Method for rapidly detecting titer of non-starch polysaccharide enzyme for feed
A non-starch polysaccharide enzyme and amylase technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, food processing, etc. The effect of evaluation, simple operation process and accurate measurement results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
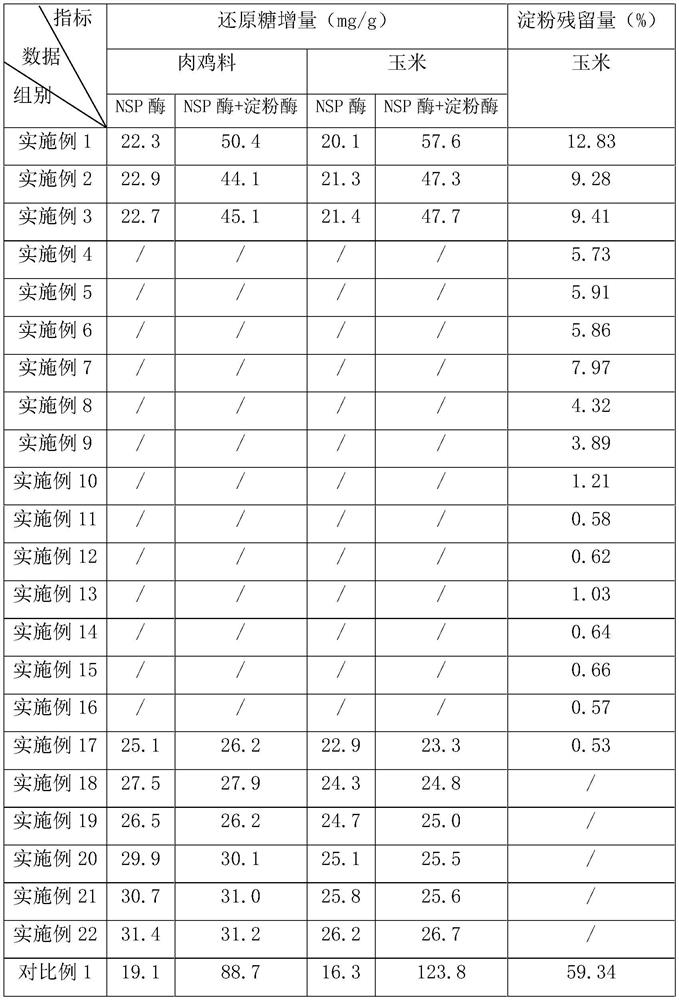
[0063] The embodiment of the present application discloses a method for rapidly detecting the titer of non-starch polysaccharide enzymes for feed, comprising the following steps:
[0064] S1, draw the standard curve: first draw the standard curve of the glucose absorbance value and the glucose concentration;
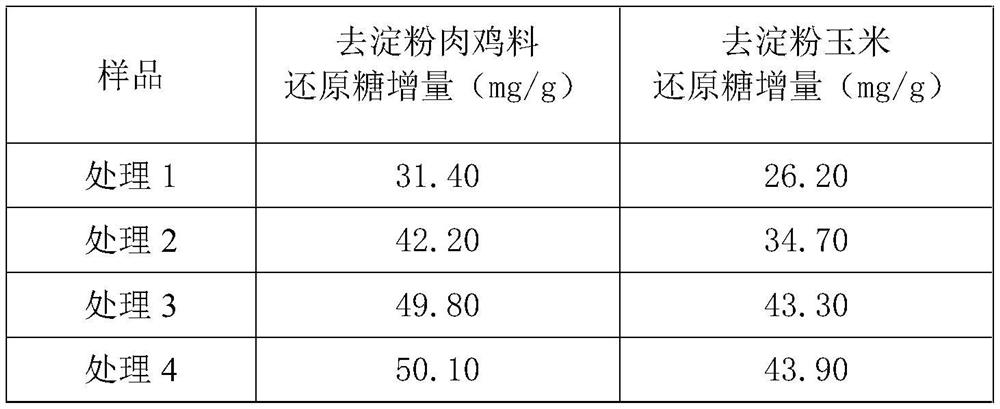
[0065] S2. De-starchization of the feed: After grinding the feed, pass it through a 500 μm aperture screen, take 10 g of the ground feed, add 20 g of water to mix, then add 0.02 g of medium-temperature α-amylase, and put it into an oil bath reactor at 50 ° C The enzymatic hydrolysis reaction was carried out for 3 hours under the condition of enzymatic hydrolysis, and after cooling to room temperature, the pH of the solution after enzymatic hydrolysis by mesophilic α-amylase was adjusted to 3.5, and 0.1 g of saccharification enzyme was added to the shaker and reacted at 50 °C for 4 hours. After 2h, centrifuge (4500rpm, 5min) to get the sediment to obtain the de-starchized...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The embodiment of the present application discloses a method for rapidly detecting the titer of non-starch polysaccharide enzymes for feed, comprising the following steps:
[0079] S1, draw the standard curve: first draw the standard curve of the glucose absorbance value and the glucose concentration;
[0080] S2. De-starchization of feed: After grinding the feed, pass it through a 500μm pore size screen, take 10g of the ground feed, add 50g of water to mix, then add 0.02g of medium-temperature α-amylase, put it in an oil bath reactor at 50°C The enzymatic hydrolysis reaction was carried out for 3 hours under the condition of enzymatic hydrolysis, and after cooling to room temperature, the pH of the solution after enzymatic hydrolysis by mesophilic α-amylase was adjusted to 3.5, and 0.1 g of saccharification enzyme was added to the shaker and reacted at 50 °C for 4 hours. After 2.5h, centrifuge (4500rpm, 5min), take the sediment to obtain the de-starchized feed; S3, in ...
Embodiment 3
[0092] The embodiment of the present application discloses a method for rapidly detecting the titer of non-starch polysaccharide enzymes for feed, comprising the following steps:
[0093] S1, draw the standard curve: first draw the standard curve of the glucose absorbance value and the glucose concentration;
[0094] S2. De-starchization of feed: After grinding the feed, pass it through a sieve with a 500 μm aperture, take 10 g of the ground feed, add 30 g of water to mix, then add 0.02 g of medium-temperature α-amylase, and put it in an oil bath reactor at 50 ° C The enzymatic hydrolysis reaction was carried out for 3 hours under the condition of enzymatic hydrolysis, and after cooling to room temperature, the pH of the solution after enzymatic hydrolysis by mesophilic α-amylase was adjusted to 3.5, and 0.1 g of saccharification enzyme was added to the shaker and reacted at 50 °C for 4 hours. After 3h, centrifuge (4500rpm, 5min) to get the sediment to obtain the de-starchized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com