Method and apparatus for preparing taxol using supercritical fluid from source materials
A supercritical fluid and paclitaxel technology, which is applied in the production of bulk chemicals and organic chemistry, can solve the problems that organic solvents cannot easily penetrate and limit extraction, and achieve simple extraction and separation, avoid extraction steps, and improve efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0127] The raw materials used in these Examples and Comparative Examples were the leaves, stems and roots of the Northeast Taxus obtained from the Medicinal Herb Garden, College of Pharmacy, Ilsan, Kyungi-Do, Korea. ).
[0128] The leaves, stems and roots of Taxus chinensis were dried in a vacuum drying oven at 50° C. for 72 hours, and then ground to a size below 0.7 mm with a grinder. The resulting material was used as a raw material in the following examples for comparing the effects of the present invention and in organic solvent extraction. For an accurate comparison, materials will be selected at random.
[0129] The paclitaxel content of Taxus brevifolia is 2-4 times higher than that in the bark of Taxus brevifolia (the existing raw material for paclitaxel, as one can see from the following comparative examples extracted using conventional organic solvents). Comparative example uses the amount of paclitaxel and its derivatives of organic solvent extraction
[0130] Th...
Embodiment 2
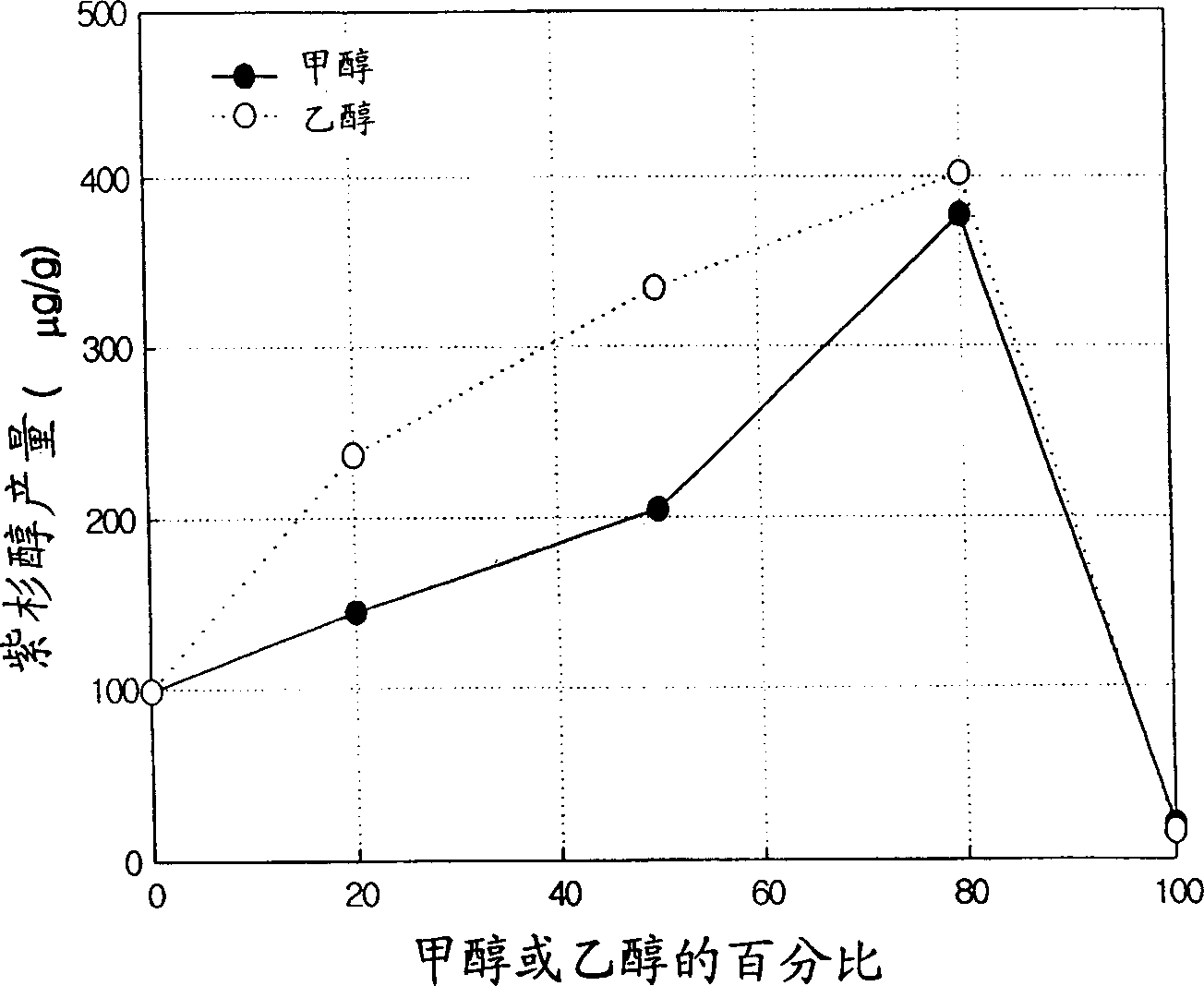
[0138] Example 2 concerns the selection of co-solvents suitable for avoiding the possible influence of the matrix on the extraction of paclitaxel and the release of paclitaxel and its derivatives from the matrix.
[0139] For this purpose, a cellulose paper-paclitaxel model was designed. If paclitaxel does not interact with the cellulose paper, then the co-solvent can be selected based solely on the ability to dissolve paclitaxel and its derivatives. However, if paclitaxel interacts with the cellulose paper, a co-solvent can be chosen for its ability to disrupt the interaction of paclitaxel and cellulose paper and its ability to dissolve.
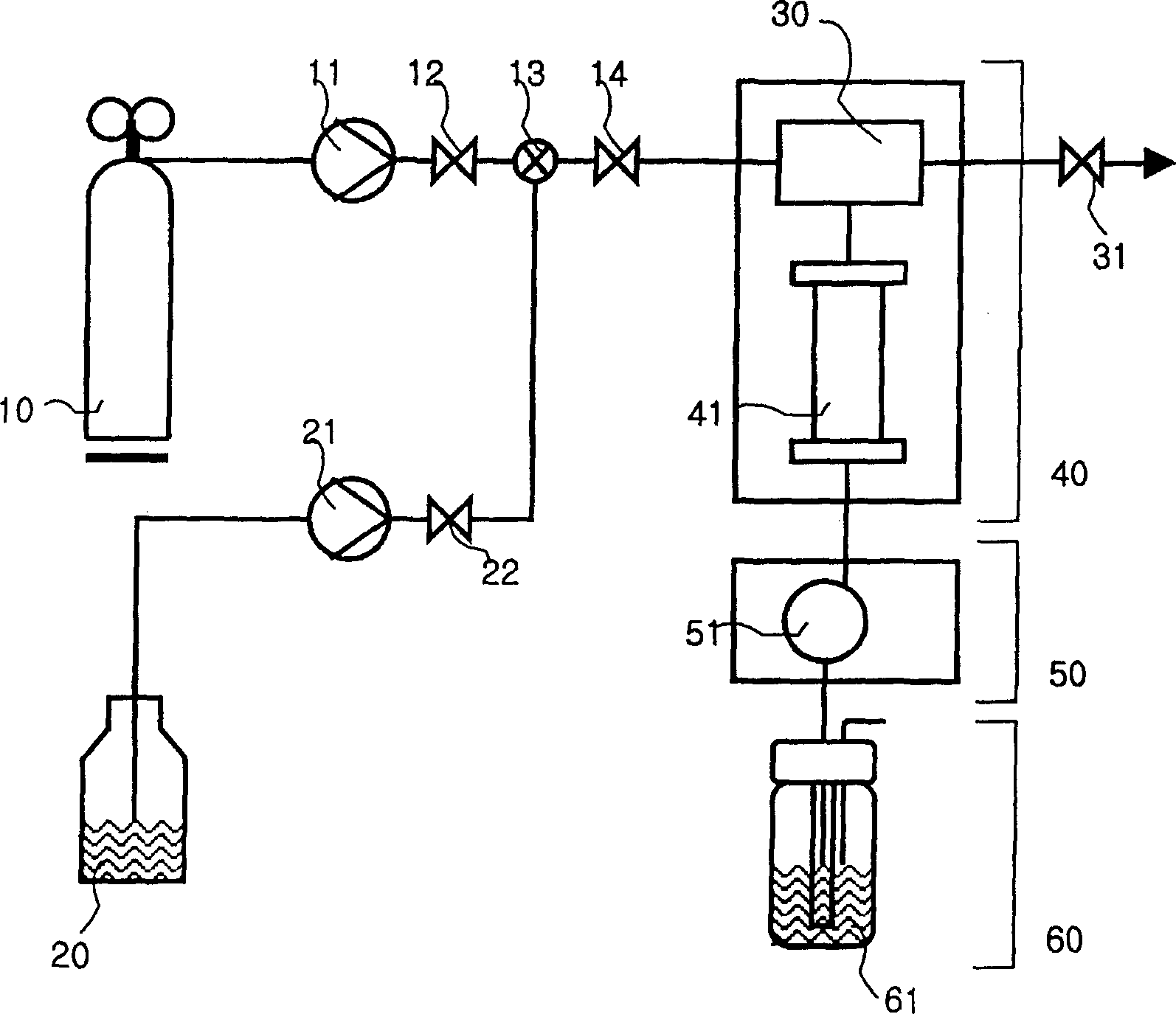
[0140] Paclitaxel was absorbed into cellulose paper and treated with pure supercritical CO 2 or supercritical CO 2 Combination extraction with various co-solvents. The absorption recovery of paclitaxel was determined and is shown in Table 2 below.
[0141] The effect of yew tree matrix on the extraction efficiency of paclitaxel in super...
Embodiment 8
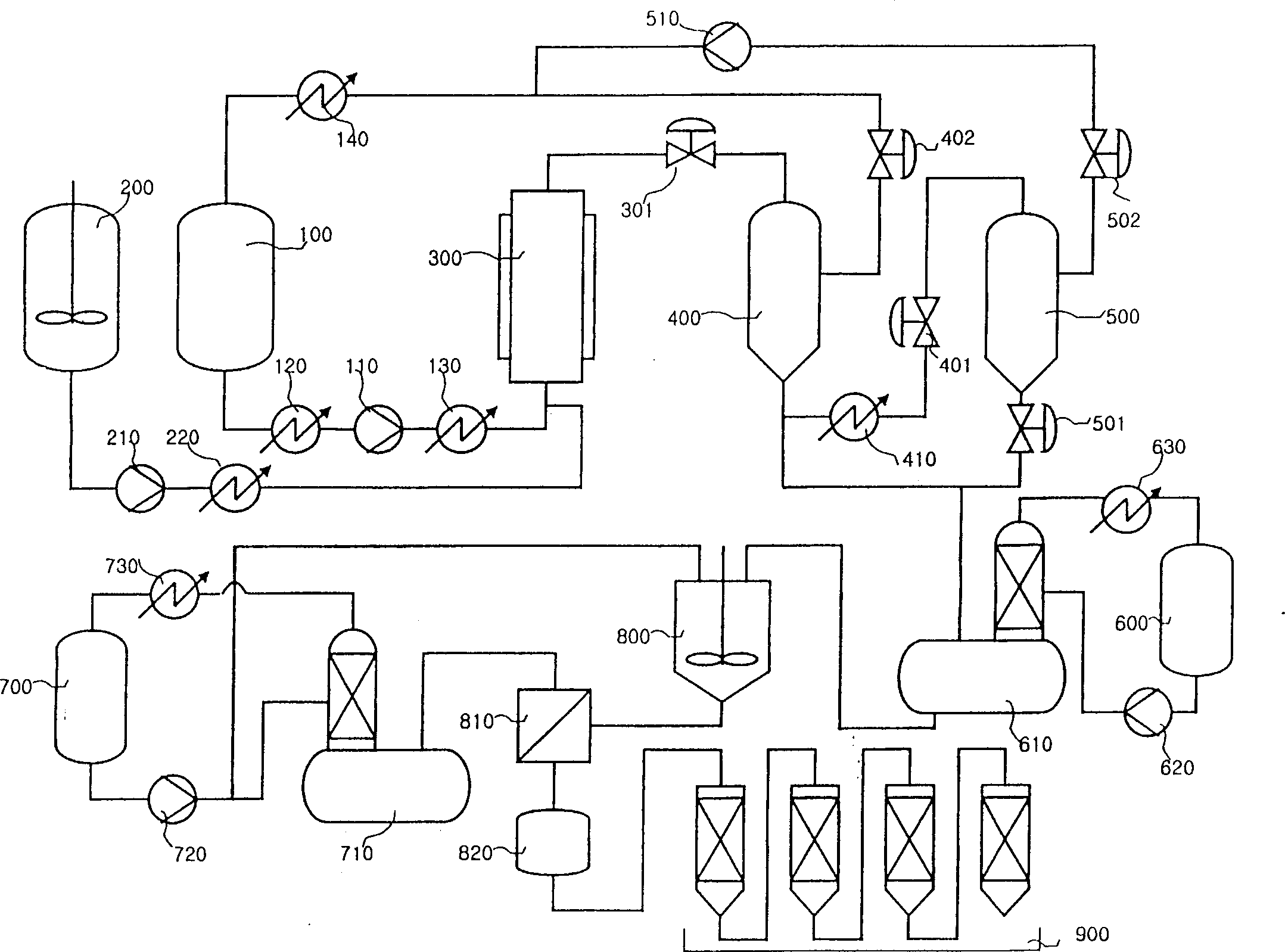
[0173] Example 8 - Extraction of Paclitaxel Using Supercritical Extraction: Paclitaxel was extracted using the supercritical fluid extraction method of the present invention. Extraction conditions were determined as follows: supercritical CO 2 - Ethanol-water = 80:16:4; the flow rate of the supercritical fluid is 40-80 kg / hr; the temperature is 80° C. and the pressure is 350 bar. The conditions were set based on the results of Examples 1-7 above. Samples for yield determination were taken at 20 minute intervals for a total of 6 hours.
[0174] Paclitaxel yield and extract yield are shown in Figure 5 and 6 . Such as Figure 5 and 6 As shown, paclitaxel was not extracted within 1 hour from the start of extraction. This is due to the need for a period of time for the co-solvent to fully contact the raw material and the supercritical CO 2 It takes a while for the co-solvent to pass through the extractor. For example, if the supercritical fluid passes through the extracto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com