Application of urine microvesicle protein as kidney cancer diagnosis marker
A technology of protein markers and vesicles, applied in the field of medical diagnosis, can solve problems such as low survival rate and poor prognosis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
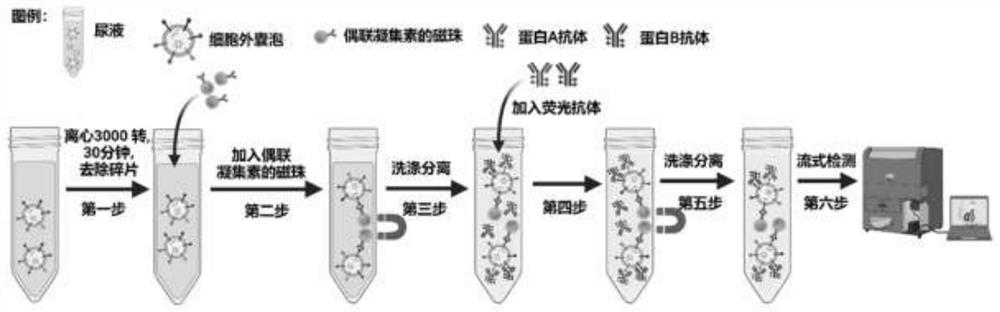
[0024] Example 1 Construction of lectin-coupled magnetic beads
[0025] 1. Purchase NHS magnetic beads (Solarbio, product number M2450) with a particle size of 2 μm, take 500 μL of magnetic bead suspension into a 1.5 mL EP tube, place the EP tube in a magnetic separation rack, enrich the magnetic beads, and remove the supernatant . Add 1 mL of 4 ℃ pre-cooled Washing Buffer A to a 1.5 mL EP tube, and vortex for 15 s to mix the magnetic beads evenly. Place the EP tube in a magnetic separation rack, enrich the magnetic beads, and remove the supernatant.
[0026] 2. Weigh the lyophilized wheat germ agglutinin powder, and resuspend it into a 3.0 mg / mL protein solution with Coupling Buffer (Solarbio, product number M2450). Add 500 μL of wheat germ agglutinin protein solution to the EP tube in the first step, and vortex for 30 s to mix well. The EP tube was vortexed for 15s, placed on a mixer, and mixed at room temperature for 2h. If the mixing is not uniform, remove the EP tube ...
Embodiment 2
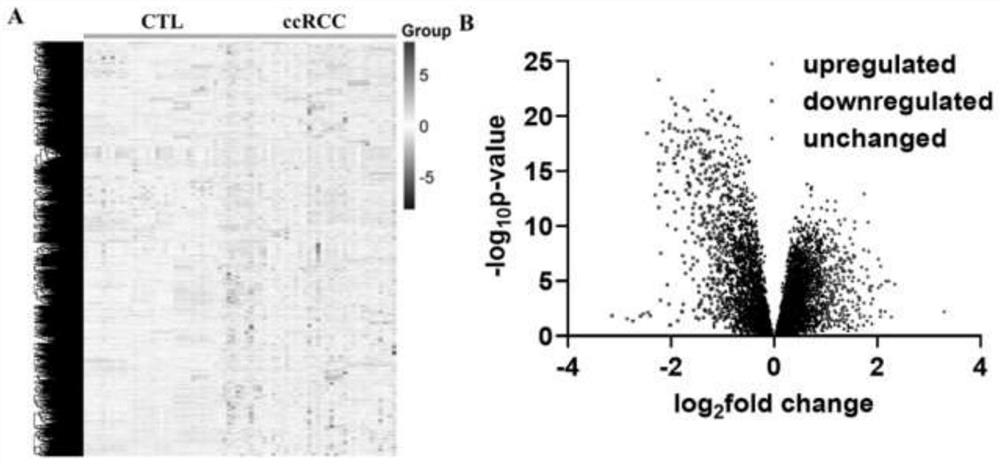
[0030] Example 2 Detection of Urine Microvesicle Protein Spectrum
[0031] 1. Collect urine from patients with renal clear cell carcinoma and control group (including healthy people, benign renal tumors and benign renal cysts), centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 30 minutes at room temperature, remove cell debris, and retain the supernatant.
[0032] 2. Since the surface of extracellular vesicles is rich in glycosylated proteins, these glycosylated proteins can bind to lectins coupled to magnetic beads. Therefore, the prepared lectin-coupled magnetic beads were added to the urine supernatant obtained in the first step, and incubated at room temperature for 1 hour, at which time the extracellular vesicles in the urine would be captured by the magnetic beads.
[0033] 3. Place the EP tube on a magnetic separation rack to magnetically separate and remove the supernatant, and retain the magnetic beads and their captured extracellular vesicles.
[0034] 4. Add 1000 μL of PBS solution (pH 7...
Embodiment 3
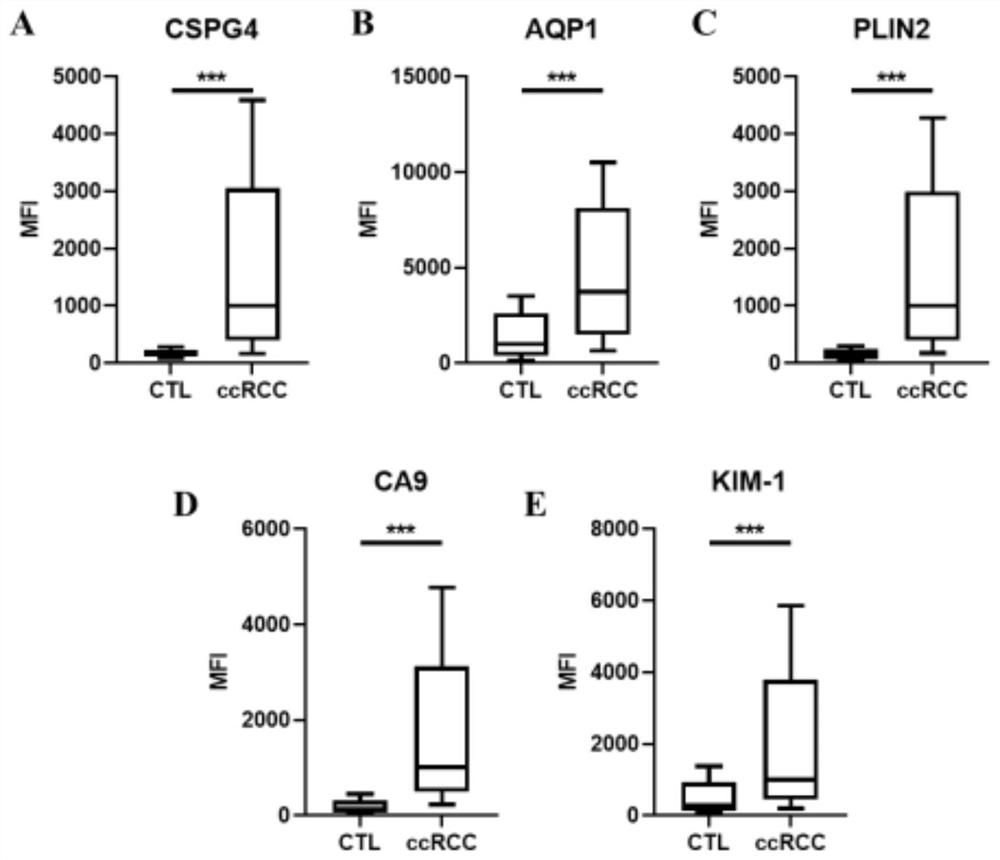
[0039] Urine microvesicle protein detection by flow cytometry
[0040] 1. Collect urine from patients with renal clear cell carcinoma and control group (including healthy people, benign renal tumors and benign renal cysts), centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 30 minutes at room temperature, remove cell debris, and retain the supernatant.
[0041] 2. Since the surface of extracellular vesicles is rich in glycosylated proteins, these glycosylated proteins can bind to lectins coupled to magnetic beads. Therefore, 0.5 ml of the prepared lectin-conjugated magnetic beads were added to 1 ml of the urine supernatant obtained in the first step, and incubated at room temperature for 1 hour. At this time, the extracellular vesicles in the urine would be captured by the magnetic beads.
[0042] 3. Place the EP tube on a magnetic separation rack to magnetically separate and remove the supernatant, and retain the magnetic beads and their captured extracellular vesicles. Then, 1000 μL of PBS solutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com