Auto-locating confocal scan microscope with optical fibre
A confocal scanning and optical fiber scanning technology, applied in the field of optical fiber confocal scanning microscope, can solve the problems of limited spatial resolution, large error, long time, etc., and achieve the effects of strong anti-interference, small field of view, and convenient operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
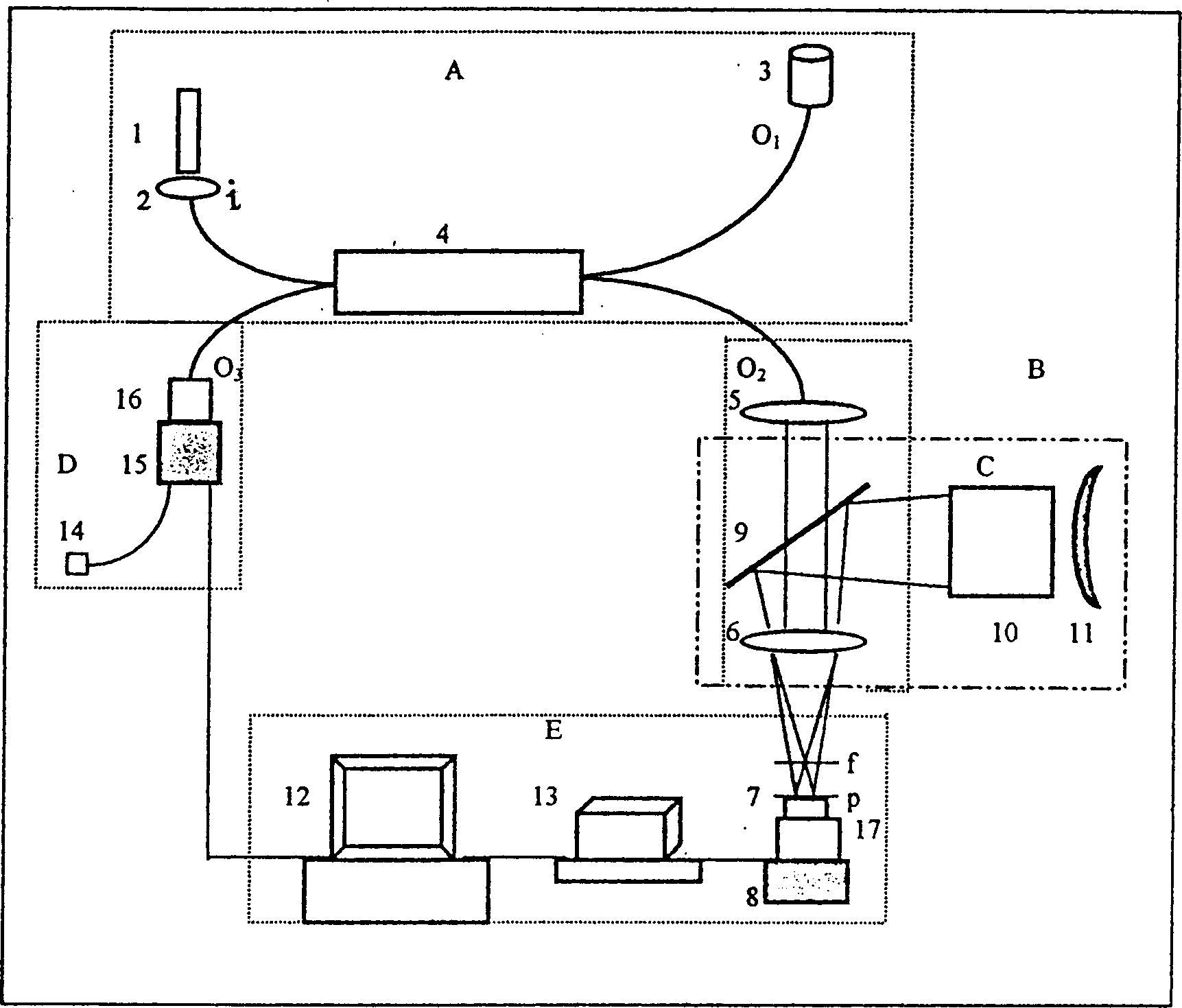
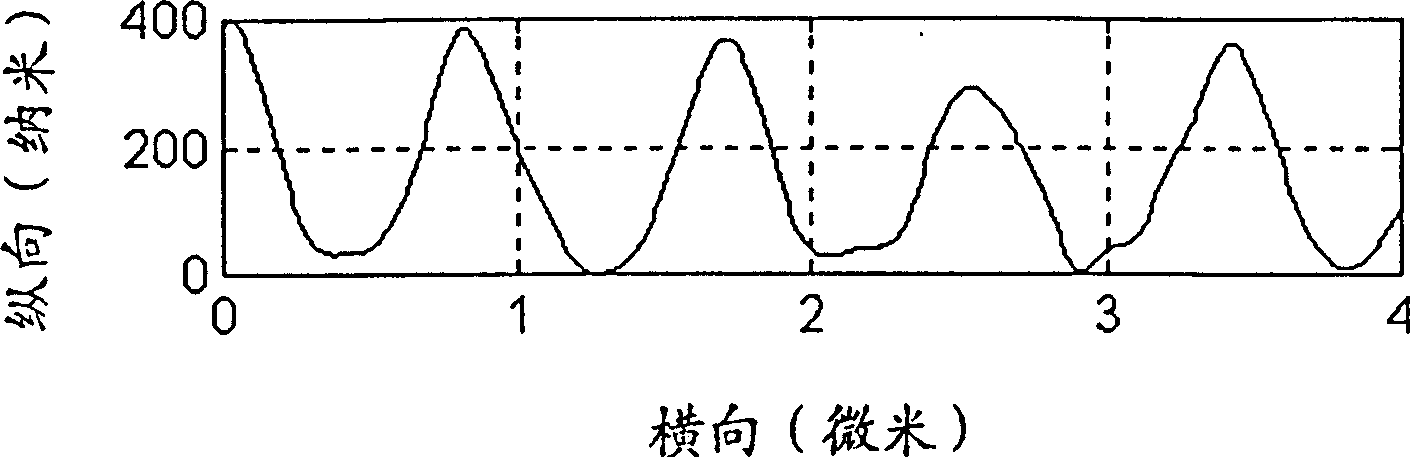
[0019] Such asfigure 1 In the structure shown, the laser 1 is a helium-neon laser, the detector 15 is a CCD detector (the image gap is 10 μm), the parameter of the sampling objective lens 6 is 40×, N(A) is 0.65, and the parameter of the beam collimator 5 is 4 ×, N(A) is 0.1, and the fiber coupler 4 is a single-mode fiber matched with the He-Ne laser beam. Its piezoelectric ceramic driver 8PZT moves with a resolution of 5nm. Test sample 7 is a blazed grating. Detect the shape and angle of the reticle. Its fineness is 1200 lines / mm, and its blaze angle is 22.3 degrees. The detection result of the present invention: the fineness is: 1200±50 lines / mm, and the detection data includes errors caused by grating manufacture and damage. Its blaze angle is 22.5±0.5 degrees. The present invention also detects the height of the reticle, and the result is 350±55nm. The test results showed that this grating was eliminated, and its surface was severely damaged. The cross-section of the ...
Embodiment 2
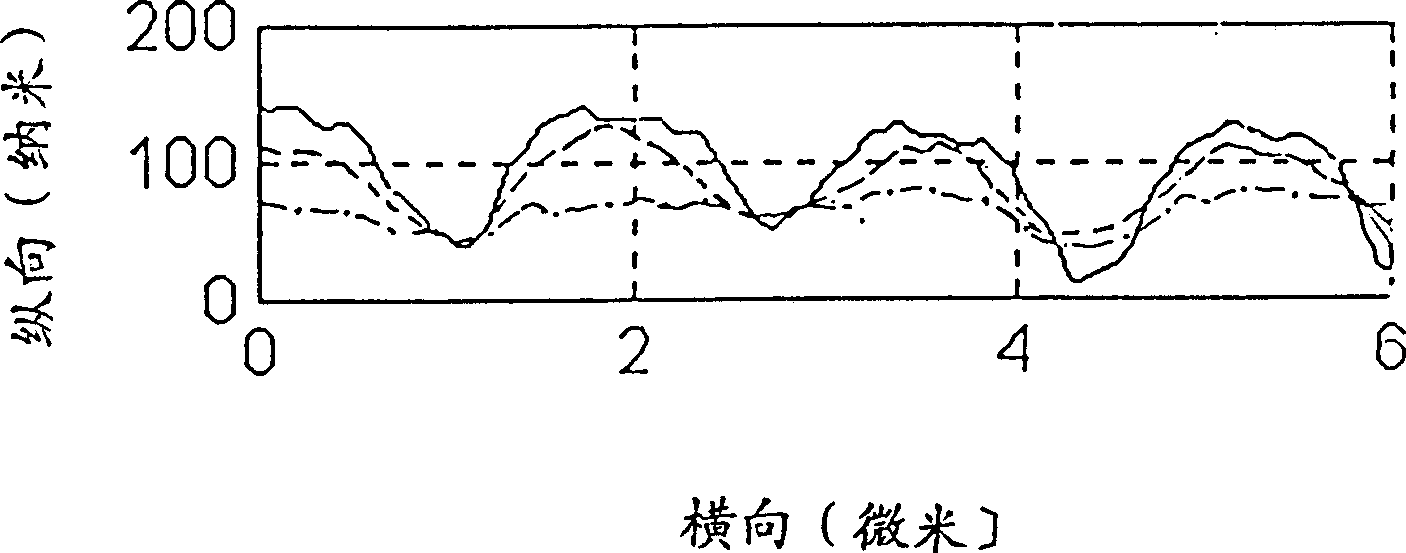
[0021] Still using the above-mentioned structure and parameters of each optical element, the tested sample 7 is an optical disc coated with a film layer, and its pre-groove is tested. The production data of the tested sample 7 are: the groove width is 0.4 μm, the groove spacing is 1.64±0.05 μm, and the groove height is 92±3 nm. The test result ( image 3 The solid line) is better than the state-of-the-art AFM ( image 3 Dashed line in the middle) and near-field scanning optical microscope ( image 3 The detection results of the dotted line). Depend on image 3 show.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com