Method for measuring gallium-manganese-arsenic-iron magnetic transition temperature of rare-magnetic semiconductor without magnetic field
A technology of dilute magnetic semiconductor and transition temperature, applied in measuring devices, material analysis through electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of expensive and time-consuming, cumbersome derivation process, etc., and achieve the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
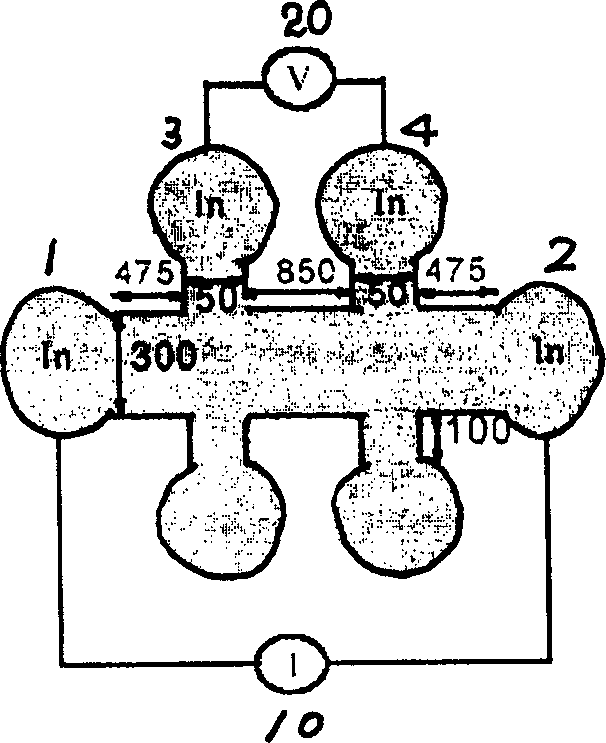
[0018] The method capable of realizing the object of the above invention includes a position closed-cycle refrigerator, a constant current source, a voltmeter, and (Ga, Mn)As samples etched into the shape of a Hall element.
[0019] The present invention is a method for determining the ferromagnetic transition temperature of the dilute magnetic semiconductor gallium manganese arsenic by measuring transport properties, comprising the following steps:
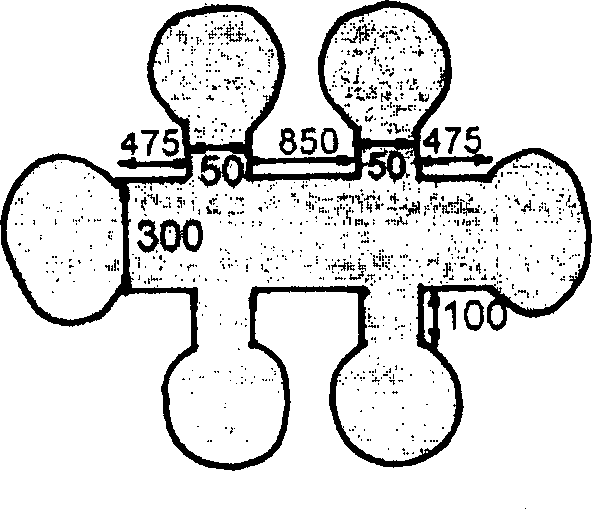
[0020] Step 1: Etching the gallium manganese arsenic sample into the shape of a Hall element, using indium pressure welding technology to make electrodes, which are connected to a constant current source and a voltmeter;
[0021] Step 2: Put the Hall element described in step 1 into a closed-cycle refrigeration system, and the temperature range of the closed-cycle refrigeration system is 10K-300K;
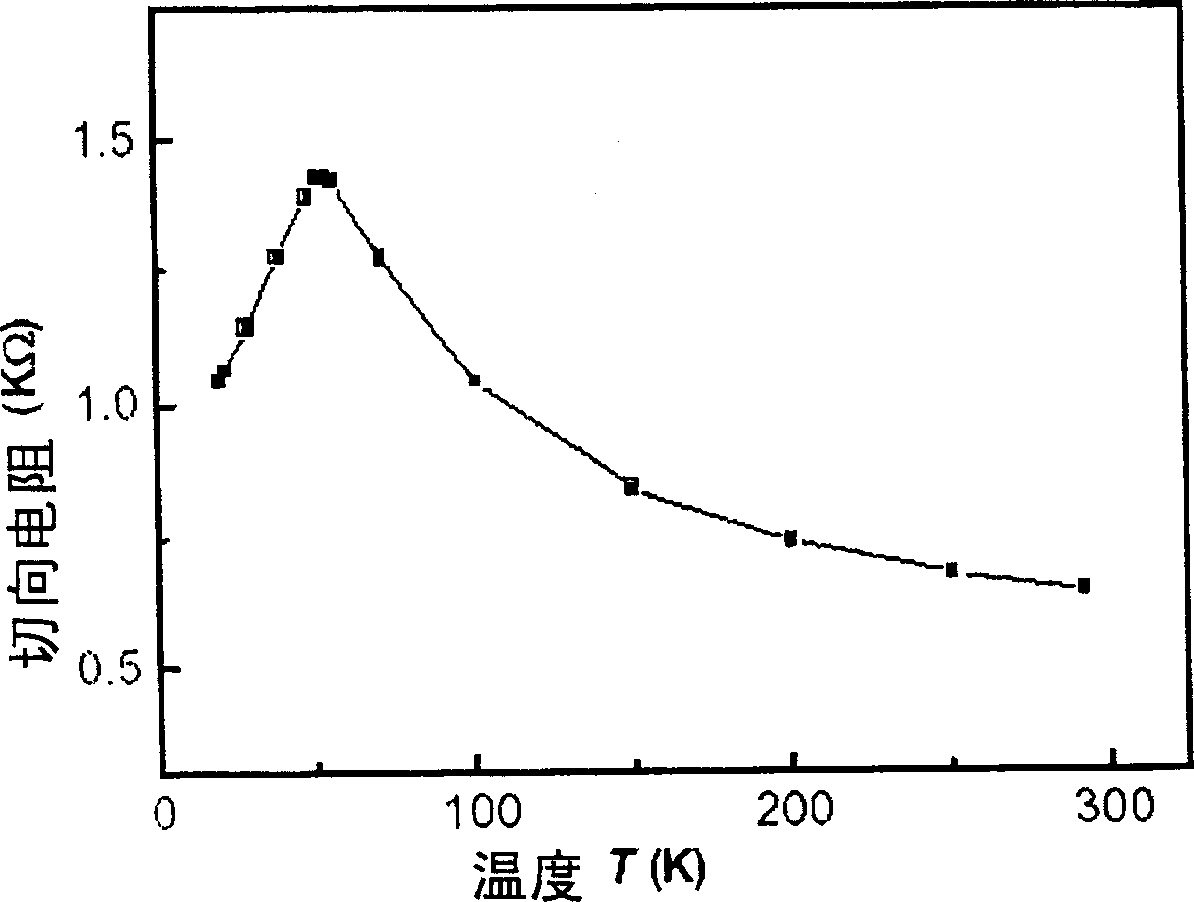
[0022] Step 3: Measure the relationship curve between the tangential resistance of the Hall element and the temperature, determine t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com