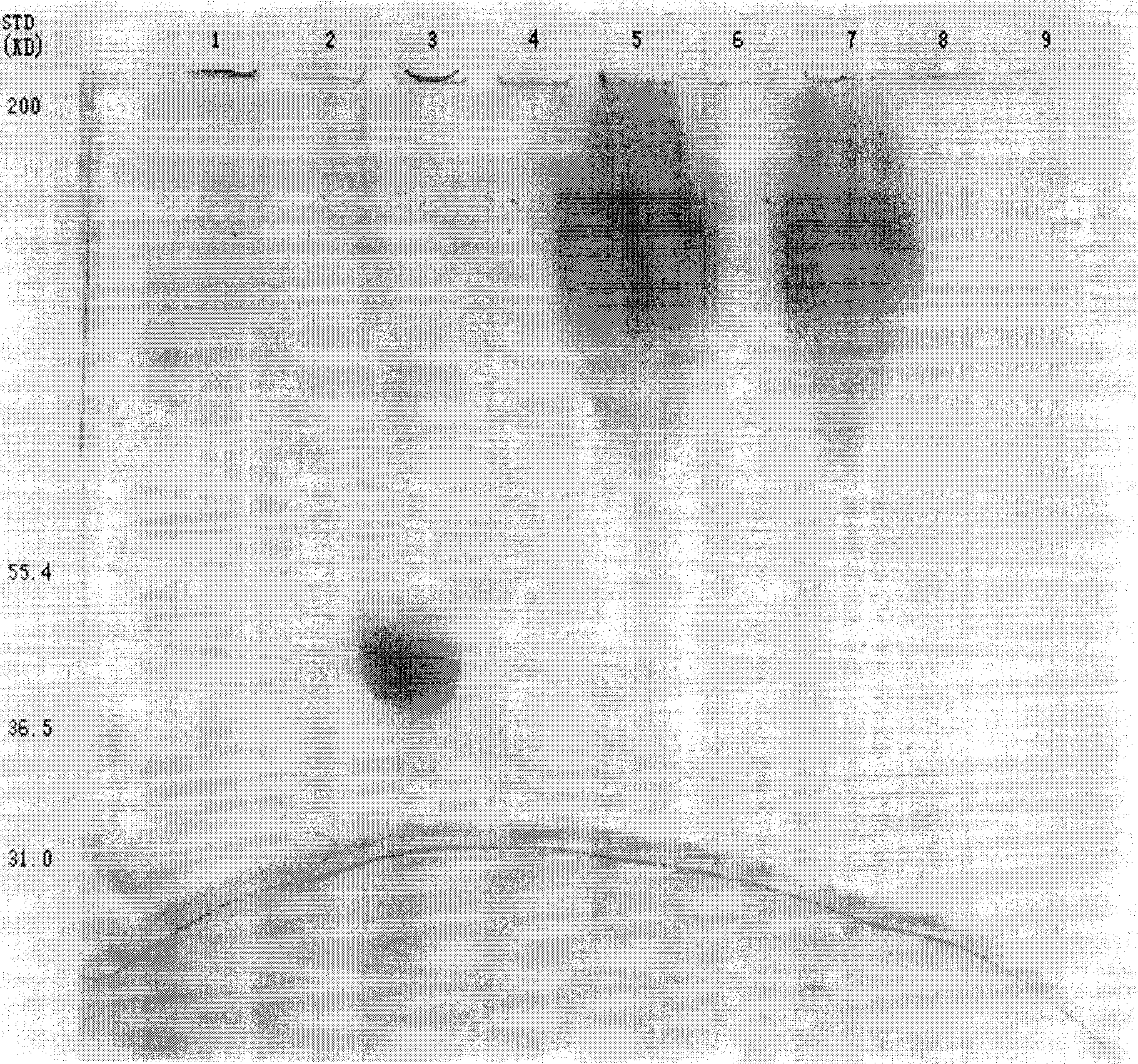Method for preparing elspar modilfied by carbowax
An asparaginase and polyethylene glycol technology, which is applied in the directions of medical preparations, hydrolase, and pharmaceutical formulations containing active ingredients, can solve problems such as loss of therapeutic effect, biological injury, and impact on treatment, and achieve prolonged biological The effect of active half-life, reducing dosage and improving product yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 Preparation of PEG-Asparaginase (PEG-Asparaginase)
[0057] First reaction
[0058] 1. Take 152ml of 0.1M pH 8.5 sodium phosphate buffer in a water bath and preheat it to 25°C, take 0.75 g of asparaginase, and slowly add it to the sodium phosphate buffer to fully dissolve it. Take 3.75 grams of activated polyethylene glycol (SS-PEG5000) with a molecular weight of 5000 and quickly add it to the above solution. Stir appropriately to completely dissolve the activated polyethylene glycol (SS-PEG5000) within 30 seconds, while avoiding a large number of bubbles. . At this time, the dosage ratio of asparaginase to polyethylene glycol is 1:5 (w / w). The reaction is carried out at 25°C for 30 minutes. After the reaction solution is concentrated and washed, it can be further purified or subjected to the second step reaction.
[0059] 2. The concentrated washing of polyethylene glycol-asparaginase reaction solution utilizes a hollow fiber separation column. First, use a peris...
experiment example 1
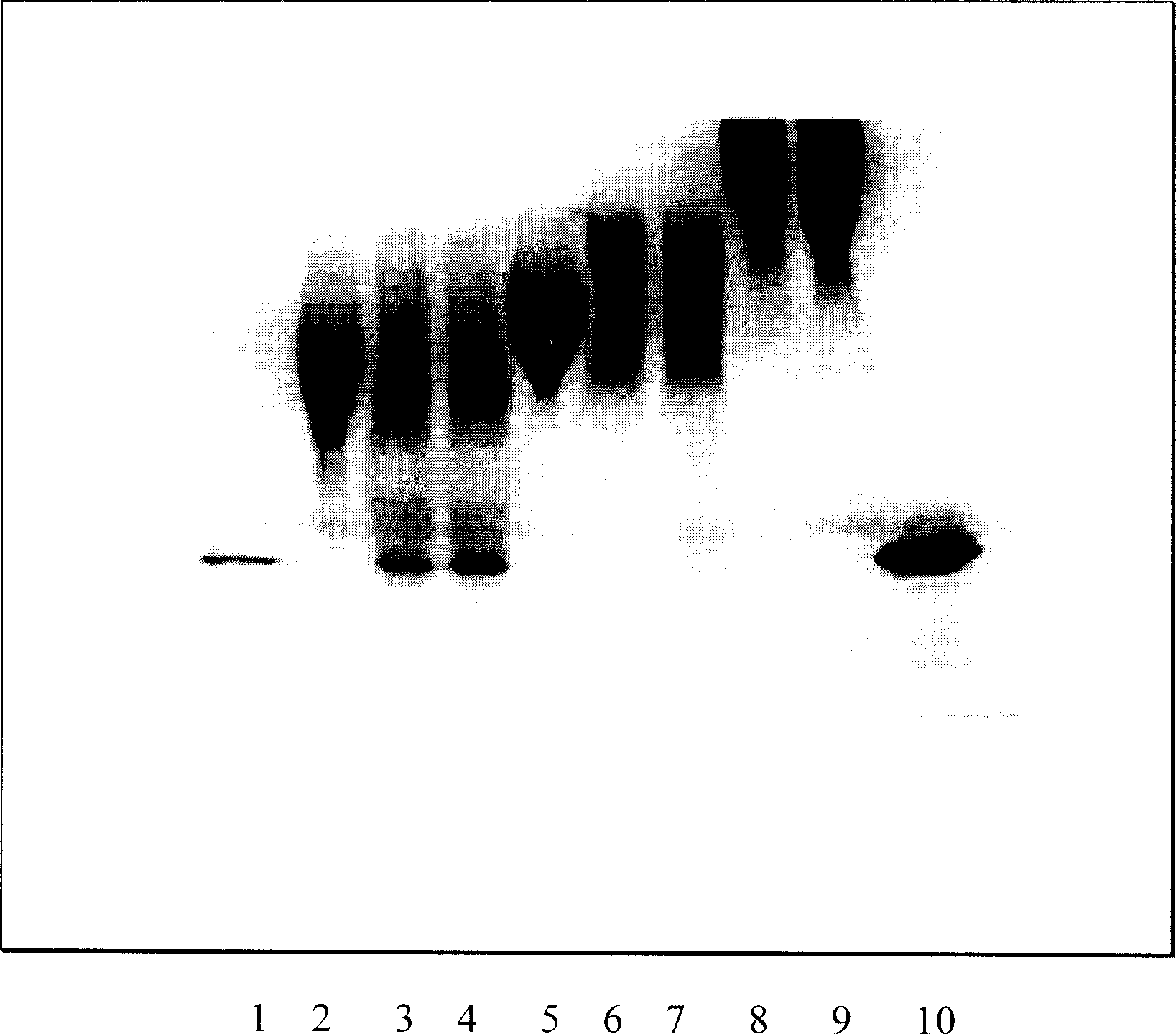
[0062] Experimental example 1 Analysis method Protein concentration analysis
[0063] Method 1: The Bradford-Lowry method was used to determine the protein concentration. The method is based on different concentrations of protein combined with the protein dye Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The data is also different. First, draw a standard curve based on the amount of dye bound to standard proteins of different concentrations known, and infer the protein sample concentration by measuring the amount of dye bound to the protein.
[0064] Method 2: Take the test solution for enzyme activity determination, and measure the absorbance at 280±1nm and 260±1nm wavelength according to the spectrophotometric method (Chinese Pharmacopoeia 1995 Edition Two Appendix), and calculate the content per ml by the following formula The number of milligrams of protein.
[0065] Protein content (mg / ml) = 1.55×D 280nm -0.76×D 260nm
experiment example 2
[0066] Experimental example 2 Protein purity analysis
[0067]Biological macromolecules, such as proteins, enzymes, peptides, amino acids, etc., have different moving directions and mobilities under the same electric field due to their different charged properties. Highly charged and low molecular weight, the electrophoresis speed is fast, so by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, different molecular weights, different types of proteins and other biological macromolecules can be separated. While determining whether the contaminated protein exists, it can also determine the purity of the unknown protein and the size of the protein molecule.
[0068] Asparaginase-polyethylene glycol activity determination
[0069] Use the Mashburn Wriston method. This method determines the rate of hydrolysis of the substrate by Asparaginase by measuring the concentration of amino acids in the product, and the amount of ammonia produced is determined by the color reaction between Nessler reagen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com