Welding process for titanium alloy workpiece
A welding process and titanium alloy technology, which is applied in the field of welding process of titanium alloy parts, can solve the problems of low tensile strength of the matrix, reduction of alloy strength, and deformation of parts, so as to avoid the reduction of alloy strength, high production efficiency and excellent welding process. easy effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
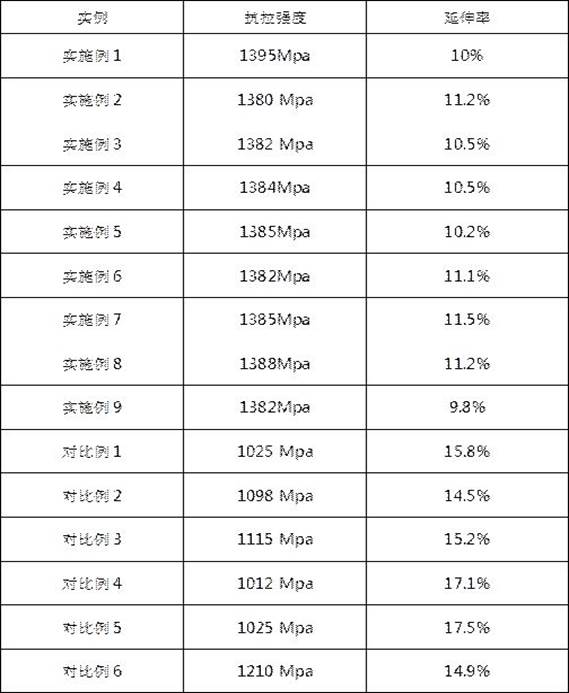
[0029] After cleaning the surface of the titanium alloy with acetone solution, fix the workpiece to be welded and put it into the vacuum heat treatment furnace. The vacuum working pressure in the vacuum chamber is 5×10 -2 Pa, use a three-stage heating method to raise the temperature with the furnace to 400°C, keep the temperature for 15 minutes, raise the temperature to 700°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, keep the temperature for 30 minutes, and continue to raise the temperature to 950°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min. ℃, hold for 30 minutes, cool with the furnace, cool the titanium alloy welded parts to below 200 ℃, and then air-cool the titanium alloy parts; test the tensile strength and elongation of the titanium alloy parts after heat treatment.
Embodiment 2
[0031] After cleaning the surface of the titanium alloy with acetone solution, the workpieces to be welded are assembled and fixed and put into the vacuum heat treatment furnace. The vacuum working pressure in the vacuum chamber is 5.5×10 -2 Pa, use a three-stage heating method to raise the temperature with the furnace to 400°C, keep the temperature for 15 minutes, raise the temperature to 700°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min, keep the temperature for 30 minutes, and continue to raise the temperature to 950°C at a heating rate of 5°C / min. ℃, hold for 30 minutes, cool with the furnace, cool the titanium alloy welded parts to below 200 ℃, and then air-cool the titanium alloy parts; test the tensile strength and elongation of the titanium alloy parts after heat treatment.
Embodiment 3
[0033] After cleaning the surface of the titanium alloy with acetone solution, fix the workpiece to be welded and put it into the vacuum heat treatment furnace. The vacuum working pressure in the vacuum chamber is 5×10 -2 Pa, use a three-stage heating method to raise the temperature with the furnace to 450°C, keep the temperature for 15 minutes, raise the temperature to 700°C at a heating rate of 7°C / min, keep the temperature for 30 minutes, and continue to raise the temperature to 950°C at a heating rate of 7°C / min. ℃, hold for 30 minutes, cool with the furnace, cool the titanium alloy welded parts to below 200 ℃, and then air-cool the titanium alloy parts; test the tensile strength and elongation of the titanium alloy parts after heat treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com