Method for using a refrigeration system to remove waste heat from an ultrasound transducer
An ultrasonic transducer and transducer technology, applied in the direction of household refrigeration equipment, machine operation mode, refrigerator, etc., can solve the problems of practical methods for transferring fluid into/out of the system, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
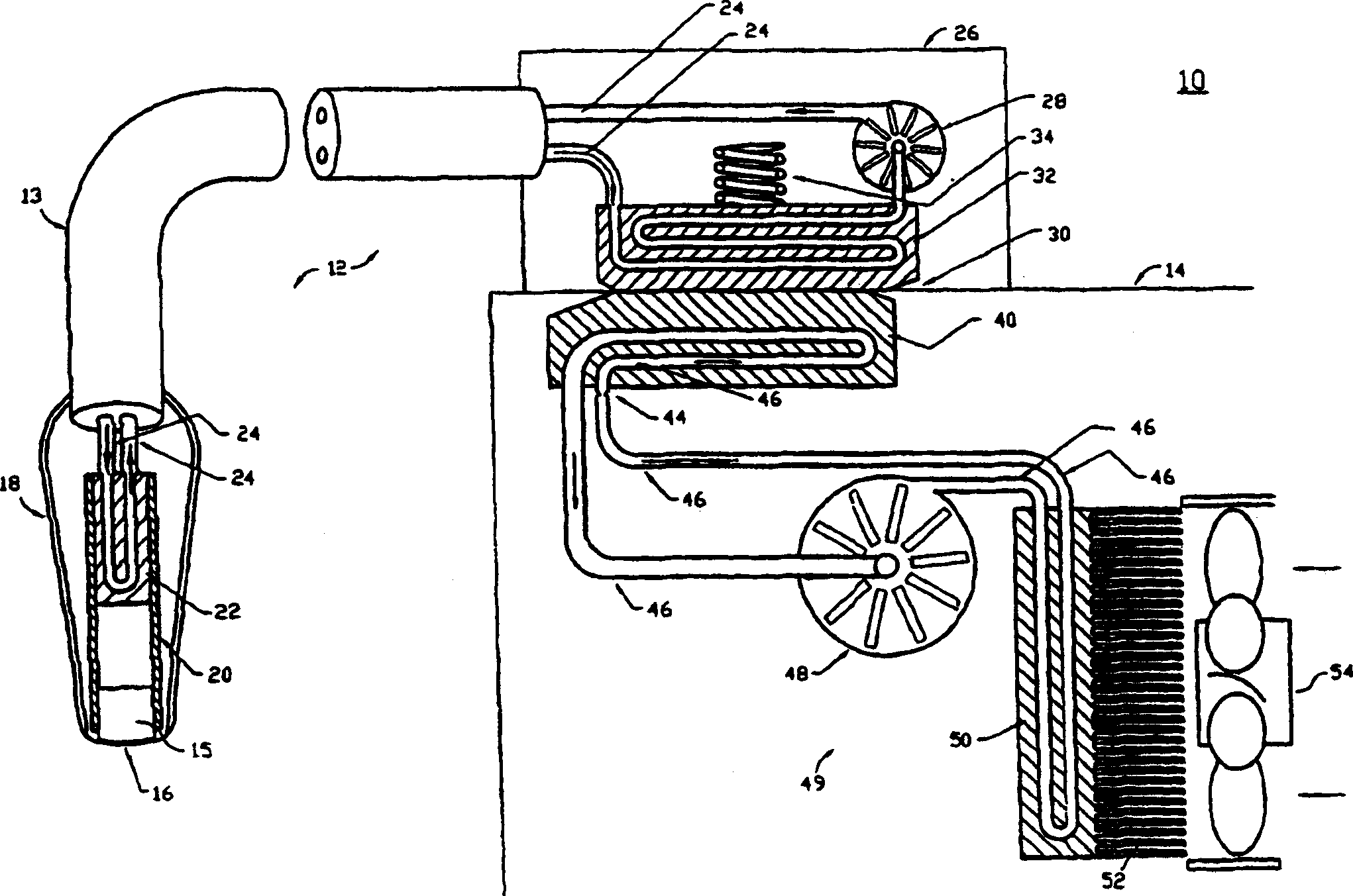
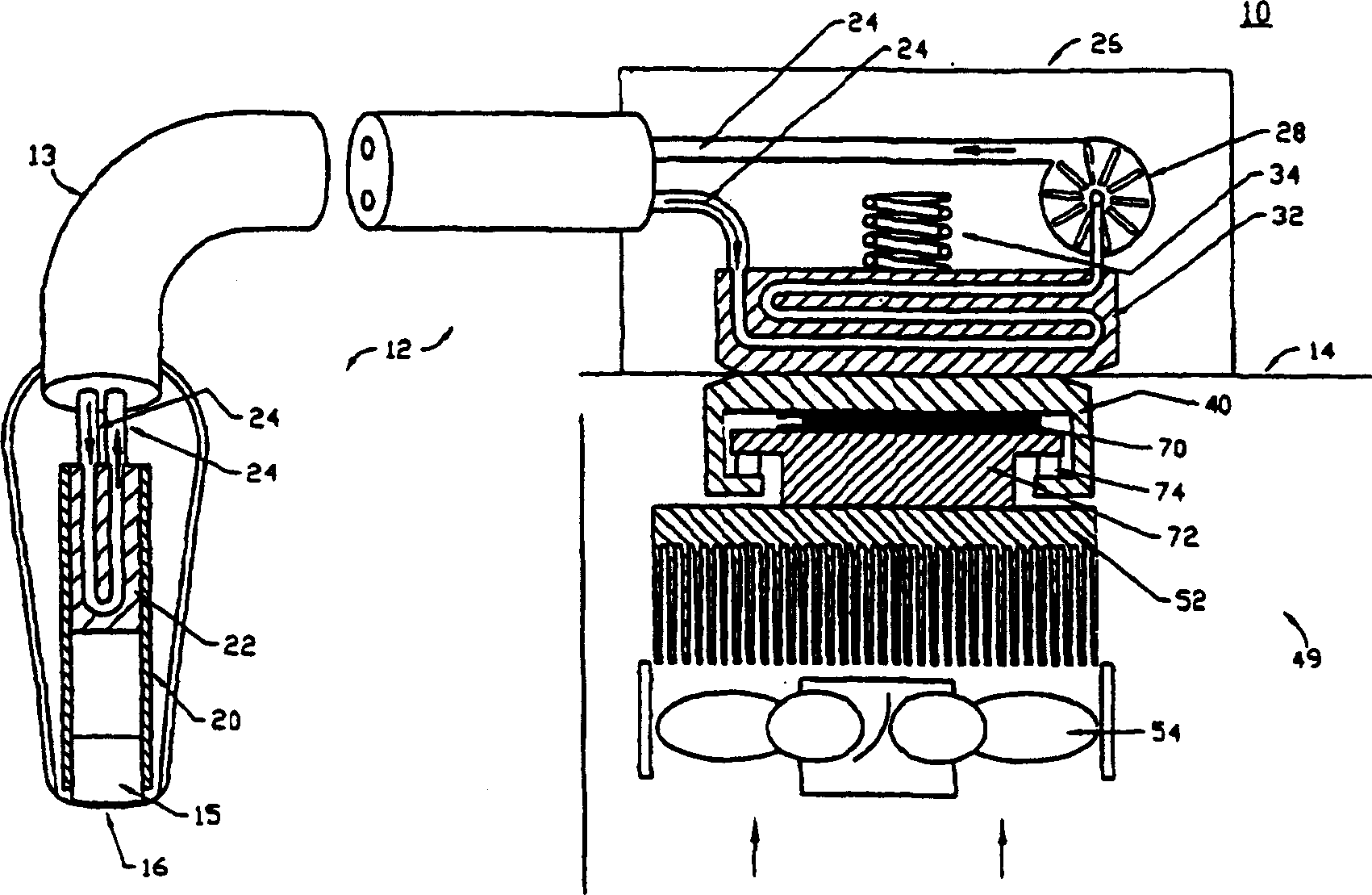
[0020] Regulations require that ultrasound transducers used in medical diagnostic procedures be limited to a temperature not exceeding 43°C, where the transducer is in contact with a patient. For an assumed ambient air temperature of 25°C, a temperature difference of only 18°C facilitates heat removal through passive methods including natural convection, conduction, and radiation.
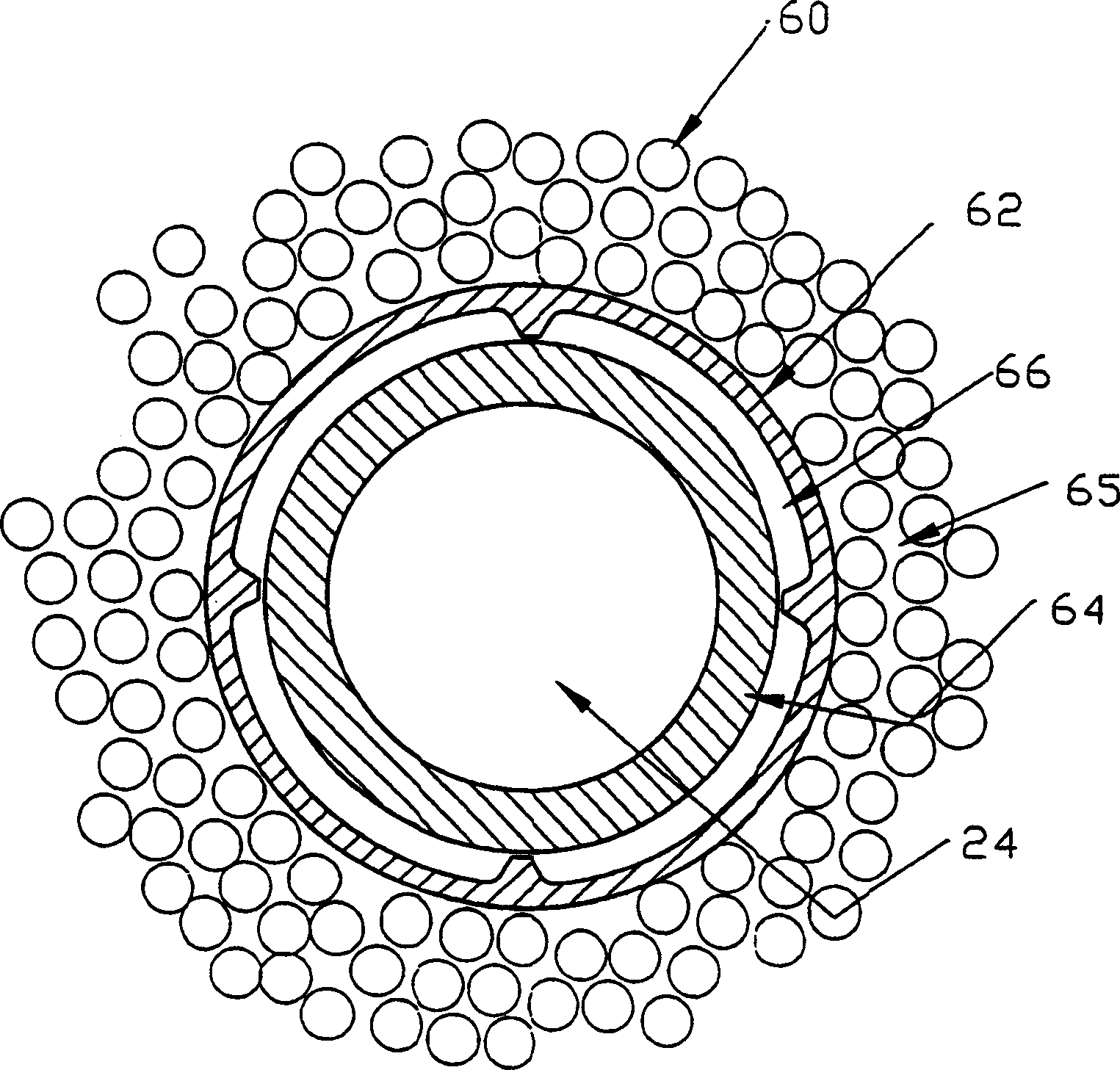
[0021] To provide additional heat removal, a cooling system within the transducer assembly utilizing recirculated liquid coolant is used, which transfers waste heat from heat-generating acoustic components or electronics within the transducer along its cables to the transducer connector. Instead of trying to dissipate waste heat in relatively small connectors, heat is transferred into the ultrasound imaging system by thermal conduction. Once in the imaging system, the waste heat is dissipated to the atmosphere with the help of a vapor / liquid or some other type of refrigeration system. Because r...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com