2D photoelectric auto collimation equipment and measuring method based on dynamic differential compensation process
A differential compensation and dynamic technology, applied in the direction of optical devices, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of poor measurement stability and repeatability of photoelectric autocollimators, difficulty in further improving measurement uncertainty, and limitations of photoelectric autocollimation In order to simplify the measurement process and data processing, improve measurement stability and repeatability, and meet the needs of high-precision two-dimensional small-angle measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
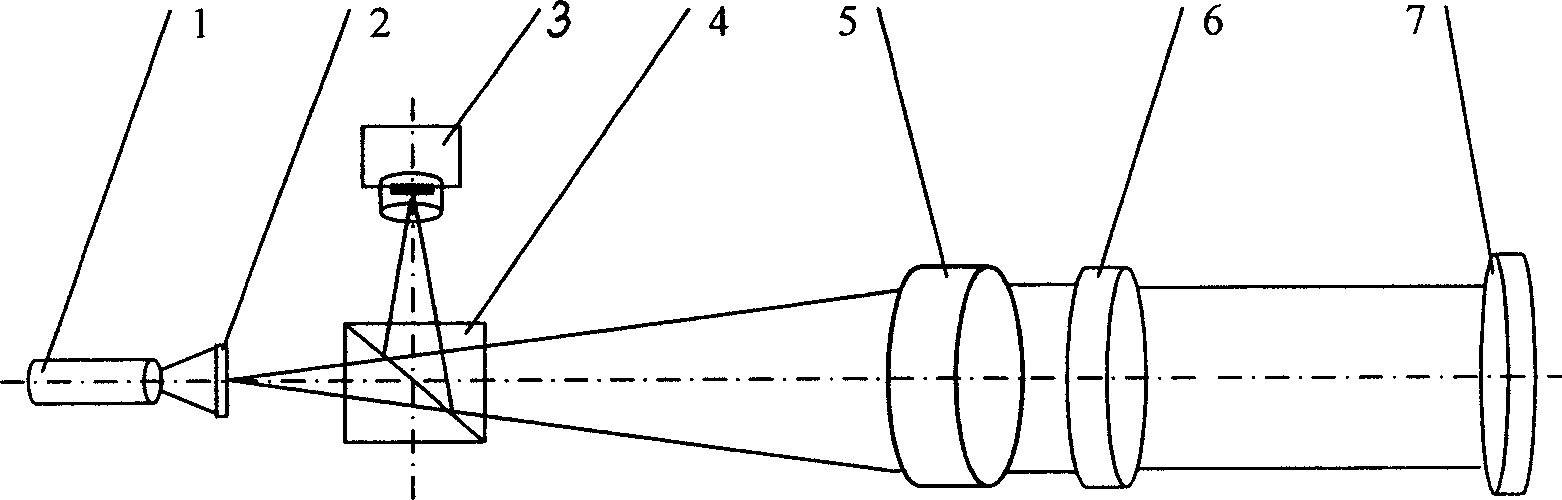
[0070] Such as figure 1 As shown, the spectroscopic lens 6 is firstly adjusted so that the reference spot 13 received on the CCD image sensor 3 is completely separated from the measurement spot 12, so as to avoid the light spot received on the CCD image sensor 3 due to overlapping of the measuring beam 11 and the reference beam 10. For the problem that the center cannot be positioned accurately, the spectroscopic lens 6 should be fixed after the adjustment, and then the device should be calibrated. After calibration, the spectroscopic lens 6 should not be adjusted during use of the device. When measuring, light source 1 adopts laser 17, and the light beam that sends illuminates the etched part 19 light-transmitting reticle 20 that is positioned at the focal point of collimating objective lens 5, and after passing through dichroic prism 4, the transmitted light beam passes through collimating objective lens 5 and becomes The parallel collimated light beam is incident on the bea...
Embodiment 2
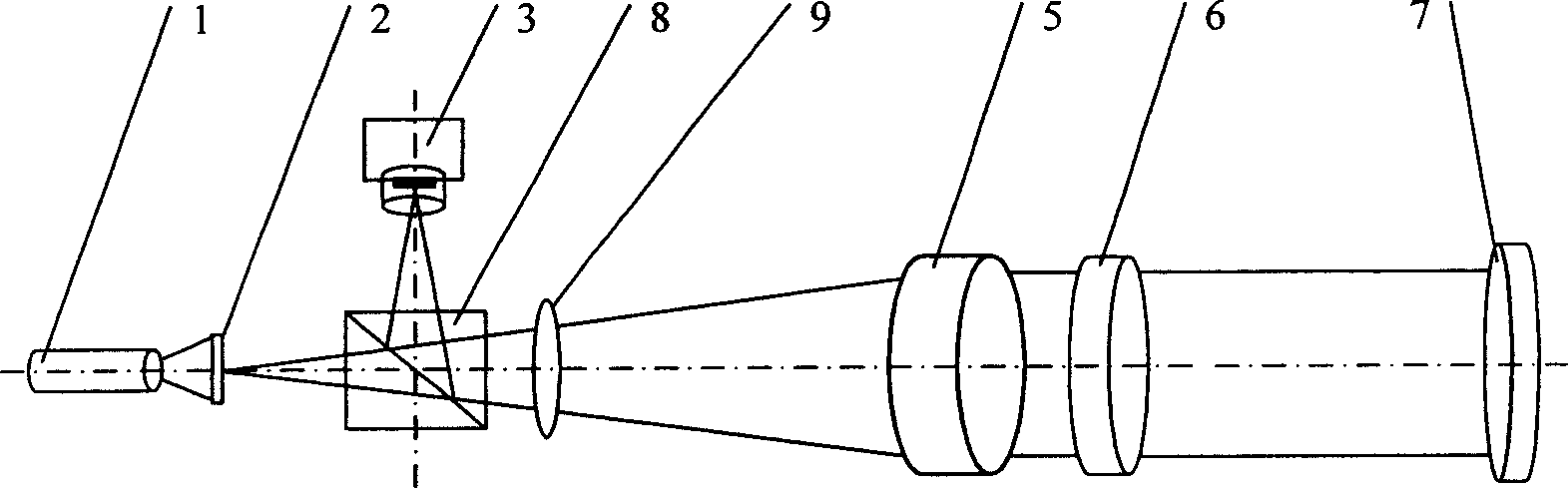
[0075] Such as figure 2 As shown, using polarized light to achieve the purpose of reducing light energy loss, firstly adjust the spectroscopic lens 6 so that the reference spot 13 received on the CCD image sensor 3 and the measurement spot 12 are completely separated, avoiding the measurement beam 11 and the reference beam 10 due to The overlap of light beams leads to the problem that the light spots received on the CCD image sensor 3 cannot be accurately positioned. After the adjustment, the spectroscopic lens 6 should be fixed, and then the device should be calibrated. After calibration, the spectroscopic lens 6 should not be adjusted during use of the device. During measurement, light source 1 adopts laser 17, and the light beam that sends illuminates the etched portion 19 light-transmitting reticle 20 that is positioned at the focal point of collimating objective lens 5, and the light beam becomes polarized light after passing through polarization beam splitter prism 8, an...
Embodiment 3
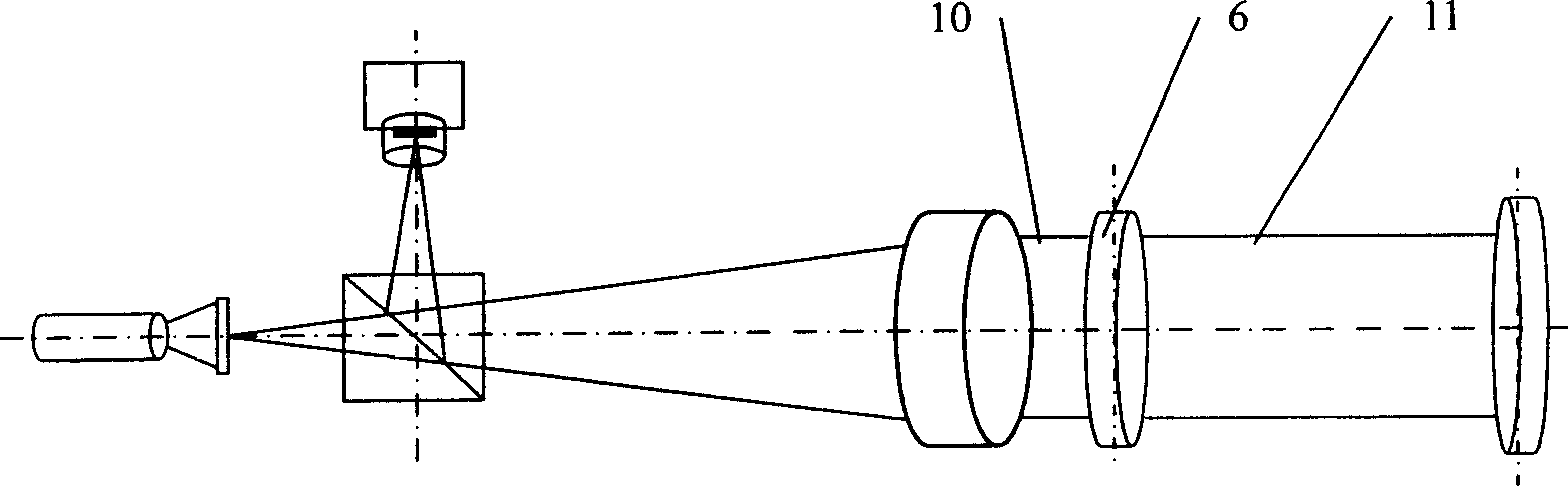
[0080] Such as figure 1 As shown, light source 1 adopts light-emitting diode (LED) 18, and the light beam that sends illuminates the etched portion 19 light-transmitting reticle 20 that is positioned at the focal point of collimating objective lens 5, and other parts and working principle of the present embodiment are all the same as Example 1 is the same.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com