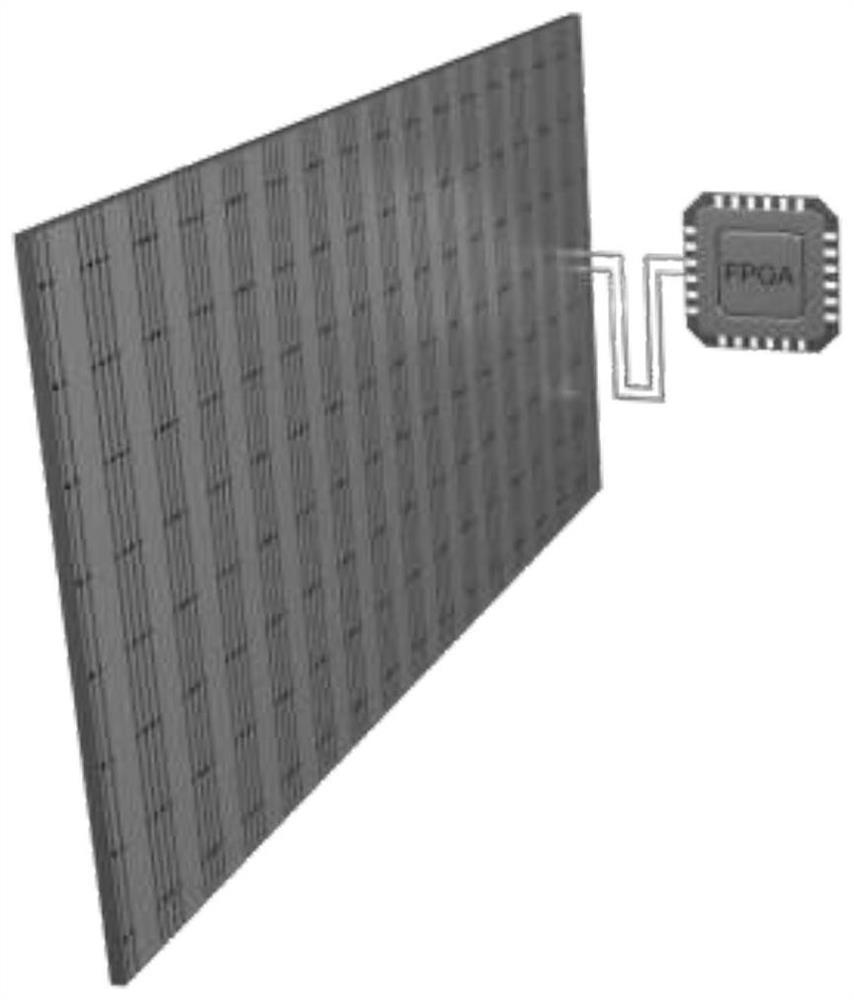
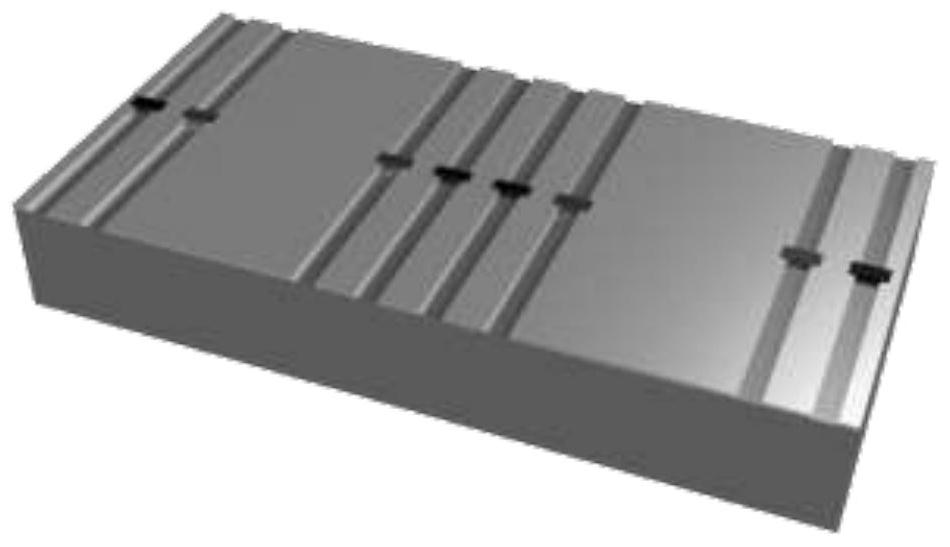
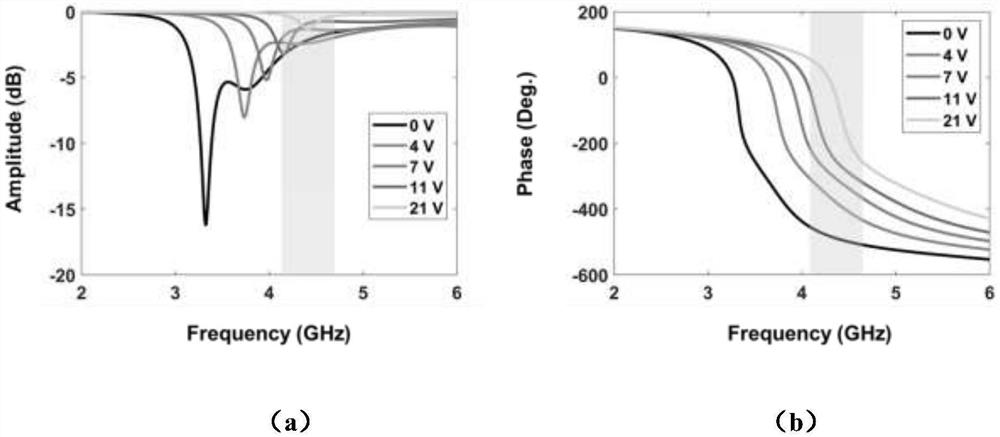
Asynchronous space-time coding metasurface
A space-time encoding and metasurface technology, applied to antennas, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as inaccessibility, and achieve the effect of simple hardware structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] In the present invention, the asynchronous space-time coding metasurface can be used to realize the automatic spatial scanning of electromagnetic waves. Specifically, using the modulation waveform described above, the modulation time of each column of cells in the coding metasurface is kept unchanged, and the modulation frequency difference between two adjacent columns remains unchanged (that is, the modulation frequency is linear on the array surface). Increase). At this time, the encoding metasurface will maintain a dynamic phase gradient, that is, generate a dynamic spatial scattering pattern, such as Figure 4 shown. Further, by adjusting the modulation frequency difference between two adjacent columns, the speed of the automatic scanning of the electromagnetic wave space can be adjusted. like Figure 5 As shown, when the modulation frequency of two adjacent columns is doubled, the time to complete the automatic scanning of the same space is reduced to half. On ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In the present invention, the asynchronous space-time encoding metasurface is regarded as a radar target, and its radar cross section (RCS) can be observed to be dynamic. Using the modulation waveform described above and applying different time modulation periods to each column on the coding metasurface at the same time, the coding metasurface can obtain a time-varying RCS. Further, by designing the spatial distribution of the modulation period on the coding metasurface (ie, the spatial coding of the temporal modulation period), the curve characteristics of its time-varying RCS can be effectively controlled. For example, under the condition that the control signal waveform of the entire encoding metasurface remains unchanged, and aiming to reduce the RCS of the asynchronous space-time encoding metasurface in a period of time, the present invention adopts random space encoding for the modulation period, genetic algorithm (GA) Spatial coding, particle swarm optimization (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com