Membrane electrode assembly, manufacturing process therefor and direct type fuel cell therewith
A membrane electrode assembly, fuel electrode technology, applied in solid electrolyte fuel cells, fuel cells, fuel cell parts and other directions, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory effects, reduced proton activity, and unsustainable electrolyte membranes. Satisfactory proton conductivity, improved proton conductivity, and the effect of preventing overflow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The porous membrane used is a hydrophilic PTFE porous membrane with a membrane thickness of 25 μm.
[0052] The aqueous monomer solution used as the raw material solution for the proton conductive polymer was passed through 6 g of acrylamide-tert-butylsulfonic acid as the monomer, 0.02 g of 2,2'-azobis-(2- Amidinopropane) dihydrogen chloride and 5 grams of water were mixed.
[0053] The porous membrane was immersed in the monomer aqueous solution for 2 minutes, and the monomer aqueous solution was injected into the micropores of the porous membrane. The film was polymerized at 60°C for 2 hours and then dried. Next, the membrane was washed by immersion in warm water at 60°C to remove unpolymerized material and oligomerized products. The above-mentioned injection, polymerization and washing processes were repeated twice.
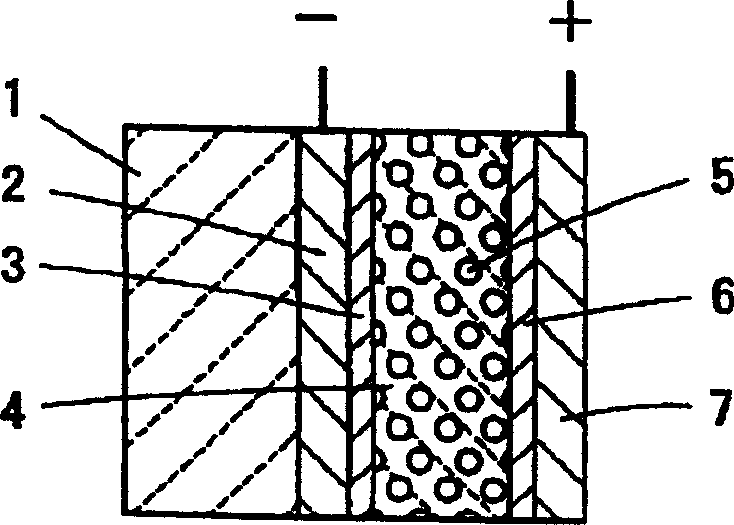
[0054] A 60% PTFE dispersion was applied to one side of the resulting electrolyte membrane so that the resulting membrane had a thickness of 1 μm fr...
Embodiment 2
[0060] MEA was prepared as described in Example 1 except that no hydrophilic material layer was formed in the electrolyte membrane.
Embodiment 3
[0062] MEA was prepared as described in Example 1 except that no hydrophobic material layer was formed in the electrolyte membrane.
[0063] conventional embodiment
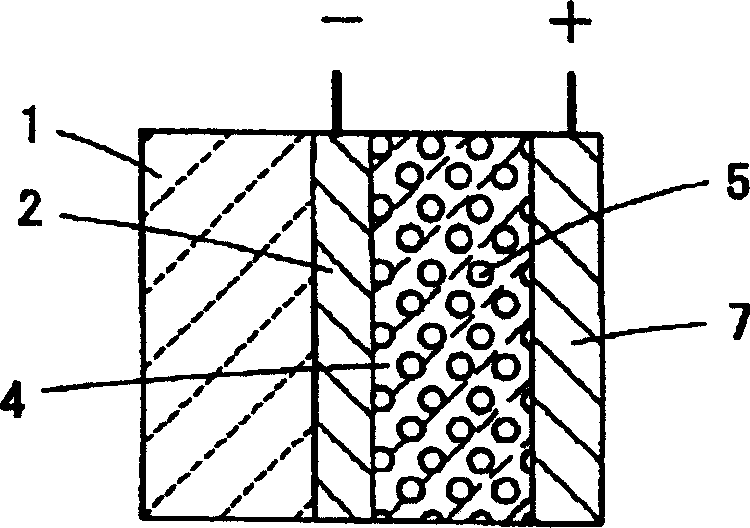
[0064] MEA was prepared as described in Example 1 except that no hydrophobic and hydrophilic material layers were formed in the electrolyte membrane. it corresponds to figure 2 Conventional example shown.
[0065] Each of the MEAs of Examples 1 to 3 and Conventional Example was used to form a unit cell configured such that a 10% by volume aqueous methanol solution was fed to a fuel electrode without pressure, and air was brought into contact with the air electrode at atmospheric pressure. Its electrical properties were evaluated by measuring the output value and discharge time at 25°C and 5°C. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0066] at 25°C maximum
Output
(mW / cm 2 )
Maximum output at 5°C
Output (mW / cm 2 )
put at 5°C
electricity time
Example 1
28
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com