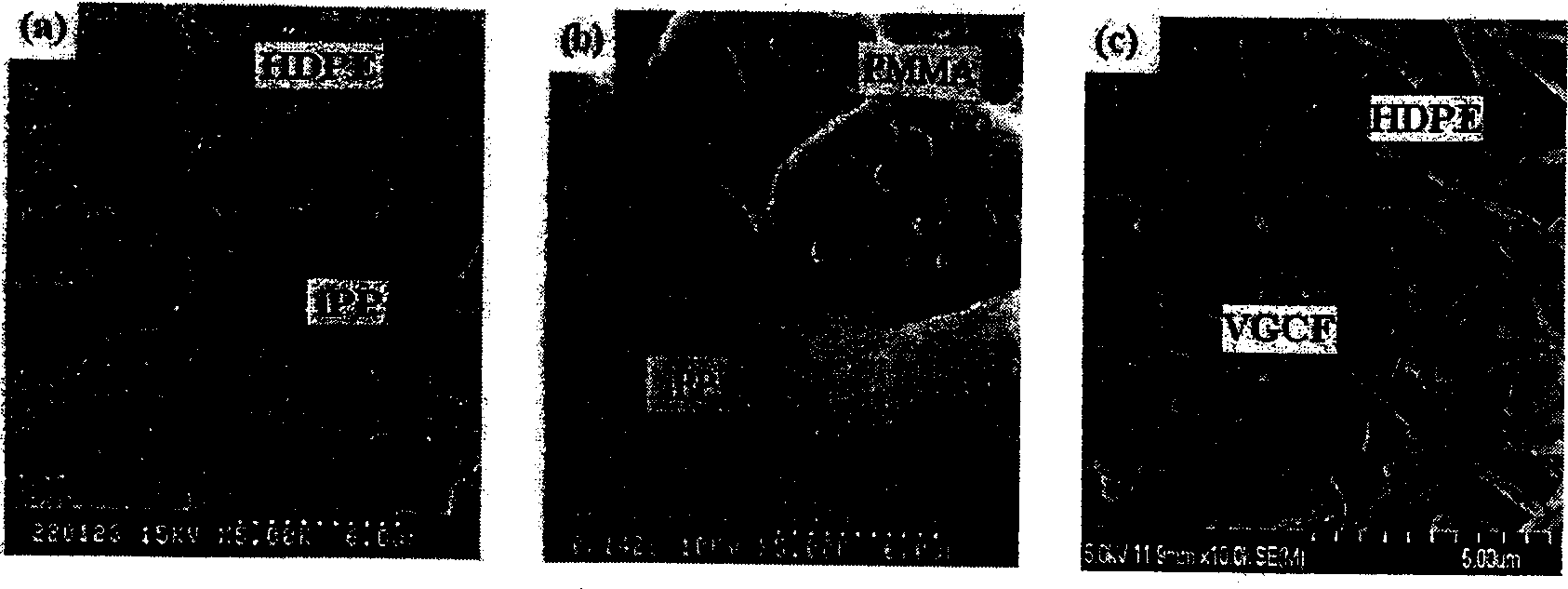Electromagnetic wave absorbing material
A technology for absorbing materials and electromagnetic waves, applied in electrical components, magnetic field/electric field shielding, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in taking into account wave impedance matching, lack of electromagnetic wave absorbers, etc., to prevent electromagnetic wave pollution, wide application prospects, The effect of good absorbing properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Materials used in this embodiment: high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and isotactic polypropylene (iPP) are selected as the polymer, and conductive carbon black (CB) is selected as the electromagnetic wave absorber.
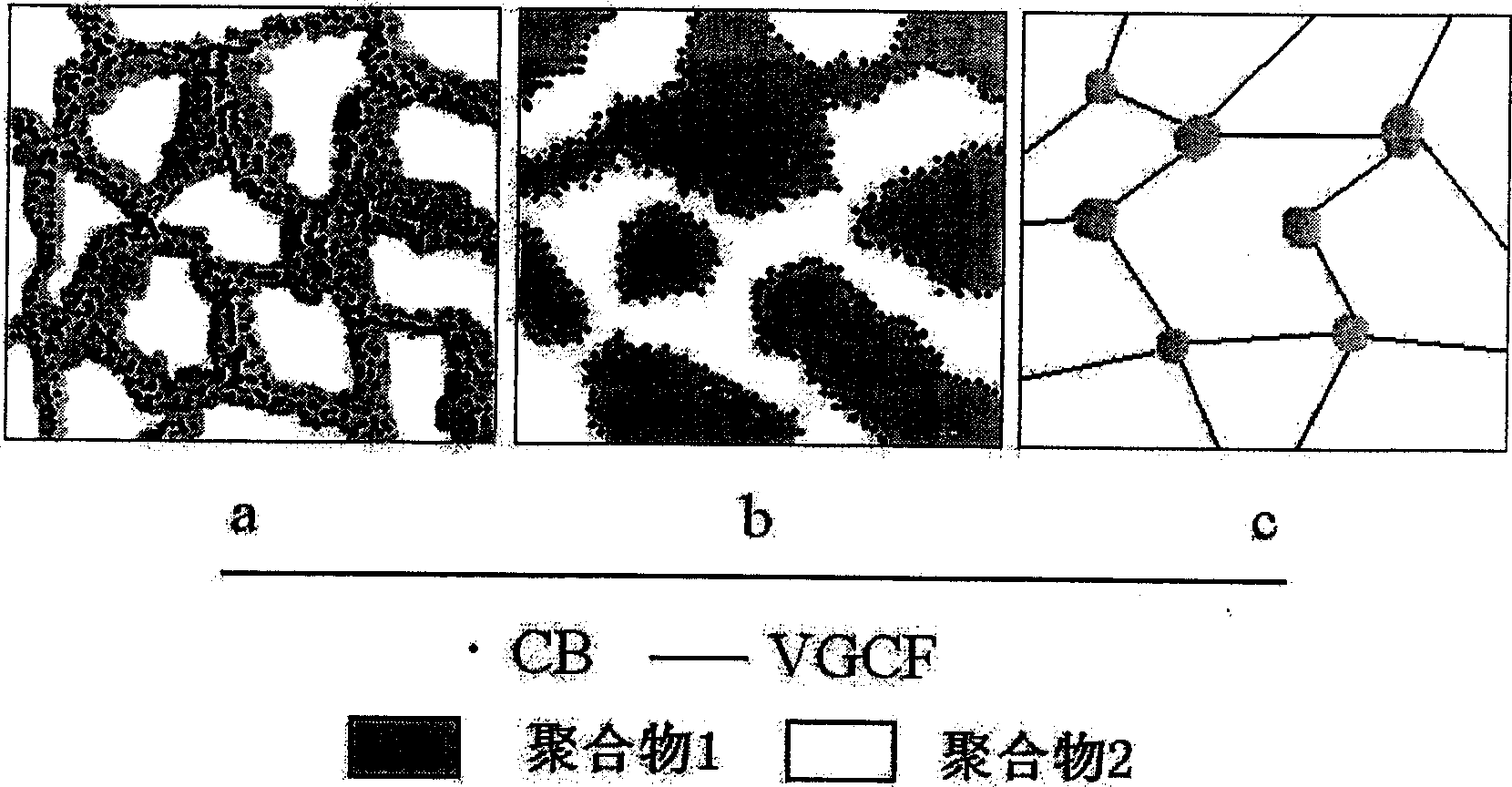
[0021] First use a two-roll mill, knead 50g of HDPE and 50g of iPP at 160°C for 5 minutes, then add 5g of CB and knead for 5 minutes, then mold at a pressure of 19.6MPa for 5 minutes, and then quench into water , to obtain a wave-absorbing sheet with a thickness of 2 mm. The phase structure of the material is as figure 1 as shown in a. From SEM figure 2 As can be seen from a, CB is selectively enriched in the HDPE phase.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Materials used in this embodiment: polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and isotactic polypropylene (iPP) are selected as polymers, and conductive carbon black (CB) is selected as electromagnetic wave absorber.
[0024] First use a two-roll mill, knead 50g of PMMA and 50g of iPP at 180°C for 5 minutes, then add 5g of CB and knead for 5 minutes, then mold at a pressure of 19.6MPa for 5 minutes, and then quench into water , to obtain a wave-absorbing sheet with a thickness of 2 mm. The phase structure of the material is as figure 1 as shown in b. From SEM figure 2 It can be seen from b that CB is selectively enriched at the interface of PMMA and iPP.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Materials used in this embodiment: high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) are selected as polymers, and vapor grown carbon fibers (VGCF) are selected as electromagnetic wave absorbers. First use a two-roll mill, knead 5g of HDPE and 95g of PMMA at 180°C for 5 minutes, then add 5g of VGCF and knead for 5 minutes, then mold at a pressure of 19.6MPa for 5 minutes, and then quench into water , to obtain a wave-absorbing sheet with a thickness of 2 mm. In order to obtain a clear picture of the phase structure, the sample was extracted with chloroform for 72 hours, and the PMMA was dissolved to obtain a mixture of HDPE / VGCF. The phase structure of the material is as figure 1 as shown in c. From SEM figure 2 It can be seen from c that HDPE bonds VGCF together like a "rivet" to form a network frame structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com