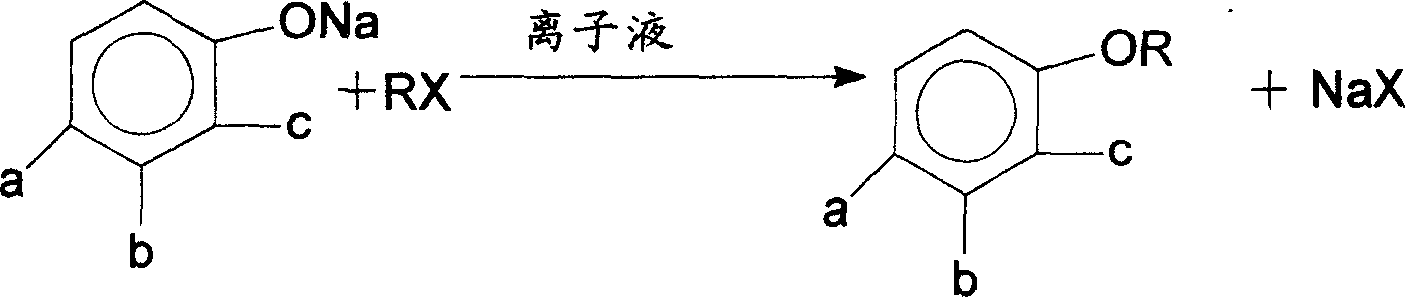
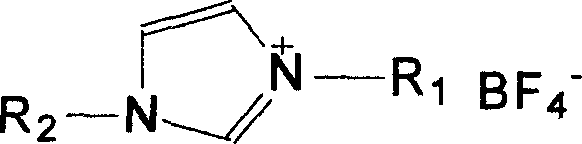
Method of synthesizing aromatic ether without solvent
A chemical synthesis, solvent-free technology, applied in the direction of ether preparation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of inability to separate, good water solubility and loss of sodium bromide, and achieve the effects of easy industrial production, accelerated reaction speed, and improved quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 18.5 g (0.1 mol) of sodium 2,4-dichlorophenolate, 1 g of ionic liquid, and 50 g of 2,4-dichlorophenyl isopropyl ether were added to the reactor. A reflux condenser, a stirring device, a dripping device and a thermometer were installed on the reactor, and the 2,4-dichlorophenyl isopropyl ether was heated and melted, and the temperature rose to above 60 °C. 18.5g of isopropane bromide (0.15mol) was added, and the dropwise addition was completed after 1 hour. The reaction temperature was around 60-120°C, and the reaction was refluxed for 3 hours. After cooling, 30g of 2,4-dichlorophenyl isopropyl ether was discharged. Then 18.5 g of sodium 2,4-dichlorophenolate was added, 18.5 g of isopropane bromide was added dropwise, and the reaction was carried out cyclically. After 15 cycles of feeding reaction, 1 g of ionic liquid was added to continue the reaction. The product ether discharged from the bottom was analyzed by gas chromatography, the purity was 99.5%, and the yield w...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Take 22.8 g (0.1 mol) of sodium 5-nitro-2,4-dichlorophenol and 3 g of ionic liquid, add them into the reactor, and add 50 g of 5-nitro-2,4-dichlorophenyl isopropyl ether. Install a reflux condenser, a stirring device, a dripping device and a thermometer on the reactor, heat and melt 5-nitro-2,4-dichlorophenyl n-propyl ether, the temperature rises to above 60 ° C, and start 14.8g (0.12mol) of n-propane bromide was added dropwise through a dropping funnel, and the dropwise addition was completed after 1 hour. The reaction temperature was around 60-120°C, and the reaction was refluxed for 3 hours. After cooling, 30g was discharged. The above-mentioned cyclic feeding reaction was continued, and after 20 reactions, 1 g of ionic liquid was added to continue the reaction. The product 5-nitro-2,4-dichlorophenyl n-propyl ether discharged from the bottom was analyzed by gas chromatography with a purity of 99% and a yield of 98%.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Take 11.6 g (0.1 mol) of sodium phenolate and 0.5 g of ionic liquid, add them into the reactor, and add 50 g of phenyl isopropyl ether. A reflux condenser, a stirring device, a dripping device and a thermometer were installed on the reactor, heated to melt the phenyl isopropyl ether, the temperature rose above 60°C, and 16g (0.13mol) of bromine was added dropwise through the dropping funnel. Substitute isopropane. After 1 hour, the dropwise addition was completed, the reaction temperature was about 60-120° C., the reaction was refluxed for 3 hours, and 20 g was discharged after cooling. The above-mentioned cyclic feeding reaction was continued, and after 15 reactions, 1 g of ionic liquid was added to continue the reaction. The product was analyzed by gas chromatography with a purity of 98.5% and a yield of 97%.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap