Digital map position information compressing method and device
A technology of digital map and location information, applied in the directions of vehicle location indication, map/plan/chart, image coding, etc., can solve the problems of reducing data compression coefficient, hindering the accurate transmission of road shape, and the shape of the receiver deviates from the original shape, etc. achieve the effect of increasing the compression factor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
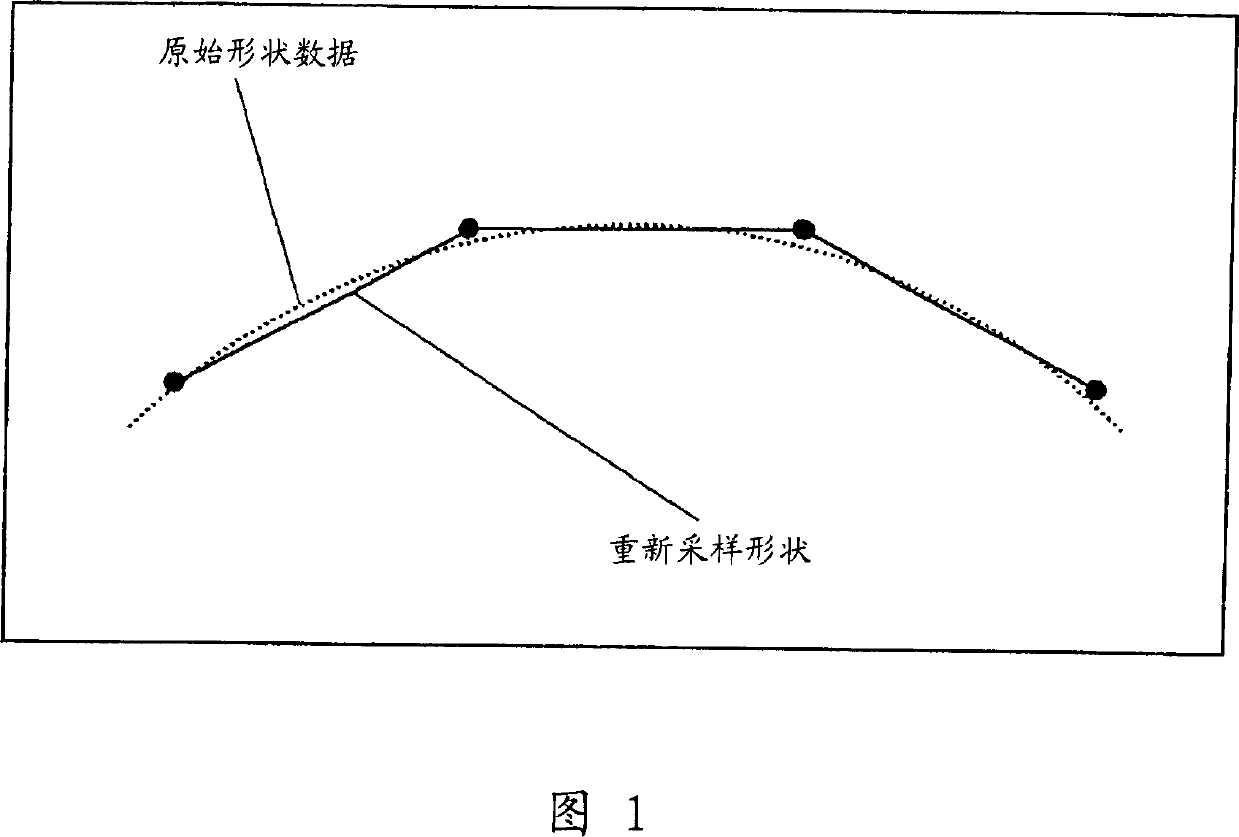
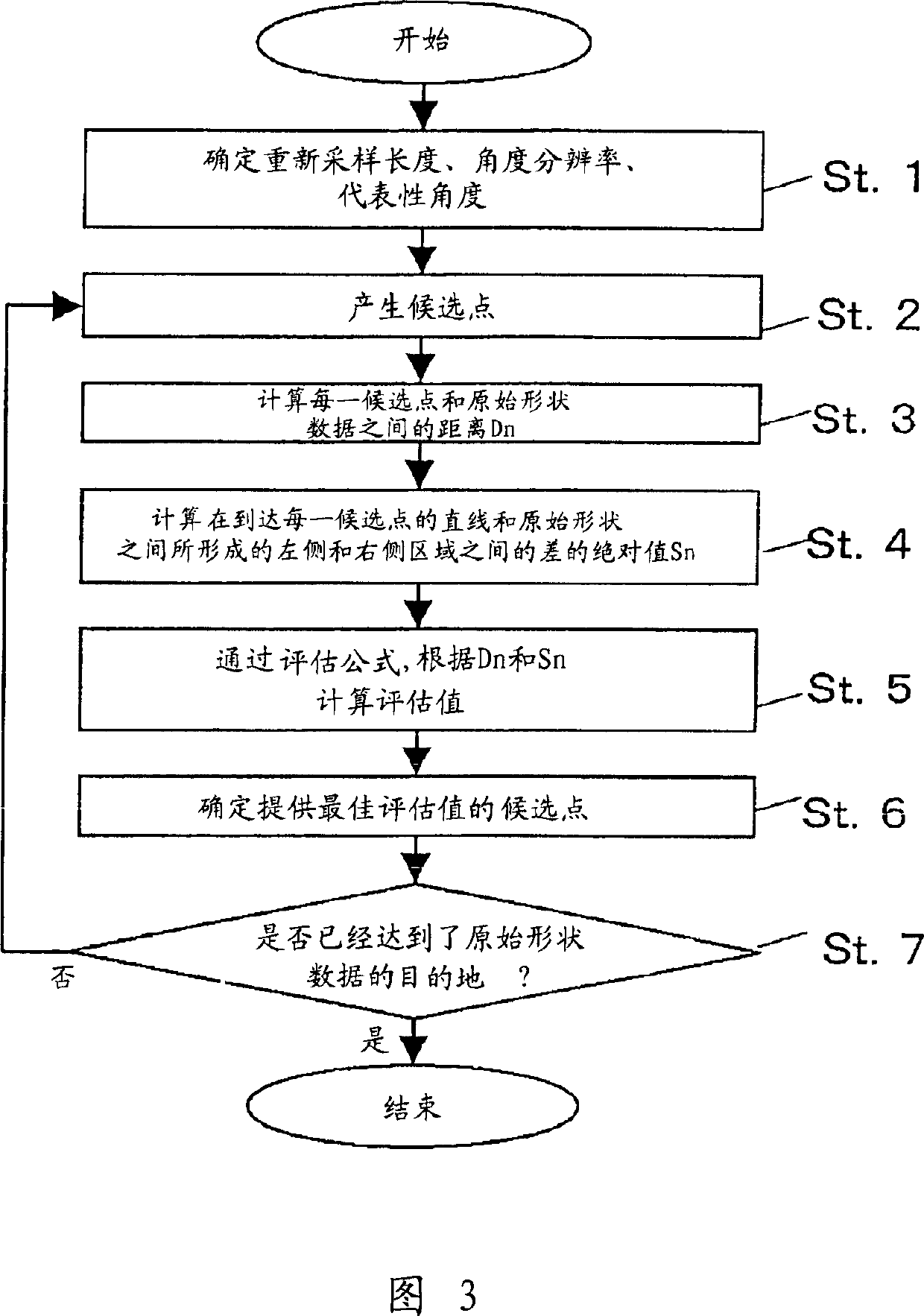
[0106] In the resampling method according to the first embodiment of the present invention, sampling points are set by paying attention to a region between a straight line linking the sampling points and the original shape.
[0107] In the process of resampling the shape of a road, equidistant resampling is performed on the target road after the resampling length L and the angular resolution (ie, the unit of quantization representing the position data of sampling points by angle) δ are determined.
[0108] When a curved road with a large curvature or a road in a mountainous area in which many such curved roads exist is the object of resampling, the resampling length L is set to be short, and when a straight road with a small curvature or in which many such curved roads exist When the road in the urban area of the straight road is the target of resampling, set the resampling length L to long. For example, as shown in FIG. 4 , the resampling length L1 for equidistantly resampl...
no. 2 example
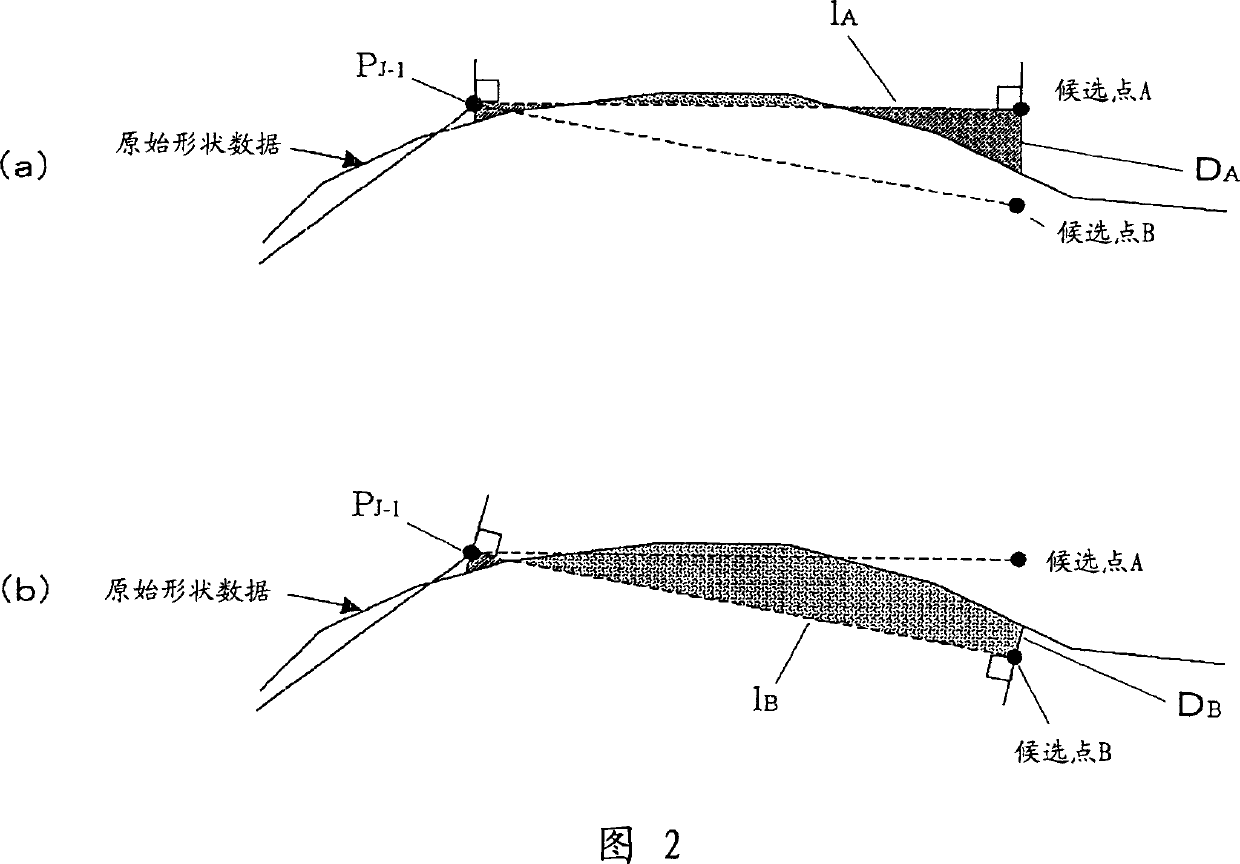
[0128] In the resampling method according to the second embodiment of the present invention, in the process of setting the sampling points, the lengths of the line segments of the original shape located on the left and right sides of the resampled shape are considered instead of the area.
[0129] In this resampling method, the process performed before setting candidates for sampling points is the same as the process performed before setting candidates for sampling points in the first embodiment. When the setting of a plurality of candidate points has been completed, as shown in FIG. In the case where the length of the line segment becomes the original shape on the left and right sides, sampling points are selected from the candidate points thus set.
[0130] When such a case occurs, the following formula (2) is used as the evaluation formula, and the candidate point providing the minimum evaluation value is used as the sampling point PJ.
[0131] Evaluation value of candidat...
no. 3 example
[0144] In the resampling method according to the third embodiment of the present invention, sampling points are set in consideration of the maximum error between the resampled shape and the original shape.
[0145] In this resampling method, the process performed before setting candidates for sampling points is the same as the process performed before setting candidates for sampling points in the first embodiment. When the setting of a plurality of candidate points has been completed, as shown in FIG. In the case of a balance between the maximum errors on both sides (that is, the maximum distance from the straight lines 1A, 1B to the shape data), sampling points are selected from the candidate points thus set.
[0146] When such a case occurs, the following formula (3) is used as the evaluation formula, and the candidate point providing the minimum evaluation value is used as the sampling point PJ.
[0147] Evaluation value of candidate point n=αDn+β(|Enr-Enl|) (3),
[0148]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com