Biodegradable material and process for producing the same
A biodegradable material and biodegradable technology, applied in the field of production of the biodegradable material, can solve the problems of inability, deformation of the biodegradable material by heating, difficulty in maintaining the shape, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
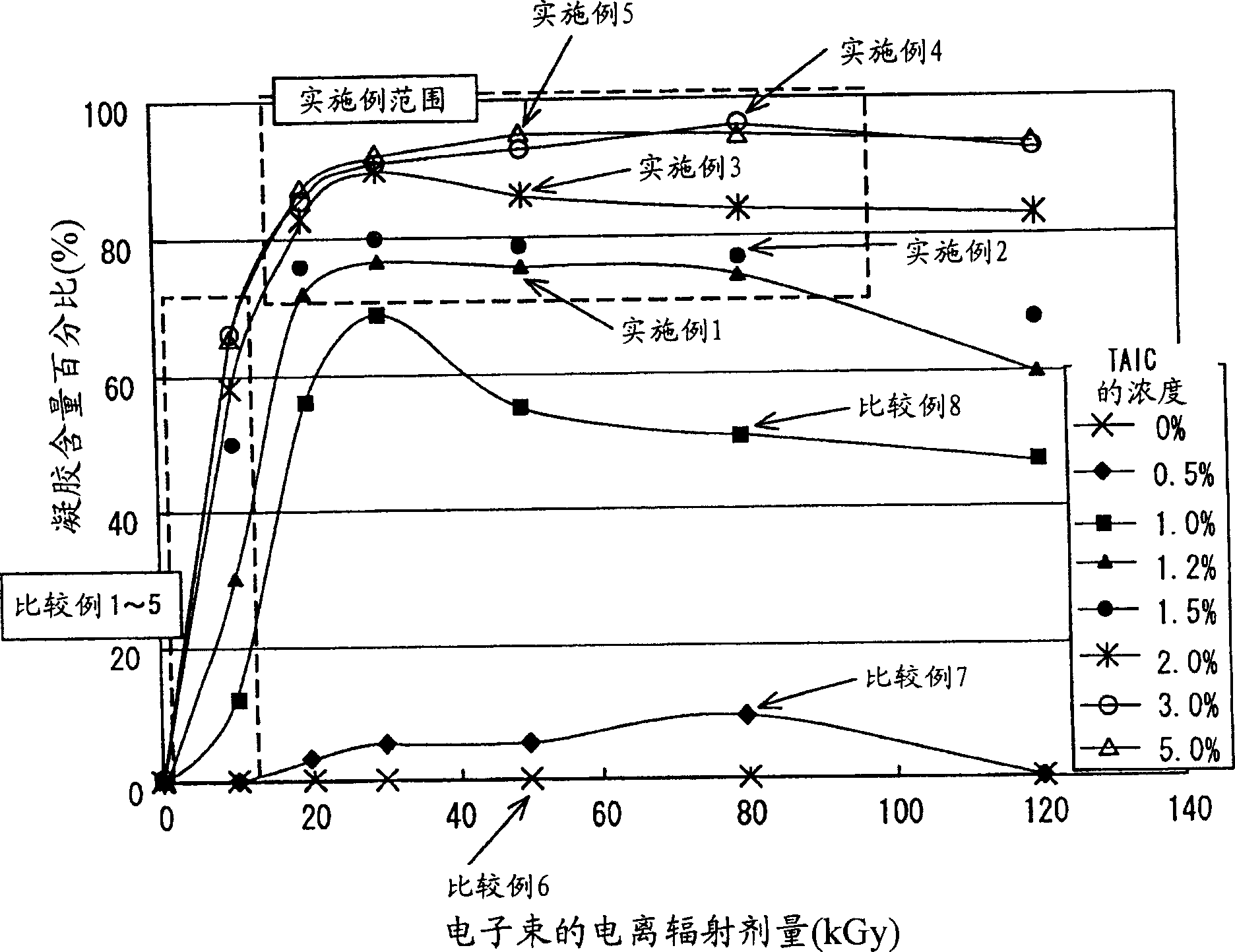
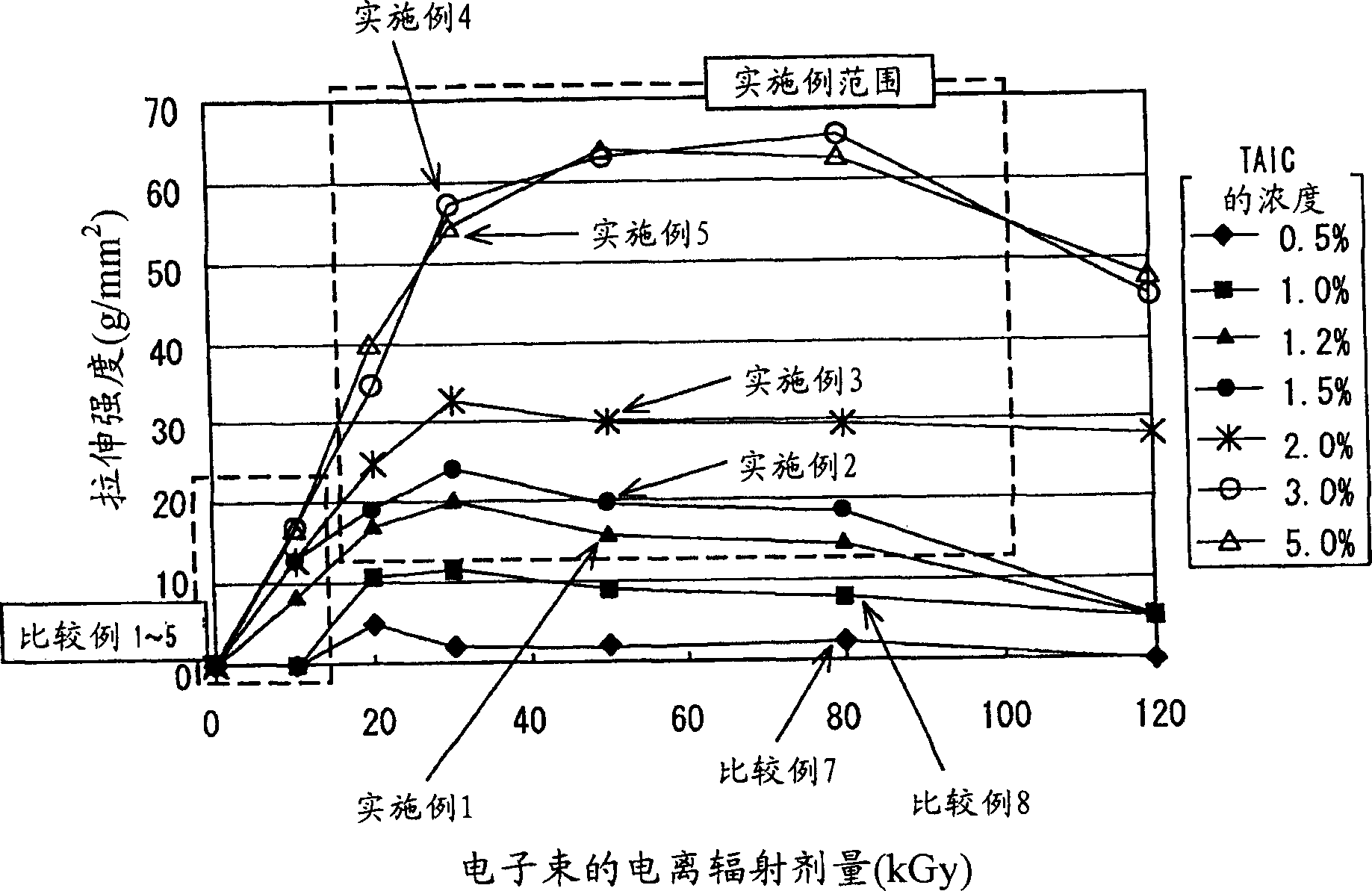
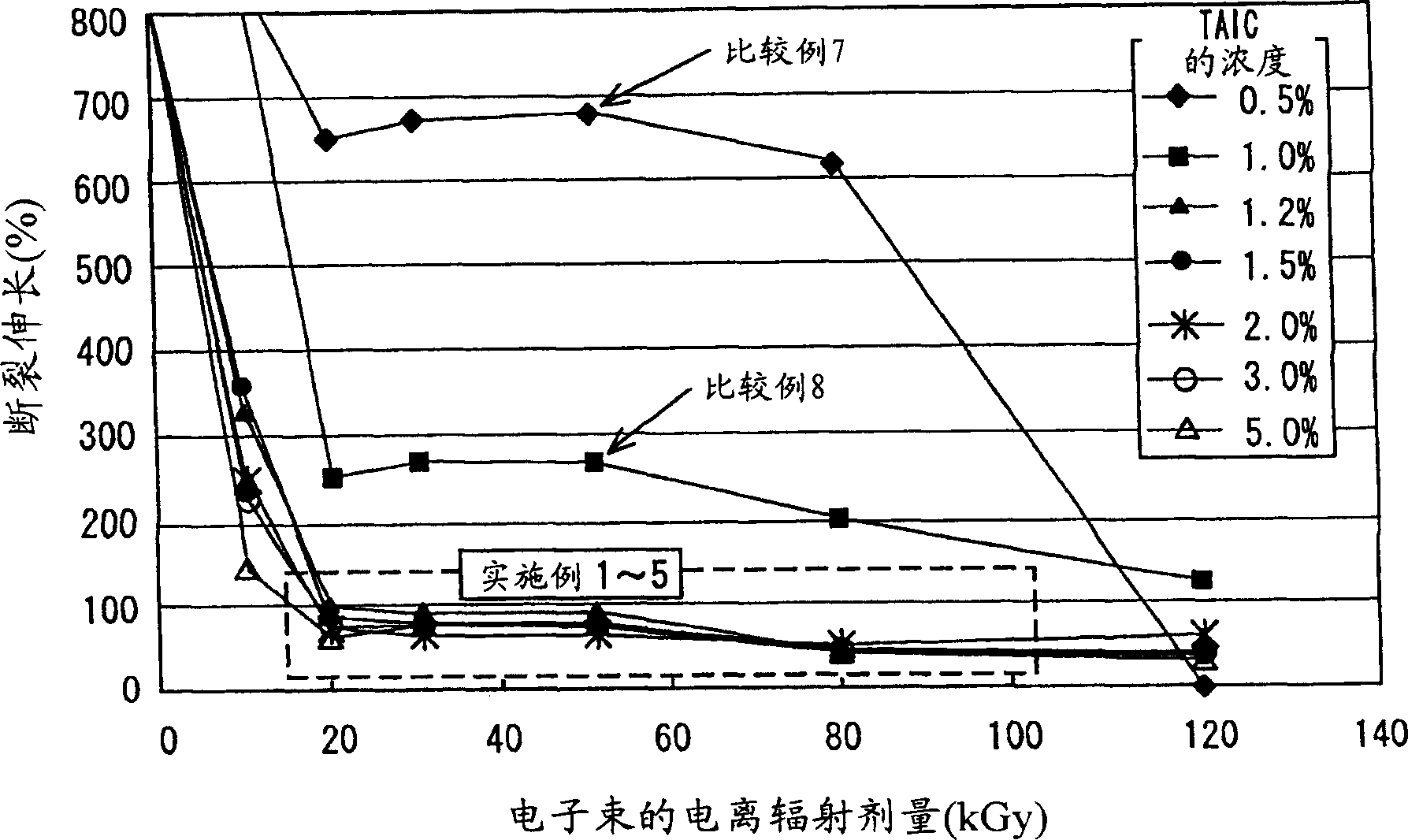
[0043] In order to achieve the first object of enhancing the heat resistance of biodegradable materials, the present inventors conducted active research and found that this object can be achieved by mixing a monomer having an allyl group with a biodegradable aliphatic polyester and combining the The mixture is irradiated with radiation to cross-link the molecules with each other to meet predetermined conditions. In particular, the present inventors have found that the configuration-retaining performance of polylactic acid at high temperature (i.e., high hardness) can be improved by sufficiently crosslinking the non-crystalline part of polylactic acid with an allyl group-containing monomer, although polylactic acid Decayed by radiation, and is generally considered non-crosslinkable with common monomers.
[0044] Based on the above findings, the first invention provides a biodegradable material comprising not less than 95% by weight and not more than 99% by weight of a biodegrad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com