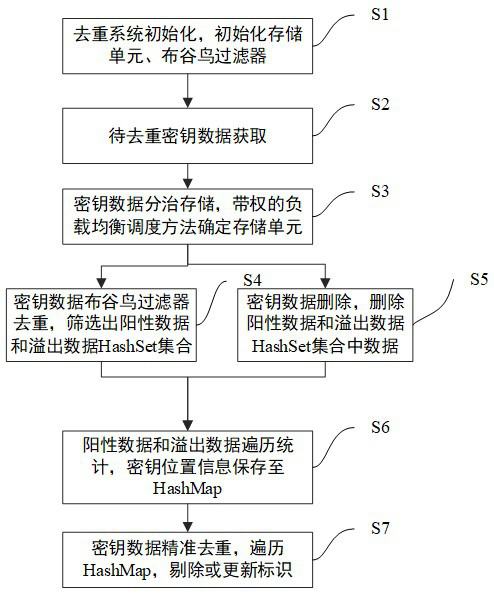
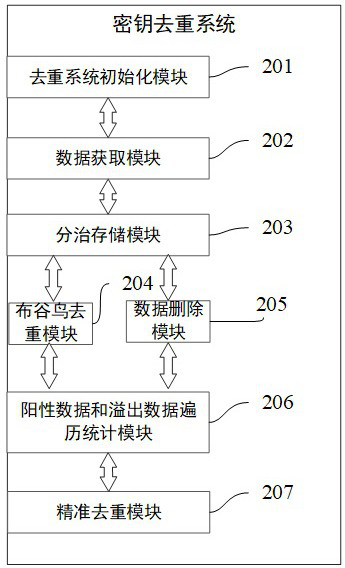
Cuckoo filter-based duplicate removal method and system for large-data-volume key
A large data volume, cuckoo technology, which is applied to encryption devices with shift registers/memory and key distribution, can solve the problems of high-efficiency deduplication and deduplication methods for large data volume keys, and achieve efficient and accurate deduplication. Achieve deduplication query efficiency, improve quality and usability, and efficiently query the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0072] Embodiment 2: as figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown, the present invention also provides a large data volume key deduplication system based on a cuckoo filter, including the following components:
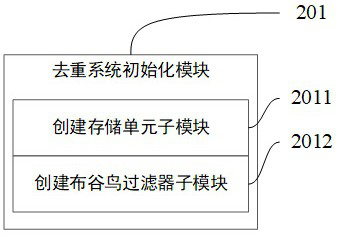
[0073] Deduplication system initialization module 201: used to create storage units and cuckoo filters according to the input parameters, such as image 3 As shown, the deduplication system initialization module 201 includes the following sub-modules:
[0074] (1) Create a storage unit submodule 2011: used to obtain the corresponding storage weight wt according to different hardware parameters according to the total amount of target keys S and the number of storage units N preset by the system, and the weights of each storage unit and is 1, and the expected storage capacity of a single persistent storage unit n = S * wt. Immediately create N database tables or N files;
[0075] (2) Create a cuckoo filter sub-module 2012: acco...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example three: as Figure 7 shown, on the basis of Embodiment 1, combined with Figure 7 Detailing the process of step S6 positive data traversal statistics, including S601, S602, S603, S604, S605, S606 and other sub-steps, as follows:
[0088] S601: Traverse and retrieve a set of keys X in the specified storage unit;
[0089] S602: Determine whether the key X already exists in the HashSet set of positive data output in step S4 or the HashSet set of overflow data. If it does not exist, it indicates that the key X is unique and does not need to be processed, jump to step S601 to start the next round of traversal statistics , if it exists, it will be processed by S603;
[0090] S603: The key X exists in the HashSet set of positive data or the HashSet set of overflow data, indicating that the key X may be repeated, and obtain the actual storage location information of the key X, that is, the file displacement or database of the key X in the storage unit A prim...
Embodiment 4
[0095] Example four: as Figure 8 shown in figure 2 Based on the structure of the key deduplication system provided by the described invention, the present invention also provides a parallel processing framework of the key deduplication system, as follows:
[0096] Deduplication system instance Inst: The deduplication system instance Inst includes N deduplication process instances, that is, N process instances such as the following deduplication process instances Inst1, InstX, and InstN, where N is the number of storage units, that is, The number of cuckoo filters required for the deduplication system.
[0097] Deduplication process instance Inst1: the key deduplication system process instance Inst1 is the first process instance in the parallel process of the key deduplication system, including a storage unit 601, a cuckoo filter 602, a HashSet collection 603 and a HashMap collection 604.
[0098] Deduplication process instance InstX: the key deduplication system...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com