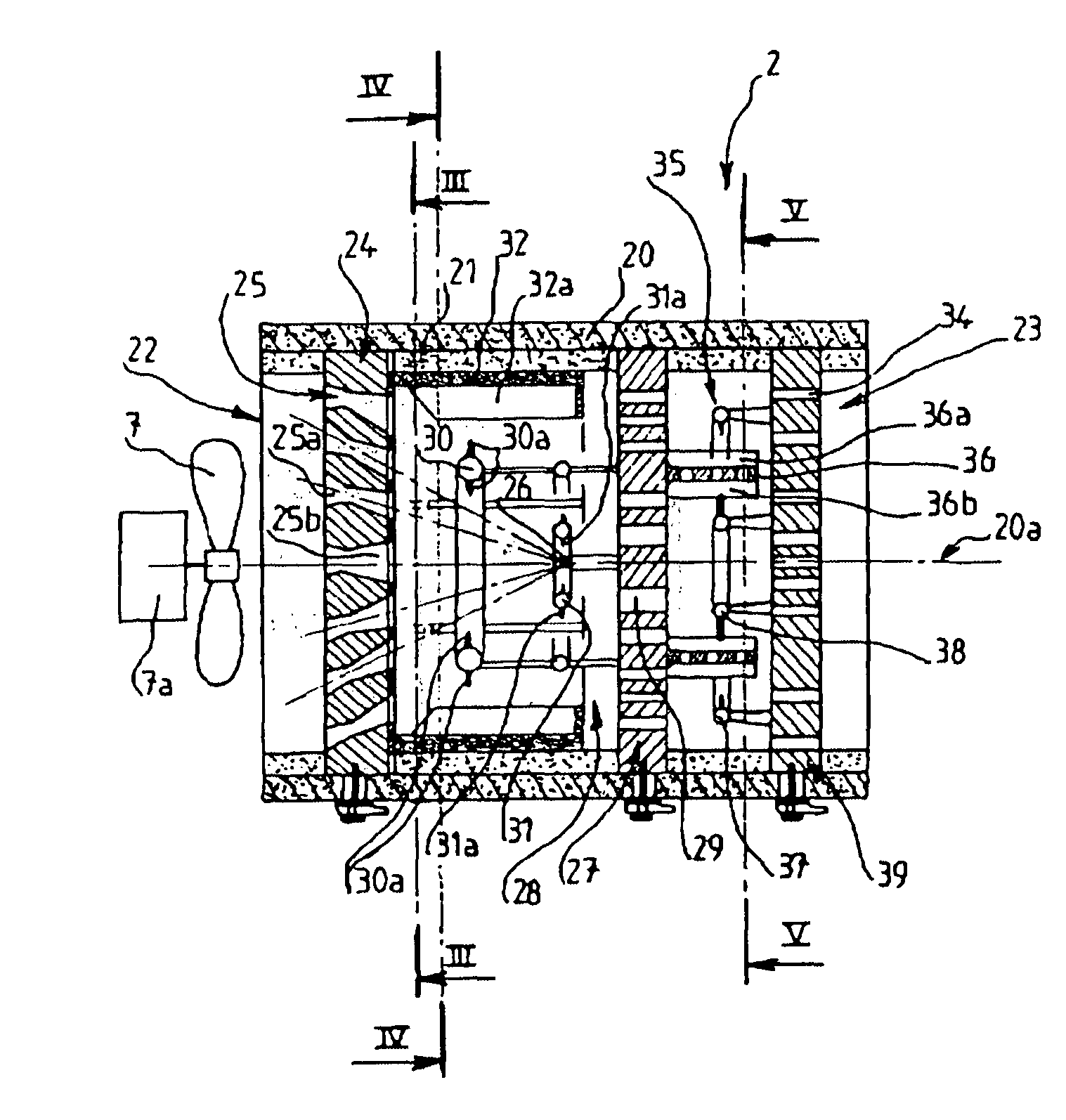
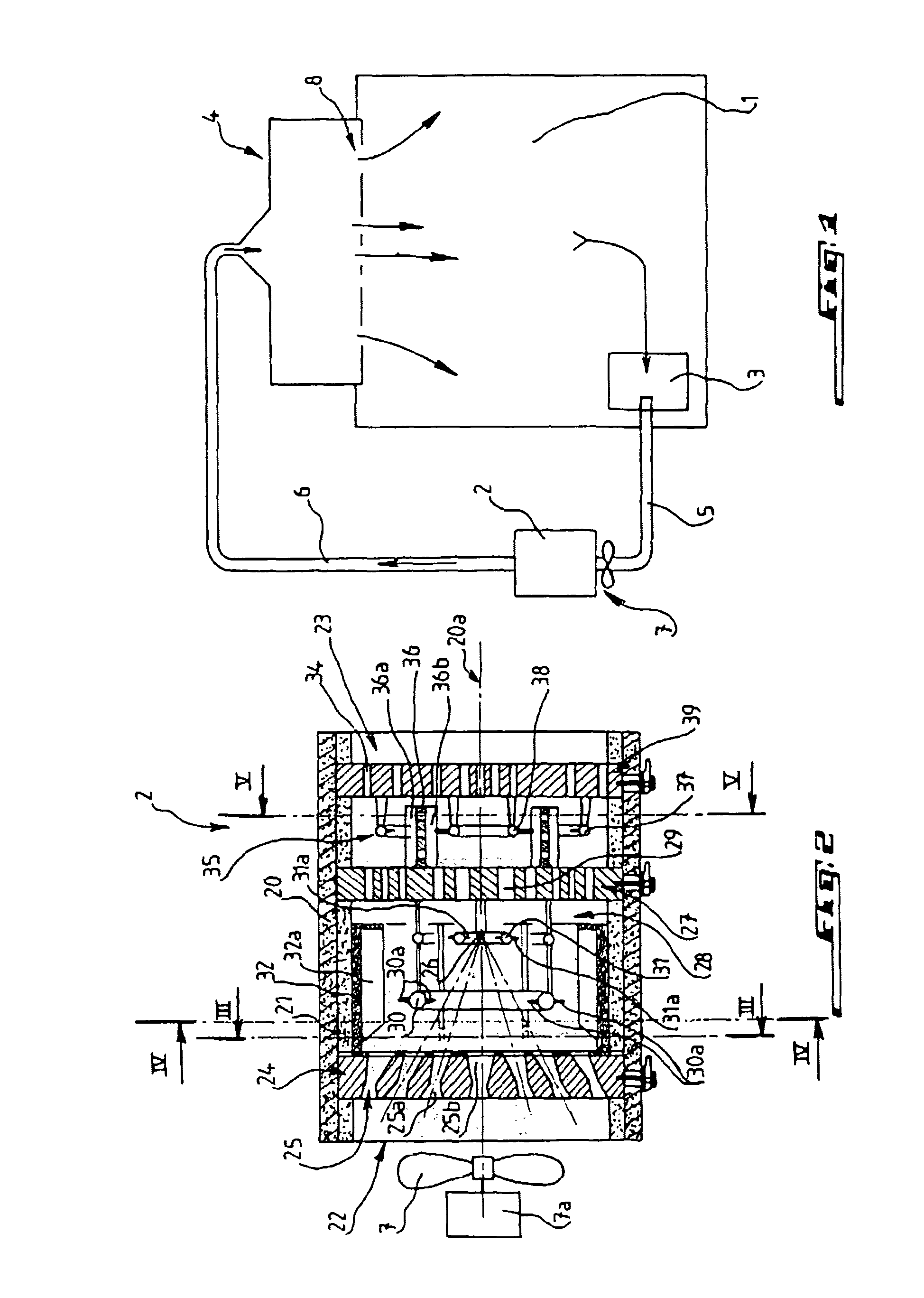
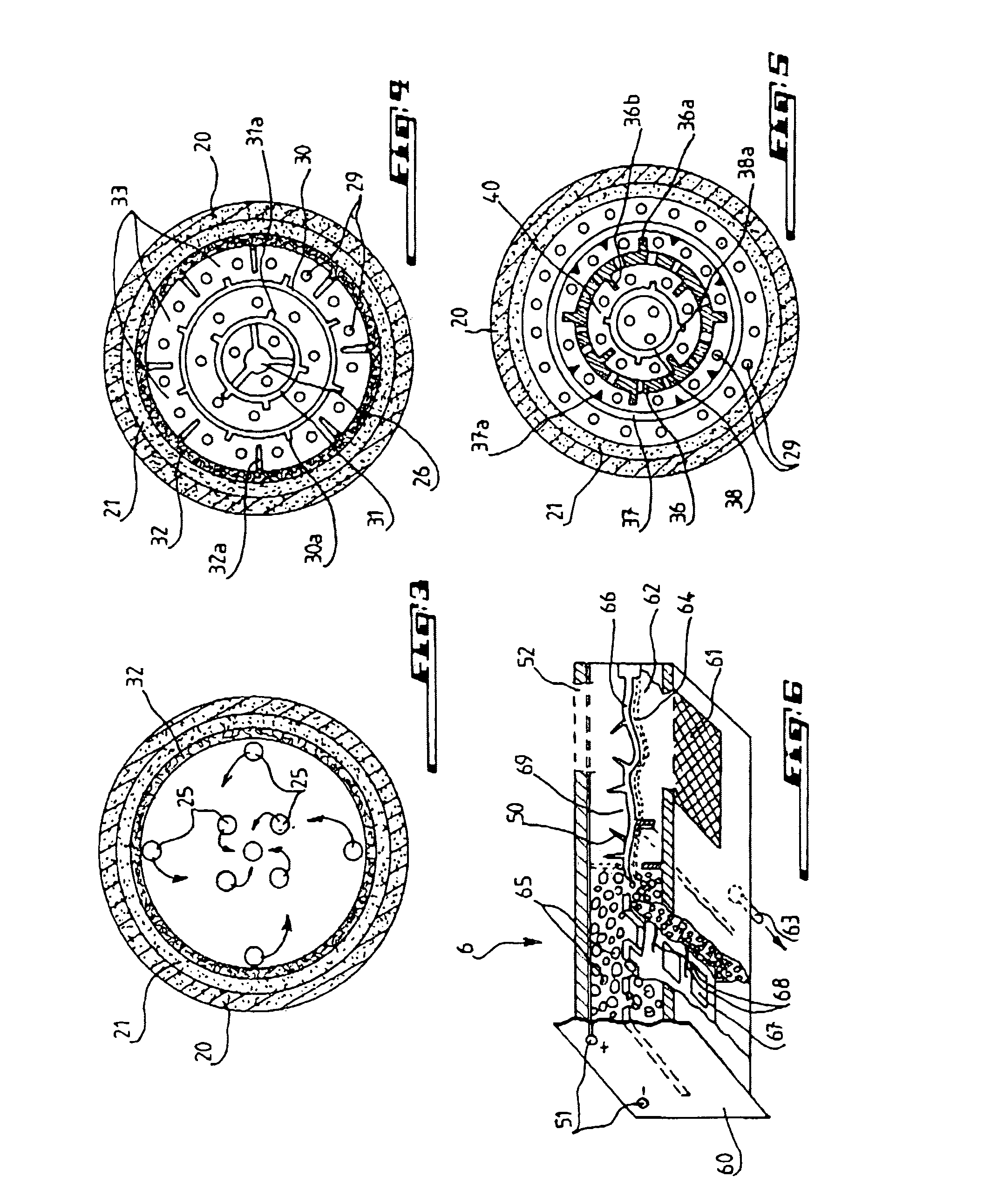
Radiation-cured coatings
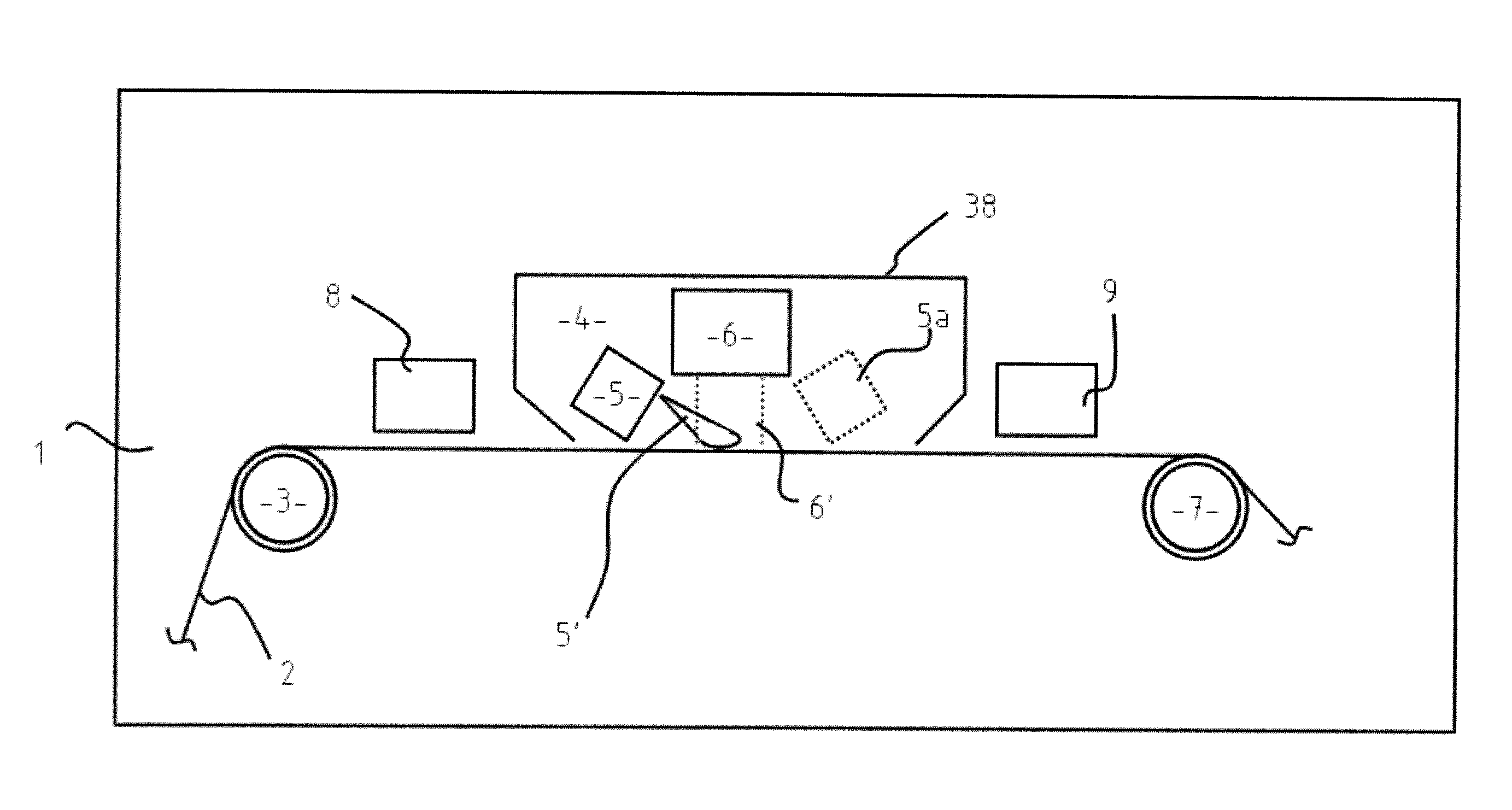
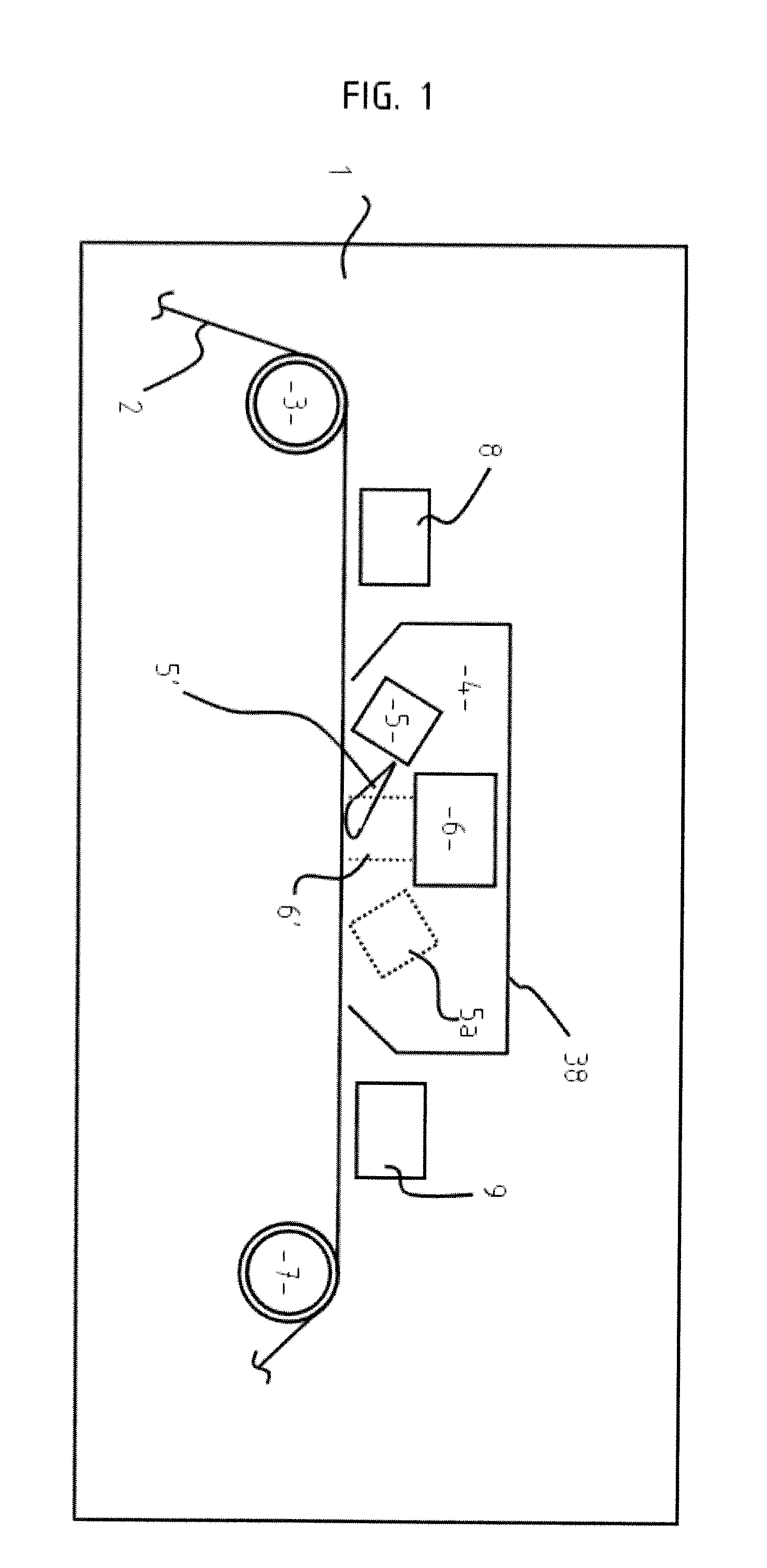
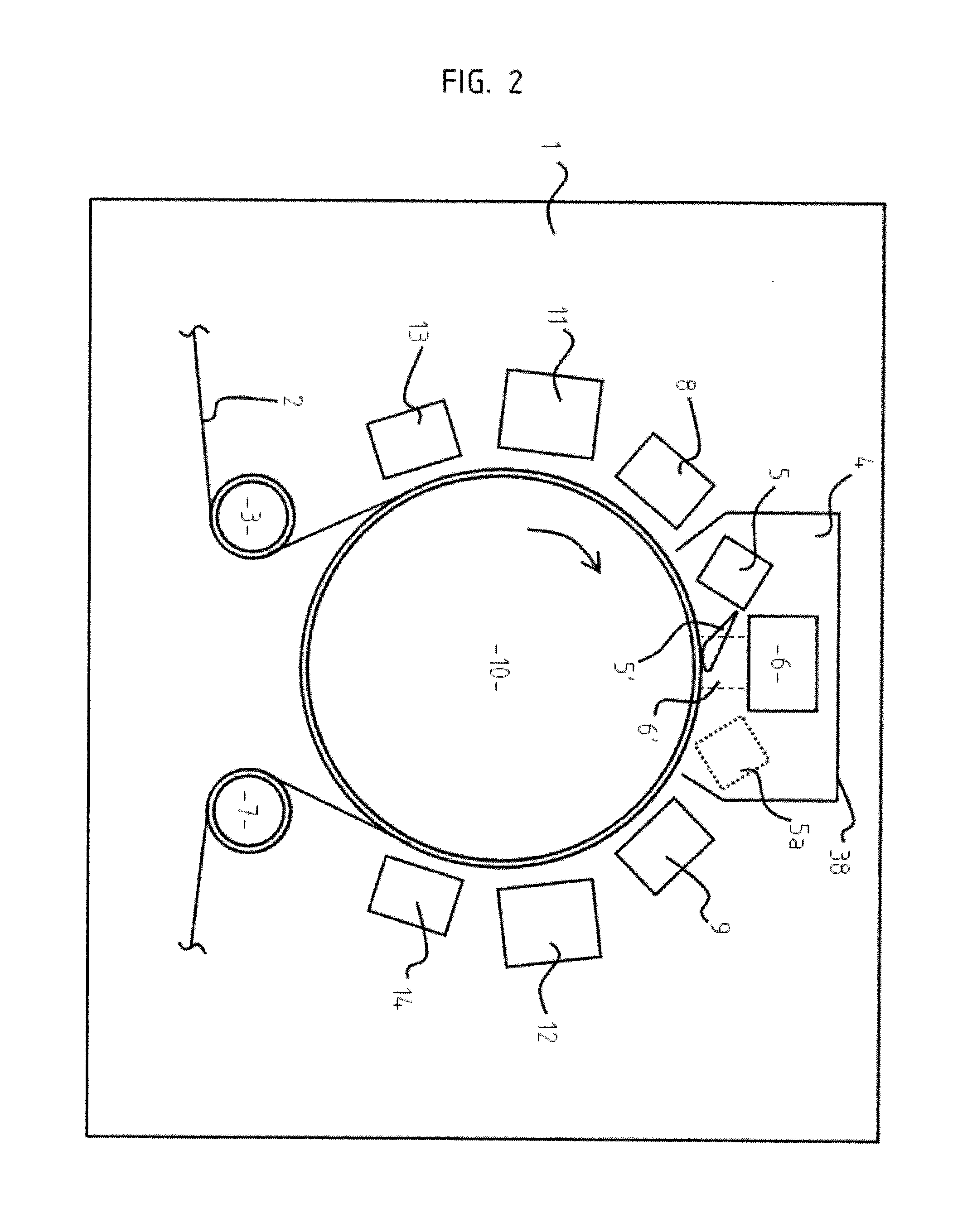
A process for coating a substrate comprising condensing a radiation curable material on a substrate and curing it using an electron flux 6' with energy between 6.5eV and 300eV. The electron flux 6' is directed at the substrate (2) either simultaneously or sequentially with delivery of the curable material (5'). Curing is preferably initiated spatially and temporally concurrently with delivery of the material to the substrate. The electron flux is preferably generated using a low pressure gas plasma source with a driving voltage negative relative to the local voltage conditions. The low pressure gas plasma (6') is preferably magnetically enhanced and, for example, incorporates a magnetron.
Owner:凯姆梵克有限公司
Direct current superposition freeze
ActiveUS9760008B2Exemption stepsReducing sideSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCross-linkResist
Systems and methods include improved techniques for patterning substrates, including improvements to double patterning techniques. Direct current superposition plasma processing is combined with photolithographic patterning techniques. An electron flux or ballistic electron beam from a plasma processing system can induce cross linking in a given photoresist, which alters the photoresist to be resistant to subsequent light exposure and / or developer treatments. Plasma processing is also used to add a protective layer of oxide on exposed surfaces of a first relief pattern, thereby protecting the photoresist from a developing acid. By protecting an initial photoresist relief pattern from developing acid, a second pattern can be applied on and / or between the first photoresist relief pattern thereby doubling an initial pattern or otherwise increasing pattern density. This combined pattern can then be used for subsequent microfabrication such as transferring the combined pattern into one or more underlying layers.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Design method of DFIG-PSS controller based on virtual impedance
ActiveCN112751346AEnhance external anti-interference abilityVerify liftPower oscillations reduction/preventionWind energy generationControl theoryVirtual impedance
The invention provides a design method of a DFIG-PSS controller based on virtual impedance, and the method comprises the steps: constructing a power grid system containing a doubly-fed induction motor model, combining a power system stabilizer with virtual impedance, and then connecting the combined power system stabilizer and virtual impedance to a rotor side converter, obtaining the relation between the output voltage of the rotor side converter and the rotor current by adopting a stator flux linkage directional vector control technology; obtaining the relation between the stator current and the output power of the stator according to the relation among the stator voltage, the electron flux linkage and the electron current; then, according to the relationship between the output voltage of the rotor side converter and the rotor current and the relationship between the stator current and the output power of the stator, obtaining the relationship between the parameter of the power system stabilizer-virtual impedance and the output power of the stator; and finally, adjusting the output power of the stator by changing the parameters of the stabilizer-virtual impedance of the power system, thereby influencing the damping characteristic of the power grid system. The low-frequency oscillation characteristic of the wind power system can be improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Control system for electrostatic discharge mitigation
InactiveUS6867391B2Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic radiation protectionControl electronicsControl system
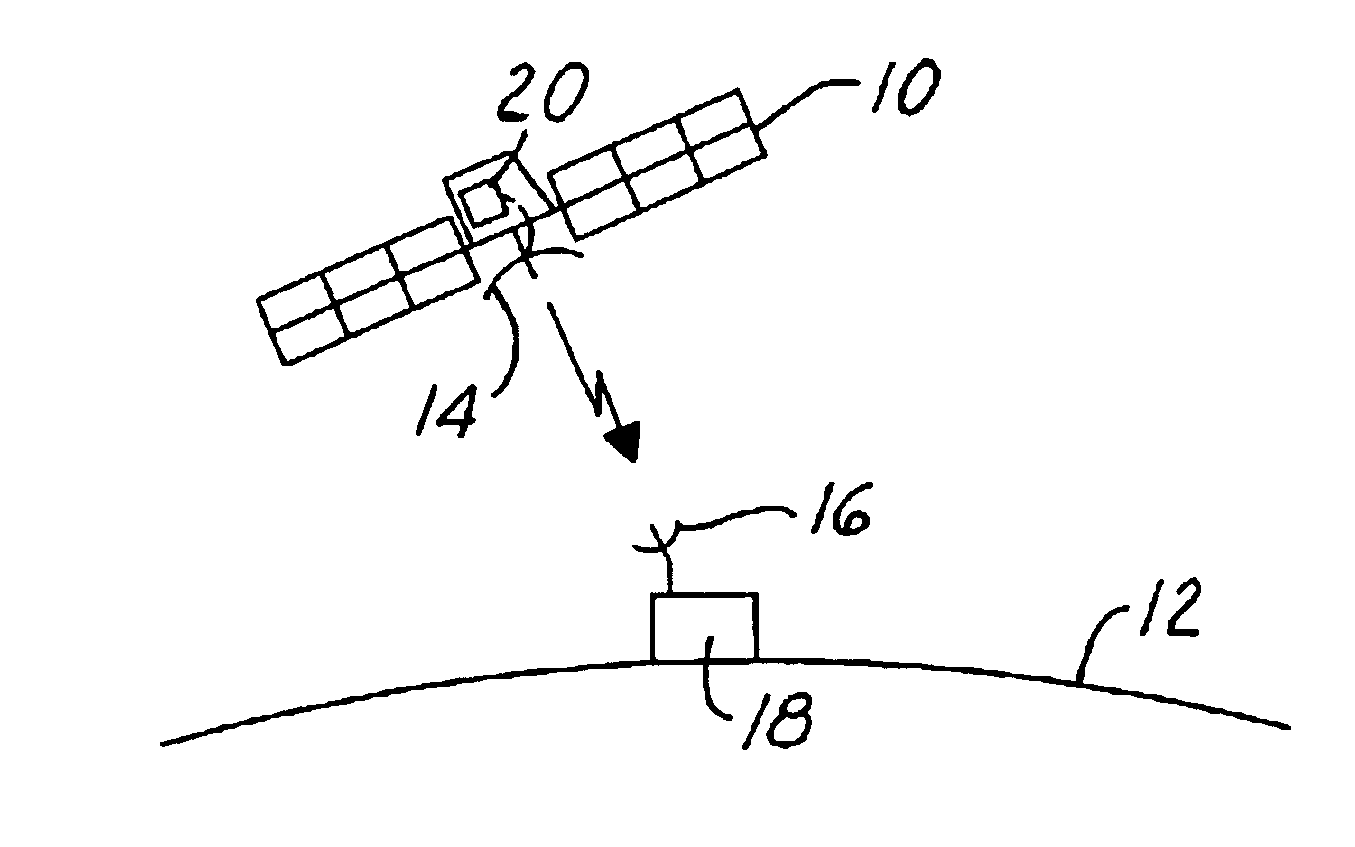
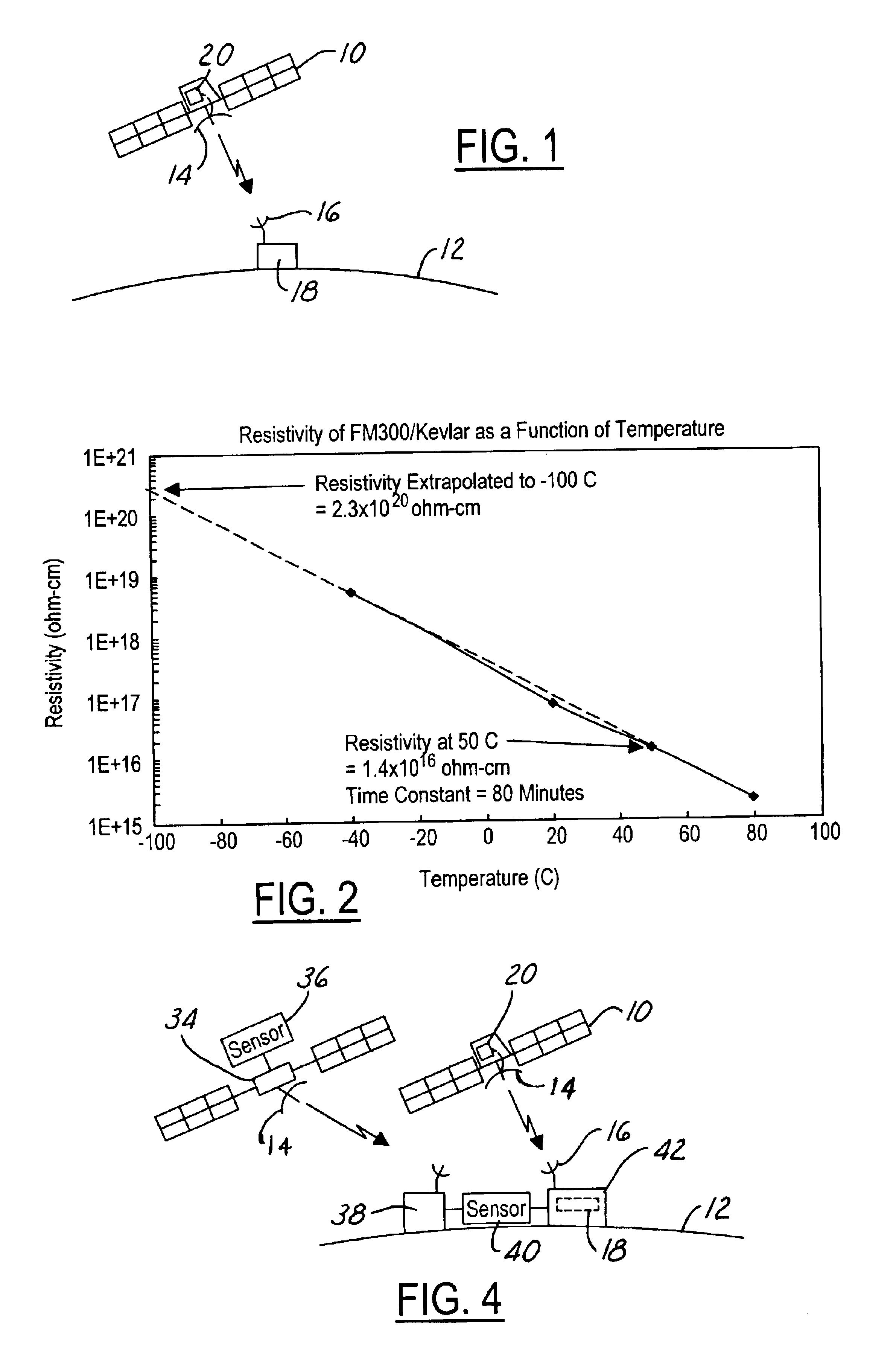
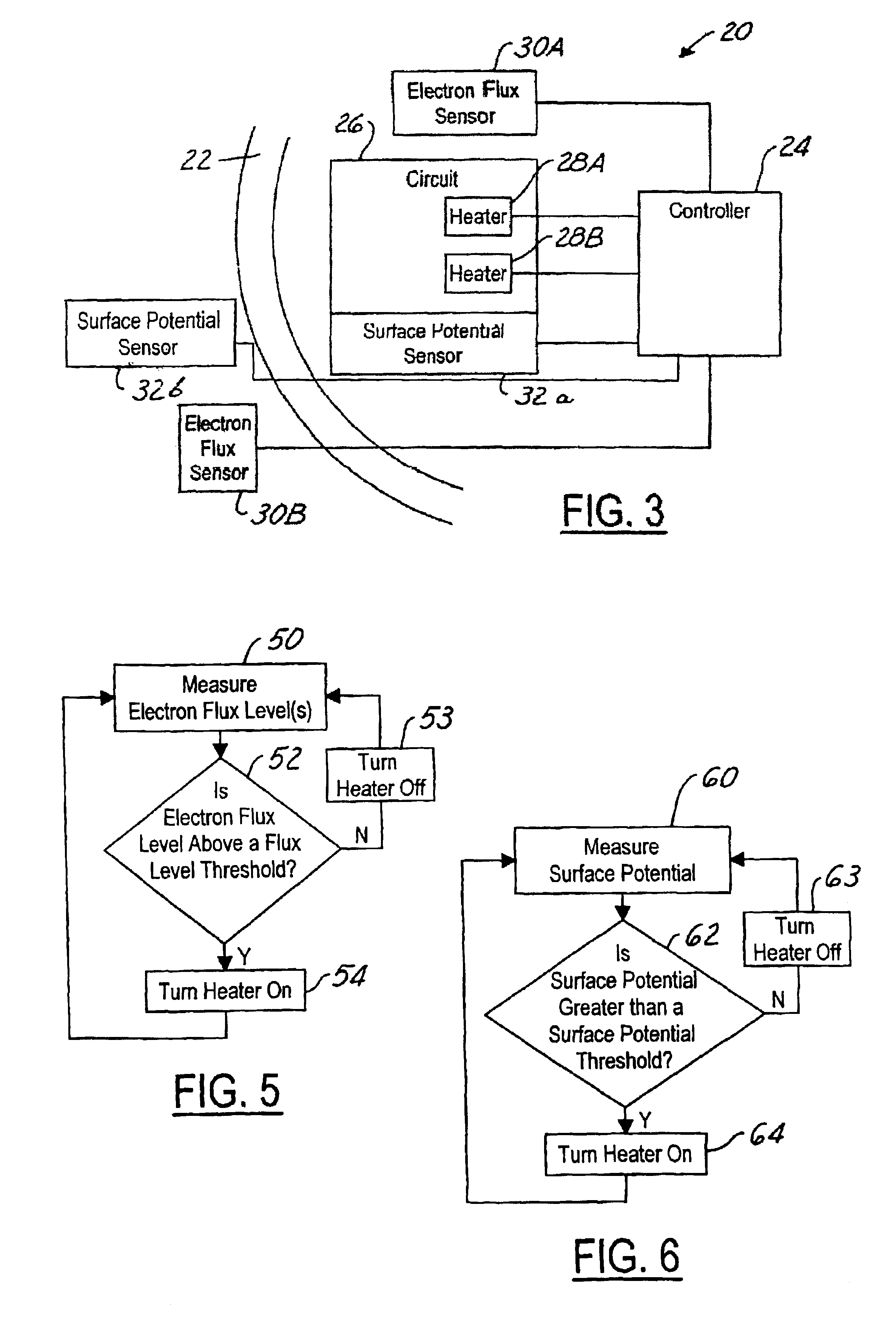
A control circuit (20) for controlling electrostatic discharge in an electric component includes a heater (28) that is thermally coupled to the component. A sensor (30) is used for sensing a sensed condition. A controller is coupled to the heater and the sensor. The controller (24) heats the component in response to the sensed condition. The sensor (30) may include an electron flux level near the component or a surface potential of the component itself.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
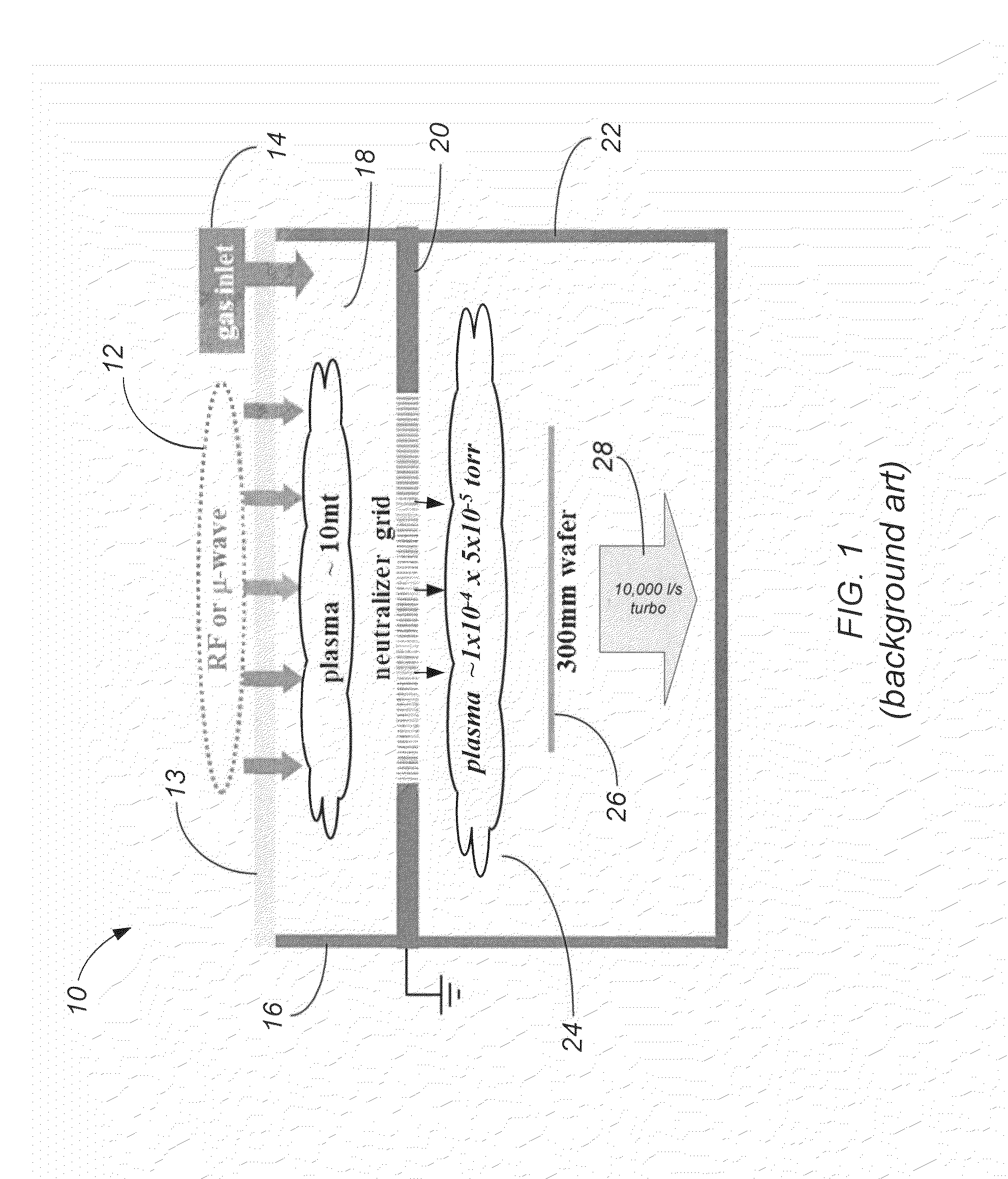
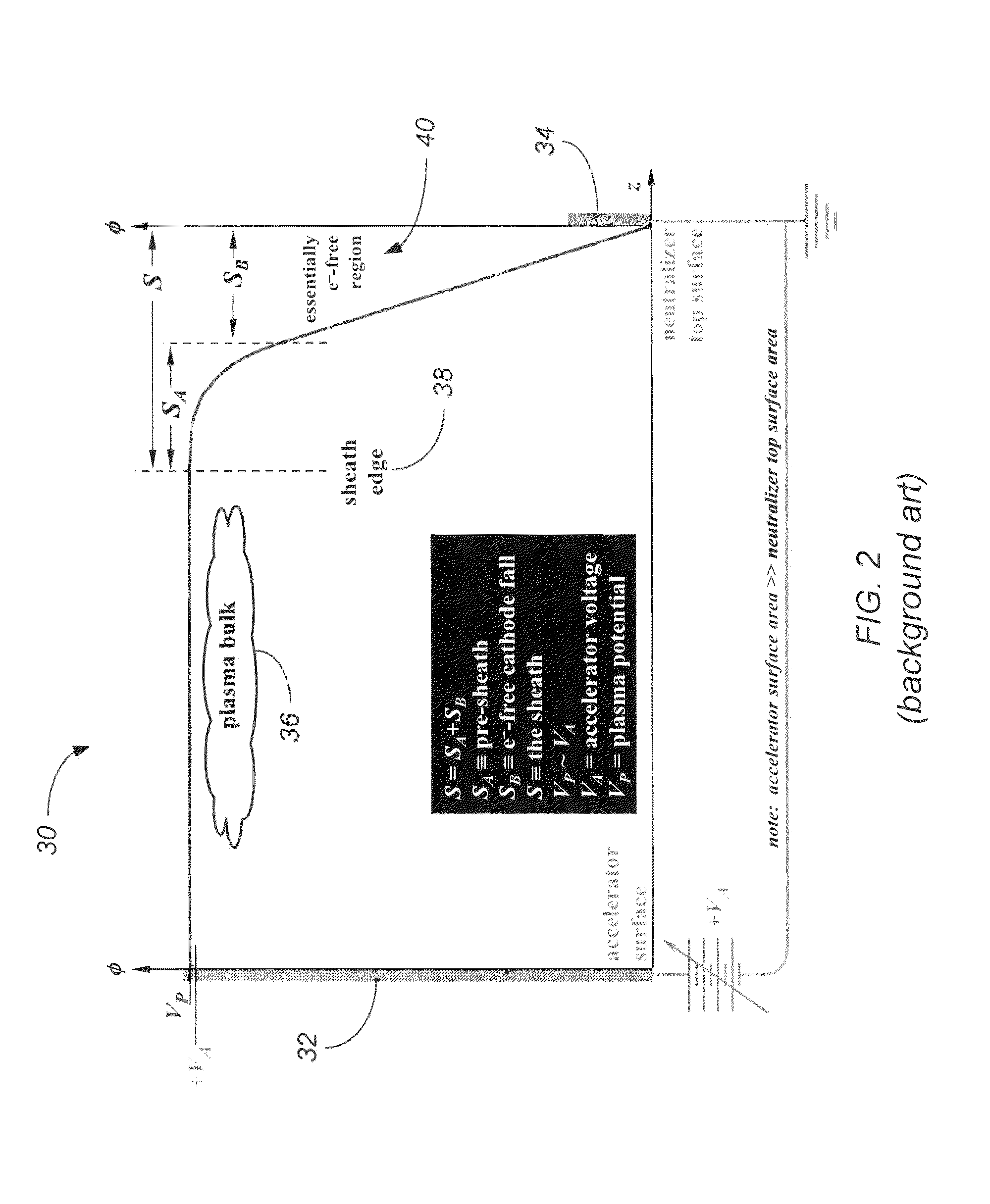
Method and apparatus for providing an anisotropic and mono-energetic neutral beam by non-ambipolar electron plasma
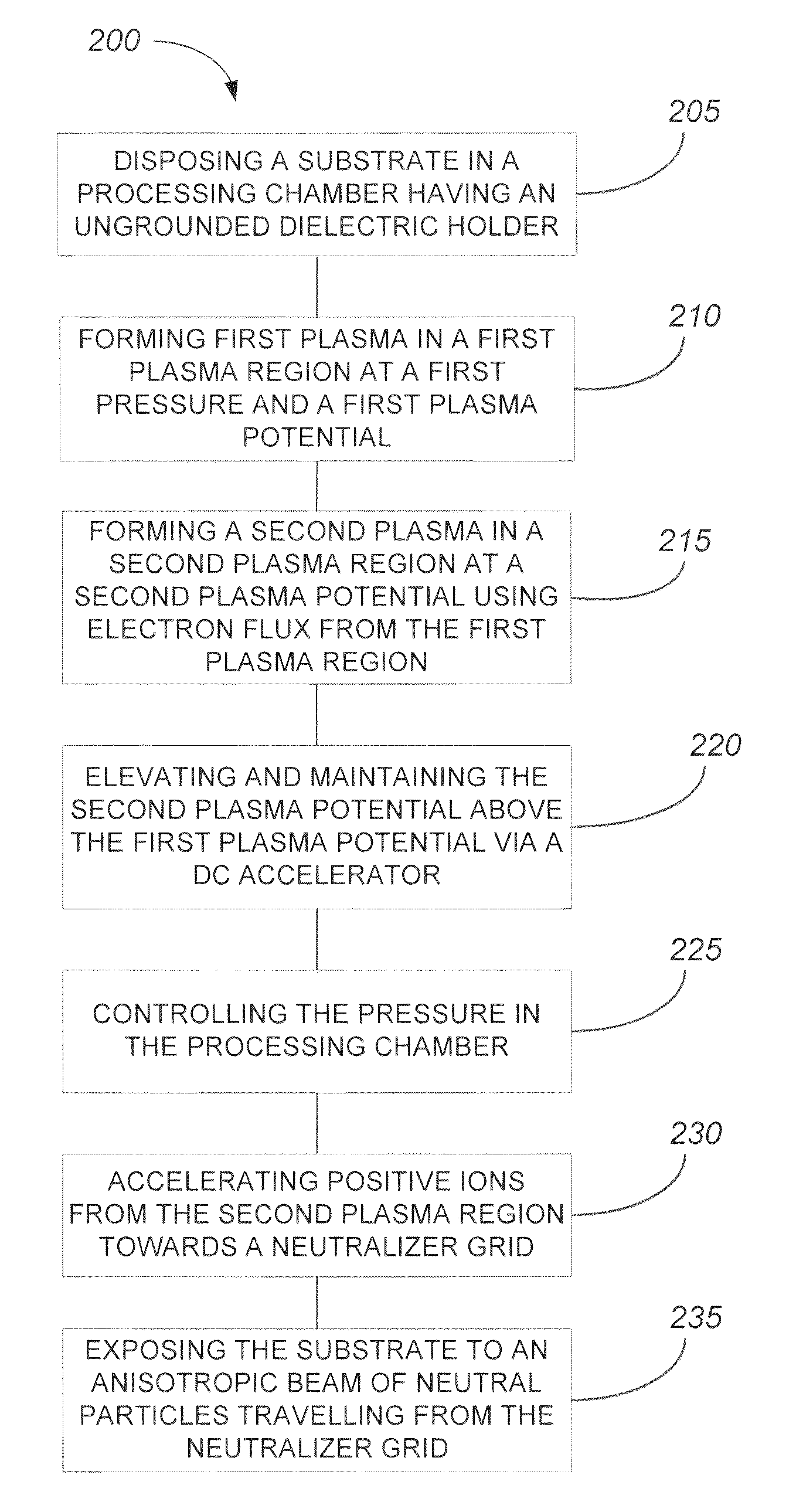
Embodiments include a chemical processing apparatus and method of using the chemical processing apparatus to treat a substrate with a mono-energetic space-charge neutralized neutral beam-activated chemical process which is comprised of a substantially anisotropic beam of neutral particles. The chemical processing apparatus comprises a first plasma chamber for forming a first plasma at a first plasma potential, and a second plasma chamber for forming a second plasma at a second plasma potential greater than the first plasma potential, wherein the second plasma is formed using electron flux from the first plasma. Further, the chemical processing apparatus comprises an ungrounded dielectric (insulator) neutralizer grid configured to expose a substrate in the second plasma chamber to the substantially anisotropic beam of neutral particles traveling from the neutralizer grid.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
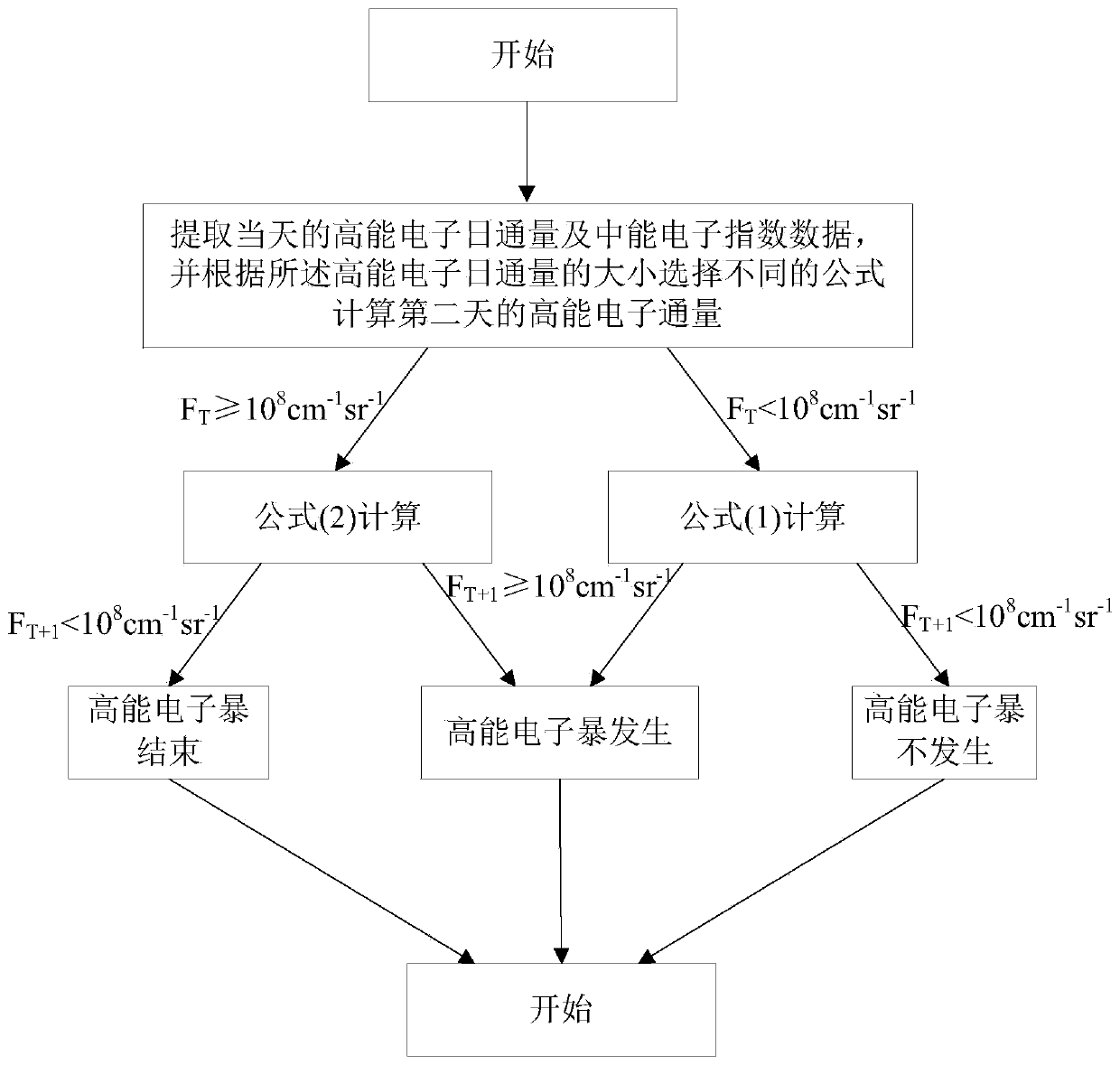
Prediction method and device of high-energy electron burst event, and storage medium and device
The present invention provides a prediction method and device of a high-energy electron burst event, and a storage medium and device. The prediction method comprises the following steps: extracting high-energy electron daily flux FT and medium-energy electron index data IT0 of a day; calculating high-energy electron flux FT+1 of a second day according to the high-energy electron daily flux FT andthe medium-energy electron index data IT0; predicting whether a high-energy electron burst event occurs according to the calculated high-energy electron flux FT+1 of the second day; predicting that the high-energy electron burst event occurs on the second day if FT+1 is greater than or equal to a first threshold of the high-energy electron daily flux generated by the high-energy electron burst; otherwise, predicting that the high-energy electron burst event does not occur on the second day. The technical solution recorded in the present invention improves the accuracy rate of prediction of thehigh-energy electron burst event in a geosynchronous orbit, and accurately predicts the high-energy electron flux of the geosynchronous orbit and especially the occurrence time of the high-energy electron burst event, so that not only a data basis is provided for the protection of service satellites of the geosynchronous orbit, but also the reference is provided for on-orbit protection of other satellites operating in a region.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT +1
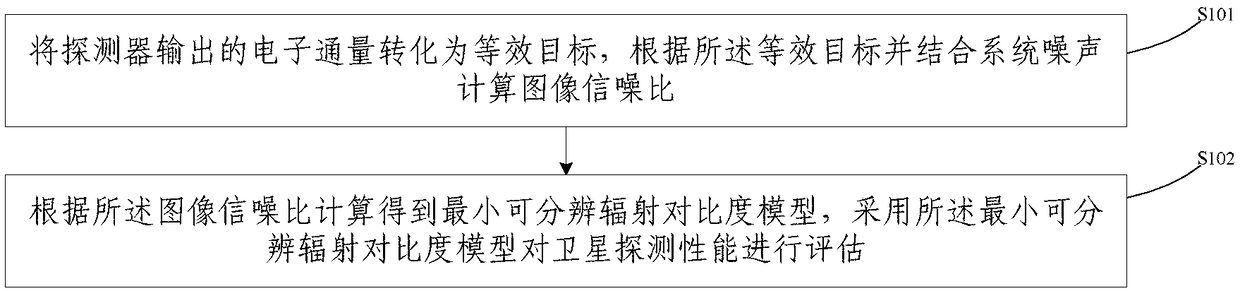
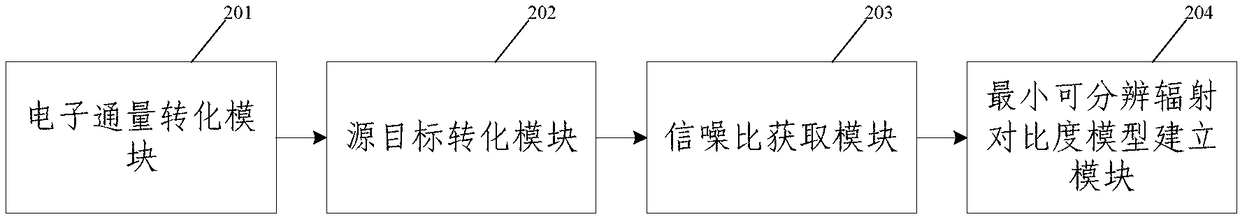
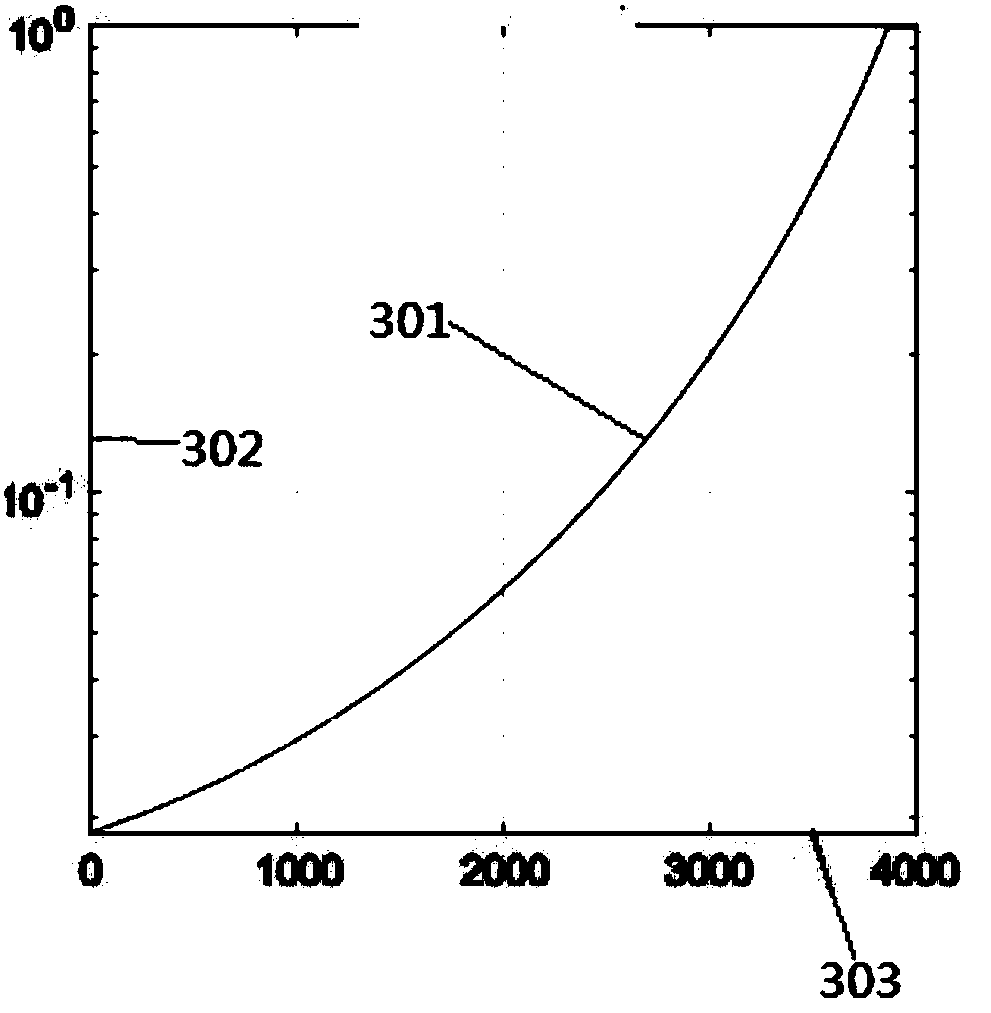
Radiation contrast-based satellite detection performance assessment method and apparatus, and memory
ActiveCN108510480AEffective assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal-to-quantization-noise ratio
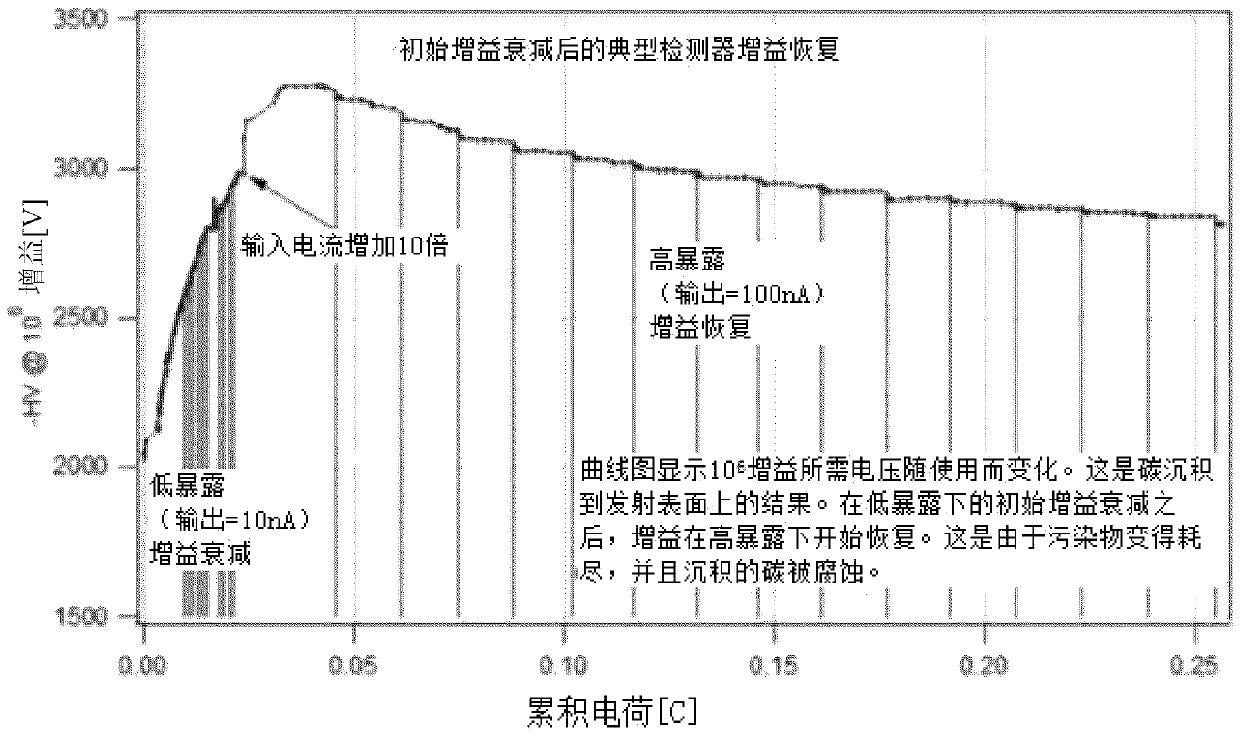
An embodiment of the invention provides a radiation contrast-based satellite detection performance assessment method. The method comprises the steps of converting an electron flux output by a detectorinto an equivalent object, and calculating an image signal-noise ratio in combination with system noises according to the equivalent object; and according to the image signal-noise ratio, performingcalculation to obtain a minimum distinguishable radiation contrast model, and by adopting the minimum distinguishable radiation contrast model, assessing satellite detection performance. Embodiments of the invention furthermore provide a radiation contrast-based satellite detection performance assessment apparatus, an active interaction apparatus and a non transient readable memory, which are usedfor realizing the method. The satellite detection performance can be effectively assessed under the condition of no human eye intervention.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Metabolic uncoupling therapy
InactiveUS20110293588A1Improve health benefitsReduce generationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHigh energyMedicine
Owner:MCCLEARY EDWARD LARRY
Mono-energetic neutral beam activated chemical processing system and method of using
ActiveUS9520275B2Electric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsChemical treatmentEnergetic space
A chemical processing system and a method of using the chemical processing system to treat a substrate with a mono-energetic space-charge neutralized neutral beam-activated chemical process is described. The chemical processing system comprises a first plasma chamber for forming a first plasma at a first plasma potential, and a second plasma chamber for forming a second plasma at a second plasma potential greater than the first plasma potential, wherein the second plasma is formed using electron flux from the first plasma. Further, the chemical processing system comprises a substrate holder configured to position a substrate in the second plasma chamber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Radiation-Cured Coatings
InactiveUS20110217477A1Prevent materialReduce riskElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesElectron fluxGas plasma
A process for coating a substrate comprising condensing a radiation curable material on a substrate and curing it using an electron flux 6′ with energy between 6.5 eV and 300 eV. The electron flux 6′ is directed at the substrate (2) either simultaneously or sequentially with delivery of the curable material (5′). Curing is preferably initiated spatially and temporally concurrently with delivery of the material to the substrate. The electron flux is preferably generated using a low pressure gas plasma source with a driving voltage negative relative to the local voltage conditions. The low pressure gas plasma (6′) is preferably magnetically enhanced and, for example, incorporates a magnetron.
Owner:CAMVAC
Fault warning method based on spacecraft in-orbit internal charged effect dynamic library table
The invention discloses a fault warning method based on a spacecraft in-orbit internal charged effect dynamic library table. An on-orbit satellite internal charged abnormal failure is used as a starting point, high energy electronic data provided by satellite-borne space environment load is used as a driving source, and a spacecraft internal charged effect matching database is generated. The spacecraft internal charged effect matching database mainly comprises a dynamic high energy electron flux library table and a relevance library table of dynamic high energy electron flux and satellite internal charged abnormality. The spacecraft in-orbit is monitored to provide support for business of relevant departments such as internal charged effect risk identification, warning and forecasting andthe like based on the relevance library table, and a wide application prospect is achieved.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
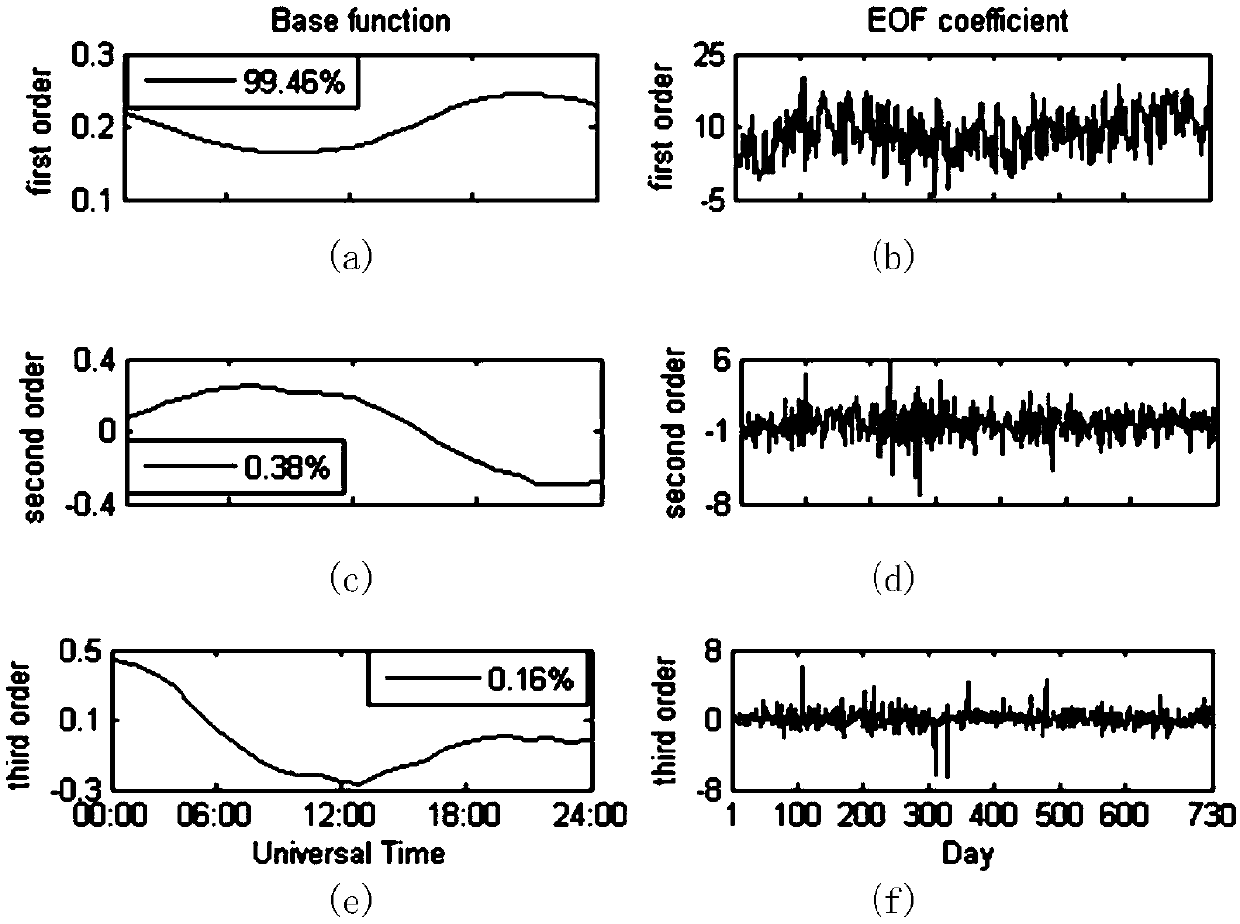
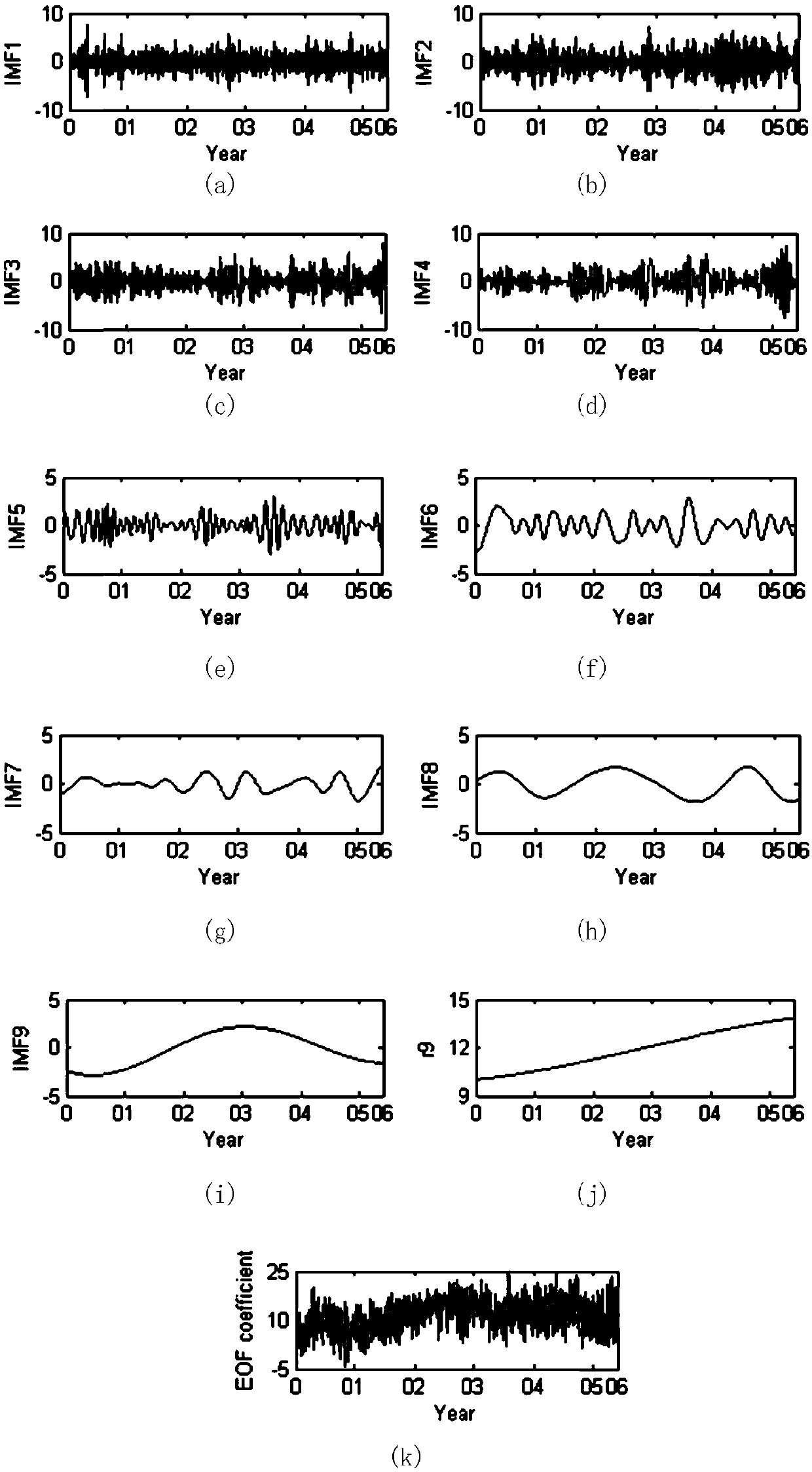
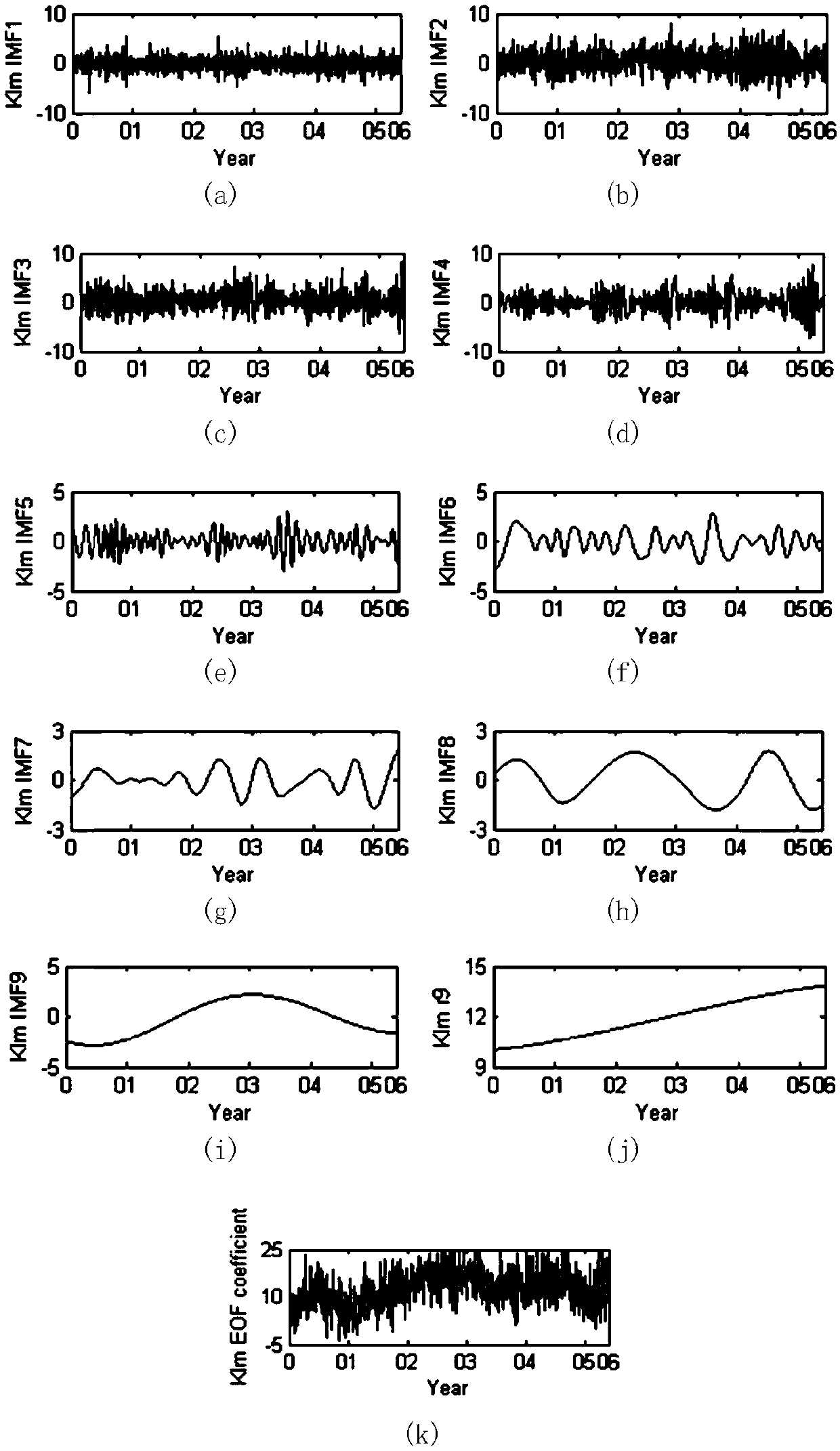
Empirical mode decomposition-based establishment method for hour prediction model of energetic electron flux
InactiveCN108776719AImprove regularityOvercome forecasting difficultiesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataDecomposition
The invention discloses an empirical mode decomposition-based establishment method for an hour prediction model of energetic electron flux. The method includes the following steps: step 1. simplifyinga time coefficient of the energetic electron flux by an empirical orthogonal function; step 2. performing reconstruction expansion on the empirical orthogonal function of the time coefficient of theenergetic electron flux by employing a first order primary function of the empirical orthogonal function; step 3. obtaining the time coefficient of the electron flux by using the known electron flux and primary function; step 4, selecting an input parameter; step 5. decomposing the time coefficient by using an empirical mode decomposition EMD algorithm; and step 6. performing fitting on each of components of the time coefficient. The method overcomes the prediction difficulty of the energetic electron flux caused by non-stationary, a decomposed data sequence is stronger in regularity than an original data sequence of the time coefficient, and the prediction accuracy can be significantly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
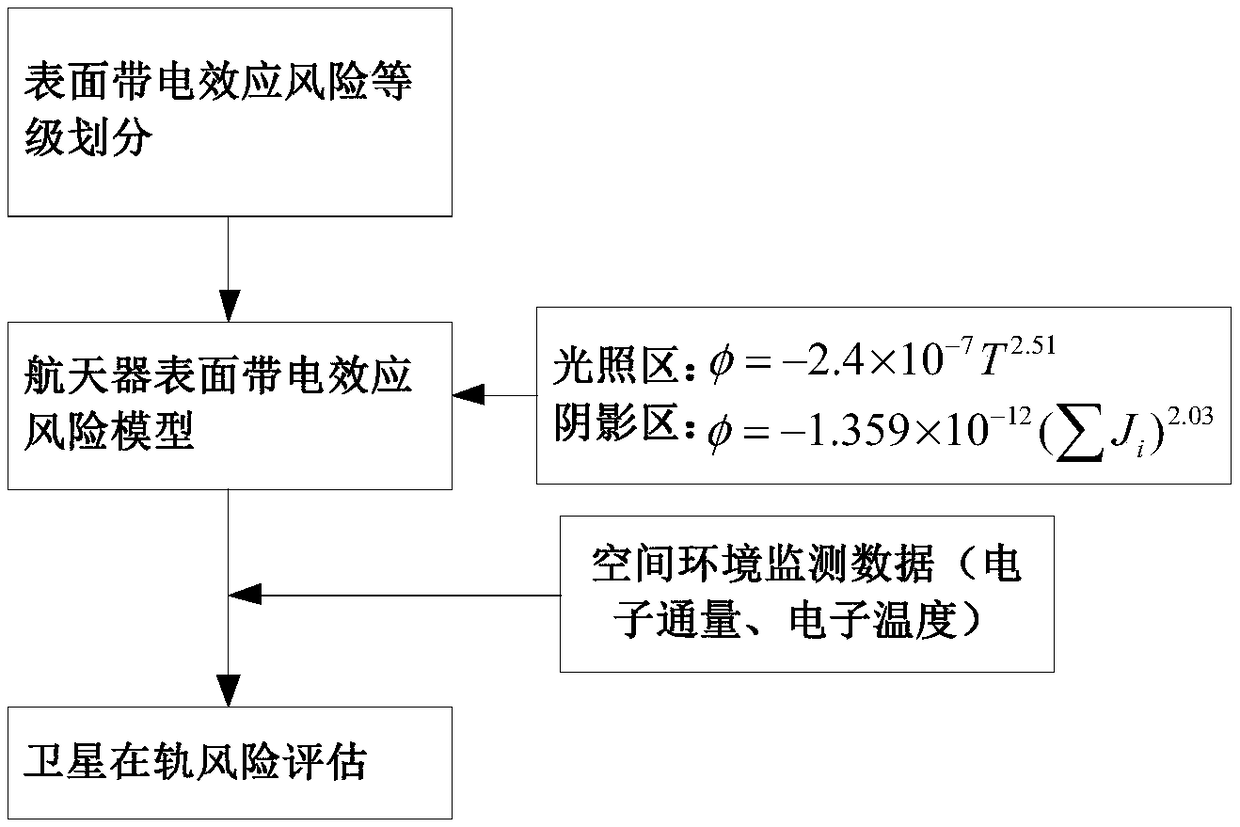
A method for evaluating the risk of charging effect on the surface of a spacecraft in-orbit surface
A method for evaluating the risk of charging effect on the surface of a spacecraft in-orbit surface which is based on the real-time monitoring of electron temperature and electron flux in the space environment of spacecraft in orbit, real-time intervention (active potential control) and emergency plan (shutdown of sensitive stand-alone) can be carried out to avoid serious failure caused by surfacecharging effect of spacecraft, which is of great significance to improve the safe and reliable operation of spacecraft in orbit. The in-orbit surface charging effect risk evaluation methods can be made according to different types of spacecraft, different orbit spacecraft, or different sensitive parts of spacecraft (such as solar cell array, etc.), so that the method has wider application range.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Treatment process for a gaseous medium containing contaminating particles
InactiveUS7147821B1Effective controlEasy to storeLighting and heating apparatusElectrostatic separationElectron fluxIonization
The invention relates to a method for treating a gaseous medium containing contaminating particles, such as microorganisms, bacteria, or viruses. The inventive method consists of generating an accelerated electron flux; the electron flux interacting with the gaseous medium, whereby the particles are broken or destroyed by ionization as a result of the interaction and the gaseous medium is sterilized. The invention can be used to treat the atmospheres of refrigerated vessels in refrigerators.
Owner:RASAR HLDG NV
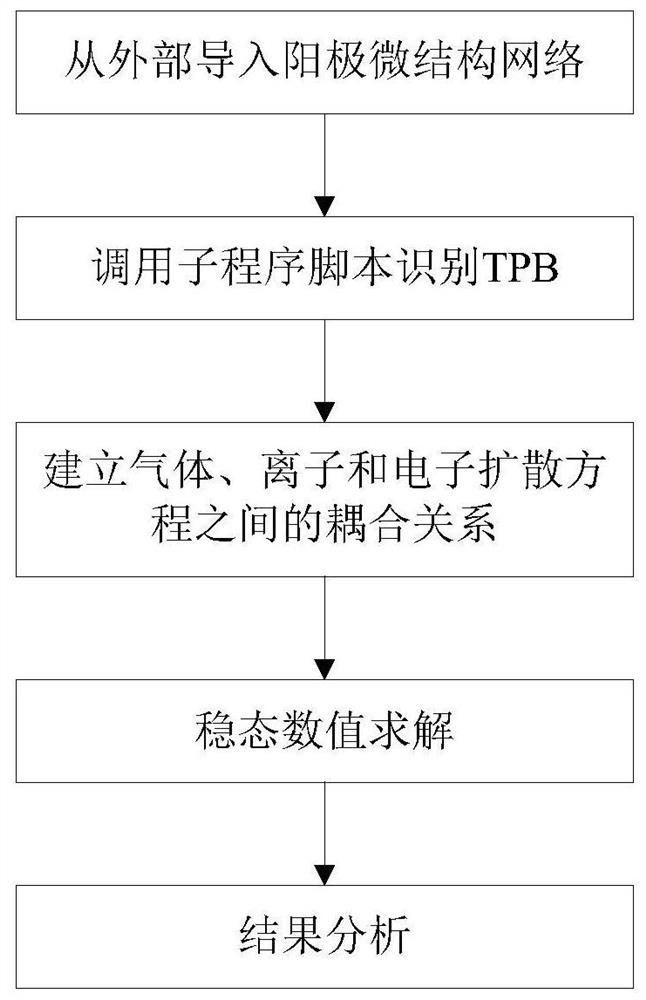
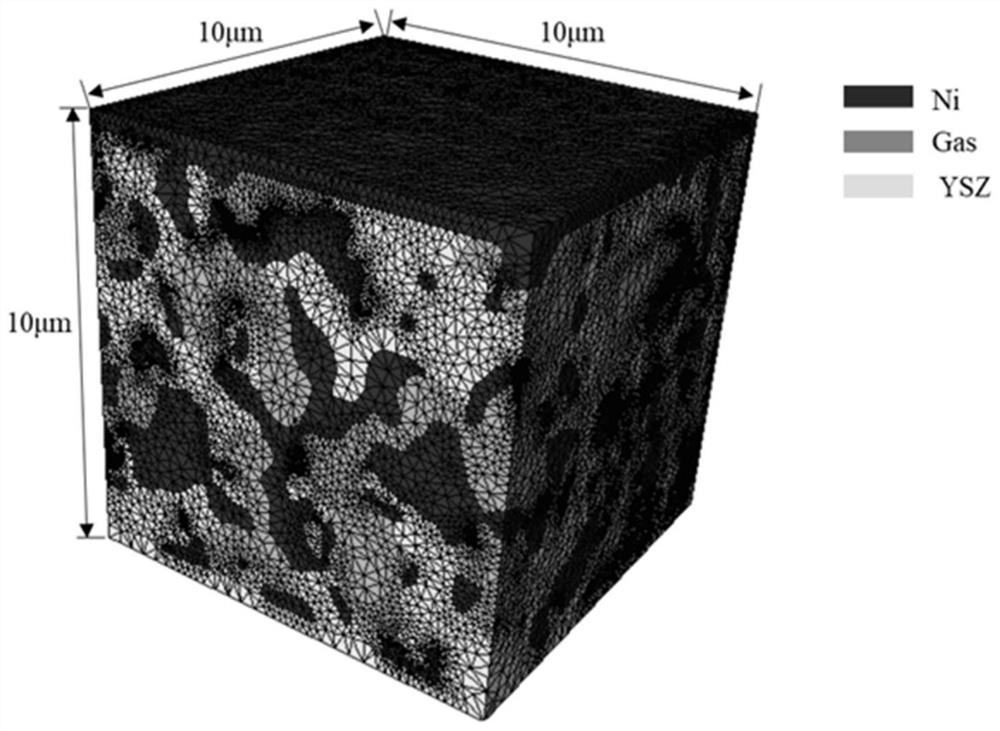
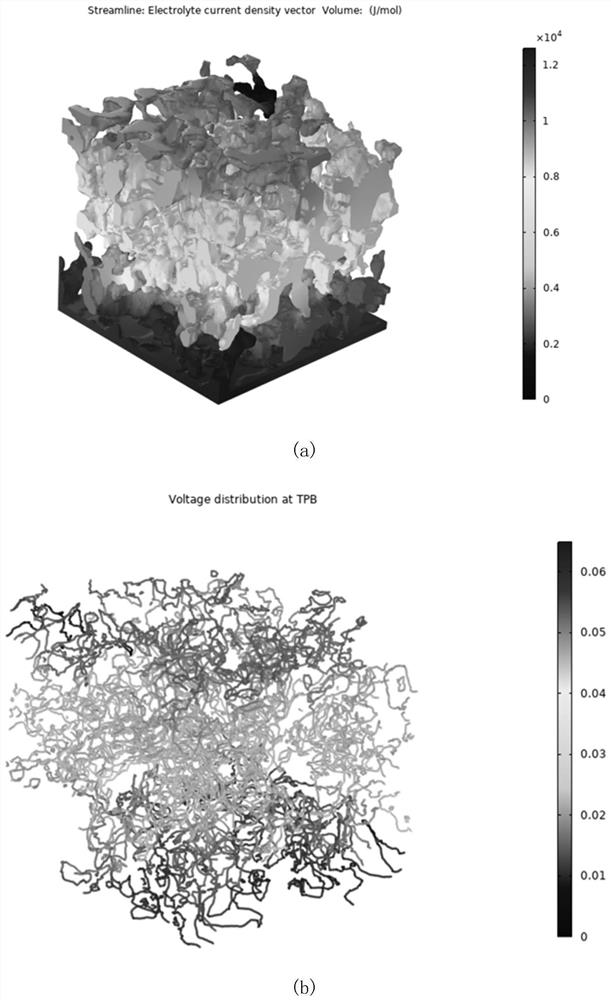
Method for establishing SOFC/SOEC electrode microstructure electrochemical model
ActiveCN113420483AAccurate identificationMake up for the defect of automatic identification of invalid TPB on TPB easy selectionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectron flowGas concentration
The invention provides a method for establishing a SOFC / SOEC electrode microstructure electrochemical model. The method comprises the following steps: identifying a three-phase boundary line at the intersection of yttrium oxide-stabilized zirconium oxide, nickel and a gaseous phase in an anode microstructure grid unit; establishing a coupling relationship among gas, ion and electron diffusion equations; applying a constant ion and electron flux boundary condition to the boundary of a current collector and an electrolyte, applying a constant gas concentration boundary condition near the current collector, and finally, using a separated solver to carry out steady-state solving to obtain the electrochemical characteristics of the microelectrode. By adopting the technical scheme, the electrochemical model with fully coupled gas, ion and electron diffusion equations is established, and a series of simulation results such as electrochemical potential distribution, ion current and electron current distribution, gas concentration distribution condition and relation between overpotential and input current density in the YSZ can be obtained according to the calculation result of the model; and the invention has certain guiding significance on electrode structure optimization and engineering design.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Methods and apparatus for controlling contaminant deposition on dynode electron-emmissive surface
InactiveCN111466010ASpectrometer detectorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsElectron flow
The present invention relates to generally to components of scientific analytical equipment, and particularly to methods for extending the operational lifetime or otherwise improving the performance of dynodes used in electron multipliers. An aspect of the invention is embodied in a method for: (i) increasing the secondary electron yield of a dynode and / or (ii) decreasing the rate of degradation of electron yield of a dynode, the method comprising the step of exposing a dynode electron-emissive surface to an electron flux under conditions causing electron-impact induced removal of a contaminant deposited on the dynode electron-emissive surface. The conditions may be selected such that the electron-mediated removal is enhanced relative to a contaminant deposition process so as to provide anet decrease in the rate of contaminant deposition and / or a decrease in the amount of contaminant present on the dynode electron-emissive surface.
Owner:艾德特斯解决方案有限公司
System and method for reducing trapped energetic proton or energetic electron flux at low earth orbits
InactiveUS20130181145A1Reduce decreaseWeaken energyRadiation/particle handlingEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSurvivabilityResonance
A system and method for improving the survivability of space systems following a High Altitude Nuclear Explosion (HANE) incident resulting in energetic electrons being trapped in the inner radiation belt of Earth is disclosed. The ULF electromagnetic waves is generated by space or ground based transmitters and the frequency range is selected such that the injected waves are in gyrofrequency resonance with trapped energetic particles. The Radiation Belt Remediation (RBR) depends on the wave-number of the injected waves and the wave-number of the injected waves increases along their propagation path when they approach the cyclotron frequency of the dominant or minority ions 0+, He+ and H+.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Electron induction based charging/discharging simulation method
InactiveCN109142924AHigh simulationImprove acceleration performanceElectrical testingElectron sourceElectron flux
The invention provides an electron induction based charging / discharging simulation method. The method comprises that the type of an electron source is determined according to a tested device / system and a using environment thereof, electron energy and flux are emitted, and material and size of a discharging sample are determined; the distance from the discharging sample and the electron source is adjusted so that the electron flux in the surface of the sample approaches that of the environment; a vacuum pump is started, the electron source is started when the vacuum degree realizes 10-4 pascal,and electrons are injected into the discharging sample; and when the maximal electric field in the discharging sample satisfies conditions, discharging occurs, and a discharging pulse is generated, led out and and injected to the tested device / system. The method can be used to simulate discharging in different conditions, can be expanded widely, and can be used to complete charging / discharging test of different types of tested systems on the ground.
Owner:景祝强
Plasma generator with at least one non-metallic component
ActiveUS9865422B2Little and no contaminantLower Level RequirementsVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIonization chamberIon beam
A plasma generator for an ion implanter is provided. The plasma generator includes an ionization chamber for forming a plasma that is adapted to generate a plurality of ions and a plurality of electrons. An interior surface of the ionization chamber is exposed to the plasma and constructed from a first non-metallic material. The plasma generator also includes a thermionic emitter including at least one surface exposed to the plasma. The thermionic emitter is constructed from a second non-metallic material. The plasma generator further includes an exit aperture for extracting at least one of the plurality of ions or the plurality of electrons from the ionization chamber to form at least one of an ion beam or an electron flux. The ion beam or the electron flux comprises substantially no metal. The first and second non-metallic materials can be the same or different from each other.
Owner:NISSIN ION EQUIP CO LTD
Evaluation and monitoring method for deep charging risk of medium in satellite
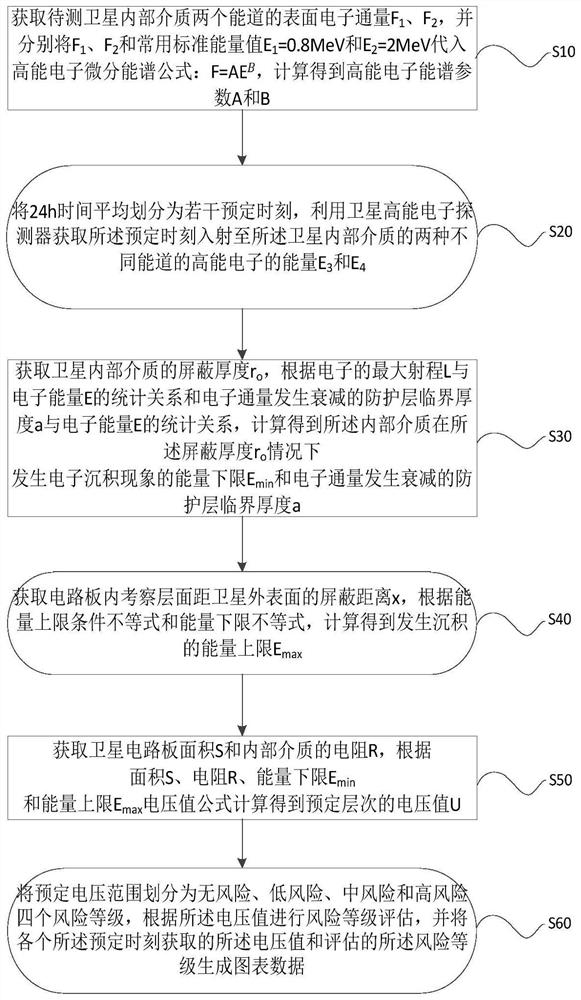
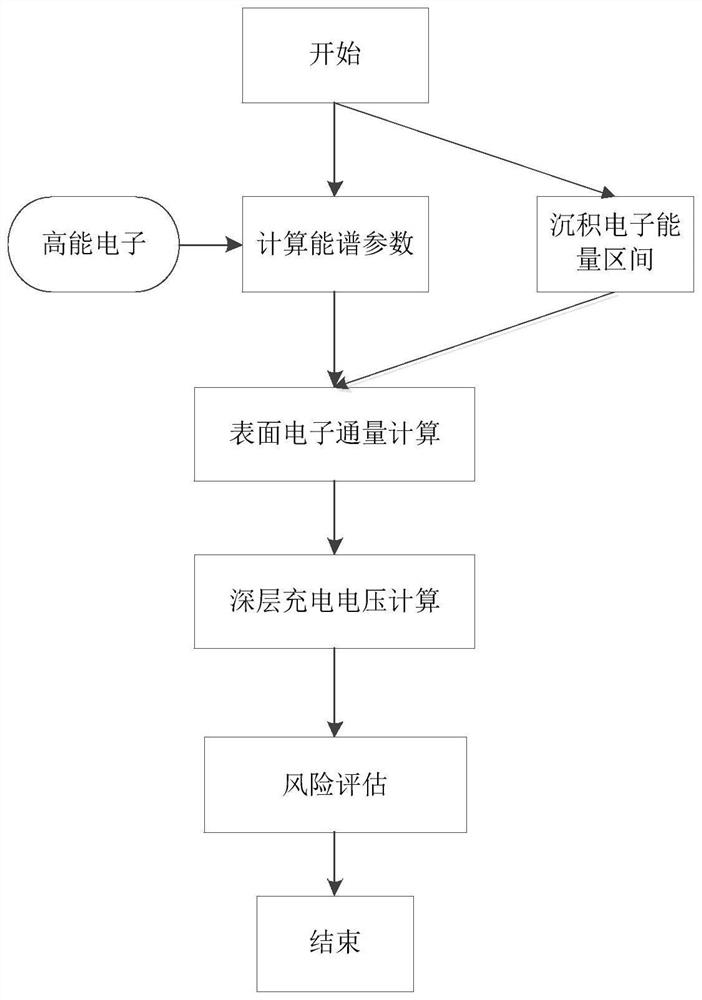
PendingCN114399221AEffective assessmentImprove experienceResourcesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The invention provides a satellite internal medium deep charging risk assessment and monitoring method, which comprises the following steps of: estimating a high-energy electron spectrum parameter through actually measured electron flux and a common standard energy value, dividing 24 hours into a plurality of preset moments, acquiring energy of high-energy electrons of two different energy channels at the preset moments, and calculating to obtain surface electron flux; obtaining the shielding thickness of the internal medium, calculating the lower limit Emin of energy for deposition according to the statistical relationship between the maximum range of electrons and energy, calculating the critical thickness of the internal medium for electron deposition, and calculating the upper limit Emax of energy for deposition according to the conditional inequality of the critical thickness and the upper limit of energy, and acquiring the area S of the satellite circuit board and the resistance R of the internal medium, and calculating a voltage value U of a predetermined level according to the area S, the resistance R, the lower energy limit Emin, the upper energy limit Emax, the voltage value and a voltage value formula. Effective assessment and continuous monitoring of the satellite deep charging risk are realized, and the assessment is more accurate and efficient.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE METEOROLOGICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com