Optical fibre wave conducting type optical submodule
An optical sub-module and optical fiber waveguide technology, which is applied in the coupling of optical waveguide and optical fiber transmission, etc., can solve the problems of low coupling light alignment tolerance, long free space coupling distance, and low coupling efficiency, so as to achieve ample coupling Alignment tolerance, reduction of optical transmission dispersion, and improvement of optical output power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
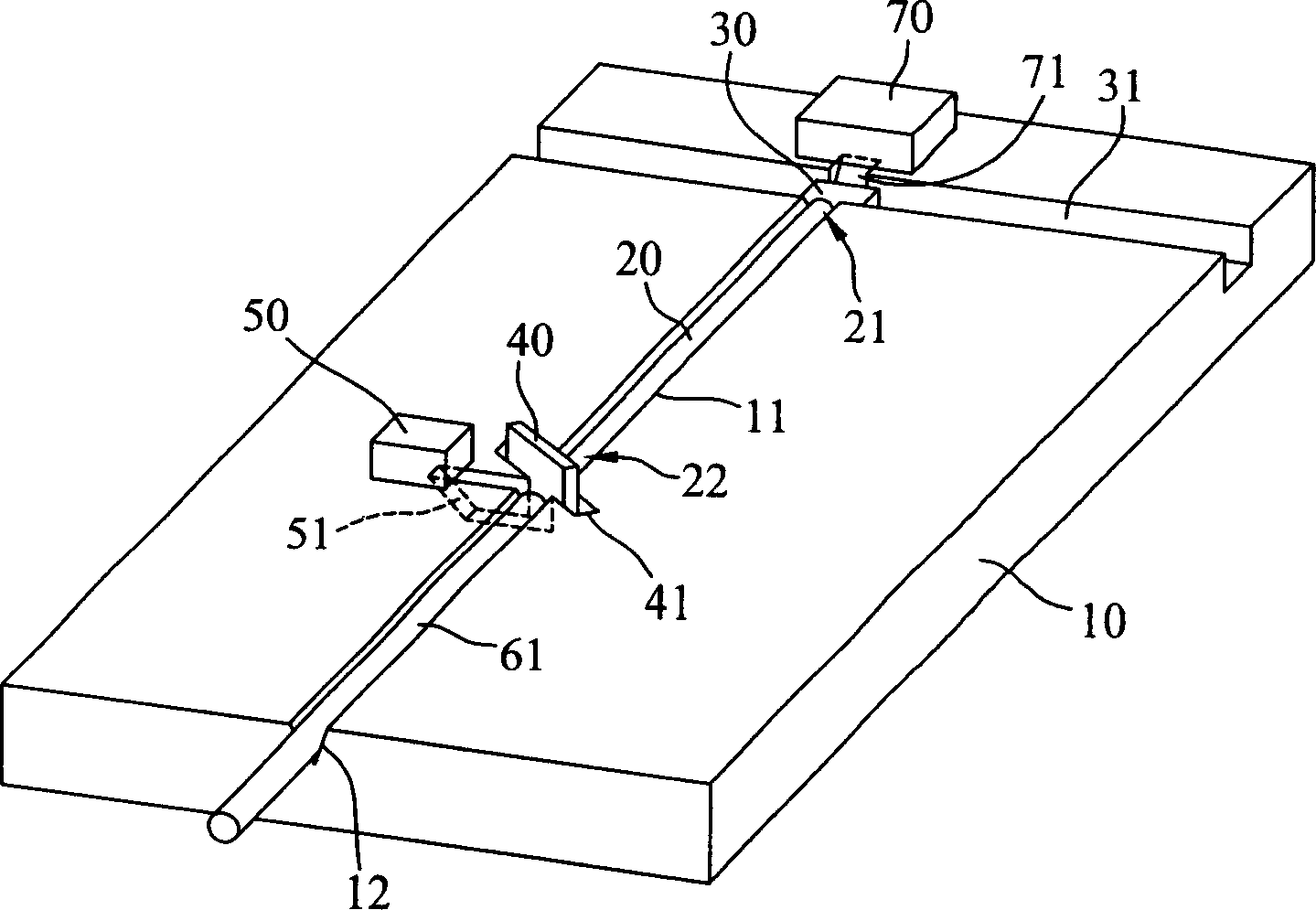
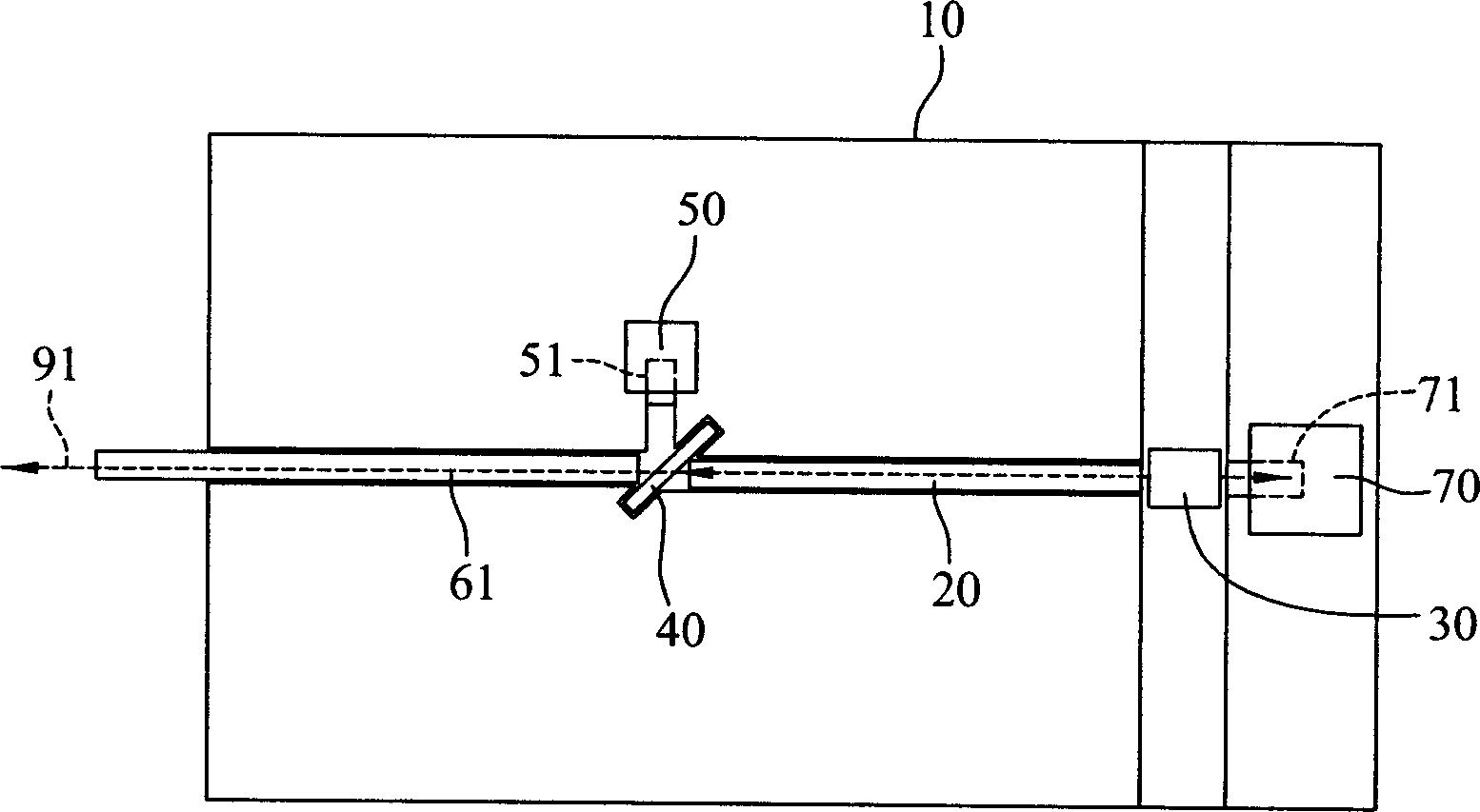
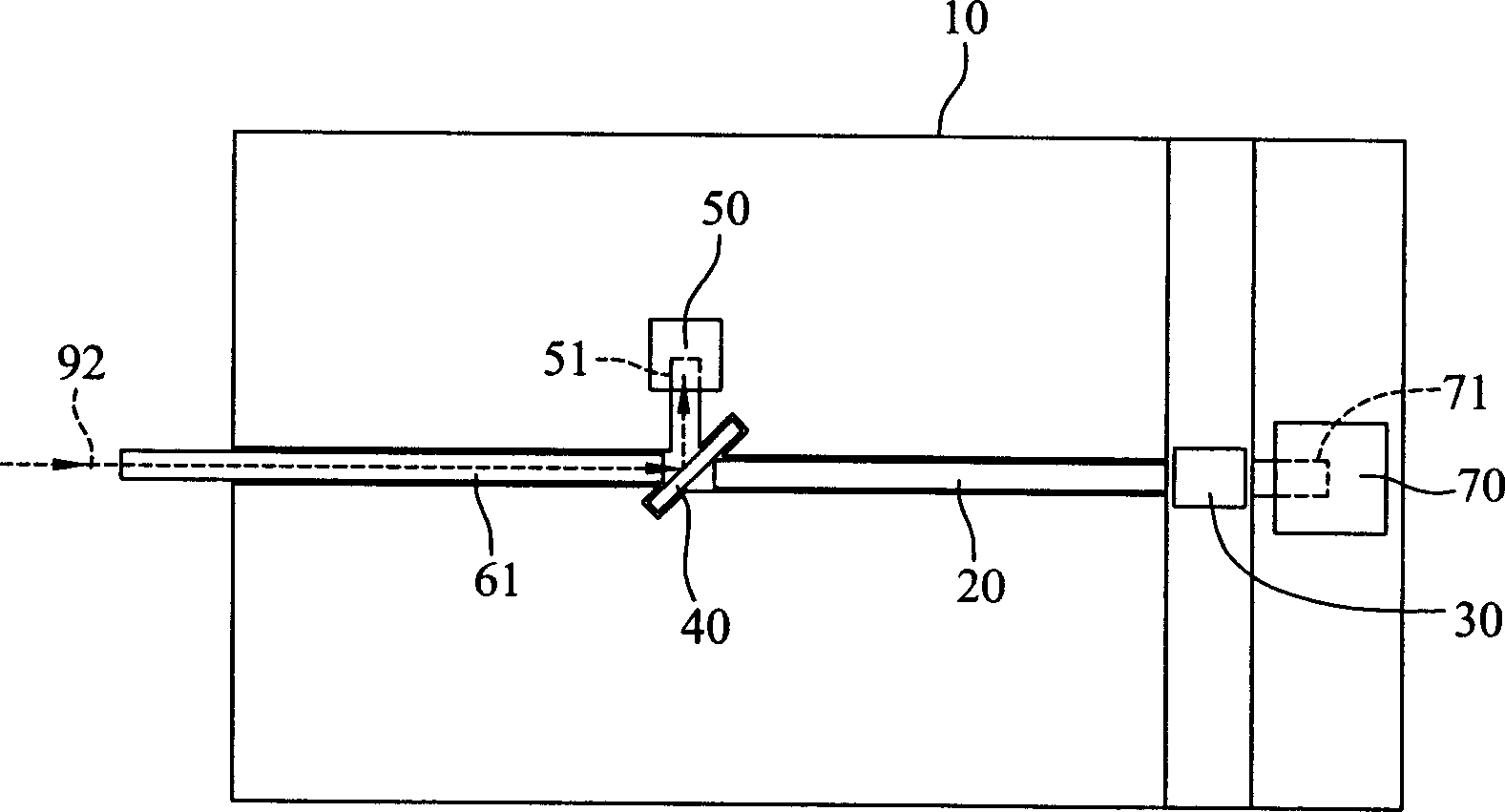
[0063] For the first embodiment of the dual-frequency optical sub-module disclosed in the present invention, please refer to figure 1 , including an optical table 10, a light emitter 30, a multimode fiber 20, a beam splitter 40, a light detector 50, and a single-mode fiber 61. The optical table 10 has two grooves 11, 12, a light emitter positioning groove 31, and a light splitter The positioning groove 41 is used to carry all optical components. The multimode optical fiber 20 has a front end 21 and an end 22 opposite to each other. The front end 21 of 20 is coupled to the light emitter 30, and the optical splitter 40 is installed in the positioning groove 41 of the optical splitter, and is joined with the rear end 22 of the multimode optical fiber 20, while the single mode optical fiber 61 is arranged in the groove 12, It is connected with the beam splitter 40 and communicated with the outside, and the photodetector 50 is arranged adjacent to the beam splitter 40 .
[0064] W...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com