Embedded steel rail profile detection light bar extraction method
An extraction method and embedded technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of low processing accuracy, poor robustness, low processing speed, etc., and achieve the effect of narrowing the search range, fast speed, and fast extraction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] A method for extracting light strips based on embedded rail profile detection, comprising the following steps:
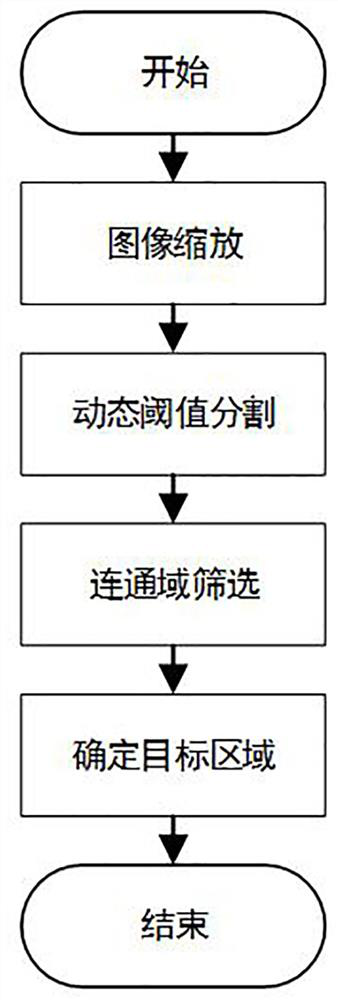
[0067] S1. Perform image scaling, dynamic threshold segmentation, and connected area screening (adaptive ROI) on the original image in turn to determine the target area on the original image;
[0068] S2. Perform selective mask smoothing, image binarization and center point extraction processing on the original image after the target area is determined, to obtain the center of the light bar of the target area.
[0069] In this embodiment, in step S1, the adaptive ROI method is used to determine the target area, which can remove the interference area to a limited extent, increase the accuracy of light strip extraction, narrow the search range during light strip extraction, and greatly improve the efficiency of the algorithm. In step S2, selective mask smoothing, image binarization and center point extraction are sequentially performed on the target area to ext...
Embodiment 2
[0072] This embodiment makes further improvements on the basis of Embodiment 1, such as figure 1 As shown, the step S1 includes the following steps:
[0073] S11. Image scaling: the original image is drawn at every 4 points in rows and columns, respectively, to obtain a scaled image reduced by 1 / 4.
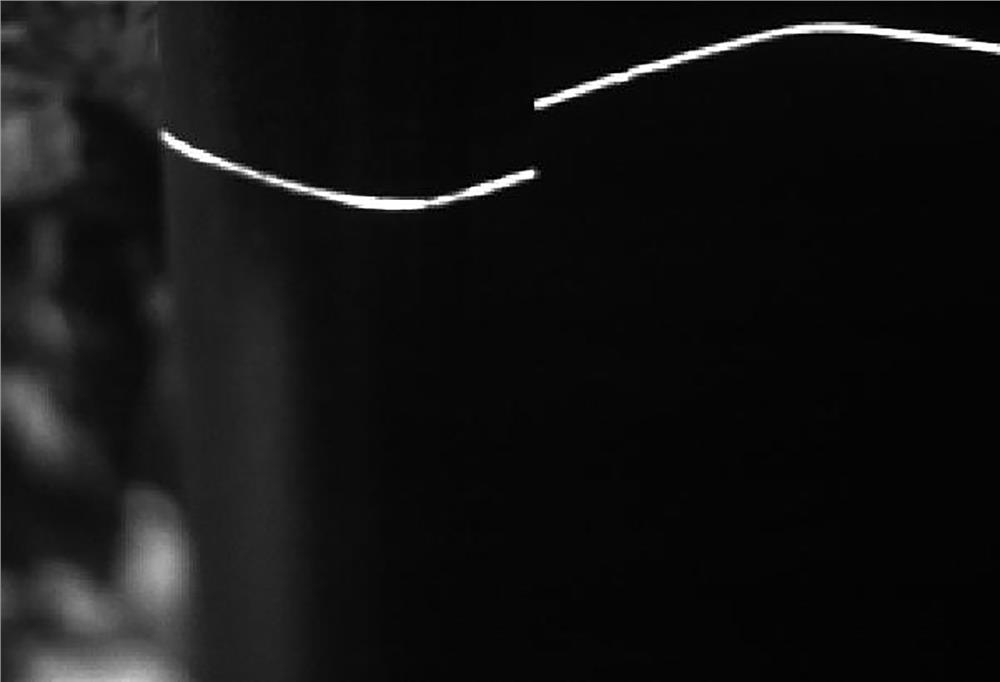
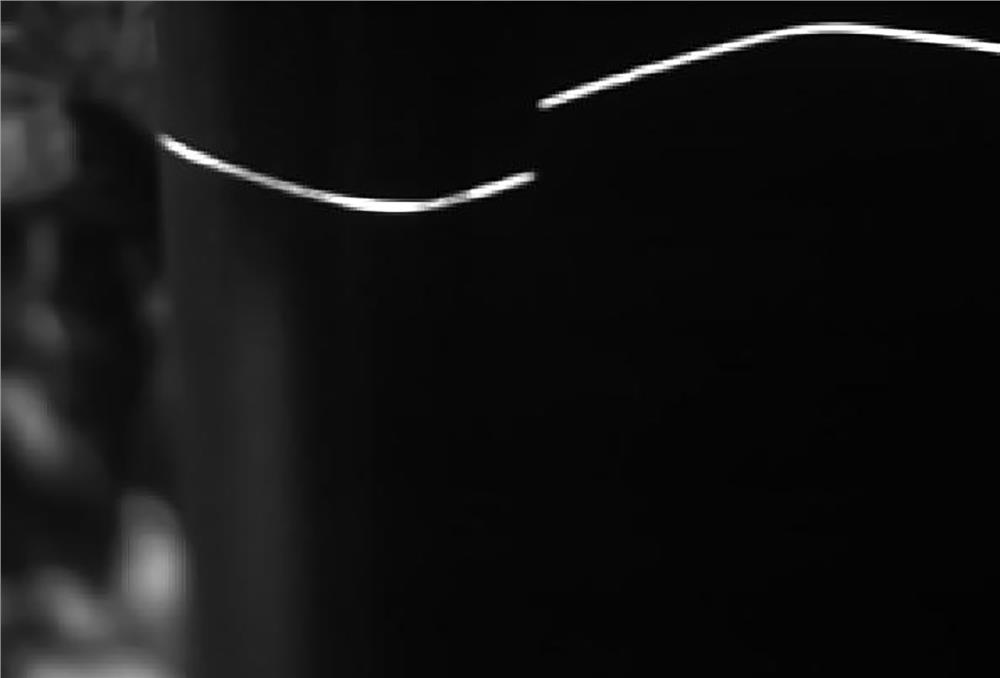
[0074] S12. Dynamic threshold segmentation: perform large-scale smoothing on the scaled image to obtain a smooth image, and make a difference between the scaled image and the smoothed image to obtain a differential image; wherein, the smoothing scale is set to the width (pixel width) of the rail head area. The dynamic threshold segmentation data flow is as follows Figure 2-4 shown.
[0075] S13. Screening of connected areas: in the differential image, filter out the connected areas of the light bars.
[0076] S14. Determine the target area: in the filtered connected area of the light bar, use geometric parameter information such as the length, width and area of the minimum...
Embodiment 3
[0079] This embodiment makes further improvements on the basis of Embodiment 2, such as Figure 9 As shown, the step S2 includes the following steps:
[0080] S21. Selective mask smoothing: perform selective mask smoothing on the original image including the target area.
[0081] In this embodiment, the selective mask smoothing is an adaptive local smoothing filtering algorithm, which can obtain better image details.
[0082] The selective mask smoothing method is based on the template operation. Taking the 5*5 template window as an example, in the window, the center pixel is used as the basic point to make 4 pentagons, 4 quadrilaterals, and a square with a side length of 3 There are 9 masks in total, as follows:
[0083]
[0084] Calculate the mean and variance of each template according to the above 9 templates. The calculation method is as follows:
[0085]
[0086] Find the gray mean value under the mask with the smallest variance among the 9 templates as the fina...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com