Dynamic cable for ocean engineering
A dynamic cable and marine engineering technology, applied in the direction of submarine cables, insulated cables, cables, etc., can solve problems such as cable breakage, poor anti-overheating effect of the cable core, melting, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing the cable core from overheating
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
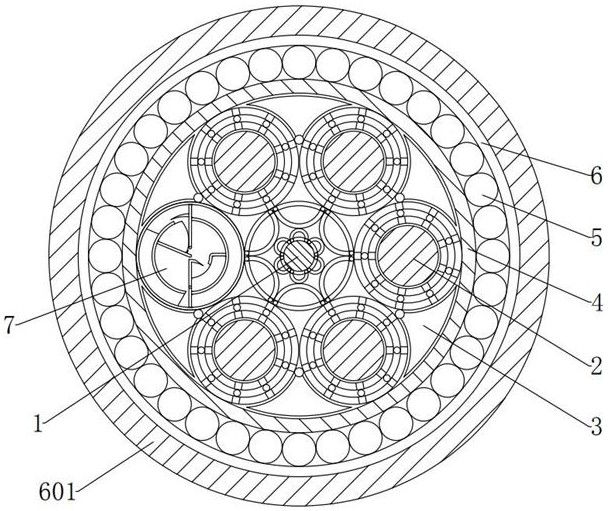
[0037] see Figure 1-2 , in the embodiment of the present invention, a dynamic cable for marine engineering, comprising:
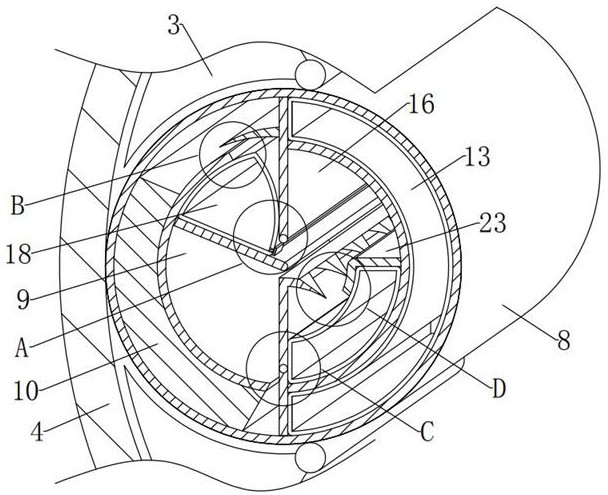
[0038] The power core 1 and the inner sheath 4, a plurality of overheating prevention components 7 that can prevent the cable core from overheating are arranged between the middle end of the left inner wall of the inner sheath 4 and the left end of the power supply core 1. The overheating prevention component 7 includes: a casing 8, The inner shell 9, the support bar 10, the thermal conduction component 11 that can guide the cable core in time after the heat is generated, and the cooling component 12 that can be cooled in time after the cable core is heated, the middle end of the left inner wall of the inner sheath 4 is connected to the power core 1. A number of outer shells 8 are arranged between the left ends of the outer shell 8, an inner shell 9 is fixedly installed in the inner center of the outer shell 8, a support bar 10 is fixedly installed between...
Embodiment 2
[0053] see Figure 2-4 and Figure 7 The difference between the embodiment of the present invention and the embodiment 1 is that the main air bag 13 is in the shape of a long fan with left concave and right convex on a longitudinal section, and the top and bottom ends of the main air bag 13 are under normal conditions. statically located at the top and bottom ends of the shell 8;
[0054] The main airbag 13 here is to facilitate the use of its top and bottom ends. When the heat is transferred to it, the top and bottom ends are respectively inflated to the left due to the common limitation of the outer shell 8 and the inner shell 9. deformation, so as to push the upper rotating plate 16 and the cooling component 12 to move respectively, so as to absorb heat and cool down in time.
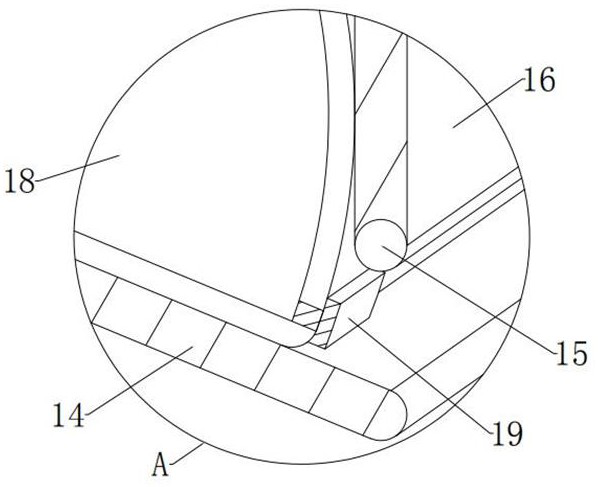
[0055] In the embodiment of the present invention, the upper limit plate 14 is in the shape of an inclined straight plate with high left and right low and an included angle of 23° with the horizont...
Embodiment 3
[0063] see figure 2 and Figure 5-7 , the difference between the embodiment of the present invention and the embodiment 1 is that the lower rotating shaft 20 is located directly above the lower groove, and the lower rotating plate 21 is vertically vertical on a longitudinal section, and the top is bent to the right. The counterclockwise rotation 90 The “¬” shape of °, the lower turning plate 21 is also in a state of vertical static equilibrium under normal conditions, and the bottom outer surface of the lower turning plate 21 is statically attached to the bottom inner wall of the housing 8 under normal conditions. 21 also has a different magnetism from that of the inner shell 9, the outer surface of the right bottom end of the lower turning plate 21 is closely attached to the outer surface of the left bottom end of the main airbag 13, and the outer surface of the lower right end of the lower turning plate 21 is in the normal state. In the case of static magnetic attraction o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com